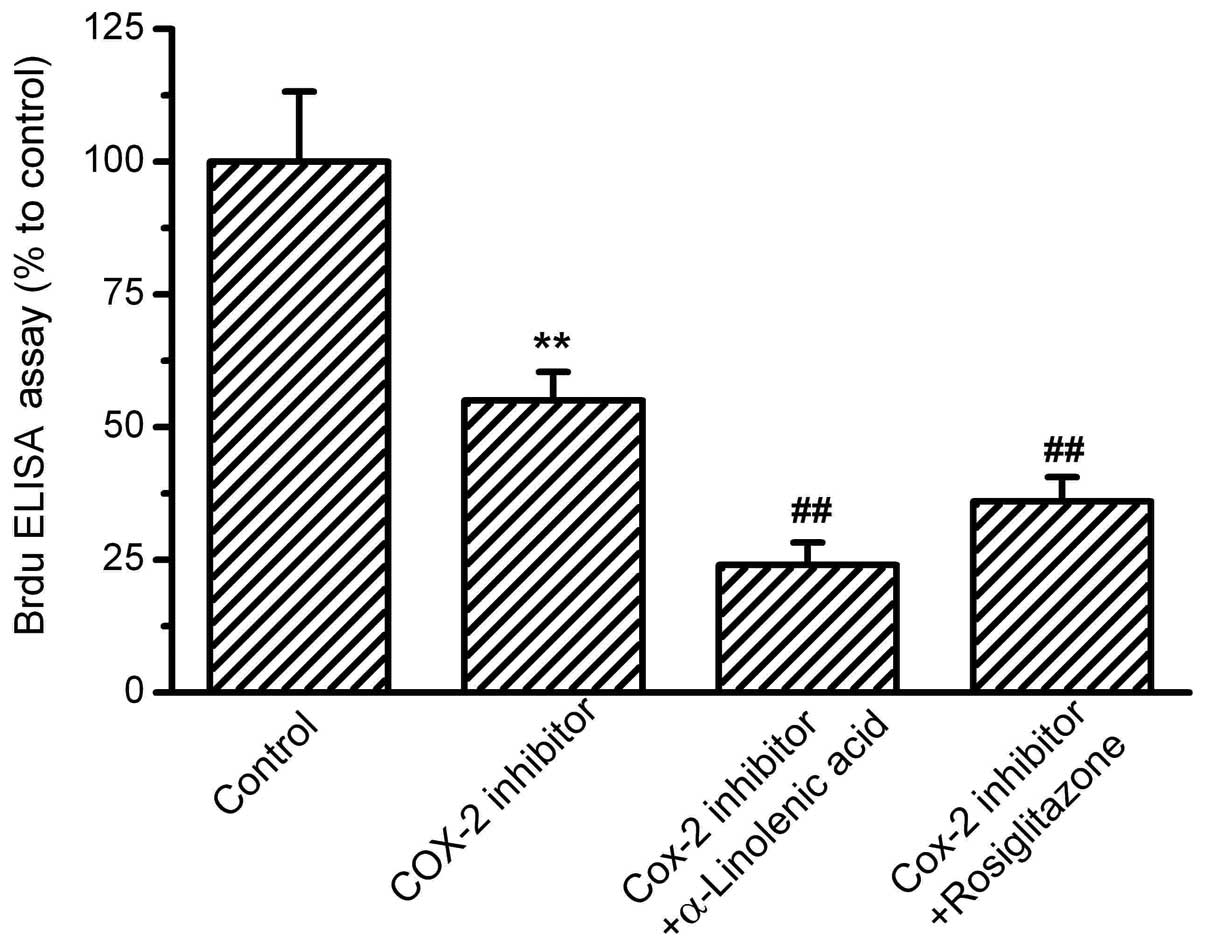
|
1.
|
Motzer RJ, Bander NH and Nanus DM:
Renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 335:865–875. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Rini BI, Rathmell WK and Godley P: Renal
cell carcinoma. Curr Opin Oncol. 20:300–306. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Rose DP and Connolly JM: Omega-3 fatty
acids as cancer chemopreventive agents. Pharmacol Ther. 83:217–244.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Rashidkhani B, Akesson A, Lindblad P and
Wolk A: Major dietary patterns and risk of renal cell carcinoma in
a prospective cohort of Swedish women. J Nutr. 135:1757–1762.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Wolk A, Larsson SC, Johansson JE and Ekman
P: Long-term fatty fish consumption and renal cell carcinoma
incidence in women. JAMA. 296:1371–1376. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Spencer L, Mann C, Metcalfe M, Webb M,
Pollard C, Spencer D, Berry D, Steward W and Dennison A: The effect
of omega-3 FAs on tumour angiogenesis and their therapeutic
potential. Eur J Cancer. 45:2077–2086. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Wendel M and Heller AR: Anticancer actions
of omega-3 fatty acids - current state and future perspectives.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 9:457–470. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Desvergne B and Wahli W: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors: Nuclear control of metabolism.
