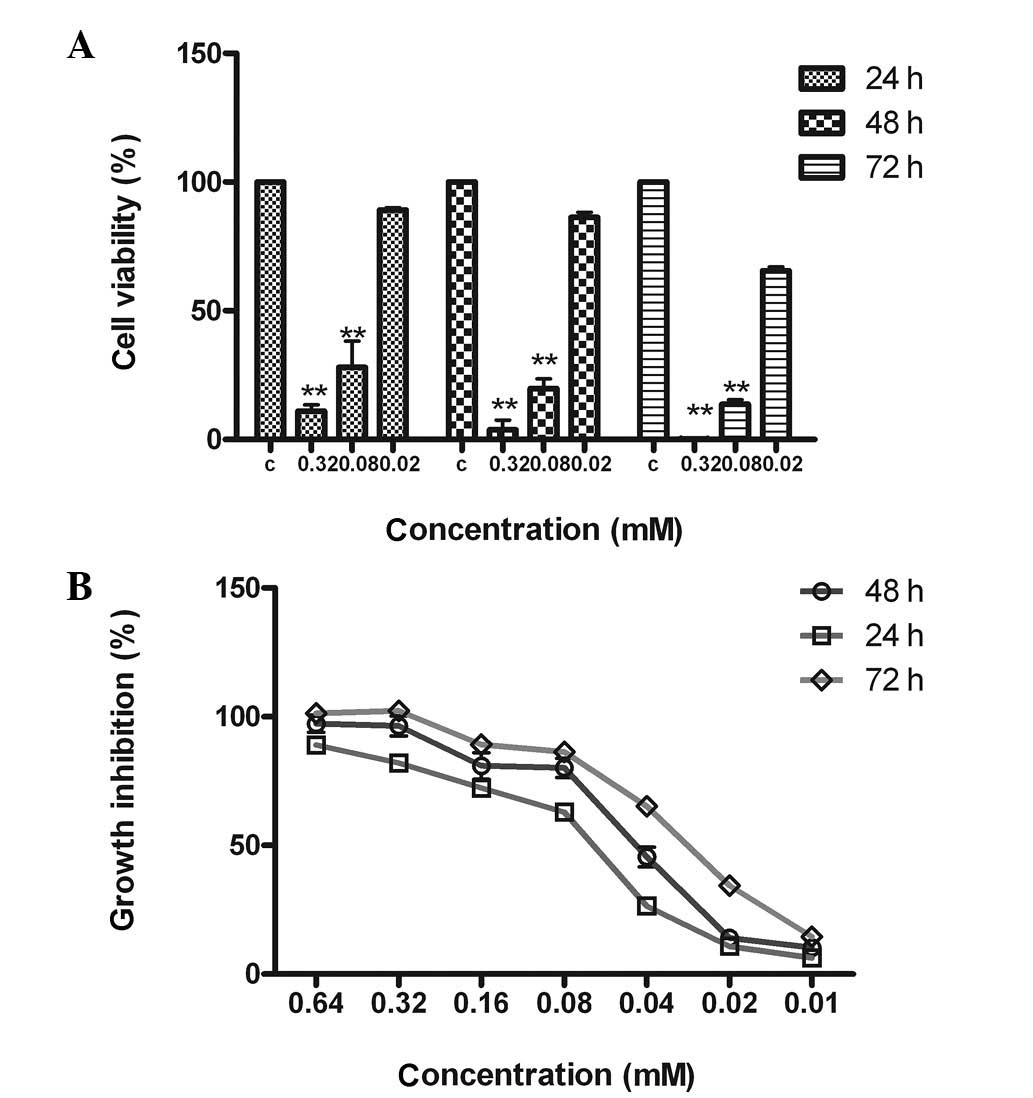
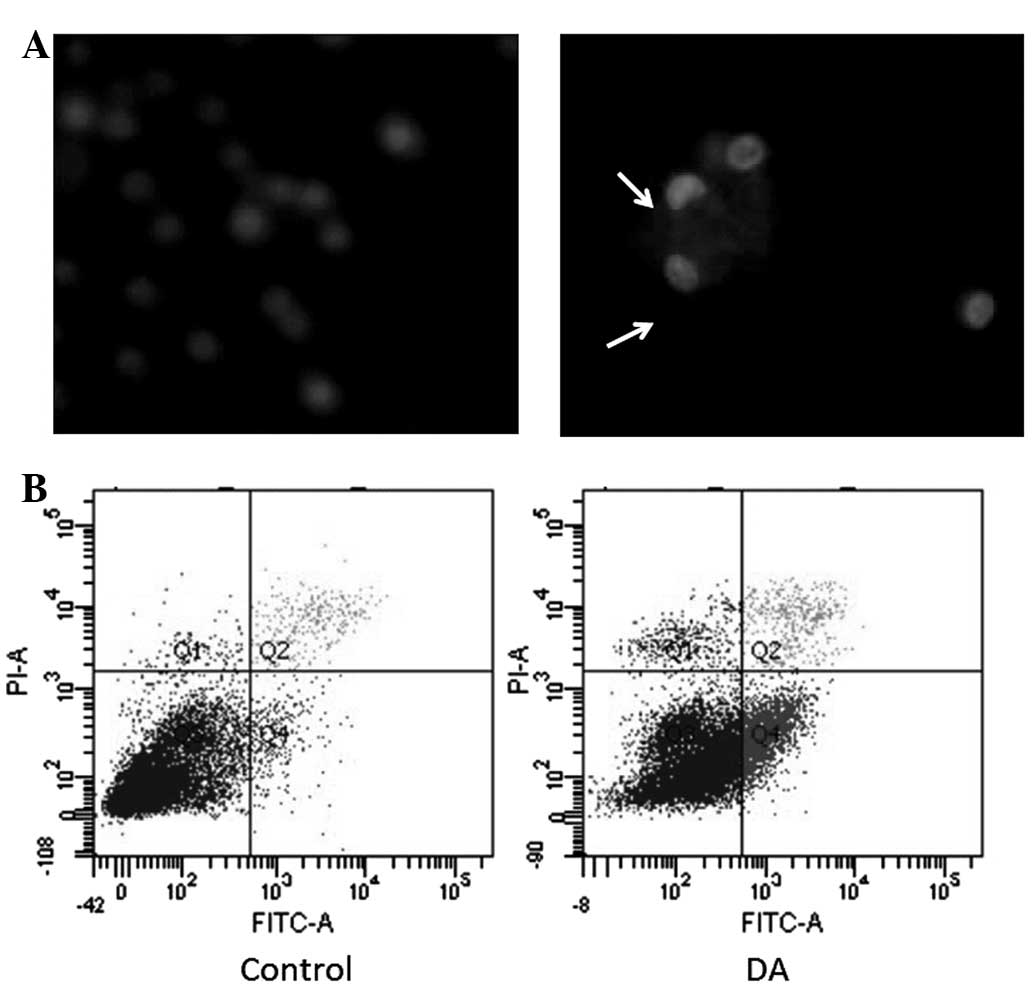
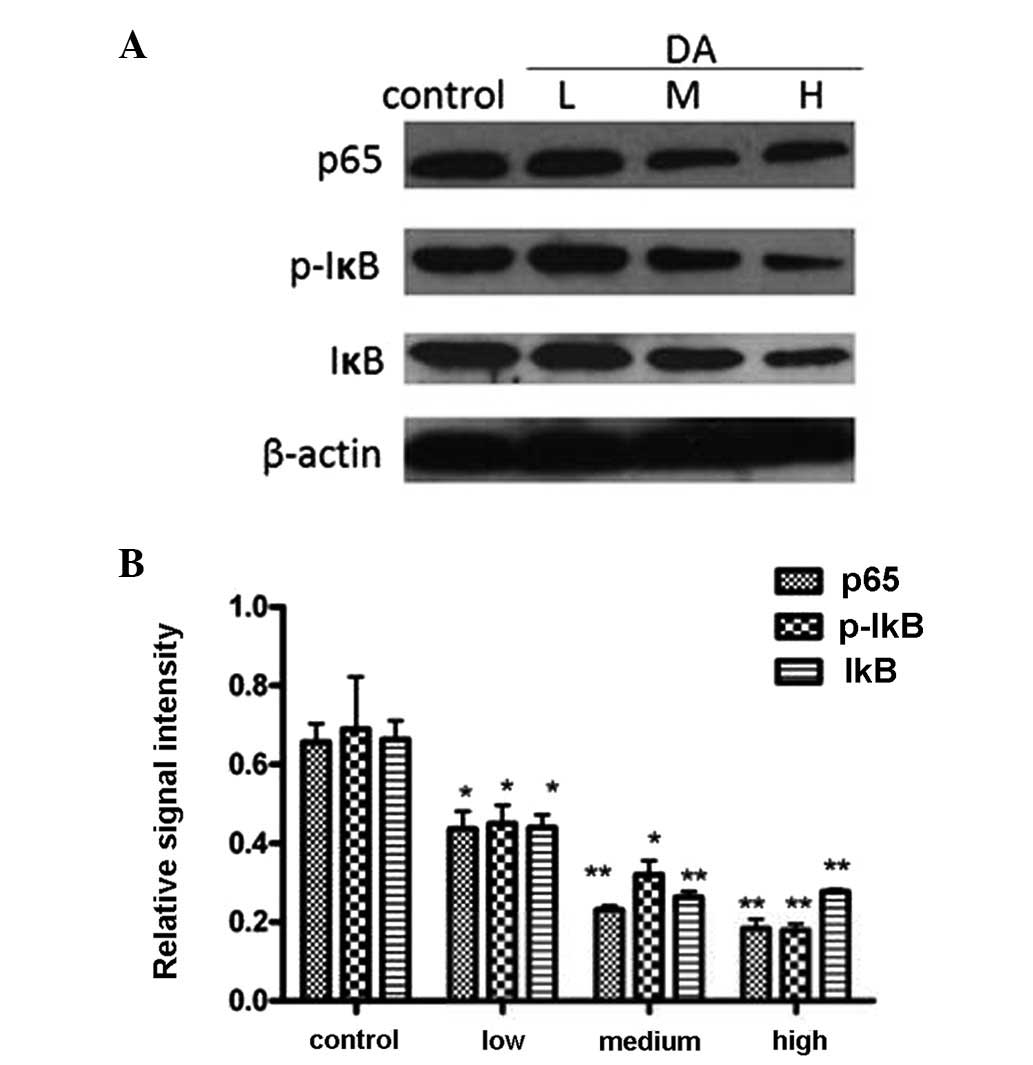
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al: Global
cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hortobagyi GN: Treatment of breast cancer.
N Engl J Med. 339:974–984. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chen X, Yang L, Zhang N, et al: Shikonin,
a component of Chinese herbal medicine, inhibits chemokine receptor
function and suppresses human immunodeficiency virus type 1.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 47:2810–2816. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mao X, Yu CR, Li WH and Li WX: Induction
of apoptosis by shikonin through a ROS/JNK-mediated process in
Bcr/Abl-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) cells. Cell
Res. 18:879–888. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang H, Zhou P, Huang H, et al: Shikonin
exerts antitumor activity via proteasome inhibition and cell death
induction in vitro and in vivo. Int J Cancer. 124:2450–2459. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu YY, Wan LH, Zheng XW, et al: Inhibitory
effects of β,β-dimethylacrylshikonin on hepatocellular carcinoma in
vitro and in vivo. Phytother Res. 26:764–771. 2012.
|
|
8
|
Pietrosiuk A, Furmanowa M,
Skopińiska-Rózewska E, et al: The effect of acetylshikonin isolated
from Lithospermum canescens roots on tumor-induced cutaneous
angiogenesis. Acta Pol Pharm. 61:379–382. 2004.
|
|
9
|
Gong K and Li W: Shikonin, a Chinese
plant-derived naphthoquinone, induces apoptosis in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells through reactive oxygen species: A potential new
treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Free Radic Biol Med.
