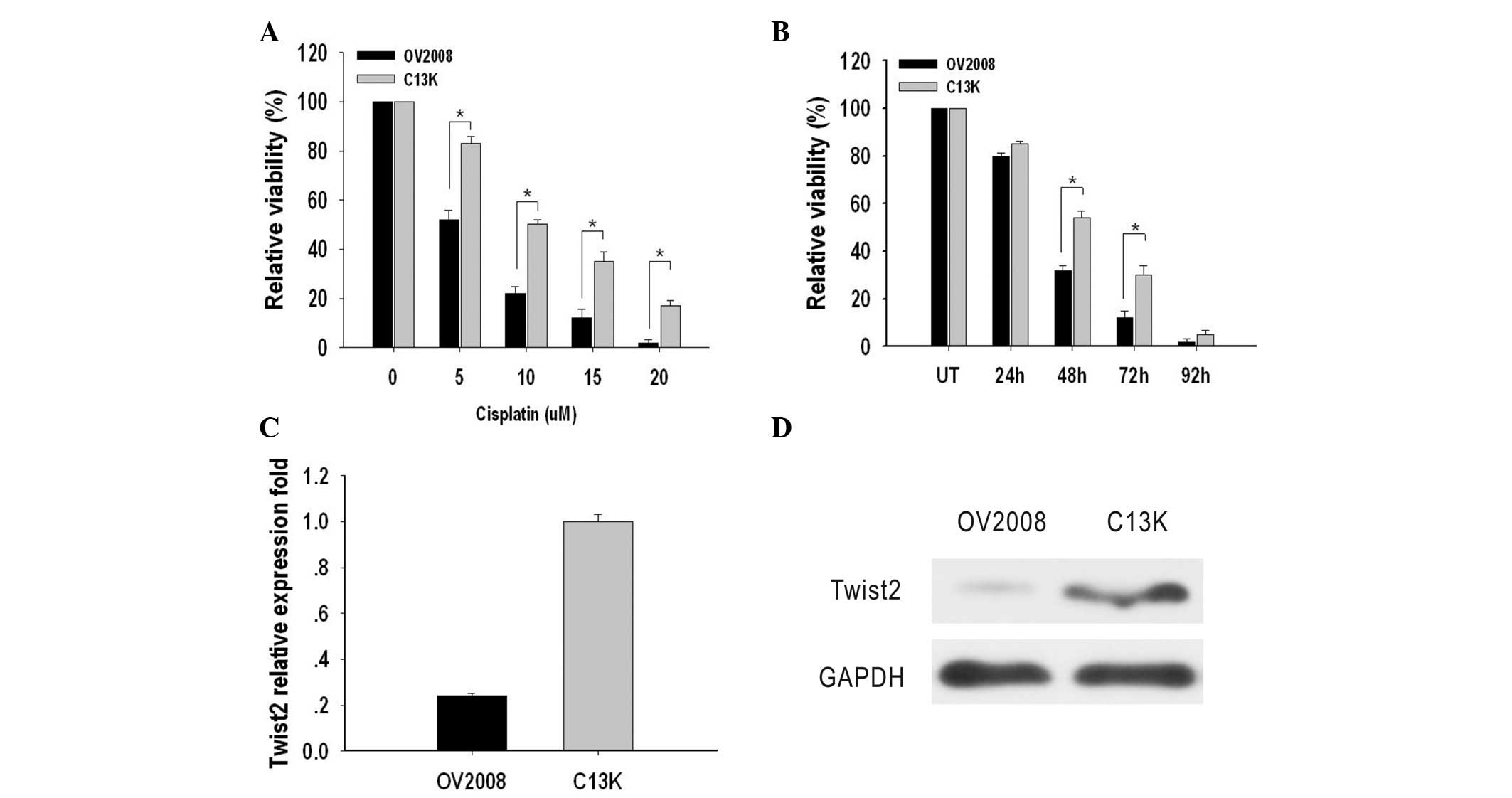
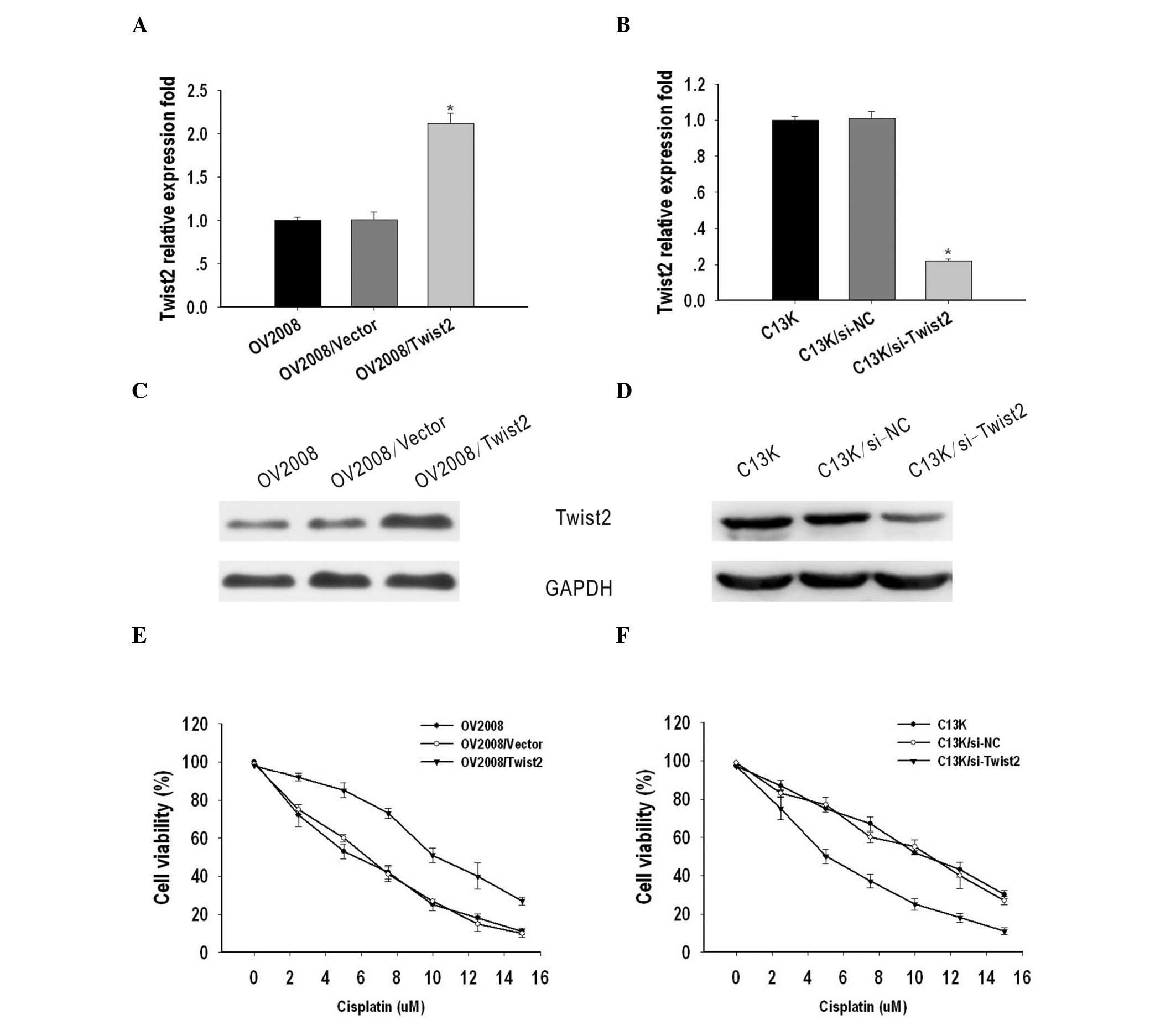
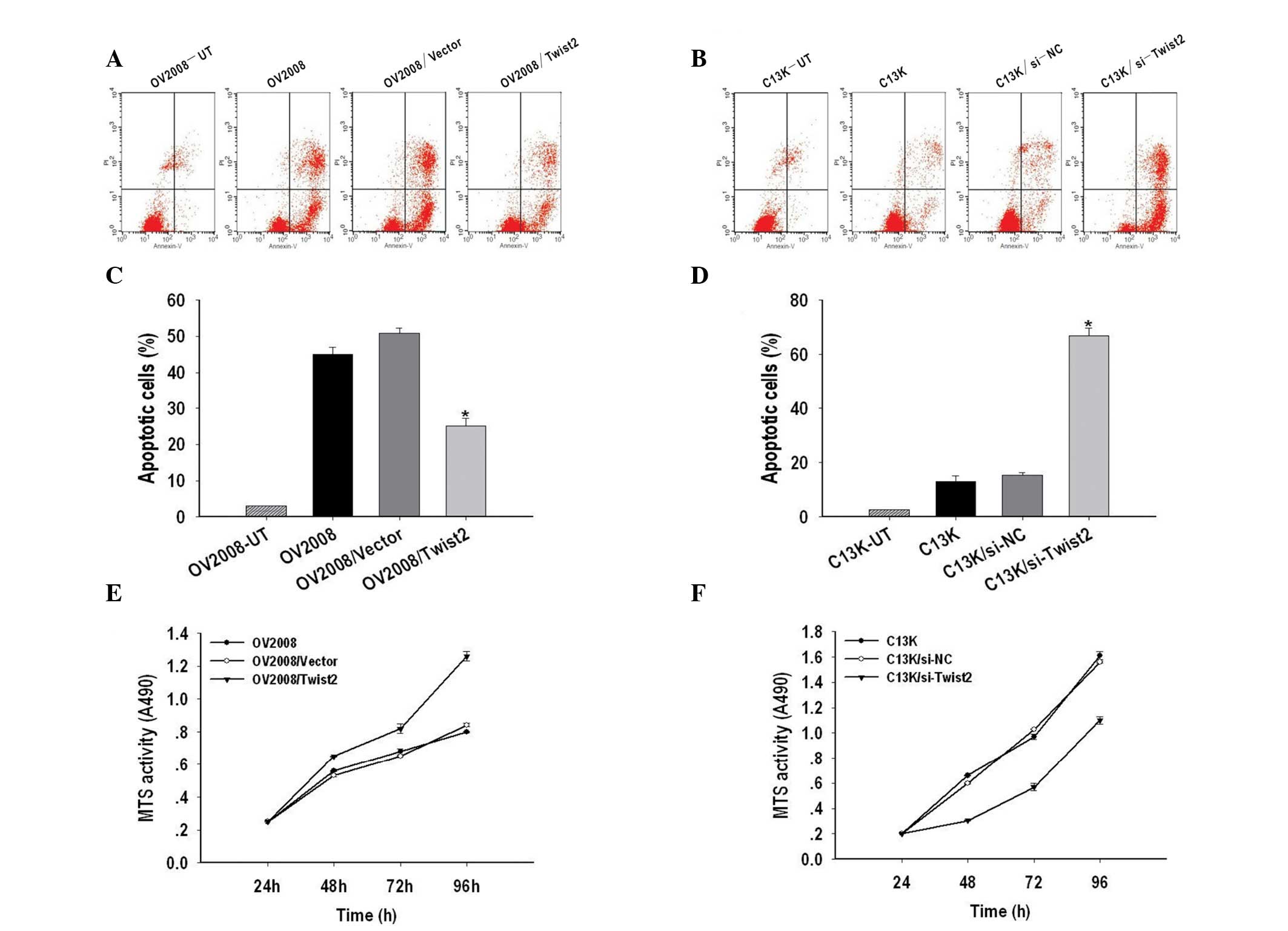
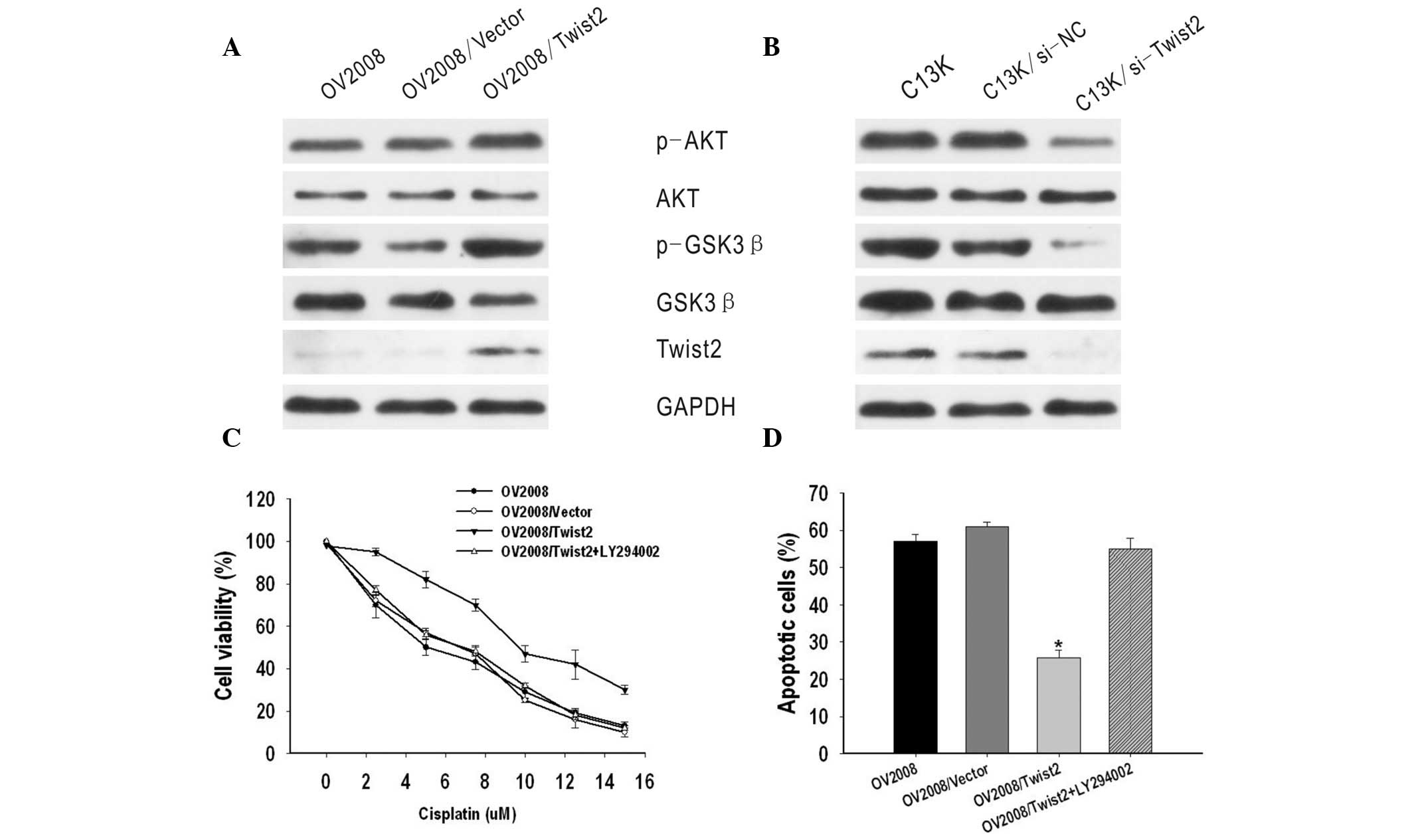
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Fraser M, Leung B, Jahani-Asl A, Yan X,
Thompson WE and Tsang BK: Chemoresistance in human ovarian cancer:
the role of apoptotic regulators. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 1:662003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J,
Smigal C and Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin.
