Introduction
Peliosis hepatis (PH) is a rare condition
characterized by blood-filled cystic cavities, ranging between 1 mm
and several centimeters in diameter (1,2). The
mechanism of PH is associated with sinusoidal expansion, which is
caused by obstructions in the junction of the sinusoidal and
central veins of the liver. This results in focal hepatic necrosis,
liver sinusoidal barrier destruction and damaged endothelial cells,
as red blood cells enter the space of Disse from the sinusoids and
form cystic cavities (3). The
current study presents the case of a 19-year-old male who
complained of right upper quadrant pain that had lasted for three
days. The patient was a student with no previous medical history.
Contrast enhanced computer tomography (CT) and ultrasonography
identified a neoplasm in the right liver, which was hypothesized to
indicate primary liver cancer by the manifestation of the disease
and the physical tests. The patient was treated successfully with
an irregular right hemihepatectomy and was in good health at
6-months post-surgery. A tissue specimen was obtained and was
determined to be PH by pathological examination and
immunohistochemistry analysis. Written informed consent was
obtained from the patient.
Case report
A 19-year-old male was admitted to Xiangya Second
Hospital (Changsha, China) complaining of right upper quadrant pain
that had lasted for three days. Enhanced CT and ultrasonography
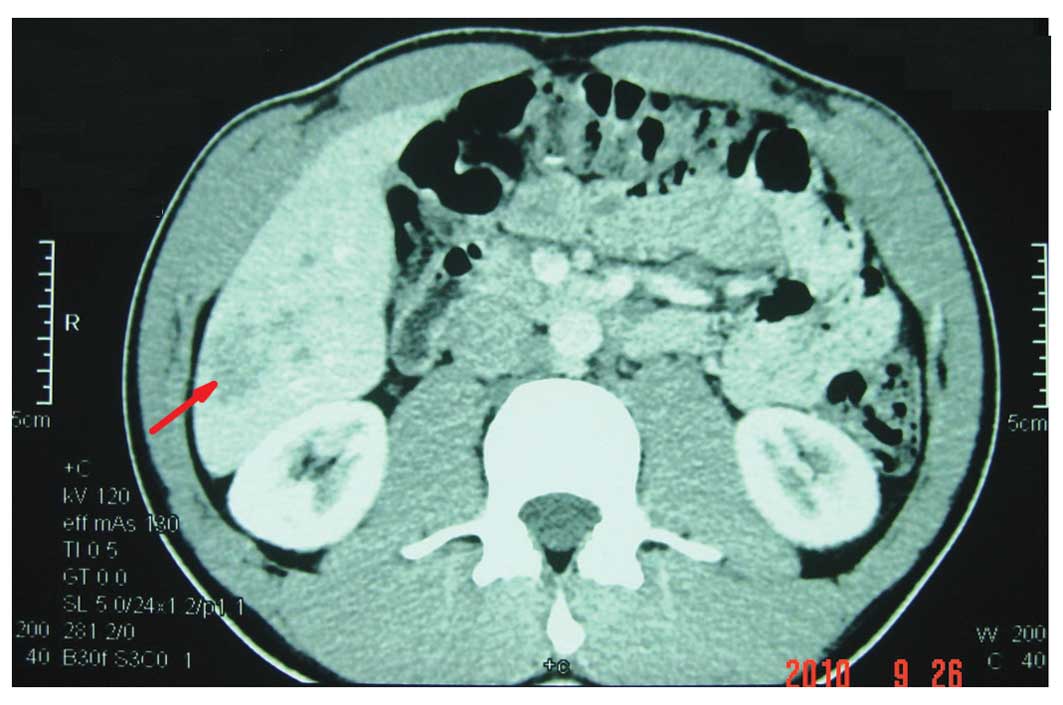
showed a neoplasm of ~3.5×4.5×4.5 cm in size in the right lobe of
the liver (Fig. 1). The periphery
of the neoplasm was significantly enhanced in the arterial phase.