51:2259–2271. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kim SH, Kang IC, Yoon TJ, et al: Antitumor
activities of a newly synthesized shikonin derivative,
2-hyim-DMNQ-S-33. Cancer Lett. 172:171–175. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Litchfield JT Jr and Wilcoxon F: A
simplified method of evaluating dose-effect experiments. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 96:99–113. 1949.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zeng Y, Liu G and Zhou LM: Inhibitory
effect of acetylshikonin on human gastric carcinoma cell line
SGC-7901 in vitro and in vivo. World J Gastroenterol. 15:1816–1820.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen X, Yang L, Oppenheim JJ and Howard
MZ: Cellular pharmacology studies of shikonin derivatives.
Phytother Res. 16:199–209. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lu L, Qin A, Huang H, et al: Shikonin
extracted from medicinal Chinese herbs exerts anti-inflammatory
effect via proteasome inhibition. Eur J Pharmacol. 658:242–247.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sankawa U, Ebizuka Y, Miyazaki T, et al:
Antitumor activity of shikonin and its derivatives. Chem Pharm Bull
(Tokyo). 25:2392–2395. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yoshimi N, Wang A, Morishita Y, et al:
Modifying effects of fungal and herb metabolites on
azoxymethane-induced intestinal carcinogenesis in rats. Jpn J
Cancer Res. 83:1273–1278. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ahn BZ, Baik KU, Kweon GR, et al:
Acylshikonin analogues: synthesis and inhibition of DNA
topoisomerase-I. J Med Chem. 38:1044–1047. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Plyta ZF, Li T, Papageorgiou VP, et al:
Inhibition of topoisomerase I by naphthoquinone derivatives. Bioorg
Med Chem Lett. 8:3385–3390. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang F, Chen Y, Duan W, et al: SH-7, a new
synthesized shikonin derivative, exerting its potent antitumor
activities as a topoisomerase inhibitor. Int J Cancer.
119:1184–1193. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gaddipati JP, Mani H, Shefali, et al:
Inhibition of growth and regulation of IGFs and VEGF in human
prostate cancer cell lines by shikonin analogue 93/637 (SA).
Anticancer Res. 20:2547–2552. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chang IC, Huang YJ, Chiang TI, et al:
Shikonin induces apoptosis through reactive oxygen
species/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway in
osteosarcoma cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 33:816–824. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhen-Jun S, Yuan-Yuan Z, Ying-Ying F, et
al: β,β-Dimethylacrylshikonin exerts antitumor activity via Notch-1
signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol.
84:507–512. 2012.
|
|
23
|
Green DR and Evan GI: A matter of life and
death. Cancer Cell. 1:19–30. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 protein
family: arbiters of cell survival. Science. 281:1322–1326. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL and Korsmeyer SJ:
Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that
accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 74:609–619. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shen HM and Tergaonkar V: NFκB signaling
in carcinogenesis and as a potential molecular target for cancer
therapy. Apoptosis. 14:348–363. 2009.
|
|
27
|
Tergaonkar V, Correa RG, Ikawa M and Verma
IM: Distinct roles of IκB proteins in regulating constitutive NF-κB
activity. Nat Cell Biol. 7:921–923. 2005.
|
|
28
|
Basak S, Kim H, Kearns JD, et al: A fourth
IκB protein within the NF-κB signaling module. Cell. 128:369–381.
2007.
|