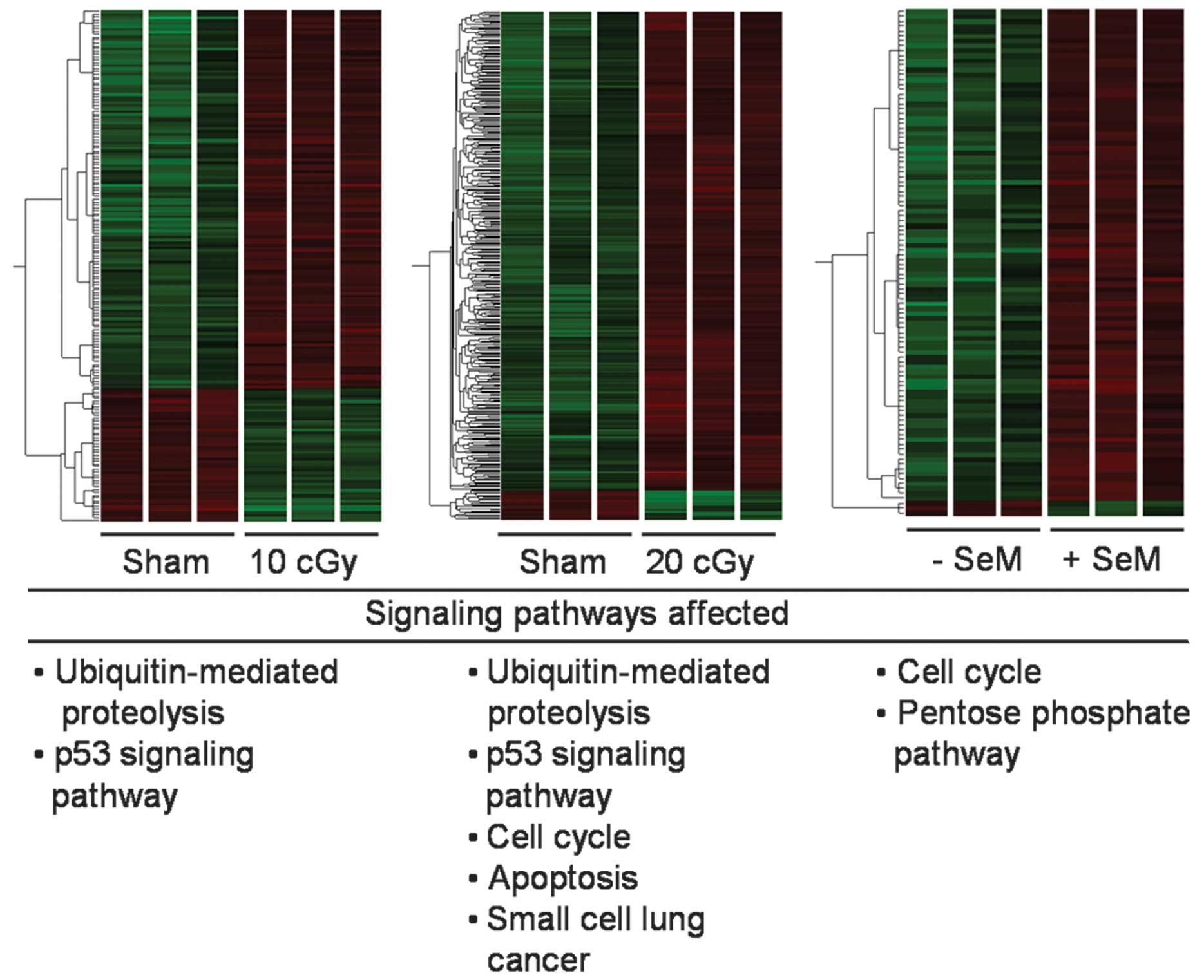
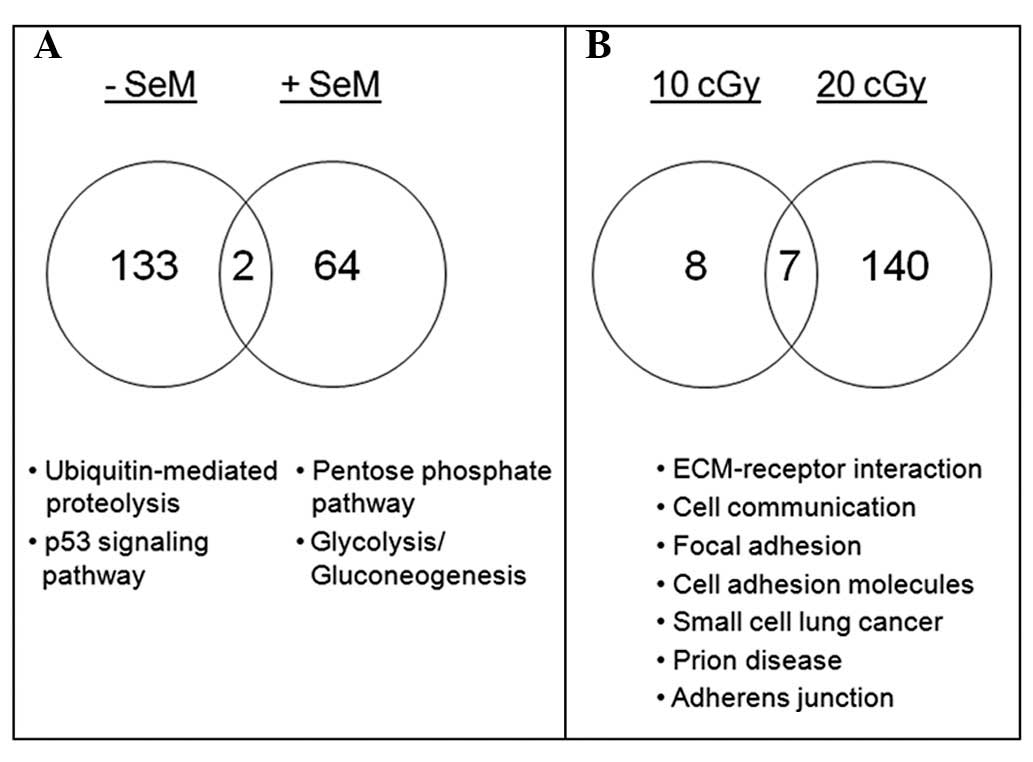
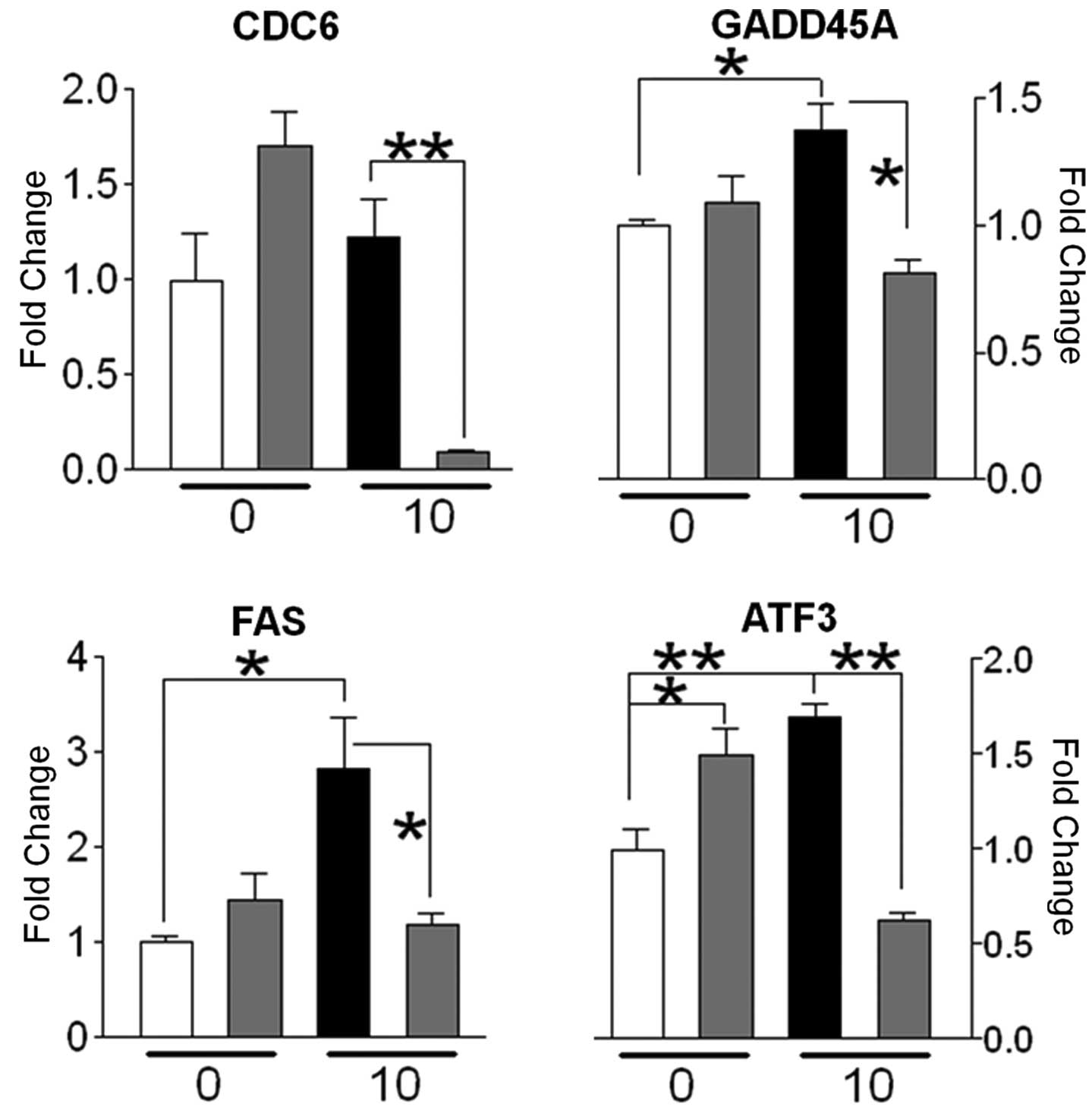
|
1.
|
Brooks A, Bao S, Rithidech K, Couch LA and
Braby LA: Relative effectiveness of HZE iron-56 particles for the
induction of cytogenetic damage in vivo. Radiat Res. 155:353–359.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Nelson GA: Fundamental space radiobiology.
Gravit Space Biol Bull. 16:29–36. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Nelson GA, Jones TA, Chesnut A and Smith
AL: Radiation-induced gene expression in the nematode
Caenorhabditis elegans. J Radiat Res. 43(Suppl): S199–S203.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Ding LH, Shingyoji M, Chen F, et al: Gene
expression profiles of normal human fibroblasts after exposure to
