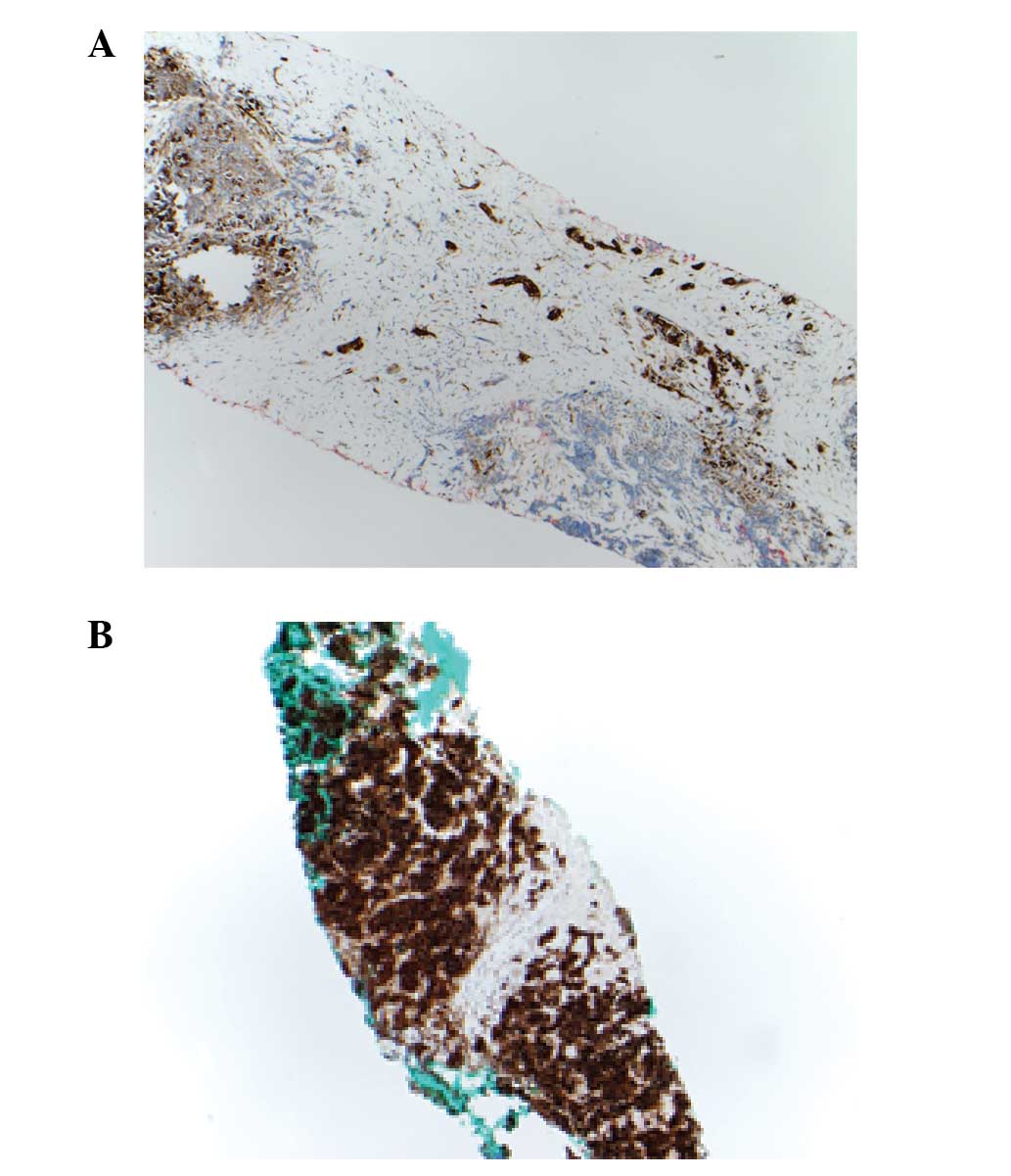
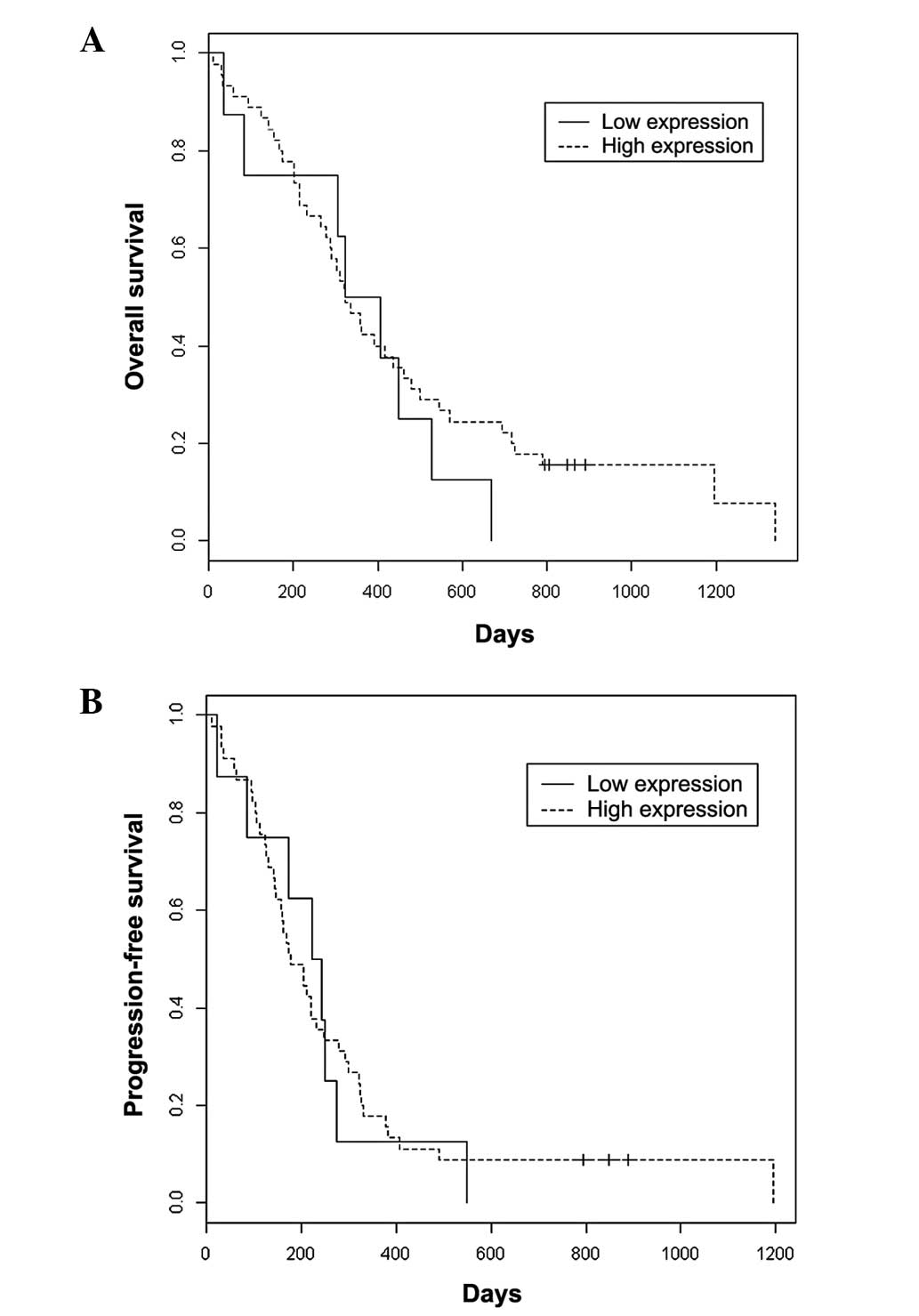
|
1
|
Argiris A and Murren JR: Staging and
clinical prognostic factors for small-cell lung cancer. Cancer J.
7:437–447. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chute JP, Chen T, Feigal E, Simon R and
Johnson BE: Twenty years of phase III trials for patients with
extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: perceptible progress. J
Clin Oncol. 17:1794–1801. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Smyth JF: Chemotherapy of small cell lung
cancer. Chest. 96(Suppl 1): 61S–62S. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Katsetos CD, Legido A, Perentes E and Mörk
SJ: Class III beta-tubulin isotype: a key cytoskeletal protein at
the crossroads of developmental neurobiology and tumor
neuropathology. J Child Neurol. 18:851–866. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Burkhart CA, Kavallaris M and Horwitz SB:
The role of beta-tubulin isotypes in resistance to antimitotic
drugs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1471:1–9. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bernard-Marty C, Treilleux I, Dumontet C,
et al: Microtubule-associated parameters as predictive markers of
docetaxel activity in advanced breast cancer patients: results of a
pilot study. Clin Breast Cancer. 3:341–345. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ohishi Y, Oda Y, Basaki Y, et al:
Expression of beta-tubulin isotypes in human primary ovarian
carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 105:586–592. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Koh Y, Kim TM, Jeon YK, et al: Class III
beta-tubulin, but not ERCC1, is a strong predictive and prognostic
marker in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Ann Oncol. 20:1414–1419. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sève P, Reiman T, Lai R, et al: Class III
beta-tubulin is a marker of paclitaxel resistance in carcinomas of
unknown primary site. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 60:27–34.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sève P and Dumontet C: Is class III
beta-tubulin a predictive factor in patients receiving
tubulin-binding agents? Lancet Oncol. 9:168–175. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sève P, Lai R, Ding K, et al: Class III
beta-tubulin expression and benefit from adjuvant
cisplatin/vinorelbine chemotherapy in operable non-small cell lung
cancer: analysis of NCIC JBR.10. Clin Cancer Res. 13:994–999.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dumontet C, Isaac S, Souquet PJ, et al:
Expression of class III beta tubulin in non-small cell lung cancer
is correlated with resistance to taxane chemotherapy. Bull Cancer.
