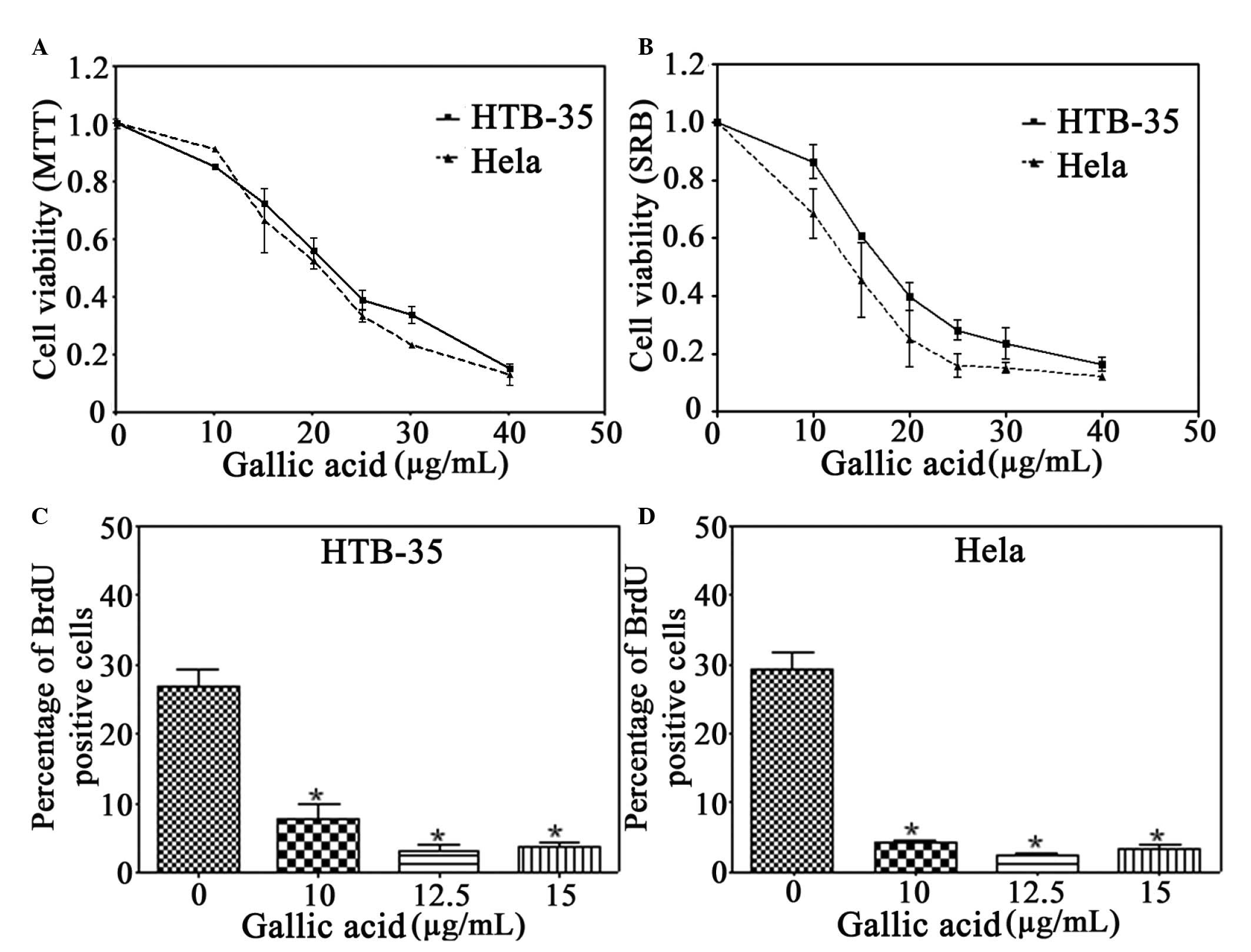
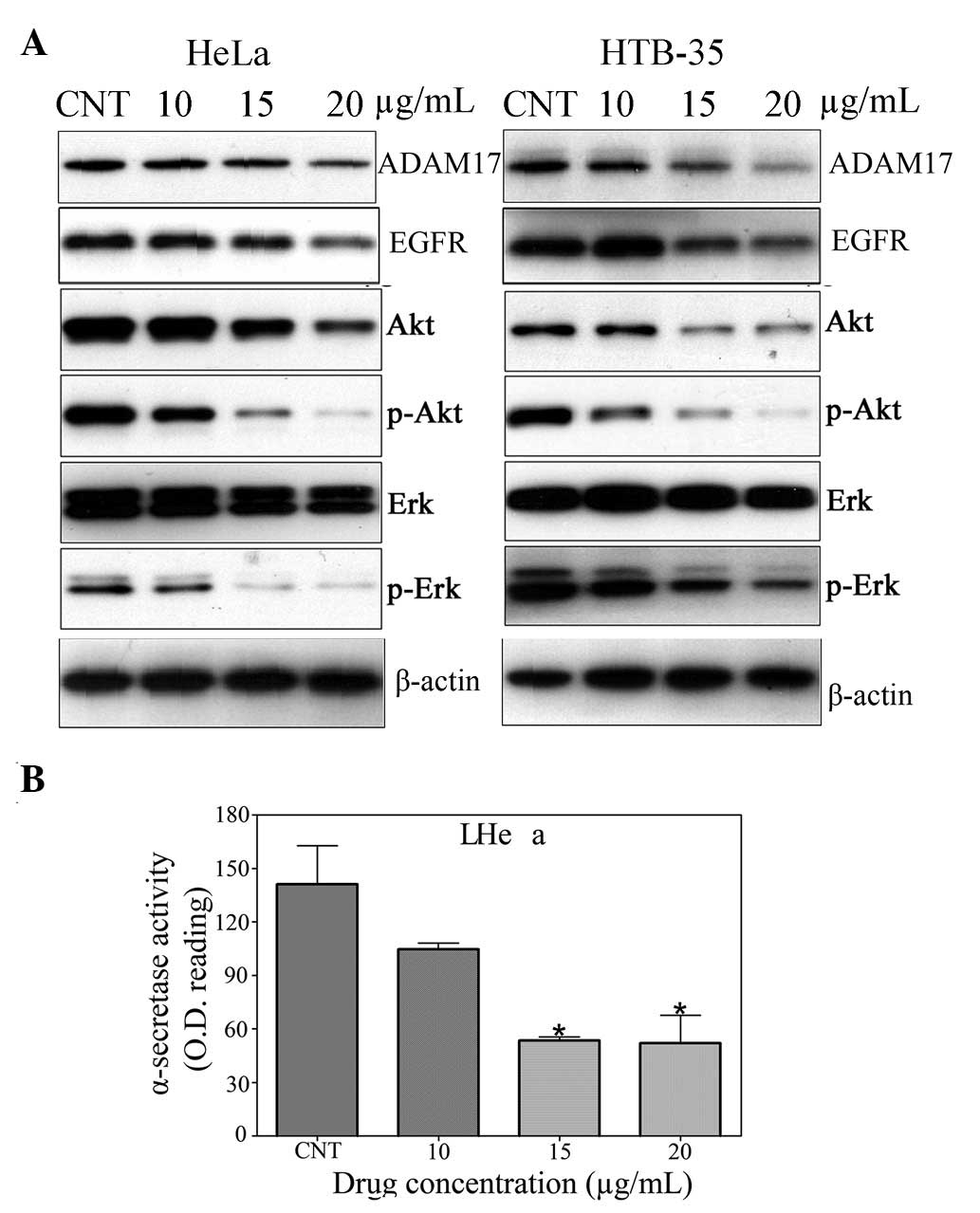
|
1
|
Armstrong EP: Prophylaxis of cervical
cancer and related cervical disease: a review of the
cost-effectiveness of vaccination against oncogenic HPV types. J
Manag Care Pharm. 16:217–230. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Globocan. 2008, IARC. http://globocan.iarc.fr/factsheets/populations/factsheet.asp?uno=900#WOMEN.
Accessed September 20, 2013
|
|
3
|
Alvarez-Salas LM and DiPaolo JA: Molecular
approaches to cervical cancer therapy. Curr Drug Discov Technol.
4:208–219. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Haroon S and Cui M: Role of Pap smear in
early diagnosis of cervical cancer - A case study of women in Saudi
Arabia. Life Science Journal. 9:1027–1036. 2012.
|
|
5
|
Roomi MW, Ivanov V, Kalinovsky T,
Niedzwiecki A and Rath M: Suppression of human cervical cancer cell
lines Hela and DoTc2 4510 by a mixture of lysine, proline, ascorbic
acid, and green tea extract. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 16:1241–1247.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Faried A, Kurnia D, Faried LS, et al:
Anticancer effects of gallic acid isolated from Indonesian herbal
medicine, Phaleria macrocarpa (Scheff.) Boerl, on human
cancer cell lines. Int J Oncol. 30:605–613. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Raina K, Rajamanickam S, Deep G, Singh M,
Agarwal R and Agarwal C: Chemopreventive effects of oral gallic
acid feeding on tumor growth and progression in TRAMP mice. Mol
Cancer Ther. 7:1258–1267. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
You BR and Park WH: Gallic acid-induced
lung cancer cell death is related to glutathione depletion as well
as reactive oxygen species increase. Toxicol In Vitro.
