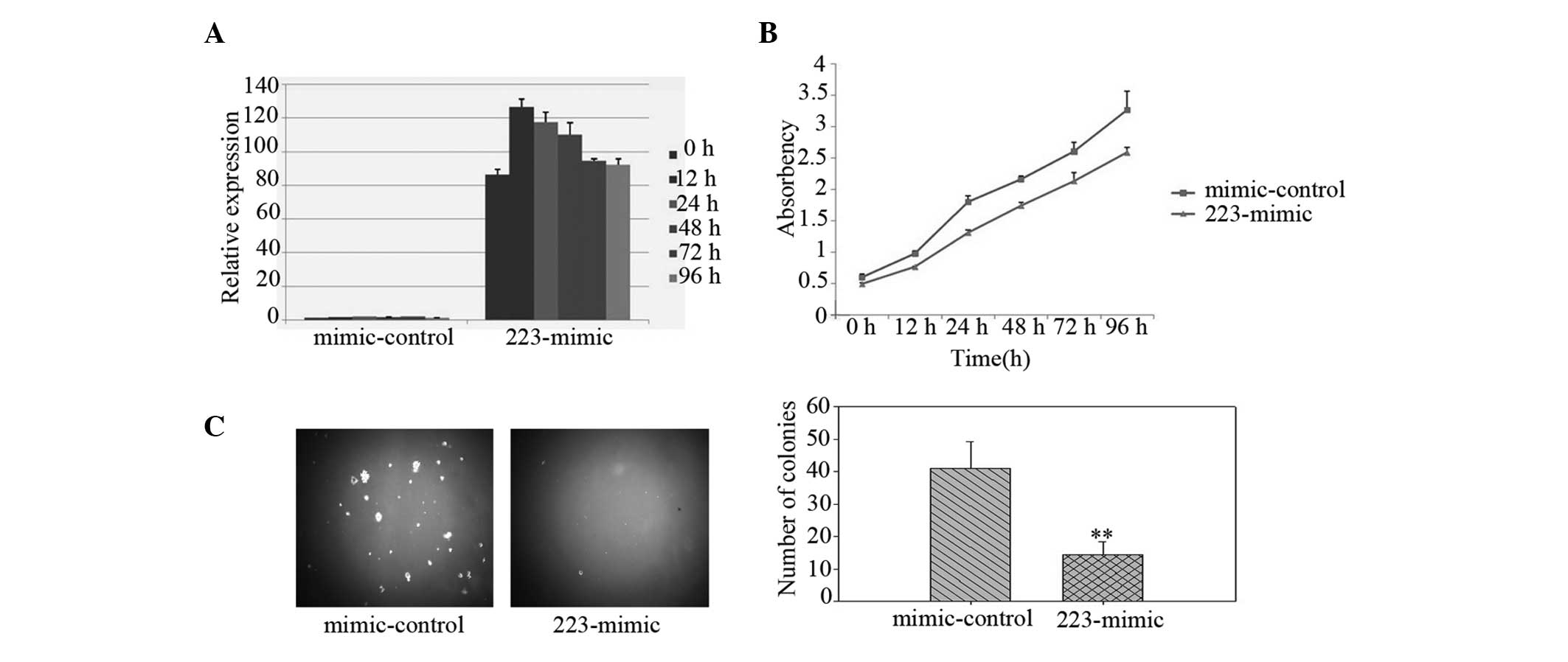
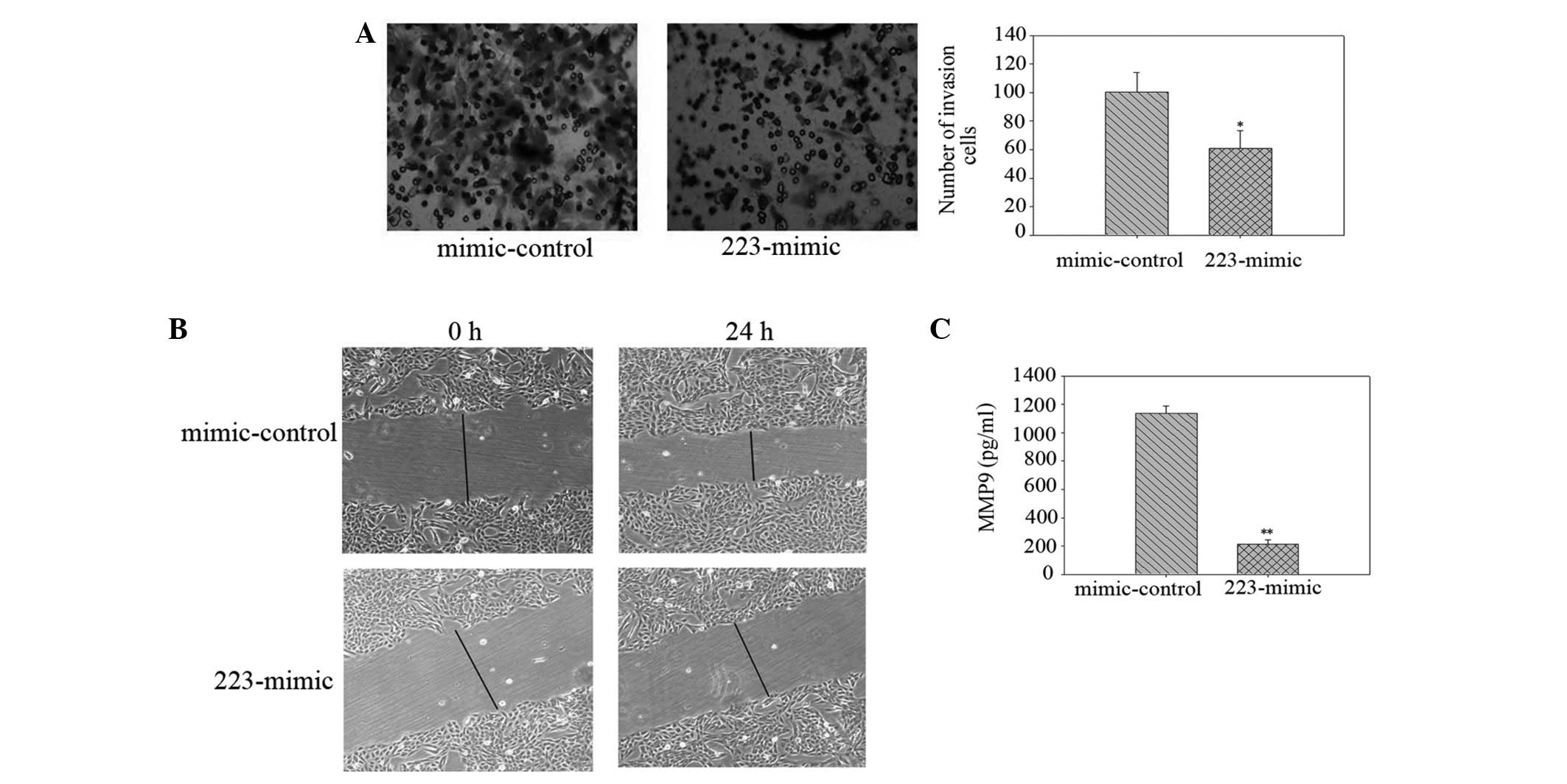
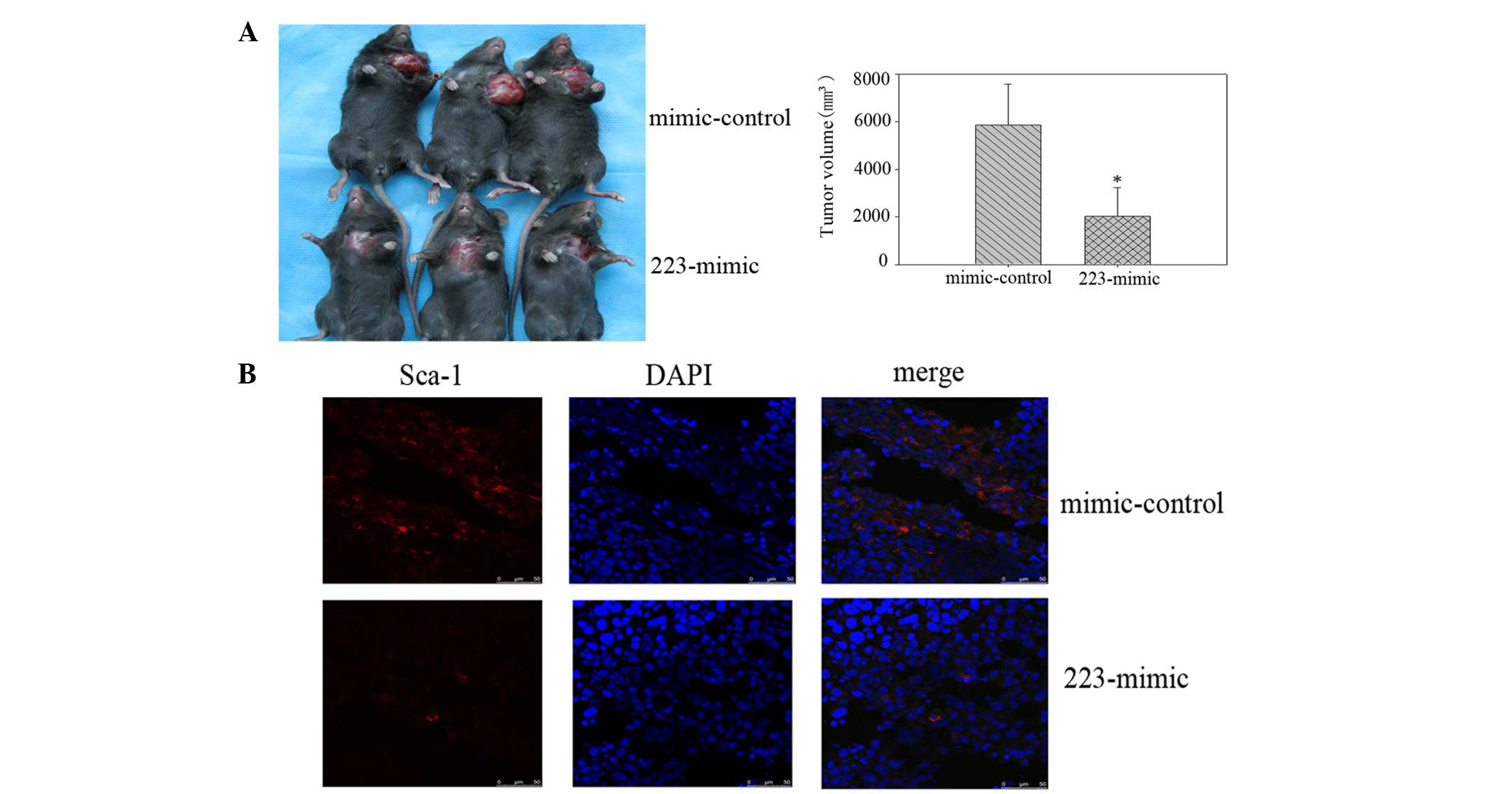
|
1.
|
Jemal A, Center MM, DeSantis C and Ward
EM: Global patterns of cancer incidence and mortality rates and
trends. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 19:1893–1907. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Bueno MJ, Pérez de Castro I and Malumbres
M: Control of cell proliferation pathways by microRNAs. Cell Cycle.
7:3143–3148. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Lee CT, Risom T and Strauss WM: MicroRNAs
in mammalian development. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today.
78:129–139. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Jovanovic M and Hengartner MO: miRNAs and
apoptosis: RNAs to die for. Oncogene. 25:6176–6187. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Mendell JT: miRiad roles for the miR-17-92
cluster in development and disease. Cell. 133:217–222. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Kent OA and Mendell JT: A small piece in
the cancer puzzle: microRNAs as tumor suppressors and oncogenes.