Laboratory tests were performed with the following results: White
blood cell count, 4.8×109/l (normal,
4–10×109/l); hemoglobin, 155 g/l (normal, 110–160 g/l);
hematocrit, 47.7% (normal, 39–52%); platelet count,
232×109/l (normal, 100–300×109/l); total
bilirubin, 12.6 μmol/l (normal, 5.1–17.1 μmol/l); prothrombin time,
12 sec (normal, 11–15 sec); and α-fetoprotein, 2.01 mg/l (normal,
<20 mg/l). In addition, electrocardiography and chest X-rays
showed no marked abnormalities. The patient had no previous medical
history and no history of exposure to toxic agents or drug use.
Right upper quadrant pain lasting three days was the only
manifestation and the degree of pain was slight, but persistent,
and was not accompanied by fever or vomiting. The case was
discussed with radiologists due to its specificity and a diagnosis
of a hepatocarcinoma was suggested.
Following the pre-operative preparations, surgery
was performed under general anesthesia. A mass was identified in
the right lobe of the liver, but it did not resemble a
hepatocarcinoma and the texture was soft. Mobilization of the right
liver lobe was carried out by cutting the ligaments, and prior to
cutting the mass, the Pringle maneuver was performed to prevent
bleeding. As predicted, the intraoperative frozen pathology of the
mass indicated that it was benign. The patient recovered well and
was discharged one week later.
The specimen was confirmed to be PH by pathological
examination and immunohistochemistry analysis. Microscopically,
there were blood filled cystic spaces of variable sizes and
hemorrhagic necroses were present adjacent to peliotic spaces
without endothelial lining (Fig.
2). Immunohistochemistry tests for CD31, CD34 and SMA were
negative in the sinusoidal dilation area, but positive in the
normal sinusoidal area.
Discussion
PH was first described in 1861 by Wagner (4) and named by Schoenlank in 1916
(5). The etiology of PH remains
unknown, but it has been reported to be associated with infectious
and non-infectious causes, including drugs, chemicals, bacterial
and viral infections and malignancies. Bartonella henselae
is hypothesized to be the primary cause of infection (6) and Kitchell et al(7) previously demonstrated that PH is
associated with Bartonella henselae in dogs. In addition,
human immunodeficiency virus infection (8) and other wasting diseases (6,9–11) are
associated with PH due to the patients weakened immune system,
which directly or indirectly increases the risk of Bartonella
henselae infection. However, a previous study reported that PH
in cats is not associated with Bartonella henselae infection
(12), indicating that cats have
limited value as models for the analysis of Bartonella
henselae in PH and that this association must be investigated
further. The action of vascular endothelial growth factor has been
observed to be important in the pathogenesis of PH (13). Drugs that act against PH include
androgenic-anabolic steroids (3),
tamoxifen (14), contraceptive
steroids (15) and corticosteroids
(16). Notably, PH may present as
the cardinal symptom of specific diseases, including Hodgkin’s
lymphoma (17). However, the causes
of PH have not be identified in 20–50% of patients (18), as observed in the current case
report.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most
common types of tumor worldwide, and particularly in China.
Enhanced CT is the primary tool used to distinguish PH from HCC.
Commonly, HCC shows hyperattenuation during the arterial phase,
with rapid washout during the portal venous phase and iso- or
hypoattenuation during the delayed phase. By contrast, during the
arterial phase of PH, the lesions usually show early globular
enhancement. In addition, multiple small accumulations of contrast
material in the center and centrifugal progression of enhancement,
without a mass effect on hepatic vessels, is present during the
portal venous phase, as determined by enhanced CT. Diffuse
increased attenuation may be observed during the delayed phase
(18–20). Small lesions (diameter, >1 cm)
may not be visible on enhanced CT (21) and magnetic resonance images are
atypical for such lesions and the lesions may therefore be confused
with hematomas, hemangiomas and HCC (2). PH may not be completely distinguished
from HCC and other liver tumors by imaging tests. In the current
case report, the patient had no previous medical history and
enhanced CT showed a neoplasm mimicking cancer with atypical
symptoms and a negative AFP value, making the formation of a
diagnosis difficult. In addition, a biopsy was not performed as it
could have caused a fatal hemorrhage.
