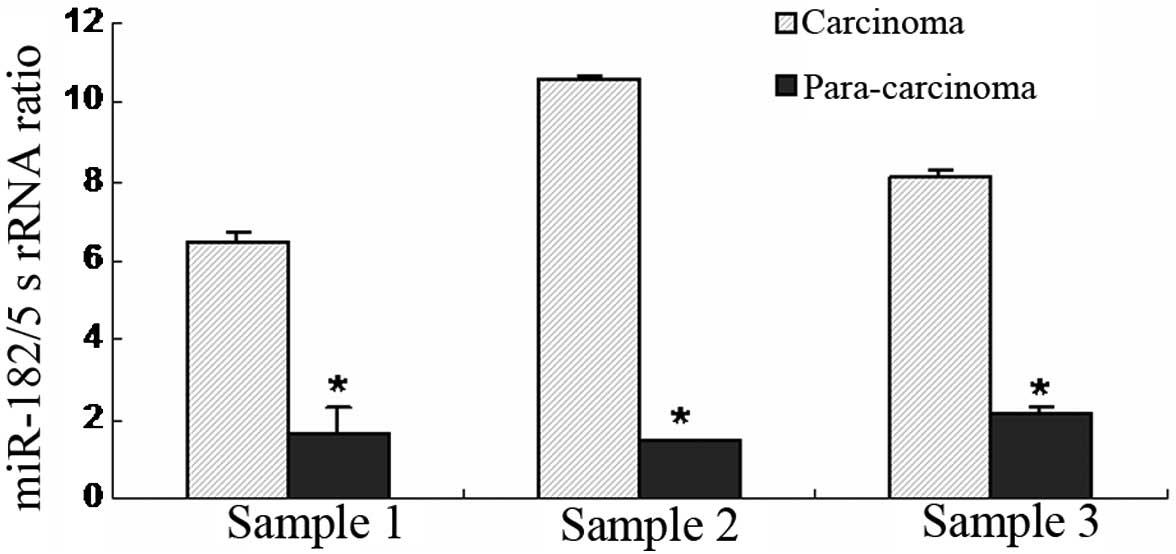
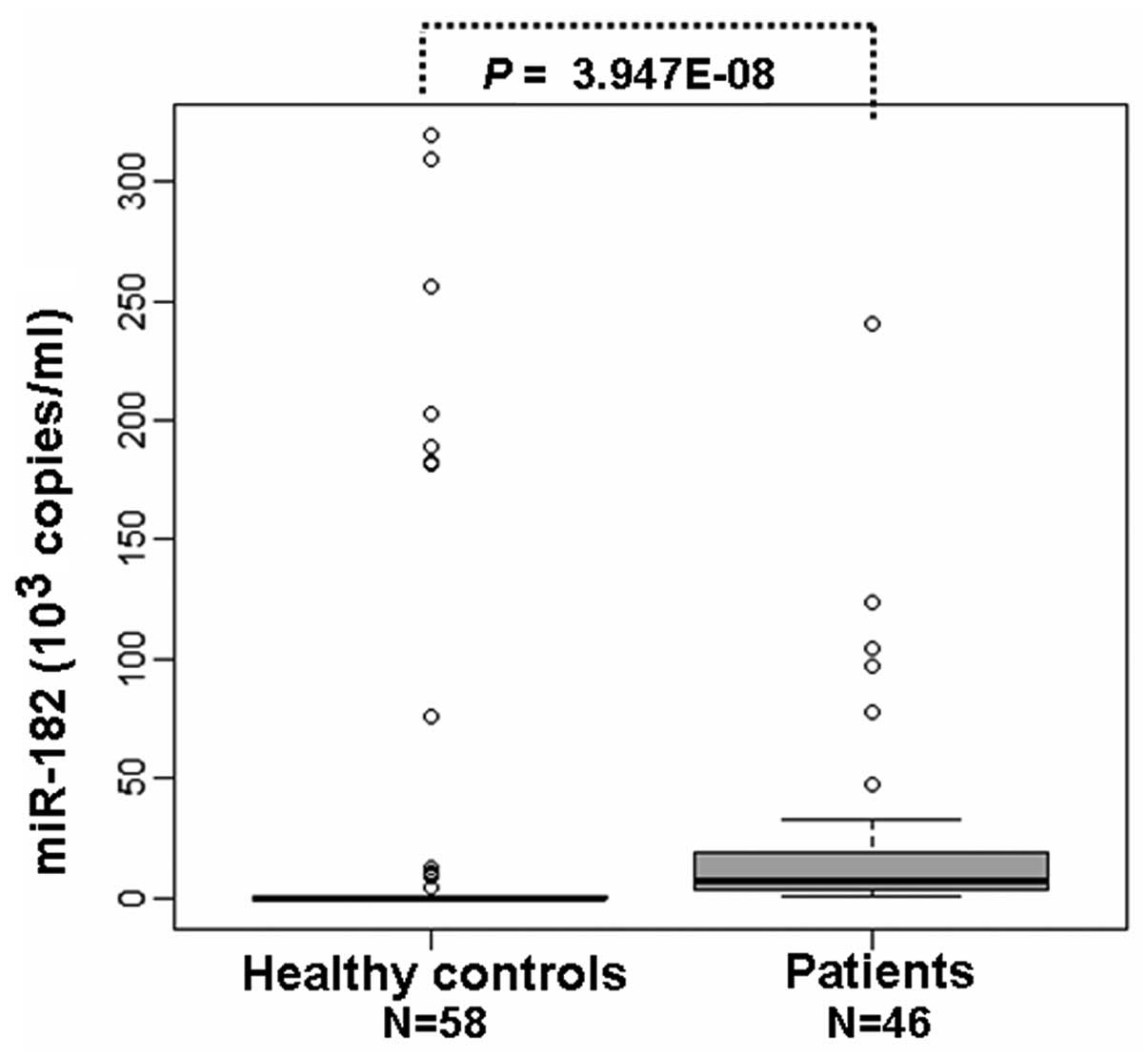
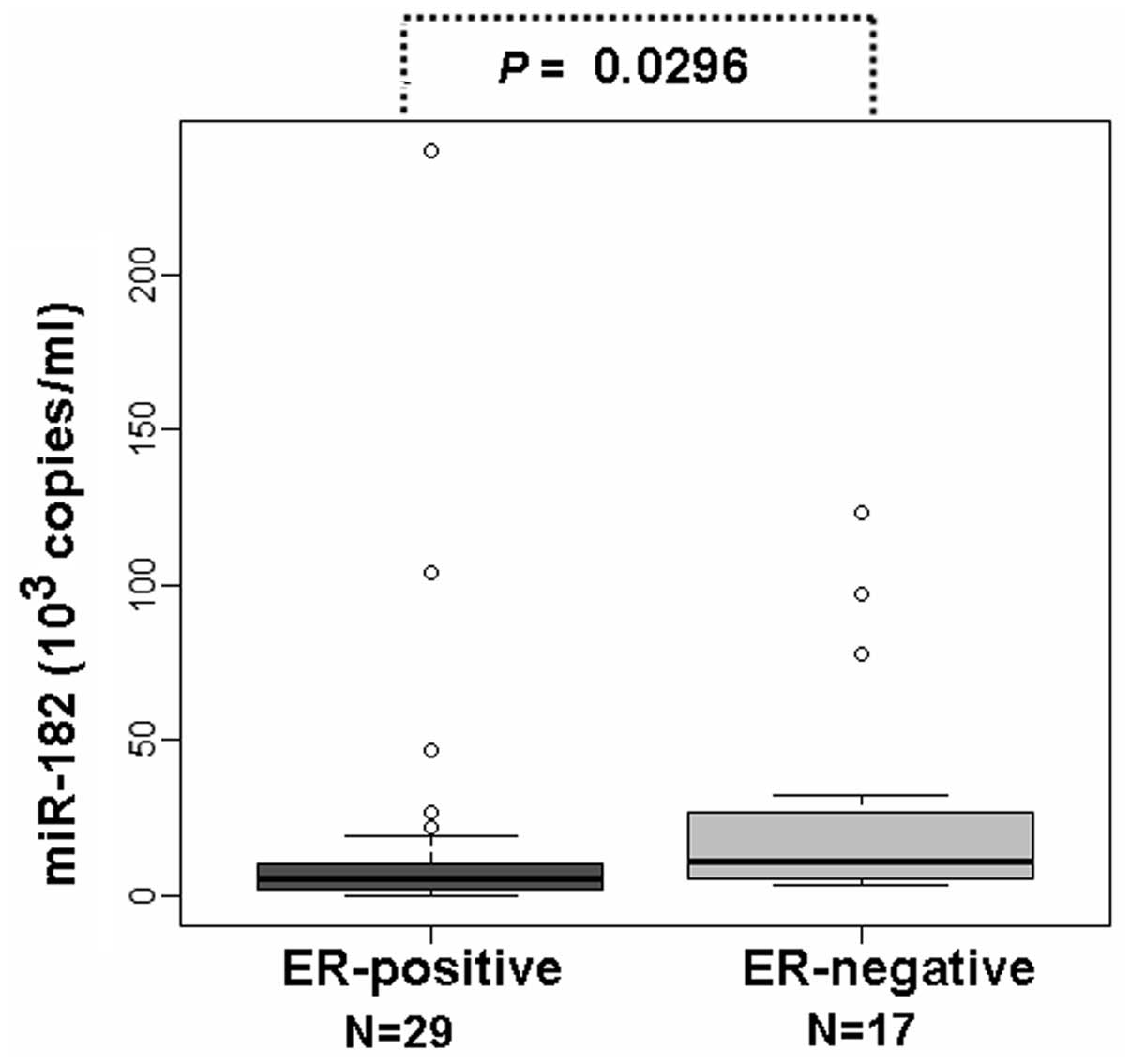
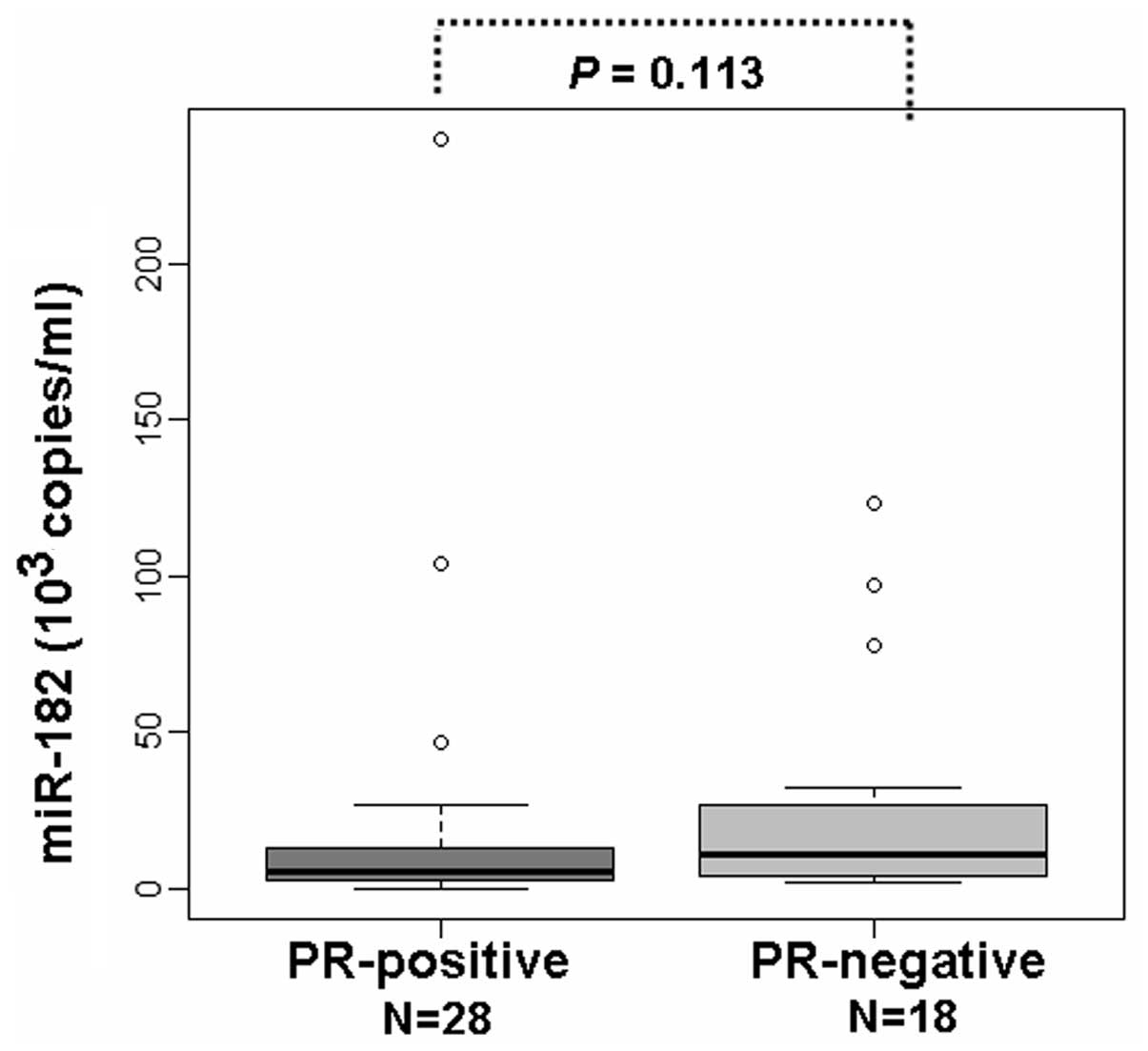
|
1
|
Sariego J: Breast cancer in the young
patient. Am Surg. 76:1397–1400. 2010.
|
|
2
|
Anders CK and Carey LA: Biology,
metastatic patterns, and treatment of patients with triple-negative
breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 9(Suppl 2): S73–S81. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kloosterman WP and Plasterk RH: The
diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease.
Dev Cell. 11:441–450. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stefani G and Slack FJ: Small non-coding
RNAs in animal development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:219–230. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Di Leva G, Piovan C, Gasparini P, et al:
Estrogen mediated-activation of miR-191/425 cluster modulates
tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells depending on estrogen
