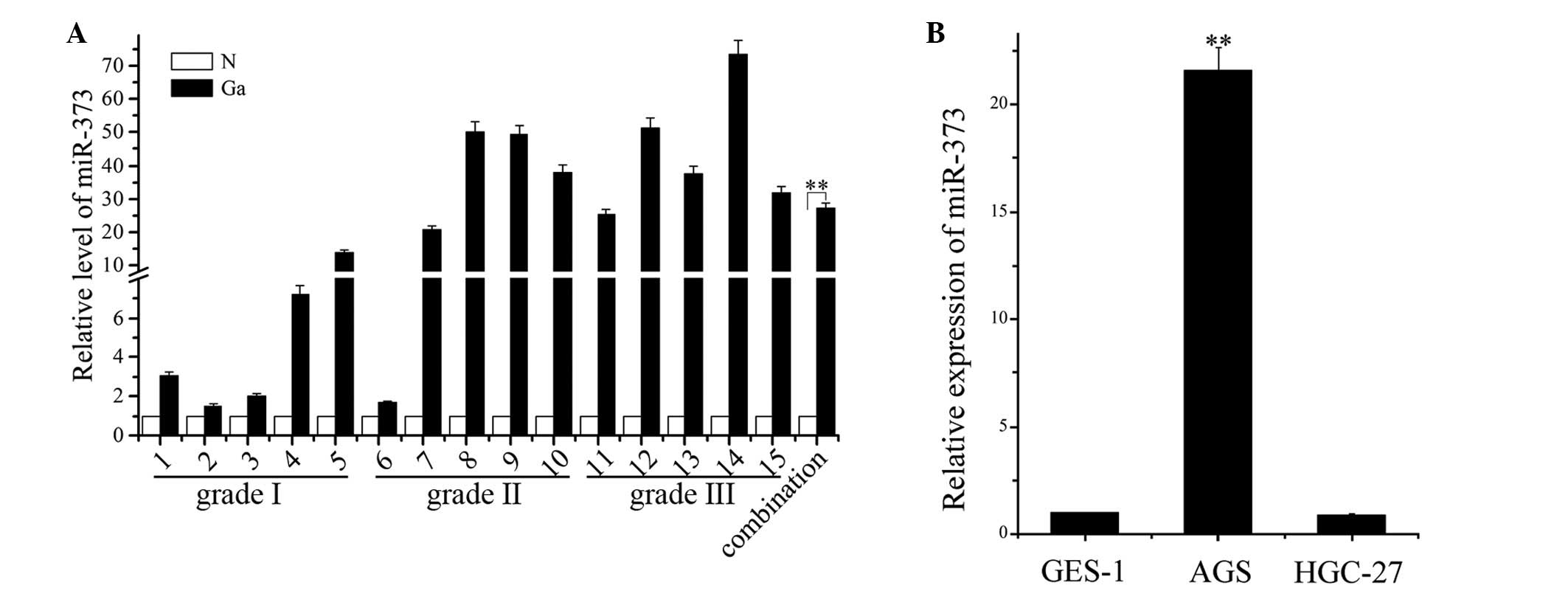
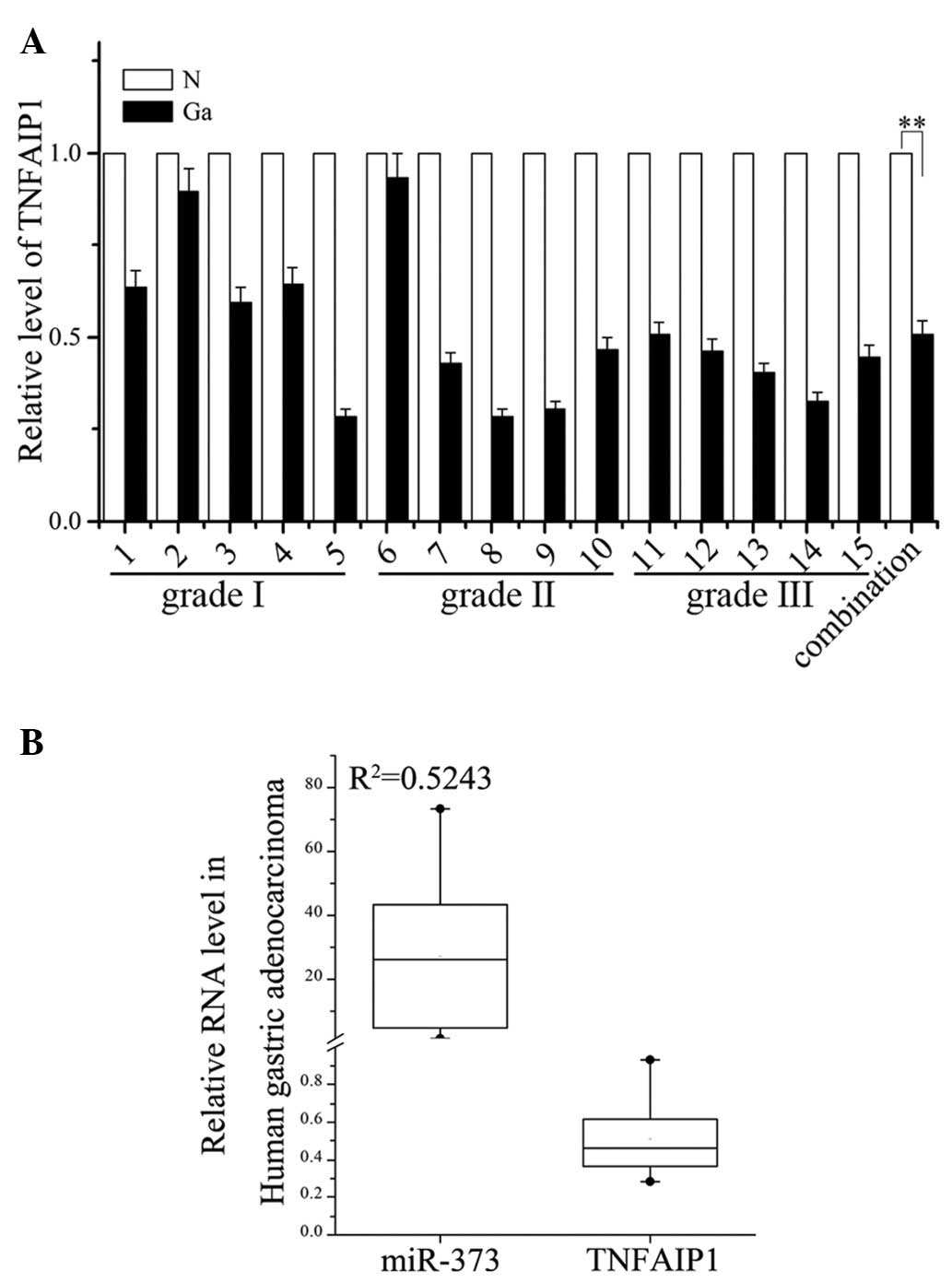
|
1
|
Kamangar F, Dores GM and Anderson WF:
Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five
continents: defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in
different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol.
