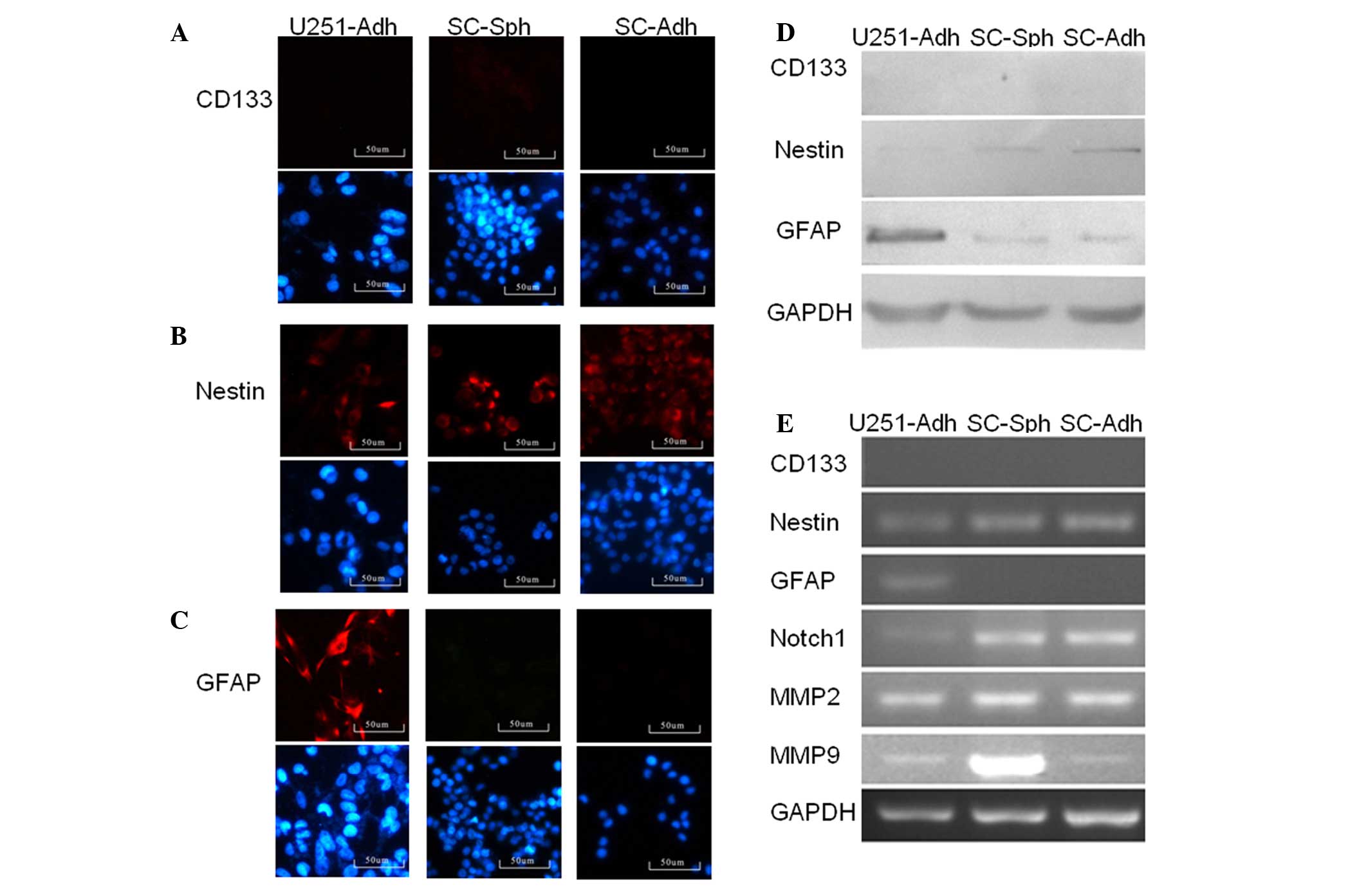
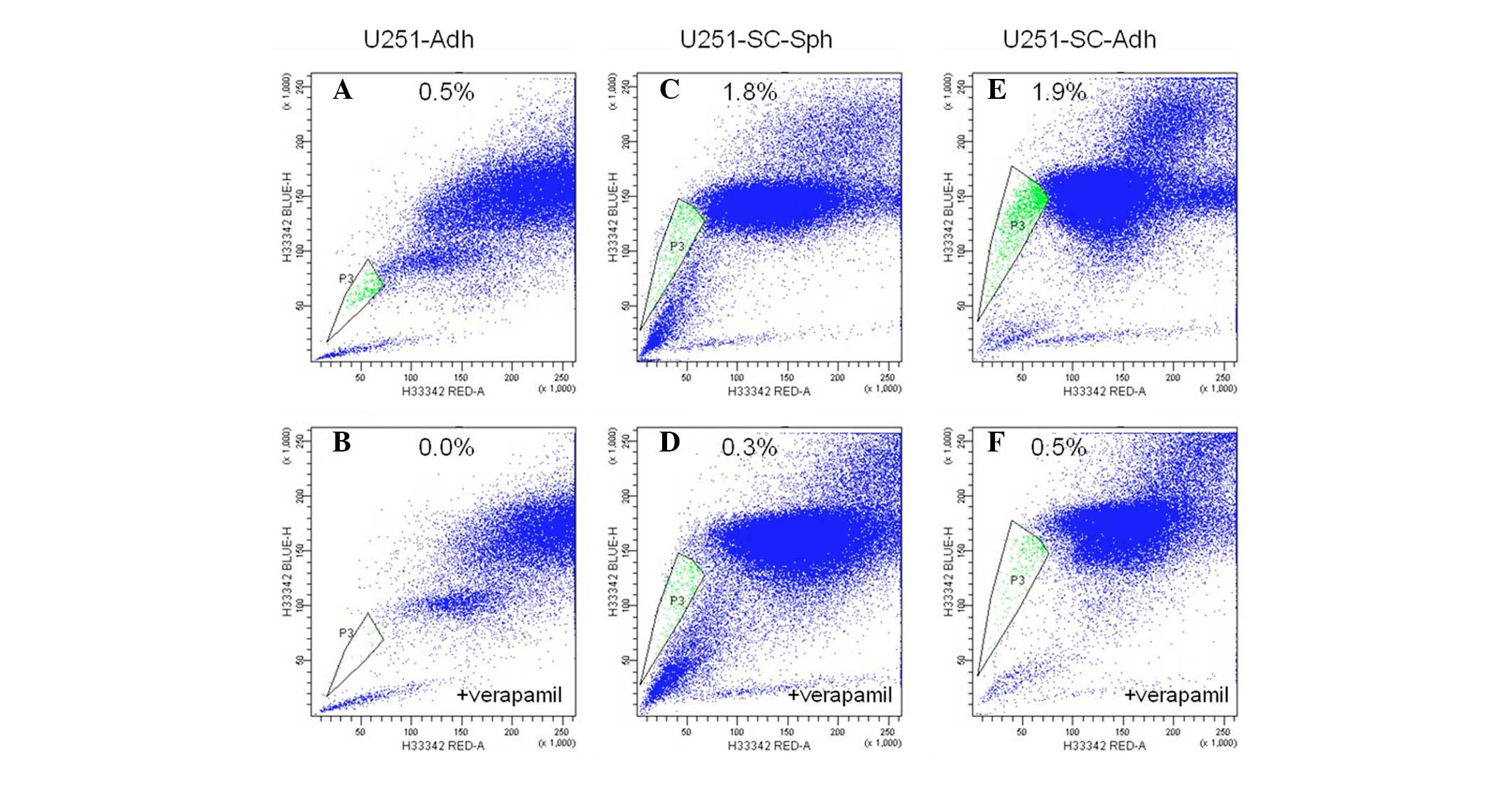
|
1
|
Van Meir EG, Hadjipanayis CG, Norden AD,
Shu HK, Wen PY and Olson JJ: Exciting new advances in
neuro-oncology: the avenue to a cure for malignant glioma. CA
Cancer J Clin. 60:166–193. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vescovi AL, Galli R and Reynolds BA: Brain
tumour stem cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:425–436. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, et al:
Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors. Cancer
Res. 63:5821–5828. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yuan X, Curtin J, Xiong Y, et al:
Isolation of cancer stem cells from adult glioblastoma multiforme.
Oncogene. 23:9392–9400. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Galli R, Binda E, Orfanelli U, et al:
Isolation and characterization of tumorigenic, stem-like neural
precursors from human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 64:7011–7021. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jeon HM, Sohn YW, Oh SY, et al: ID4
imparts chemoresistance and cancer stemness to glioma cells by
derepressing miR-9*-mediated suppression of SOX2. Cancer
Res. 71:3410–3421. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ulasov IV, Nandi S, Dey M, Sonabend AM and
Lesniak MS: Inhibition of Sonic hedgehog and Notch pathways
enhances sensitivity of CD133(+) glioma stem cells to temozolomide
therapy. Mol Med. 17:103–112. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yamada R and Nakano I: Glioma stem cells:
their role in chemoresistance. World Neurosurg. 77:237–240. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang J, Wakeman TP, Lathia JD, et al:
Notch promotes radioresistance of glioma stem cells. Stem Cells.
28:17–28. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nicholas MK, Lukas RV, Chmura S, Yamini B,
Lesniak M and Pytel P: Molecular heterogeneity in glioblastoma:
therapeutic opportunities and challenges. Semin Oncol. 38:243–253.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bonavia R, Inda MM, Cavenee WK and Furnari
FB: Heterogeneity maintenance in glioblastoma: a social network.
Cancer Res. 71:4055–4060. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Piccirillo SG, Binda E, Fiocco R, Vescovi
AL and Shah K: Brain cancer stem cells. J Mol Med (Berl).
87:1087–1095. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Inda MM, Bonavia R, Mukasa A, et al: Tumor
heterogeneity is an active process maintained by a mutant
EGFR-induced cytokine circuit in glioblastoma. Genes Dev.