Endocr Rev. 20:649–688. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Feige JN, Gelman L, Michalik L, Desvergne
B and Wahli W: From molecular action to physiological outputs:
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors are nuclear receptors
at the crossroads of key cellular functions. Prog Lipid Res.
45:120–159. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Krishnan A, Nair SA and Pillai MR: Biology
of PPAR gamma in cancer: a critical review on existing lacunae.
Curr Mol Med. 7:532–540. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Kliewer SA, Sundseth SS, Jones SA, Brown
PJ, Wisely GB, Koble CS, Devchand P, Wahli W, Willson TM, Lenhard
JM and Lehmann JM: Fatty acids and eicosanoids regulate gene
expression through direct interactions with peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors alpha and gamma. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 94:4318–4323. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12.
|
Xu HE, Lambert MH, Montana VG, Parks DJ,
Blanchard SG, Brown PJ, Sternbach DD, Lehmann JM, Wisely GB,
Willson TM, Kliewer SA and Milburn MV: Molecular recognition of
fatty acids by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Mol
Cell. 3:397–403. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Lim K, Han C, Dai Y, Shen M and Wu T:
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids inhibit hepatocellular
carcinoma cell growth through blocking beta-catenin and
cyclooxygenase-2. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:3046–3055. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Hashimoto Y, Kondo Y, Kimura G, Matsuzawa
I, Sato S, Ishizaki M, Imura N, Akimoto M and Hara S:
Cyclooxygenase-2 expression and relationship to tumour progression
in human renal cell carcinoma. Histopathology. 44:353–359. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Khan KN, Stanfield KM, Trajkovic D and
Knapp DW: Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in canine renal cell
carcinoma. Vet Pathol. 38:116–119. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Chen Q, Shinohara N, Abe T, Watanabe T,
Nonomura K and Koyanagi T: Significance of COX-2 expression in
human renal cell carcinoma cell lines. Int J Cancer. 108:825–832.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Xin X, Yang S, Kowalski J and Gerritsen
ME: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma ligands are
potent inhibitors of angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. J Biol
Chem. 274:9116–9121. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Rose DP and Connolly JM: Effects of fatty
acids and inhibitors of eicosanoid synthesis on the growth of a
human breast cancer cell line in culture. Cancer Res. 50:7139–7144.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Rose DP, Connolly JM, Rayburn J and
Coleman M: Influence of diets containing eicosapentaenoic or
docosahexaenoic acid on growth and metastasis of breast cancer
cells in nude mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 87:587–592. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Karmali RA, Reichel P, Cohen LA, Terano T,
Hirai A, Tamura Y and Yoshida S: The effects of dietary omega-3
fatty acids on the du-145 transplantable human prostatic tumor.
Anticancer Res. 7:1173–1179. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Prentice RL and Sheppard L: Dietary fat
and cancer: consistency of the epidemiologic data, and disease
prevention that may follow from a practical reduction in fat
consumption. Cancer Causes Control. 1:81–109. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Stolzenberg-Solomon RZ, Pietinen P, Taylor
PR, Virtamo J and Albanes D: Prospective study of diet and
pancreatic cancer in male smokers. Am J Epidemiol. 155:783–792.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Takezaki T, Inoue M, Kataoka H, Ikeda S,
Yoshida M, Ohashi Y, Tajima K and Tominaga S: Diet and lung cancer
risk from a 14-year population-based prospective study in Japan:
with special reference to fish consumption. Nutr Cancer.
45:160–167. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Savage DB: PPAR gamma as a metabolic
regulator: insights from genomics and pharmacology. Expert Rev Mol
Med. 7:1–16. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Knouff C and Auwerx J: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma calls for activation in
moderation: lessons from genetics and pharmacology. Endocr Rev.