24:2137–2150. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Catalano V, Labianca R, Beretta GD, Gatta
G, de Braud F and Van Cutsem E: Gastric cancer. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 71:127–164. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gao C, Zhang Z, Liu W, Xiao S, Gu W and Lu
H: Reduced microRNA-218 expression is associated with high nuclear
factor kappa B activation in gastric cancer. Cancer. 116:41–49.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shah MA, Jhawer M, Ilson DH, et al: Phase
II study of modified docetaxel, cisplatin, and fluorouracil with
bevacizumab in patients with metastatic gastroesophageal
adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 29:868–874. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mukherji S, Ebert MS, Zheng GX, Tsang JS,
Sharp PA and van Oudenaarden A: MicroRNAs can generate thresholds
in target gene expression. Nat Genet. 43:854–859. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pichinuk E, Broday L and Wreschner DH:
Endogenous RNA cleavages at the ribosomal SRL site likely reflect
miRNA (miR) mediated translational suppression. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 414:706–711. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xiao B, Guo J, Miao Y, et al: Detection of
miR-106a in gastric carcinoma and its clinical significance. Clin
Chim Acta. 400:97–102. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang Z, Li Z, Gao C, et al: miR-21 plays
a pivotal role in gastric cancer pathogenesis and progression. Lab
Invest. 88:1358–1366. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Voorhoeve PM, le Sage C, Schrier M, et al:
A genetic screen implicates miRNA-372 and miRNA-373 as oncogenes in
testicular germ cell tumors. Cell. 124:1169–1181. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lee KH, Goan YG, Hsiao M, et al:
MicroRNA-373 (miR-373) post-transcriptionally regulates large tumor
suppressor, homolog 2 (LATS2) and stimulates proliferation in human
esophageal cancer. Exp Cell Res. 315:2529–2538. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhou C, Li X, Zhang X, et al: microRNA-372
maintains oncogene characteristics by targeting TNFAIP1 and affects
NFκB signaling in human gastric carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol.
42:635–642. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hamilton SR and Aaltonen LA: Pathology and
genetics Tumours of the digestive system. WHO Classification of
Tumours. Kleihues P and Sobin LH: 2. IARC Press; Lyon: 2000
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
16
|
Zeng Y and Cullen BR: Sequence
requirements for micro RNA processing and function in human cells.
RNA. 9:112–123. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cho WJ, Shin JM, Kim JS, et al: miR-372
regulates cell cycle and apoptosis of ags human gastric cancer cell
line through direct regulation of LATS2. Mol Cells. 28:521–527.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chan SH, Wu CW, Li AF, Chi CW and Lin WC:
miR-21 microRNA expression in human gastric carcinomas and its
clinical association. Anticancer Res. 28:907–911. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lai KW, Koh KX, Loh M, et al:
MicroRNA-130b regulates the tumour suppressor RUNX3 in gastric
cancer. Eur J Cancer. 46:1456–1463. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Motoyama K, Inoue H, Nakamura Y, Uetake H,
Sugihara K and Mori M: Clinical significance of high mobility group
A2 in human gastric cancer and its relationship to let-7 microRNA
family. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2334–2340. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ueda T, Volinia S, Okumura H, et al:
Relation between microRNA expression and progression and prognosis
of gastric cancer: a microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol.
11:136–146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang Y, Chao T, Li R, et al: MicroRNA-128
inhibits glioma cells proliferation by targeting transcription
factor E2F3a. J Mol Med (Berl). 87:43–51. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Spizzo R, Nicoloso M, Lupini L, et al:
miR-145 participates with TP53 in a death-promoting regulatory loop
and targets estrogen receptor-alpha in human breast cancer cells.
Cell Death Differ. 17:246–254. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Hayashita Y, Osada H, Tatematsu Y, et al:
A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17–92, is overexpressed in
human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res.
65:9628–9632. 2005.
|
|
25
|
Martinez NJ and Gregory RI: MicroRNA gene
regulatory pathways in the establishment and maintenance of ESC
identity. Cell Stem Cell. 7:31–35. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou J, Hu X, Xiong X, et al: Cloning of
two rat PDIP1 related genes and their interactions with
proliferating cell nuclear antigen. J Exp Zool A Comp Exp Biol.
303:227–240. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Link CD, Taft A, Kapulkin V, et al: Gene
expression analysis in a transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans
Alzheimer’s disease model. Neurobiol Aging. 24:397–413. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang L, Zhou A, Li H, et al: Expression
profile in the cell lines of human TNFAIP1 gene. Yi Chuan.
28:918–922. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
29
|
Wolf F, Marks R, Sarma V, et al:
Characterization of a novel tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced
endothelial primary response gene. J Biol Chem. 267:1317–1326.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang L, Liu N, Hu X, et al: CK2
phosphorylates TNFAIP1 to affect its subcellular localization and
interaction with PCNA. Mol Biol Rep. 37:2967–2973. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|