56:106–130. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yang X, Xing H, Gao Q, Chen G, Lu Y, Wang
S and Ma D: Regulation of HtrA2/Omi by X-linked inhibitor of
apoptosis protein in chemoresistance in human ovarian cancer cells.
Gynecol Oncol. 97:413–421. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yu H, Jin GZ, Liu K, Dong H, Yu H, Duan
JC, Li Z, Dong W, Cong WM and Yang JH: Twist2 is a valuable
prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol.
19:2404–2411. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gasparotto D, Polesel J, Marzotto A,
Colladel R, Piccinin S, Modena P, Grizzo A, Sulfaro S, Serraino D,
Barzan L, Doglioni C and Maestro R: Overexpression of TWIST2
correlates with poor prognosis in head and neck squamous cell
carcinomas. Oncotarget. 2:1165–1175. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhou C, Liu J, Tang Y, Zhu G, Zheng M,
Jiang J, Yang J and Liang X: Coexpression of hypoxia-inducible
factor-2α, TWIST2, and SIP1 may correlate with invasion and
metastasis of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med.
41:424–431. 2012.
|
|
8
|
Li Y, Wang W, Wang W, Yang R, Wang T, Su
T, Weng D, Tao T, Li W, Ma D and Wang S: Correlation of TWIST2
up-regulation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition during
tumorigenesis and progression of cervical carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol.
124:112–118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Koh HS, Lee C, Lee KS, Park EJ, Seong RH,
Hong S and Jeon SH: Twist2 regulates CD7 expression and
galectin-1-induced apoptosis in mature T-cells. Mol Cells.