Oncogene. 25:6188–6196. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Kumar MS, Erkeland SJ and Pester RE:
Suppression of non-small cell lung tumor development by the let-7
microRNA family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:3903–3908. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Fazi F, Rosa A, Fatica A, Gelmetti V, De
Marchis ML, Nervi C and Bozzoni I: Aminicircuitry comprised of
microRNA-223 and transcription factors NFI-A and C/EBPalpha
regulates human granulopoiesis. Cell. 123:819–831. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Johnnidis JB, Harris MH, Wheeler RT,
Stehling-Sun S, Lam MH and Kirak O: Regulation of progenitor cell
proliferation and granulocyte function by microRNA-223. Nature.
451:1125–1129. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Jia CY, Li HH, Zhu XC, Dong YW, Fu D, Zhao
QL, Wu W and Wu XZ: MiR-223 suppresses cell proliferation by
targeting IGF-1R. Plos One. 6:e270082011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Liu Q, Zhang M, Jiang X, Zhang Z, Dai L,
Min S, Wu X, He Q, Liu J, Zhang Y, Zhang Z and Yang R: miR-223
suppresses differentiation of tumor-induced CD11b+ Gr1+
myeloid-derived suppressor cells from bone marrow cells. Int J
Cancer. 129:2662–2673. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Kang W, Tong JH, Chan AW, Lung RW, Chau
SL, Wong QW, Wong N, Yu J, Cheng AS and To KF: Stathmin1 plays
oncogenic role and is a target of microRNA-223 in gastric cancer.
PLoS One. 7:e339192012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Li S, Li Z, Guo F, Qin X, Liu B, Lei Z,
Song Z, Sun L, Zhang HT, You J and Zhou Q: miR-223 regulates
migration and invasion by targeting Artemin in human esophageal
carcinoma. J Biomed Sci. 18:242011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Wu L, Li H, Jia CY, Cheng W, Yu M, Peng M,
Zhu Y, Zhao Q, Dong YW, Shao K, Wu A and Wu XZ: MicroRNA-223
regulates FOXO1 expression and cell proliferation. FEBS Lett.
586:1038–1043. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Izzotti A, Calin GA, Arrigo P, Steele VE,
Croce CM and De Flora S: Downregulation of microRNA expression in
the lungs of rats exposed to cigarette smoke. FASEB J. 23:806–812.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Heegaard NH, Schetter AJ, Welsh JA, Yoneda
M, Bowman ED and Harris CC: Circulating micro-RNA expression
profiles in early stage nonsmall cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer.
130:1378–1386. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Nian WQ, Chen FL, Ao XJ and Chen ZT: CXCR4
positive cells from Lewis lung carcinoma cell line have cancer
metastatic stem cell characteristics. Mol Cell Biochem.
355:241–248. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Nian WQ, Chen FL, Ao XJ and Chen ZT: Lowly
expression of miR-223 in CXCR4 positive cells from Lewis lung
carcinoma cell line and its target gene prediction. Di San Jun Yi
Da Xue Xue Bao. 31:2202–2205. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
22.
|
Moon DO, Kim MO, Kang SH, Lee KJ, Heo MS,
Choi KS, Choi YH and Kim GY: Induction of G2/M arrest,
endoreduplication and apoptosis by actin depolymerization agent
pextenotoxin-2 in human leukemia cells, involving activation of ERK
and JNK. Biochem Pharmacol. 76:312–321. 2008.
|
|
23.
|
Dufourny B, Alblas J and van Teeffelen HA:
Mitogenic signaling of insulin-like growth factor I in MCF-7 human
breast cancer cells requires phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and is
independent of mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem.