ionizing radiation: a comparative study of low and high doses.
Radiat Res. 164:17–26. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Fornace AJ Jr, Amundson SA, Bittner M,
Myers TG, Meltzer P, Weinsten JN and Trent J: The complexity of
radiation stress responses: analysis by informatics and functional
genomics approaches. Gene Expr. 7:387–400. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Barcellos-Hoff MH: The potential influence
of radiation-induced microenvironments in neoplastic progression. J
Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 3:165–175. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Azzam EI, de Toledo SM and Little JB:
Expression of CONNEXIN43 is highly sensitive to ionizing radiation
and other environmental stresses. Cancer Res. 63:7128–7135.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Zhou BB and Elledge SJ: The DNA damage
response: putting checkpoints in perspective. Nature. 408:433–439.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Amundson SA, Do KT and Fornace AJ Jr:
Induction of stress genes by low doses of gamma rays. Radiat Res.
152:225–231. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Amundson SA, Bittner M, Meltzer P, Trent J
and Fornace AJ Jr: Induction of gene expression as a monitor of
exposure to ionizing radiation. Radiat Res. 156:657–661. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Ding LH, Shingyoji M, Chen F, Chatterjee
A, Kasai KE and Chen DJ: Gene expression changes in normal human
skin fibroblasts induced by HZE-particle radiation. Radiat Res.