receptor status. PLoS Genet. 9:e10033112013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ozgün A, Karagoz B, Bilgi O, Tuncel T,
Baloglu H and Kandemir EG: MicroRNA-21 as an indicator of
aggressive phenotype in breast cancer. Onkologie. 36:115–118.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Han M, Liu M, Wang Y, et al: Re-expression
of miR-21 contributes to migration and invasion by inducing
epithelial-mesenchymal transition consistent with cancer stem cell
characteristics in MCF-7 cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 363:427–436.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yu SJ, Hu JY, Kuang XY, et al:
MicroRNA-200a promotes anoikis resistance and metastasis by
targeting YAP1 in human breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
19:1389–1399. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Castilla MÁ, Díaz-Martín J, Sarrió D, et
al: MicroRNA-200 family modulation in distinct breast cancer
phenotypes. PLoS One. 7:e477092012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sun X, Qin S, Fan C, Xu C, Du N and Ren H:
Let-7: a regulator of the ERα signaling pathway in human breast
tumors and breast cancer stem cells. Oncol Rep. 29:2079–2087.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Taylor DD and Gercel-Taylor C: MicroRNA
signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of
ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 110:13–21. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hunter MP, Ismail N, Zhang X, et al:
Detection of microRNA expression in human peripheral blood
microvesicles. PLoS One. 3:e36942008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, et al:
Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer
detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:10513–10518. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu W, Qin W, Atasoy U and Sauter ER:
Circulating microRNAs in breast cancer and healthy subjects. BMC
Res Notes. 2:892009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Heneghan HM, Miller N, Lowery AJ, Sweeney
KJ, Newell J and Kerin MJ: Circulating microRNAs as novel minimally
invasive biomarkers for breast cancer. Ann Surg. 251:499–505. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schrauder MG, Strick R, Schulz-Wendtland
R, et al: Circulating micro-RNAs as potential blood-based markers
for early stage breast cancer detection. PLoS One. 7:e297702012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu AH, Vigen C, Razavi P, Tseng CC and
Stancyzk FZ: Alcohol and breast cancer risk among Asian-American
women in Los Angeles County. Breast Cancer Res. 14:R1512012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shrubsole MJ, Gao YT, Dai Q, et al:
Passive smoking and breast cancer risk among non-smoking Chinese
women. Int J Cancer. 110:605–609. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gammon MD, Eng SM, Teitelbaum SL, et al:
Environmental tobacco smoke and breast cancer incidence. Environ
Res. 96:176–185. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chiang CH, Hou MF and Hung WC:
Up-regulation of miR-182 by β-catenin in breast cancer increases
tumorigenicity and invasiveness by targeting the matrix
metalloproteinase inhibitor RECK. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1830:3067–3076. 2013.