92:E25–E30. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rosell R, Scagliotti G, Danenberg KD, et
al: Transcripts in pretreatment biopsies from a three-arm
randomized trial in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer.
Oncogene. 22:3548–3553. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sève P, Isaac S, Trédan O, et al:
Expression of class III {beta}-tubulin is predictive of patient
outcome in patients with non-small cell lung cancer receiving
vinorelbine-based chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 11:5481–5486.
2005.
|
|
15
|
Sève P, Mackey J, Isaac S, et al: Class
III beta-tubulin expression in tumor cells predicts response and
outcome in patients with non-small cell lung cancer receiving
paclitaxel. Mol Cancer Ther. 4:2001–2007. 2005.
|
|
16
|
Katsetos CD, Kontogeorgos G, Geddes JF, et
al: Differential distribution of the neuron-associated class III
beta-tubulin in neuroendocrine lung tumors. Arch Pathol Lab Med.
124:535–544. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zelen M: Keynote address on biostatistics
and data retrieval. Cancer Chemother Rep 3. 4:31–42.
1973.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, et
al: New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid
tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer,
National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer
Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst. 92:205–216. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Urano N, Fujiwara Y, Doki Y, et al:
Clinical significance of class III beta-tubulin expression and its
predictive value for resistance to docetaxel-based chemotherapy in
gastric cancer. Int J Oncol. 28:375–381. 2006.
|
|
20
|
Leandro-García LJ, Leskelä S, Landa I, et
al: Tumoral and tissue-specific expression of the major human
beta-tubulin isotypes. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 67:214–23.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Raspaglio G, Filippetti F, Prislei S, et
al: Hypoxia induces class III beta-tubulin gene expression by
HIF-1alpha binding to its 3′ flanking region. Gene. 409:100–108.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Levallet G, Bergot E, Antoine M, et al:
High TUBB3 expression, an independent prognostic marker in patients
with early non-small cell lung cancer treated by preoperative
chemotherapy, is regulated by K-Ras signaling pathway. Mol Cancer
Ther. 11:1203–1213. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Pentheroudakis G, Batistatou A, Kalogeras
KT, et al: Prognostic utility of β-tubulin isotype III and
correlations with other molecular and clinicopathological variables
in patients with early breast cancer: a translational Hellenic
Cooperative Oncology Group (HeCOG) study. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
127:179–193. 2011.
|
|
24
|
Ettinger DS, Finkelstein DM, Sarma RP and
Johnson DH: Phase II study of paclitaxel in patients with
extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer: an Eastern Cooperative
Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol. 13:1430–1435. 1995.
|
|
25
|
Kirschling RJ, Grill JP, Marks RS, et al:
Paclitaxel and G-CSF in previously untreated patients with
extensive stage small-cell lung cancer: a phase II study of the
North Central Cancer Treatment Group. Am J Clin Oncol. 22:517–522.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Graziano SL, Herndon JE II, Socinski MA,
et al: Phase II trial of weekly dose-dense paclitaxel in
extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: cancer and leukemia group B
study 39901. J Thorac Oncol. 3:158–162. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Thomas P, Castelnau O, Paillotin D, et al:
Phase II trial of paclitaxel and carboplatin in metastatic
small-cell lung cancer: a Groupe Français de Pneumo-Cancérologie
study. J Clin Oncol. 19:1320–1325. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stinchcombe TE, Mauer AM, Hodgson LD, et
al: Phase II trial of paclitaxel and cisplatin in patients with
extensive stage small cell lung cancer: Cancer and Leukemia Group B
Trial 9430. J Thorac Oncol. 3:1301–1307. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Evans WK, Shepherd FA, Feld R, Osoba D,
Dang P and Deboer G: VP-16 and cisplatin as first-line therapy for
small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 3:1471–1477. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Smith IE, Evans BD, Gore ME, et al:
Carboplatin (Paraplatin; JM8) and etoposide (VP-16) as first-line
combination therapy for small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol.
5:185–189. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rivera E, Lee J and Davies A: Clinical
development of ixabepilone and other epothilones in patients with
advanced solid tumors. Oncologist. 13:1207–1223. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dumontet C, Jordan MA and Lee FF:
Ixabepilone: targeting beta III-tubulin expression in
taxane-resistant malignancies. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:17–25. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|