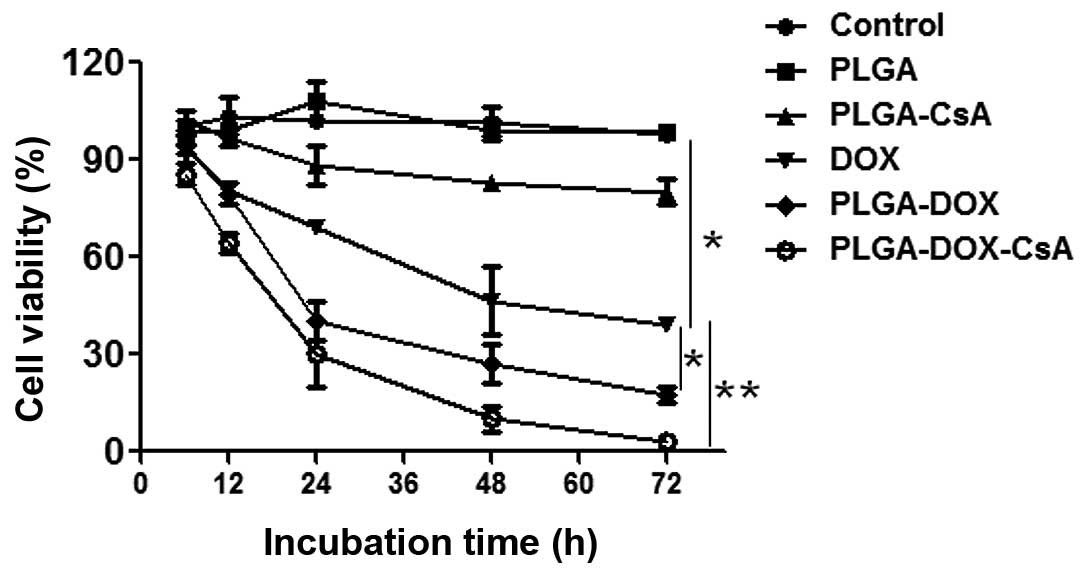
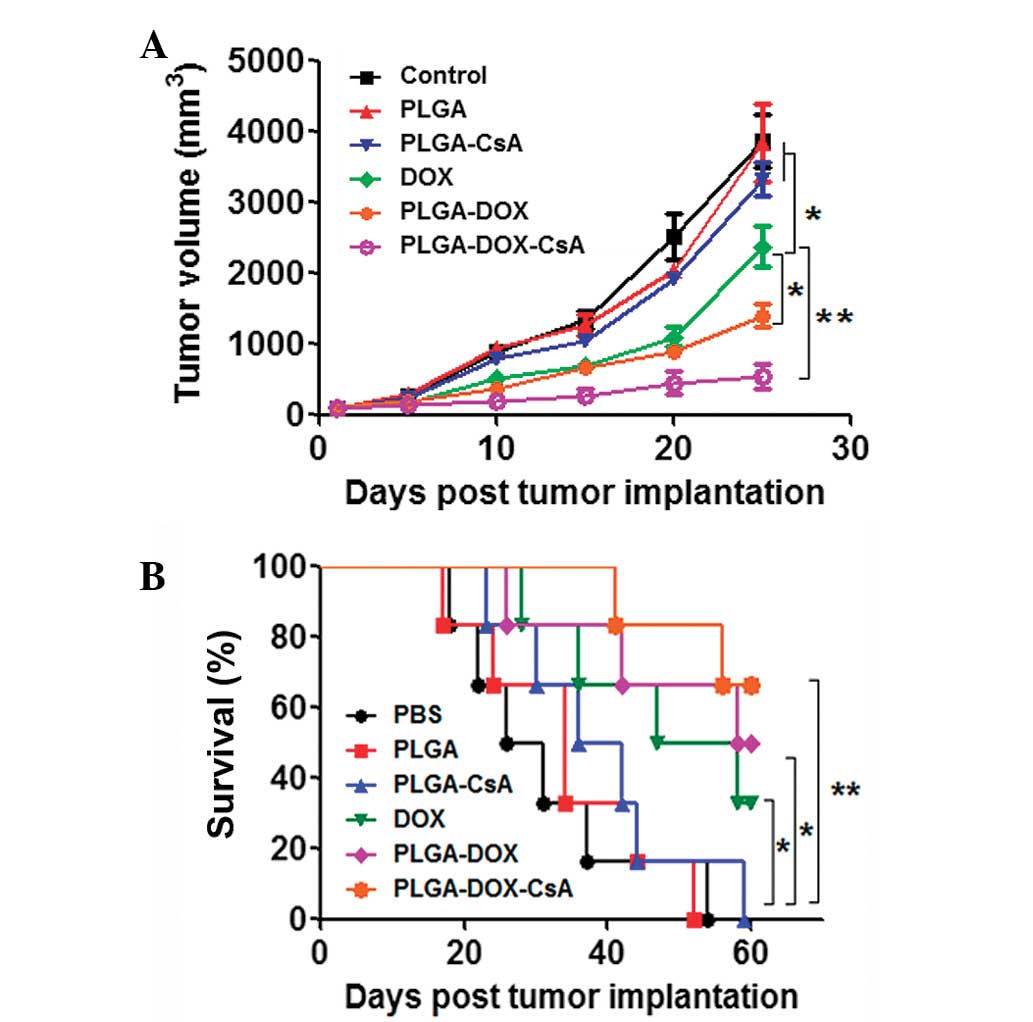
|
1
|
Schimrosczyk K, Song YH, Vykoukal J, et
al: Liposome-mediated transfection with extract from neonatal rat
cardiomyocytes induces transdifferentiation of human
adipose-derived stem cells into cardiomyocytes. Scand J Clin Lab
Invest. 68:464–472. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Villanueva J, Infante JR, Krepler C, et
al: Concurrent MEK2 mutation and BRAF amplification confer
resistance to BRAF and MEK inhibitors in melanoma. Cell Rep.