|
|
21
|
Krishnan K, Steptoe AL, Martin HC, et al:
MicroRNA-182-5p targets a network of genes involved in DNA repair.
RNA. 19:230–242. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cui X, Schiff R, Arpino G, Osborne CK and
Lee AV: Biology of progesterone receptor loss in breast cancer and
its implications for endocrine therapy. J Clin Oncol. 23:7721–7735.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Diaz NM: Laboratory testing for HER2/neu
in breast carcinoma: an evolving strategy to predict response to
targeted therapy. Cancer Control. 8:415–418. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Heneghan HM, Miller N, Lowery AJ, Sweeney
KJ and Kerin MJ: MicroRNAs as Novel Biomarkers for Breast Cancer. J
Oncol. 2009:9502012009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xi Y, Nakajima G, Gavin E, et al:
Systematic analysis of microRNA expression of RNA extracted from
fresh frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples. RNA.
13:1668–1674. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li J, Smyth P, Flavin R, et al: Comparison
of miRNA expression patterns using total RNA extracted from matched
samples of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) cells and snap
frozen cells. BMC Biotechnol. 7:362007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, et al: MicroRNA
expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 435:834–838.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, et al:
MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 65:7065–7070. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mattie MD, Benz CC, Bowers J, et al:
Optimized high-throughput microRNA expression profiling provides
novel biomarker assessment of clinical prostate and breast cancer
biopsies. Mol Cancer. 5:242006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhong S, Chen Z, Xu J, Li W and Zhao J:
Pre-mir-27a rs895819 polymorphism and cancer risk: a meta-analysis.
Mol Biol Rep. 40:3181–3186. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pastrello C, Polesel J, Della Puppa L,
Viel A and Maestro R: Association between hsa-mir-146a genotype and
tumor age-of-onset in BRCA1/BRCA2-negative familial breast and
ovarian cancer patients. Carcinogenesis. 31:2124–2126. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Linhares JJ, Azevedo M Jr, Siufi AA, et
al: Evaluation of single nucleotide polymorphisms in microRNAs
(hsa-miR-196a2 rs11614913 C/T) from Brazilian women with breast
cancer. BMC Med Genet. 13:1192012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Moskwa P, Buffa FM, Pan Y, et al:
miR-182-mediated downregulation of BRCA1 impacts DNA repair and
sensitivity to PARP inhibitors. Mol Cell. 41:210–220. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Guttilla IK and White BA: Coordinate
regulation of FOXO1 by miR-27a, miR-96, and miR-182 in breast
cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 284:23204–23216. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, et al:
Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers
for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 18:997–1006.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu J, Mao Q, Liu Y, Hao X, Zhang S and
Zhang J: Analysis of miR-205 and miR-155 expression in the blood of
breast cancer patients. Chin J Cancer Res. 25:46–54.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen W, Cai F, Zhang B, Barekati Z and
Zhong XY: The level of circulating miRNA-10b and miRNA-373 in
detecting lymph node metastasis of breast cancer: potential
biomarkers. Tumour Biol. 34:455–462. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Si H, Sun X, Chen Y, et al: Circulating
microRNA-92a and microRNA-21 as novel minimally invasive biomarkers
for primary breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 139:223–229.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Osborne CK, Schiff R, Arpino G, Lee AS and
Hilsenbeck VG: Endocrine responsiveness: understanding how
progesterone receptor can be used to select endocrine therapy.
Breast. 14:458–465. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Faheem M, Mahmood H, Khurram M, Qasim U
and Irfan J: Estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and Her 2
Neu positivity and its association with tumour characteristics and
menopausal status in a breast cancer cohort from northern Pakistan.
Ecancermedicalscience. 6:2832012.
|