An increasing number of studies have analyzed PH and
possible differential diagnoses include hemangioma, hepatic
adenoma, focal nodular hyperplasia, hepatic abscess and
hypervascular metastases. In patients with atypical liver lesions,
a diagnosis of PH must be considered, particularly in patients with
no previous medical history or identifiable causes. Currently,
there are no specific treatments available for PH, however, surgery
must be performed on patients with a hemorrhage, long-term medical
history or limited lesions. In addition, a liver transplant is
necessary when patients have serious accompanying symptoms,
including hepatic function failure. In these cases, the termination
of any prescribed drugs is vital.
Abbreviations:
|
PH
|
peliosis hepatis
|
|
CT
|
computer tomography
|
References
|
1
|
Zak FG: Peliosis hepatis. Am J Pathol.
26:1–15. 1950.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Iannaccone R, Federle MP, Brancatelli G,
et al: Peliosis hepatis: spectrum of imaging findings. AJR Am J
Roentgenol. 187:W43–W52. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Garcia-Tsao G, Panzini L, Yoselevitz M and
West AB: Bacillary peliosis hepatis as a cause of acute anemia in a
patient with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
Gastroenterology. 102:1065–1070. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wagner E: Ein fall von blutcysten in der
leber. Arc Heilkunde. 2:369–370. 1861.(In German).
|
|
5
|
Schoenlank W: Ein fall von peliosis
hepatis. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat. 222:358–364. 1916.(In
German).
|
|
6
|
Slater LN, Welch DF and Min KW:
Rochalimaea henselae causes bacillary angiomatosis and
peliosis hepatis. Arch Intern Med. 152:602–606. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kitchell BE, Fan TM, Kordick D,
Breitschwerdt EB, Wollenberg G and Lichtensteiger CA: Peliosis
hepatis in a dog infected with Bartonella henselae. J Am Vet
Med Assoc. 216:519–523. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Koehler JE: Bartonella-associated
infections in HIV-infected patients. AIDS Clin Care. 7:97–102.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lie JT: Pulmonary peliosis. Arch Pathol
Lab Med. 109:878–879. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nadell J and Kosek J: Peliosis hepatis.
Twelve cases associated with oral androgen therapy. Arch Pathol Lab
Med. 101:405–410. 1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tsutsumi Y, Ito S, Ichiki K, et al:
Systemic amyloidosis complicated with peliosis. Ann Hematol.
88:917–920. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Buchmann AU, Kempf VA, Kershaw O and
Gruber AD: Peliosis hepatis in cats is not associated with
Bartonella henselae infections. Vet Pathol. 47:163–166.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Edwards R, Colombo T and Greaves P: ‘Have
you seen this?’peliosis hepatis. Toxicologic Pathol. 30:521–523.
2002.
|
|
14
|
Malet PF and Moonka D: Peliosis hepatis:
old disease, new cause. Gastroenterology. 101:864–866.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zafrani ES, Pinaudeau Y, Le Cudonnec B,
Julien M and Dhumeaux D: Focal hemorrhagic necrosis of the liver. A
clinicopathological entity possibly related to oral contraceptives.
Gastroenterology. 79:1295–1299. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bagheri SA and Boyer JL: Peliosis hepatis
associated with androgenic-anabolic steroid therapy. A severe form
of hepatic injury. Ann Intern Med. 81:610–618. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kleger A, Bommer M, Kunze M, et al: First
reported case of disease: peliosis hepatis as cardinal symptom of
Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Oncologist. 14:1088–1094. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim SH, Lee JM, Kim WH, Han JK, Lee JY and
Choi BI: Focal peliosis hepatis as a mimicker of hepatic tumors:
radiological-pathological correlation. J Comput Assist Tomogr.
31:79–85. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gouya H, Vignaux O, Legmann P, de Pigneux
G and Bonnin A: Peliosis hepatis: triphasic helical CT and dynamic
MRI findings. Abdom Imaging. 26:507–509. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Savastano S, San Bortolo O, Velo E,
Rettore C and Altavilla G: Pseudotumoral appearance of peliosis
hepatis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 185:558–559. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Radin DR and Kanel GC: Peliosis hepatis in
a patient with human immunodeficiency virus infection. AJR Am J
Roentgenol. 156:91–92. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|