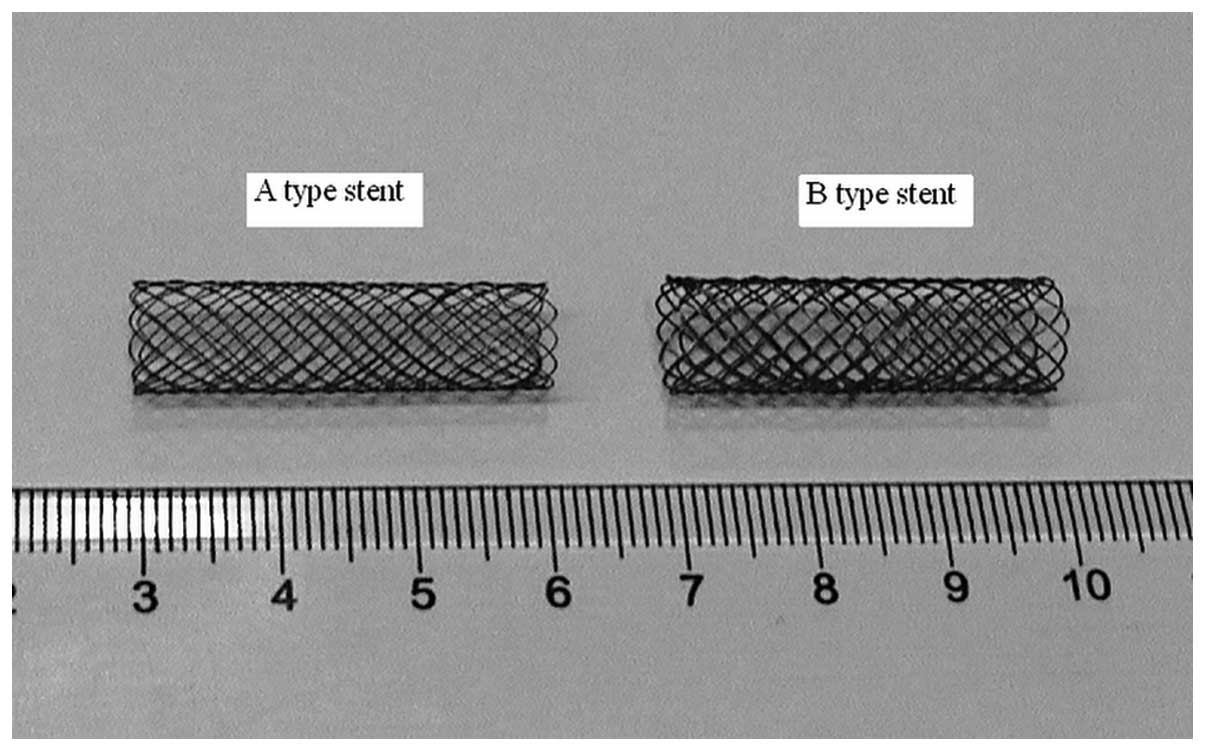
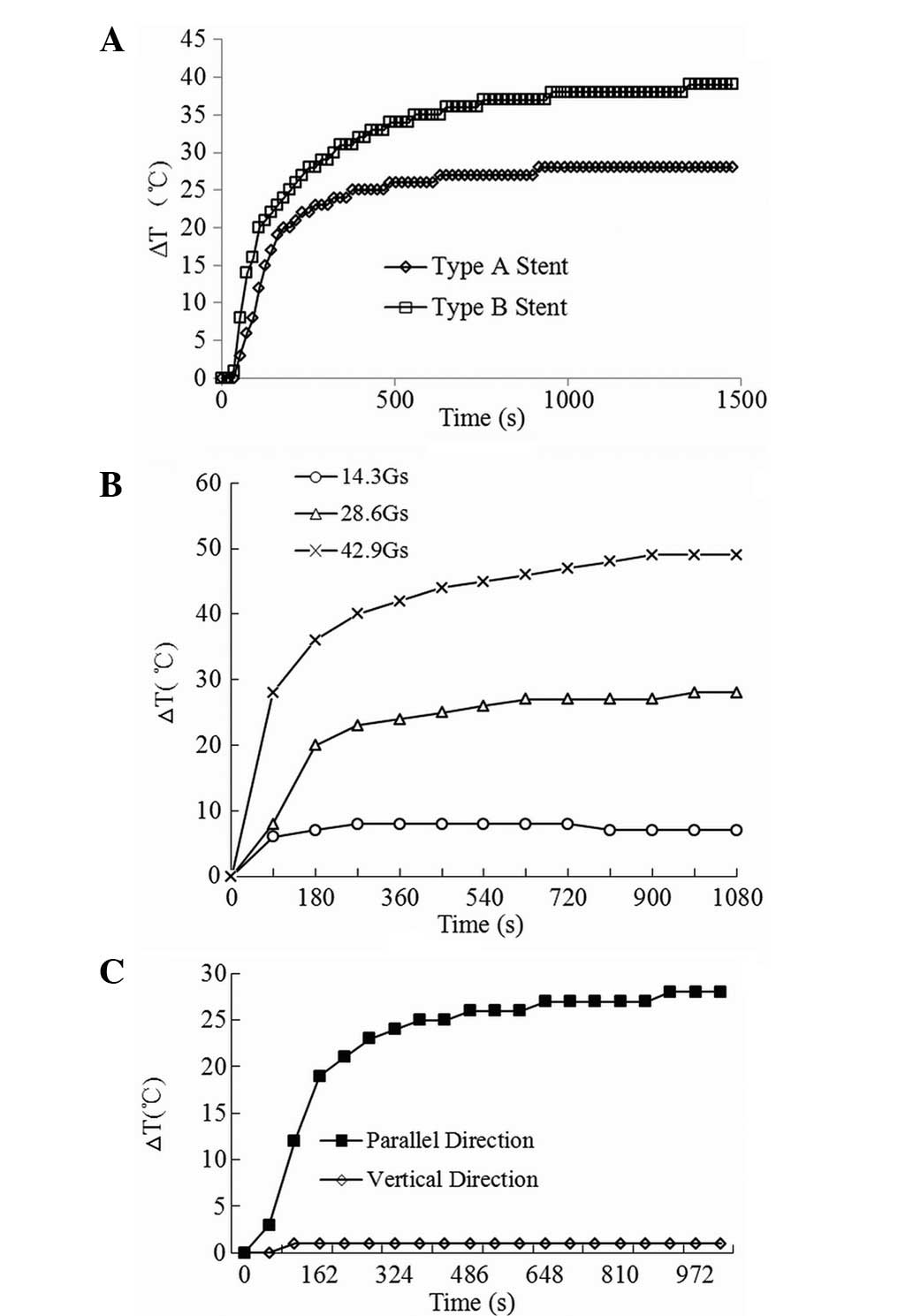
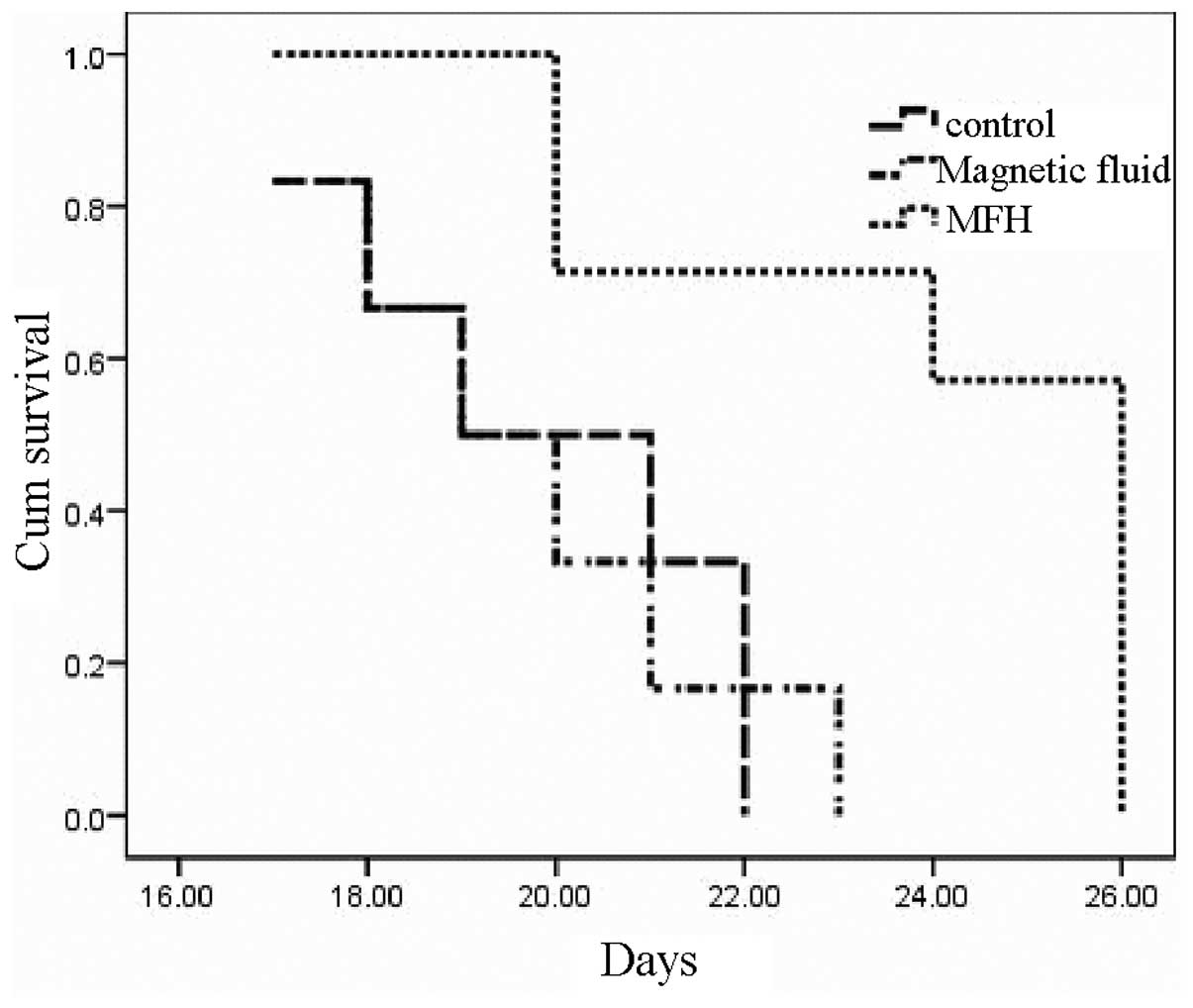
|
1
|
Jemal A, Center MM, DeSantis C and Ward
EM: Global patterns of cancer incidence and mortality rates and
trends. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 19:1893–1907. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guo P and Li K: Trends in esophageal
cancer mortality in China during 1987–2009: age, period and birth
cohort analyzes. Cancer Epidemiol. 36:99–105. 2012.
|
|
3
|
Corti L, Skarlatos J, Boso C, et al:
Outcome of patients receiving photodynamic therapy for early
esophageal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 47:419–24. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tew WP, Kelsen DP and Ilson DH: Targeted