164:523–526. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Franco N, Lamartine J, Frouin V, Le Minter
P, et al: Low-dose exposure to gamma rays induces specific gene
regulations in normal human keratinocytes. Radiat Res. 163:623–635.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Combs GF Jr and Gray WP: Chemopreventive
agents: selenium. Pharmacol Ther. 79:179–192. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Clark LC, Combs GF Jr, Turnbull BW, Slate
EH, et al: Effects of selenium supplementation for cancer
prevention in patients with carcinoma of the skin. A randomized
controlled trial Nutritional Prevention of Cancer Study Group JAMA.
276:1957–1963. 1996.
|
|
15.
|
Lu J, Kaeck M, Jiang C, Wilson AC and
Thompson HJ: Selenite induction of DNA strand breaks and apoptosis
in mouse leukemic L1210 cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 47:1531–1535.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Garberg P, Stahl A, Warholm M and Hogberg
J: Studies of the role of DNA fragmentation in selenium toxicity.
Biochem Pharmacol. 37:3401–3406. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Kennedy AR, Ware JH, Guan J, Donahue JJ,
et al: Selenomethionine protects against adverse biological effects
induced by space radiation. Free Radic Biol Med. 36:259–266. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Guan J, Wan XS, Zhou Z, Ware J, Donahue
JJ, Biaglow JE and Kennedy AR: Effects of dietary supplements on
space radiation-induced oxidative stress in Sprague-Dawley rats.
Radiat Res. 162:572–579. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Guan J, Stewart J, Ware JH, Zhou Z,
Donahue JJ and Kennedy AR: Effects of dietary supplements on the
space radiation-induced reduction in total antioxidant status in
CBA mice. Radiat Res. 165:373–378. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Wan XS, Ware JH, Zhou Z, Donahue JJ, Guan
J and Kennedy AR: Protection against radiation-induced oxidative
stress in cultured human epithelial cells by treatment with
antioxidant agents. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 64:1475–1481.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC, et al: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Hai T, Wolfgang CD, Marsee DK, Allen AE
and Sivaprasad U: ATF3 and stress responses. Gene Expr. 7:321–335.
1999.
|
|
23.
|
Gaiddon C, Moorthy NC and Prives C: Ref-1
regulates the trans-activation and pro-apoptotic functions of p53
in vivo. EMBO J. 18:5609–5621. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Seo YR, Kelley MR and Smith ML:
Selenomethionine regulation of p53 by a ref1-dependent redox
mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:14548–14553. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Gius D, Botero A, Shah S and Curry HA:
Intracellular oxidation/reduction status in the regulation of
transcription factors NF-kappaB and AP-1. Toxicol Lett. 106:93–106.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Reynaert NL, van der Vliet A, Guala AS,
McGovern T, Hristova M, Pantano C, et al: Dynamic redox control of
NF-kappaB through glutaredoxin-regulated S-glutathionylation of
inhibitory kappaB kinase beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:13086–13091. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Menter DG, Sabichi AL and Lippman SM:
Selenium effects on prostate cell growth. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 9:1171–1182. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Dong Y, Ip C and Ganther H: Evidence of a
field effect associated with mammary cancer chemoprevention by
methylseleninic acid. Anticancer Res. 22:27–32. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Dong Y, Ganther HE, Stewart C and Ip C:
Identification of molecular targets associated with
selenium-induced growth inhibition in human breast cells using cDNA
microarrays. Cancer Res. 62:708–714. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Goulet AC, Chigbrow M, Frisk P and Nelson
M: Selenomethionine induces sustained ERK phosphorylation leading
to cell-cycle arrest in human colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis.
26:109–117. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Goulet AC, Watts G, Lord JL and Nelson MA:
Profiling of selenomethionine responsive genes in colon cancer by
microarray analysis. Cancer Biol Ther. 6:494–503. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Hurst R, Elliott RM, Goldson AJ and
Fairweather-Tait SJ: Se-methylselenocysteine alters collagen gene
and protein expression in human prostate cells. Cancer Lett.
269:117–126. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|