4:1090–1099. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Niu C, Sun Q, Zhou J, et al:
Folate-functionalized polymeric micelles based on biodegradable
PEG-PDLLA as a hepatic carcinoma-targeting delivery system. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:1995–1999. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dreaden EC, Austin LA, Mackey MA and
El-Sayed MA: Size matters: gold nanoparticles in targeted cancer
drug delivery. Ther Deliv. 3:457–478. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Parhi P, Mohanty C and Sahoo SK:
Nanotechnology-based combinational drug delivery: an emerging
approach for cancer therapy. Drug Discov Today. 17:1044–1052. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shive MS and Anderson JM: Biodegradation
and biocompatibility of PLA and PLGA microspheres. Adv Drug Deliv
Rev. 28:5–24. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Makadia HK and Siegel SJ: Poly
Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) as Biodegradable Controlled Drug
Delivery Carrier. Polymers (Basel). 3:1377–1397. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ullah MF: Cancer multidrug resistance
(MDR): a major impediment to effective chemotherapy. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 9:1–6. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pluchino KM, Hall MD, Goldsborough AS, et
al: Collateral sensitivity as a strategy against cancer multidrug
resistance. Drug Resist Updat. 15:98–105. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang L, Xiao R, Xiong J, et al: Activated
ERM protein plays a critical role in drug resistance of MOLT4 cells
induced by CCL25. PLoS One. 8:e523842013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Larsen UL, Hyldahl Olesen L, Guldborg
Nyvold C, et al: Human intestinal P-glycoprotein activity estimated
by the model substrate digoxin. Scand J Clin Lab Invest.
67:123–134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Han M, Lv Q, Tang XJ, et al: Overcoming
drug resistance of MCF-7/ADR cells by altering intracellular
distribution of doxorubicin via MVP knockdown with a novel siRNA
polyamidoamine-hyaluronic acid complex. J Control Release.
163:136–144. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Nieto Montesinos R, Béduneau A, Pellequer
Y and Lamprecht A: Delivery of P-glycoprotein substrates using
chemosensitizers and nanotechnology for selective and efficient
therapeutic outcomes. J Control Release. 161:50–61. 2012.
|
|
14
|
Shen F, Chu S, Bence AK, et al:
Quantitation of doxorubicin uptake, efflux, and modulation of
multidrug resistance (MDR) in MDR human cancer cells. J Pharmacol
Exp Ther. 324:95–102. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu R, Zhang Y, Chen Y, et al: A novel
calmodulin antagonist O-(4-ethoxyl-butyl)-berbamine overcomes
multidrug resistance in drug-resistant MCF-7/ADR breast carcinoma
cells. J Pharm Sci. 99:3266–3275. 2010.
|
|
16
|
Harmsen S, Meijerman I, Febus CL, et al:
PXR-mediated induction of P-glycoprotein by anticancer drugs in a
human colon adenocarcinoma-derived cell line. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 66:765–771. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liow JS, Lu S, McCarron JA, et al: Effect
of a P-glycoprotein inhibitor, Cyclosporin A, on the disposition in
rodent brain and blood of the 5-HT1A receptor radioligand,
[11C](R)-(-)-RWAY. Synapse. 61:96–105. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Warren KE, Patel MC, McCully CM, et al:
Effect of P-glycoprotein modulation with cyclosporine A on
cerebrospinal fluid penetration of doxorubicin in non-human
primates. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 45:207–212. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
He Q, Gao Y, Zhang L, et al: A
pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles-based multi-drug
delivery system for overcoming multi-drug resistance. Biomaterials.
32:7711–7720. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen YT, Feng B and Chen LB: Update of
research on drug resistance in small cell lung cancer chemotherapy.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:3577–3581. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
van Vlerken LE, Duan Z, Little SR, et al:
Augmentation of therapeutic efficacy in drug-resistant tumor models
using ceramide coadministration in temporal-controlled
polymer-blend nanoparticle delivery systems. AAPS J. 12:171–180.
2010.
|
|
22
|
Shin HC, Alani AW, Cho H, et al: A 3-in-1
polymeric micelle nanocontainer for poorly water-soluble drugs. Mol
Pharm. 8:1257–1265. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nakamura K, Abu Lila AS, Matsunaga M, et
al: A double-modulation strategy in cancer treatment with a
chemotherapeutic agent and siRNA. Mol Ther. 19:2040–2047. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Batist G, Gelmon KA, Chi KN, et al:
Safety, pharmacokinetics, and efficacy of CPX-1 liposome injection
in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res.
15:692–700. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu J, Lu Y, Lee A, et al: Reversal of
multidrug resistance by transferrin-conjugated liposomes
co-encapsulating doxorubicin and verapamil. J Pharm Pharm Sci.
10:350–357. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Qadir M, O’Loughlin KL, Fricke SM, et al:
Cyclosporin A is a broad-spectrum multidrug resistance modulator.
Clin Cancer Res. 11:2320–2326. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|