therapies for esophageal cancer. Oncologist. 10:590–601. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
McCann P, Stafinski T, Wong C and Menon D:
The safety and effectiveness of endoscopic and non-endoscopic
approaches to the management of early esophageal cancer: A
systematic review. Cancer Treat Rev. 37:11–62. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mi Y, Liu X, Zhao J, Ding J and Feng SS:
Multimodality treatment of cancer with herceptin conjugated,
thermomagnetic iron oxides and docetaxel loaded nanoparticle of
biodegradable polymers. Biomaterials. 33:7519–7529. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hildebrandt B, Wust P, Ahlers O, et al:
The cellular and molecular basis of hyperthermia. Crit Rev Oncol
Hemato. 43:33–56. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Soares PI, Ferreira IM, Igreja RA, Novo CM
and Borges JP: Application of hyperthermia for cancer treatment:
recent patents review. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 7:64–73.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Laurent S, Dutz S, Häfeli UO and Mahmoudi
M: Magnetic fluid hyperthermia: focus on superparamagnetic iron
oxide nanoparticles. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 166:8–23.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Khot VM, Salunkhe AB, Thorat ND,
Ningthoujam RS and Pawar SH: Induction heating studies of dextran
coated MgFe2O4 nanoparticles for magnetic
hyperthermia. Dalton Trans. 42:1249–1258. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Akiyama S, Kawasaki S, Kodera Y, Hibi K,
Kato S, Ito K and Nakao A: A new method of thermo-chemotherapy
using a stent for patients with esophageal cancer. Surg Today.