24:1356–1362. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
You BR, Kim SZ, Kim SH and Park WH: Gallic
acid-induced lung cancer cell death is accompanied by ROS increase
and glutathione depletion. Mol Cell Biochem. 357:295–303. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Verma S, Singh A and Mishra A: Gallic
acid: Molecular rival of cancer. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol.
35:473–485. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
You BR, Moon HJ, Han YH and Park WH:
Gallic acid inhibits the growth of HeLa cervical cancer cells via
apoptosis and/or necrosis. Food Chem Toxicol. 48:1334–1340. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Skehan P, Storeng R, Scudiero D, et al:
New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening.
J Natl Cancer Inst. 82:1107–1112. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Agarwal C, Tyagi A and Agarwal R: Gallic
acid causes inactivating phosphorylation of cdc25A/cdc25C-cdc2 via
ATM-Chk2 activation, leading to cell cycle arrest, and induces
apoptosis in human prostate carcinoma DU145 cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
5:3294–3302. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhai Y, Bommer GT, Feng Y, Wiese AB,
Fearon ER and Cho KR: Loss of estrogen receptor 1 enhances cervical
cancer invasion. Am J Pathol. 177:884–895. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Di Leo S, Caschetto S, Garozzo G, et al:
Angiogenesis as a prognostic factor in cervical carcinoma. Eur J
Gynaecol Oncol. 19:158–162. 1998.
|
|
16
|
Triratanachat S, Niruthisard S,
Trivijitsilp P, Tresukosol D and Jarurak N: Angiogenesis in
cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and early-staged uterine
cervical squamous cell carcinoma: clinical significance. Int J
Gynecol Cancer. 16:575–580. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lin P, Sun X, Feng T, et al: ADAM17
regulates prostate cancer cell proliferation through mediating cell
cycle progression by EGFR/PI3K/AKT pathway. Mol Cell Biochem.
359:235–243. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xiao LJ, Lin P, Lin F, et al: ADAM17
targets MMP-2 and MMP-9 via EGFR-MEK-ERK pathway activation to
promote prostate cancer cell invasion. Int J Oncol. 40:1714–1724.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jeong JH, Jeong YJ, Cho HJ, et al:
Ascochlorin inhibits growth factor-induced HIF-1α activation and
tumor-angiogenesis through the suppression of EGFR/ERK/p70S6K
signaling pathway in human cervical carcinoma cells. J Cell
Biochem. 113:1302–1313. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mathur SP, Mathur RS and Young RC:
Cervical epidermal growth factor-receptor (EGF-R) and serum
insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) levels are potential markers
for cervical cancer. Am J Reprod Immunol. 44:222–230. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lakshmi S, Nair M, Jayaprakash P and
Pillai M: Epidermal growth factor and its receptor in cervical
cancer. Oncol Rep. 4:1103–1106. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gaffney DK, Haslam D, Tsodikov A, et al:
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and vascular endothelial
growth factor (VEGF) negatively affect overall survival in
carcinoma of the cervix treated with radiotherapy. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 56:922–928. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Madlener S, Illmer C, Horvath Z, et al:
Gallic acid inhibits ribonucleotide reductase and cyclooxygenases
in human HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cells. Cancer Lett.
245:156–162. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hawighorst H, Knapstein PG, Weikel W, et
al: Angiogenesis of uterine cervical carcinoma: characterization by
pharmacokinetic magnetic resonance parameters and histological
microvessel density with correlation to lymphatic involvement.
Cancer Res. 57:4777–4786. 1997.
|
|
25
|
Liu Z, Schwimer J, Liu D, et al: Gallic
acid is partially responsible for the antiangiogenic activities of
Rubus leaf extract. Phytother Res. 20:806–813. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Soonthornthum T, Arias-Pulido H, Joste N,
et al: Epidermal growth factor receptor as a biomarker for cervical
cancer. Ann Oncol. 22:2166–2178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Baselga J: Why the epidermal growth factor
receptor? The rationale for cancer therapy. Oncologist. 7(Suppl 4):
2–8. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lu X, Lu D, Scully M and Kakkar V: ADAM
proteins - therapeutic potential in cancer. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 8:720–732. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kheradmand F and Werb Z: Shedding light on
sheddases: role in growth and development. Bioessays. 24:8–12.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zheng X, Jiang F, Katakowski M, Zhang ZG,
Lu QE and Chopp M: ADAM17 promotes breast cancer cell malignant
phenotype through EGFR-PI3K-AKT activation. Cancer Biol Ther.
8:1045–1054. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|