25:899–918. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Picard F and Auwerx J: PPAR(gamma) and
glucose homeostasis. Annu Rev Nutr. 22:167–197. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Itoh T, Fairall L, Amin K, Inaba Y, Szanto
A, Balint BL, Nagy L, Yamamoto K and Schwabe JW: Structural basis
for the activation of PPARgamma by oxidized fatty acids. Nat Struct
Mol Biol. 15:924–931. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Edwards IJ and O’Flaherty JT: Omega-3
fatty acids and PPARgamma in cancer. PPAR Res. 2008:3580522008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Gani OA: Are fish oil omega-3 long-chain
fatty acids and their derivatives peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor agonists? Cardiovasc Diabetol. 7:62008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Mansure JJ, Nassim R and Kassouf W:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in bladder cancer:
a promising therapeutic target. Cancer Biol Ther. 8:6–15. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Roman J: Peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor gamma and lung cancer biology: implications for therapy. J
Investig Med. 56:528–533. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Voutsadakis IA: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) and colorectal
carcinogenesis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 133:917–928. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
de Souza Pereira R: Selective
cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors used for preventing or
regressing cancer. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 4:157–163.
2009.
|
|
34.
|
Harris RE: Cyclooxygenase-2 (cox-2)
blockade in the chemo-prevention of cancers of the colon, breast,
prostate, and lung. Inflammopharmacology. 17:55–67. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Fujimura T, Ohta T, Oyama K, Miyashita T
and Miwa K: Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in carcinogenesis and
selective COX-2 inhibitors for chemoprevention in gastrointestinal
cancers. J Gastrointest Cancer. 38:78–82. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Gilhooly EM and Rose DP: The association
between a mutated ras gene and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human
breast cancer cell lines. Int J Oncol. 15:267–270. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Hussain T, Gupta S and Mukhtar H:
Cyclooxygenase-2 and prostate carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett.
191:125–135. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Lee KS, Lee HJ, Ahn KS and Kim SH, Nam D,
Kim DK, Choi DY, Ahn KS, Lu J and Kim SH:
Cyclooxygenase-2/prostaglandin e2 pathway mediates icariside II
induced apoptosis in human PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
280:93–100. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Sun WH, Chen GS, Ou XL, Yang Y, Luo C,
Zhang Y, Shao Y, Xu HC, Xiao B, Xue YP, Zhou SM, Zhao QS and Ding
GX: Inhibition of COX-2 and activation of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma synergistically inhibits
proliferation and induces apoptosis of human pancreatic carcinoma
cells. Cancer Lett. 275:247–255. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40.
|
Chen Q, Shinohara N, Abe T, Harabayashi T
and Nonomura K: Impact of cyclooxygenase-2 gene expression on tumor
invasiveness in a human renal cell carcinoma cell line. J Urol.
172:2153–2157. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Hemmerlein B, Galuschka L, Putzer N,
Zischkau S and Heuser M: Comparative analysis of COX-2, vascular
endothelial growth factor and microvessel density in human renal
cell carcinomas. Histopathology. 45:603–611. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Bren-Mattison Y, Meyer AM, Van Putten V,
Li H, Kuhn K, Stearman R, Weiser-Evans M, Winn RA, Heasley LE and
Nemenoff RA: Antitumorigenic effects of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma in non-small-cell lung cancer
cells are mediated by suppression of cyclooxygenase-2 via
inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB. Mol Pharmacol. 73:709–717.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43.
|
Chêne G, Dubourdeau M, Balard P,
Escoubet-Lozach L, Orfila C, Berry A, Bernad J, Aries MF, Charveron
M and Pipy B: n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids induce the
expression of COX-2 via PPARgamma activation in human keratinocyte
HaCaT cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1771:576–589. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Andrade LN, de Lima TM, Curi R and
Castrucci AM: Toxicity of fatty acids on murine and human melanoma
cell lines. Toxicol In Vitro. 19:553–560. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Azevedo-Martins AK, Monteiro AP, Lima CL,
Lenzen S and Curi R: Fatty acid-induced toxicity and neutral lipid
accumulation in insulin-producing RINm5F cells. Toxicol In Vitro.
20:1106–1113. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46.
|
Otton R and Curi R: Toxicity of a mixture
of fatty acids on human blood lymphocytes and leukaemia cell lines.
Toxicol In Vitro. 19:749–755. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|