272:31163–31171. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24.
|
Khandwala HM, McCutcheon IE and Flyvbjerg
A: The effects of insulin-like growth factors on tumorigenesis and
neoplastic growth. Endocr Rev. 21:215–244. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Blakesley VA, Stannard BS and Kalebic T:
Role of the IGF-I receptor in mutagenesis and tumor promotion. J
Endocrinol. 152:339–344. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Moats-Staats BM, Price WA, Xu L, Jarvis HW
and Stiles AD: Regulation of the insulin-like growth factor system
during normal rat lung development. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
12:56–64. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Linnerth NM, Siwicky MD, Campbell CI,
Watson KL, Petrik JJ, Whitsett JA and Moorehead RA: Type I
insulin-like growth factor receptor induces pulmonary
tumorigenesis. Neoplasia. 11:672–682. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Goetsch L, Gonzalez A, Leger O, Beck A,
Pauwels PJ, Haeuw JF and Corvaia N: A recombinant humanized
anti-insulin-like growth factor receptor type I antibody (h7C10)
enhances the antitumor activity of vinorelbine and anti-epidermal
growth factor receptor therapy against human cancer xenografts. Int
J Cancer. 113:316–328. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29.
|
Cosaceanu D, Carapancea M, Castro J,
Ekedahl J, Kanter L, Lewensohn R and Dricu A: Modulation of
response to radiation of human lung cancer cells following
insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inactivation. Cancer Lett.
222:173–181. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Chung JH and Bunz F: Cdk2 Is required for
p53-independent G2/M checkpoint control. PLoS Genet.
6:e10008632010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Goldstone S, Pavey S, Forrest A, Sinnamon
J and Gabrielli B: Cdc25-dependent activation of cyclin A/cdk2 is
blocked in G2 phase arrested cells independently of
ATM/ATR. Oncogene. 209:921–932. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Strömberg T, Ekman S, Girnita L, Dimberg
LY, Larsson O, Axelson M, Lennartsson J, Hellman U, Carlson K,
Osterborg A, Vanderkerken K, Nilsson K and Jernberg-Wiklund H:
IGF-1 receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition by the cyclolignan PPP
induces G2/M-phase accumulation and apoptosis in
multiple myeloma cells. Blood. 107:669–678. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Lin CC, Kuo CT, Cheng CY, Wu CY, Lee CW,
Hsieh HL, Lee IT and Yang CM: IL-1β promotes A549 cell migration
via MAPKs/AP-1- and NF-κB-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-9
expression. Cell Signal. 21:1652–1662. 2009.
|
|
34.
|
Ellerbroek SM, Halbleib JM, Benavidez M,
Warmka JK, Wattenberg EV, Stack MS and Hudson LG:
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity in epidermal growth
factor-stimulated matrix metalloproteinase-9 production and cell
surface association. Cancer Res. 61:1855–1861. 2001.
|
|
35.
|
Wu X, Pang L, Lei W, Lu W, Li J, Li Z,
Frassica FJ, Chen X, Wan M and Cao X: Inhibition of Sca-1-positive
skeletal stem cell recruitment by alendronate blunts the anabolic
effects of parathyroid hormone on bone remodeling. Cell Stem Cell.
7:571–580. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Lu G, Haider HK, Jiang S and Ashraf M:
Sca-1+ stem cell survival and engraftment in the
infarcted heart: dual role for preconditioning induced connexin-43.
Circulation. 119:2587–2596. 2009.
|
|
37.
|
Jin C, Samuelson L, Cui CB, Sun Y and
Gerber DA: MAPK/ERK and Wnt/β-catenin pathways are synergistically
involved in proliferation of Sca-1 positive hepatic progenitor
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 409:803–807. 2011.
|
|
38.
|
Valentinis B, Morrione A, Peruzzi F,
Prisco M and Reiss K: Antiapoptotic signaling of the IGF-I receptor
in fibroblasts following loss of matrix adhesion. Oncogene.
18:1827–1836. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Wang YK, Zhu YL, Qiu FM, Zhang T, Chen ZG,
Zheng S and Huang J: Activation of Akt and MAPK pathways enhances
the tumorigenicity of CD133+ primary colon cancer cells.
Carcinogenesis. 31:1376–1380. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|