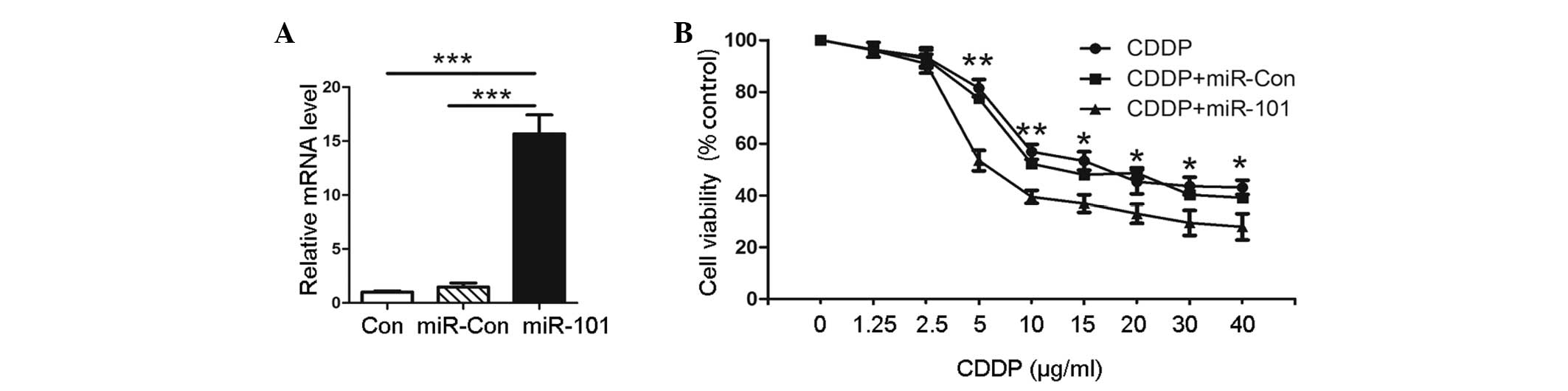
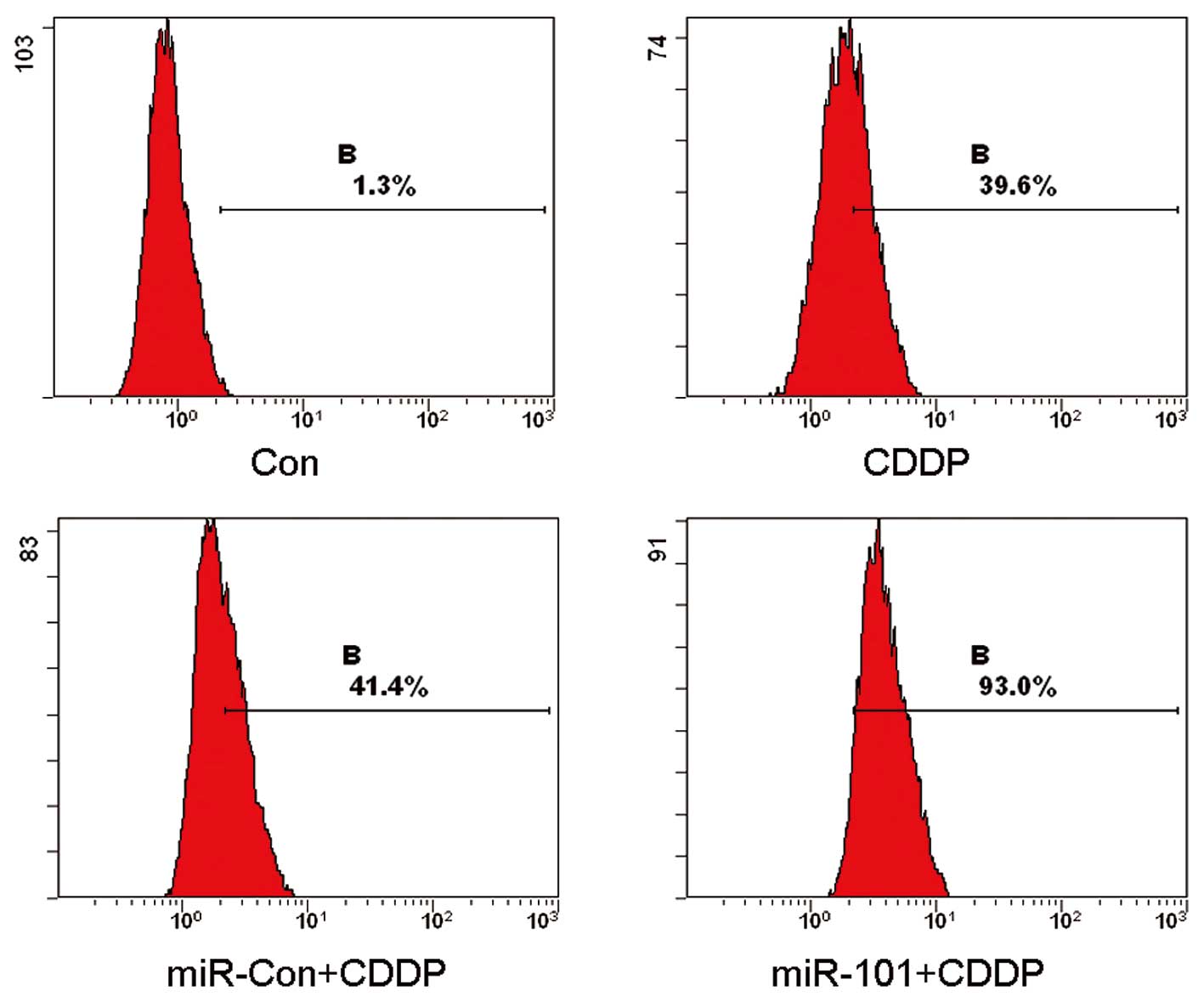
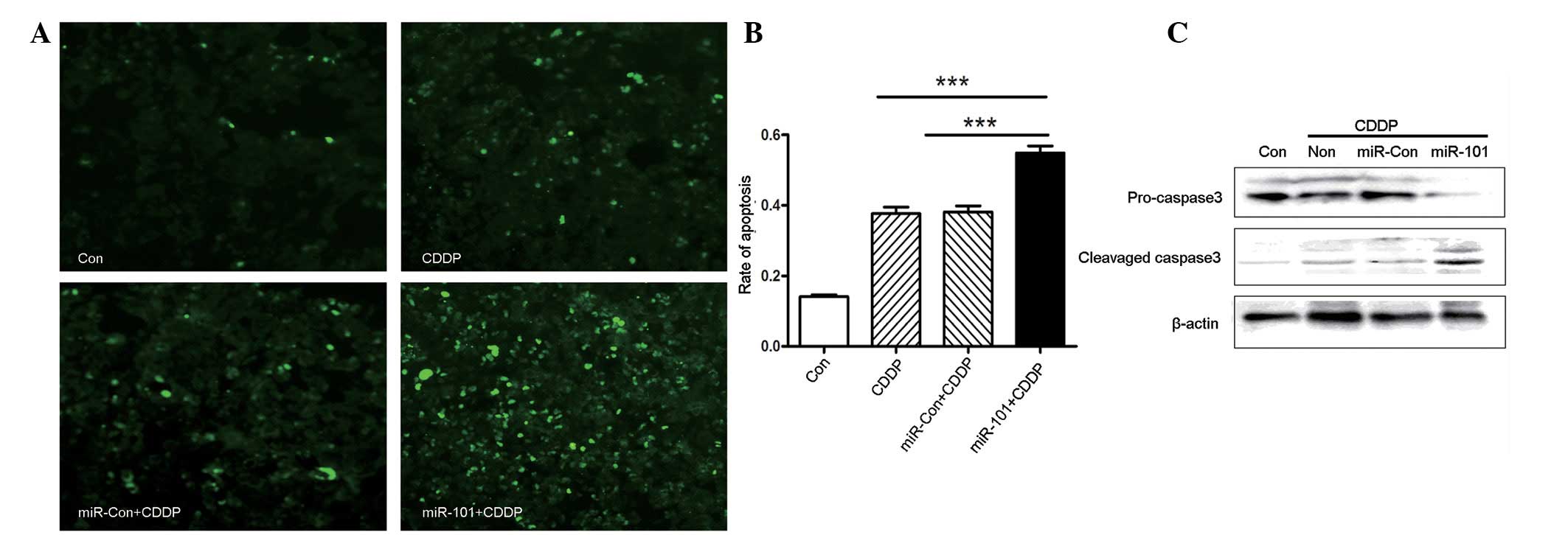
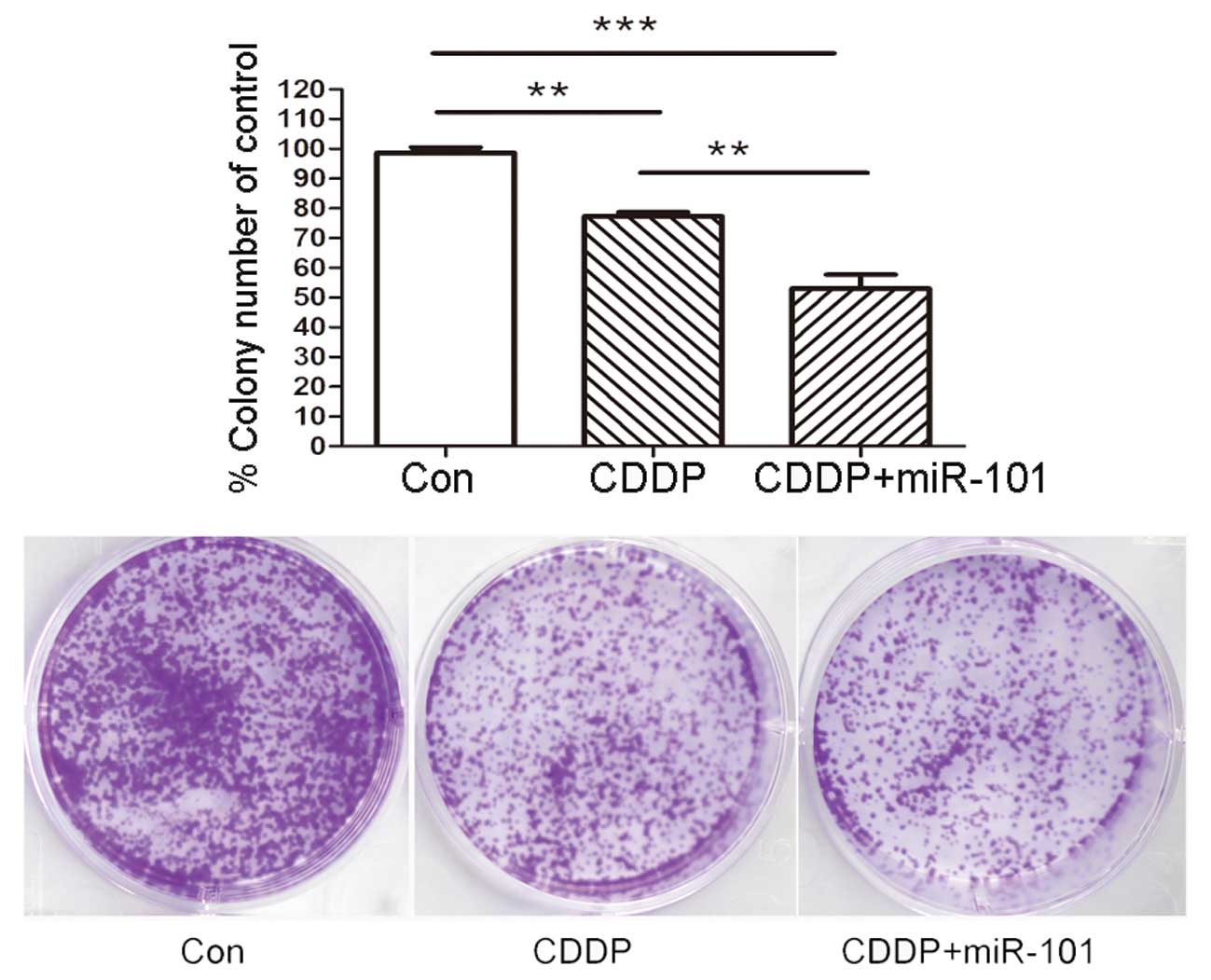
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic
and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J
Clin. 61:212–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kelly K, Crowley J, Bunn PA Jr, et al:
Randomized phase III trial of paclitaxel plus carboplatin versus
vinorelbine plus cisplatin in the treatment of patients with
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a Southwest Oncology Group
trial. J Clin Oncol. 19:3210–3218. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee MW, Kim DS, Min NY and Kim HT: Akt1
inhibition by RNA interference sensitizes human non-small cell lung
cancer cells to cisplatin. Int J Cancer. 122:2380–2384. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cheng AM, Byrom MW, Shelton J and Ford LP:
Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an
involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids
Res. 33:1290–1297. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xu P, Guo M and Hay BA: MicroRNAs and the
regulation of cell death. Trends Genet. 20:617–624. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Doench JG and Sharp PA: Specificity of
microRNA target selection in translational repression. Genes Dev.