24:1731–1745. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li Z, Wang H, Eyler CE, Hjelmeland AB and
Rich JN: Turning cancer stem cells inside out: an exploration of
glioma stem cell signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 284:16705–16709.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Charles NA, Holland EC, Gilbertson R,
Glass R and Kettenmann H: The brain tumor microenvironment. Glia.
59:1169–1180. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Campos B, Wan F, Farhadi M, et al:
Differentiation therapy exerts antitumor effects on stem-like
glioma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2715–2728. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pollard SM, Yoshikawa K, Clarke ID, et al:
Glioma stem cell lines expanded in adherent culture have
tumor-specific phenotypes and are suitable for chemical and genetic
screens. Cell Stem Cell. 4:568–580. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, et al:
Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature.
432:396–401. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wan F, Zhang S, Xie R, et al: The utility
and limitations of neurosphere assay, CD133 immunophenotyping and
side population assay in glioma stem cell research. Brain Pathol.
20:877–889. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang SJ, Ye F, Xie RF, et al: Comparative
study on the stem cell phenotypes of C6 cells under different
culture conditions. Chin Med J (Engl). 124:3118–3126.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Laks DR, Masterman-Smith M, Visnyei K, et
al: Neurosphere formation is an independent predictor of clinical
outcome in malignant glioma. Stem Cells. 27:980–987. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zeppernick F, Ahmadi R, Campos B, et al:
Stem cell marker CD133 affects clinical outcome in glioma patients.
Clin Cancer Res. 14:123–129. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lottaz C, Beier D, Meyer K, et al:
Transcriptional profiles of CD133+ and CD133−
glioblastoma-derived cancer stem cell lines suggest different cells
of origin. Cancer Res. 70:2030–2040. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hua W, Yao Y, Chu Y, et al: The CD133+
tumor stem-like cell-associated antigen may elicit highly intense
immune responses against human malignant glioma. J Neurooncol.
105:149–157. 2011.
|
|
25
|
McCord AM, Jamal M, Williams ES,
Camphausen K and Tofilon PJ: CD133+ glioblastoma
stem-like cells are radiosensitive with a defective DNA damage
response compared with established cell lines. Clin Cancer Res.
15:5145–5153. 2009.
|
|
26
|
Chiao MT, Yang YC, Cheng WY, Shen CC and
Ko JL: CD133+ glioblastoma stem-like cells induce vascular mimicry
in vivo. Curr Neurovasc Res. 8:210–219. 2011.
|
|
27
|
Jamal M, Rath BH, Tsang PS, Camphausen K
and Tofilon PJ: The brain microenvironment preferentially enhances
the radioresistance of CD133(+) glioblastoma stem-like cells.
Neoplasia. 14:150–158. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang J, Sakariassen PØ, Tsinkalovsky O, et
al: CD133 negative glioma cells form tumors in nude rats and give
rise to CD133 positive cells. Int J Cancer. 122:761–768. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zheng X, Shen G, Yang X and Liu W: Most C6
cells are cancer stem cells: evidence from clonal and population
analyses. Cancer Res. 67:3691–3697. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Goodell MA, Brose K, Paradis G, Conner AS
and Mulligan RC: Isolation and functional properties of murine
hematopoietic stem cells that are replicating in vivo. J Exp Med.
183:1797–1806. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Harris MA, Yang H, Low BE, et al: Cancer
stem cells are enriched in the side population cells in a mouse
model of glioma. Cancer Res. 68:10051–10059. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bleau AM, Hambardzumyan D, Ozawa T, et al:
PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway regulates the side population phenotype and
ABCG2 activity in glioma tumor stem-like cells. Cell Stem Cell.
4:226–235. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Patrawala L, Calhoun T,
Schneider-Broussard R, Zhou J, Claypool K and Tang DG: Side
population is enriched in tumorigenic, stem-like cancer cells,
whereas ABCG2+ and ABCG2− cancer cells are
similarly tumorigenic. Cancer Res. 65:6207–6219. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Stockhausen MT, Kristoffersen K and
Poulsen HS: The functional role of Notch signaling in human
gliomas. Neuro Oncol. 12:199–211. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hovinga KE, Shimizu F, Wang R, et al:
Inhibition of notch signaling in glioblastoma targets cancer stem
cells via an endothelial cell intermediate. Stem Cells.
28:1019–1029. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xu P, Qiu M, Zhang Z, et al: The oncogenic
roles of Notch1 in astrocytic gliomas in vitro and in vivo. J
Neurooncol. 97:41–51. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fan X, Matsui W, Khaki L, et al: Notch
pathway inhibition depletes stem-like cells and blocks engraftment
in embryonal brain tumors. Cancer Res. 66:7445–7452. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Heddleston JM, Hitomi M, Venere M, et al:
Glioma stem cell maintenance: the role of the microenvironment.
Curr Pharm Des. 17:2386–2401. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Christensen K, Schrøder HD and Kristensen
BW: CD133+ niches and single cells in glioblastoma have
different phenotypes. J Neurooncol. 104:129–143. 2011.
|