36:19–24. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou JM, Li N, Xia QS, et al: Hyperthermia
by a nitinol stent in an alternating magnetic field: safety and
feasibility in rabbit esophageal cancer. Prog Nat Sci.
19:1713–1719. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Liu JY, Zhao LY, Wang YY, Li DY, Tao D, Li
LY and Tang JT: Magnetic stent hyperthermia for esophageal cancer:
An in vitro investigation in the ECA-109 cell line. Oncol Rep.
27:791–797. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu JY, Li DY, Chen HH, et al: Evaluation
on the feasibility and safety of magnetic stent hyperthermia for
esophageal cancer. IFMBE Proc. 39:1632–1635. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhao LY, Tang JT and Feng SS:
Nanothermotherapy by high performance magnetic nanoparticles.
Nanomedicine (Lond). 5:1305–1308. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Thiesen B and Jordan A: Clinical
applications of magnetic nanoparticles for hyperthermia. Int J
Hyperthermia. 24:467–74. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Schütz CA, Juillerat-Jeanneret L, Mueller
H, et al: Therapeutic nanoparticles in clinics and under clinical
evaluation. Nanomedicine (Lond). 8:449–467. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Johannsen M, Thiesen B, Wust P and Jordan
A: Magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia for prostate cancer. Int J
Hyperthermia. 26:790–795. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
van Landeghem FK, Maier-Hauff K, Jordan A,
et al: Post-mortem studies in glioblastoma patients treated with
thermotherapy using magnetic nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 30:52–57.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang L, Dong J, Ouyang W, Wang X and Tang
J: Anticancer effect and feasibility study of hyperthermia
treatment of pancreatic cancer using magnetic nanoparticles. Oncol
Rep. 27:719–726. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yoshida M, Sato M, Yamamoto Y, et al:
Tumor local chemohyperthermia using docetaxel-embedded
magnetoliposomes: Interaction of chemotherapy and hyperthermia. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 27:406–411. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Du LH, Zhou JM, Wang XW, et al: Effect of
local hyperthermia induced by nanometer magnetic fluid of the
rabbit VX2 liver tumor model. Prog Nat Sci. 19:1705–1712. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lee H, Kim S, Choi BH, et al: Hyperthermia
improves therapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin carried by mesoporous
silica nanocontainers in human lung cancer cells. Int J
Hyperthermia. 27:698–707. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao L, Yang B, Dai X, Wang X, Gao F,
Zhang X and Tang J: Glutaraldehyde mediated conjugation of
amino-coated magnetic nanoparticles with albumin protein for
nanothermotherapy. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 10:7117–7120. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gilchrist RK, Medal R, Shorey WD,
Hanselman RC, Rarrott JC and Taylor CB: Selective inductive heating
of lymph nodes. Annals Srug. 146:596–606. 1957. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang XF, Tang JT and Shi LQ: Induction
heating of magnetic fluids for hyperthermia treatment. IEEE Trans
Magn. 46:1043–1051. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Pallepati P and Averill-Bates DA: Mild
thermotolerance induced at 40°C protects HeLa cells against
activation of death receptor-mediated apoptosis by hydrogen
peroxide. Free Radic Biol Med. 50:667–679. 2011.
|