18:504–511. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, et al:
Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human
microRNAs. Nat Genet. 37:766–770. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
O'Day E and Lal A: MicroRNAs and their
target gene networks in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res.
12:2012010. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Smits M, Nilsson J, Mir SE, et al: miR-101
is down-regulated in glioblastoma resulting in EZH2-induced
proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis. Oncotarget. 1:710–720.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Semaan A, Qazi AM, Seward S, et al:
MicroRNA-101 inhibits growth of epithelial ovarian cancer by
relieving chromatin-mediated transcriptional repression of
p21(waf(1)/cip(1)). Pharm Res. 28:3079–3090. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang HJ, Ruan HJ, He XJ, et al:
MicroRNA-101 is down-regulated in gastric cancer and involved in
cell migration and invasion. Eur J Cancer. 46:2295–2303. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pang Y, Young CY and Yuan H: MicroRNAs and
prostate cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 42:363–369.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Su H, Yang JR, Xu T, et al: MicroRNA-101,
down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma, promotes apoptosis and
suppresses tumorigenicity. Cancer Res. 69:1135–1142. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang JG, Guo JF, Liu DL, Liu Q and Wang
JJ: MicroRNA-101 exerts tumor-suppressive functions in non-small
cell lung cancer through directly targeting enhancer of zeste
homolog 2. J Thorac Oncol. 6:671–678. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen S, Wang H, Ng WL, Curran WJ and Wang
Y: Radiosensitizing effects of ectopic miR-101 on non-small-cell
lung cancer cells depend on the endogenous miR-101 level. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 81:1524–1529. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Batchu RB, Gruzdyn O, Qazi AM, Bouwman D,
Gruber SA and Weaver DW: MicroRNA-101 (miR-101) enhances
chemosensitivity of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cells
by inhibition of MTOR signaling via PRAS40. J Surg Res.
172:2332012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Xu Y, An Y, Wang Y, et al: miR-101
inhibits autophagy and enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 29:2019–2024.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sachdeva M, Wu H, Ru P, Hwang L, Trieu V
and Mo YY: MicroRNA-101-mediated Akt activation and
estrogen-independent growth. Oncogene. 30:822–831. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gui T and Shen K: miRNA-101: a potential
target for tumor therapy. Cancer Epidemiol. 36:537–540. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chiang CW, Huang Y, Leong KW, et al:
PKCalpha mediated induction of miR-101 in human hepatoma HepG2
cells. J Biomed Sci. 17:352010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Buechner J, Tomte E, Haug BH, et al:
Tumor-suppressor microRNAs let-7 and mir-101 target the
proto-oncogene MYCN and inhibit cell proliferation in
MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma. Br J Cancer. 105:296–303. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Varambally S, Cao Q, Mani RS, et al:
Genomic loss of microRNA-101 leads to overexpression of histone
methyltransferase EZH2 in cancer. Science. 322:1695–1699. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|