28:553–558. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ansieau S, Bastid J, Doreau A, Morel AP,
Bouchet BP, Thomas C, Fauvet F, Puisieux I, Doglioni C, Piccinin S,
Maestro R, Voeltzel T, Selmi A, Valsesia-Wittmann S, Caron de
Fromentel C and Puisieux A: Induction of EMT by twist proteins as a
collateral effect of tumor-promoting inactivation of premature
senescence. Cancer Cell. 14:79–89. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Acloque H, Adams MS, Fishwick K,
Bronner-Fraser M and Nieto MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions:
the importance of changing cell state in development and disease. J
Clin Invest. 119:1438–1449. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Singh A and Settleman J: EMT, cancer stem
cells and drug resistance: an emerging axis of evil in the war on
cancer. Oncogene. 29:4741–4751. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Johnson-Holiday C, Singh R, Johnson EL,
Grizzle WE, Lillard JW Jr and Singh S: CCR9-CCL25 interactions
promote cisplatin resistance in breast cancer cell through Akt
activation in a PI3K-dependent and FAK-independent fashion. World J
Surg Oncol. 9:462011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ali AY, Farrand L, Kim JY, Byun S, Suh JY,
Lee HJ and Tsang BK: Molecular determinants of ovarian cancer
chemoresistance: new insights into an old conundrum. Ann N Y Acad
Sci. 1271:58–67. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cheng JQ, Jiang X, Fraser M, Li M, Dan HC,
Sun M and Tsang BK: Role of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein
in chemoresistance in ovarian cancer: possible involvement of the
phosphoinositide-3 kinase/Akt pathway. Drug Resist Updat.
5:131–146. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mao Y, Zhang N, Xu J, Ding Z, Zong R and
Liu Z: Significance of heterogeneous Twist2 expression in human
breast cancers. PLoS One. 7:e481782012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tiwari N, Gheldof A, Tatari M and
Christofori G: EMT as the ultimate survival mechanism of cancer
cells. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:194–207. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Smit MA, Geiger TR, Song JY, Gitelman I
and Peeper DS: A Twist-Snail axis critical for TrkB-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition-like transformation, anoikis
resistance, and metastasis. Mol Cell Biol. 29:3722–3737. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Tsai CC, Chen YJ, Yew TL, Chen LL, Wang
JY, Chiu CH and Hung SC: Hypoxia inhibits senescence and maintains
mesenchymal stem cell properties through down-regulation of E2A-p21
by HIF-TWIST. Blood. 117:459–469. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li QQ, Xu JD, Wang WJ, Cao XX, Chen Q,
Tang F, Chen ZQ, Liu XP and Xu ZD: Twist1-mediated
adriamycin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition relates to
multidrug resistance and invasive potential in breast cancer cells.
Clin Cancer Res. 15:2657–2665. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Bialek P, Kern B, Yang X, Schrock M, Sosic
D, Hong N, Wu H, Yu K, Ornitz DM, Olson EN, Justice MJ and Karsenty
G: A twist code determines the onset of osteoblast differentiation.
Dev Cell. 6:423–435. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tsuji T, Ibaragi S, Shima K, Hu MG,
Katsurano M, Sasaki A and Hu GF: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition
induced by growth suppressor p12CDK2-AP1 promotes tumor cell local
invasion but suppresses distant colony growth. Cancer Res.
68:10377–10386. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Tukel T, Šošić D, Al-Gazali LI, Erazo M,
Casasnovas J, Franco HL, Richardson JA, Olson EN, Cadilla CL and
Desnick RJ: Homozygous nonsense mutations in TWIST2 cause Setleis
syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 87:289–296. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Franco HL, Casasnovas J, Rodríguez-Medina
JR and Cadilla CL: Redundant or separate entities? - roles of
Twist1 and Twist2 as molecular switches during gene transcription.
Nucleic Acids Res. 39:1177–1186. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Perez RP: Cellular and molecular
determinants of cisplatin resistance. Eur J Cancer. 34:1535–1542.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Aoki K, Ogawa T, Ito Y and Nakashima S:
Cisplatin activates survival signals in UM-SCC-23 squamous cell
carcinoma and these signal pathways are amplified in
cisplatin-resistant squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 11:375–379.
2004.
|
|
28
|
Testa JR and Bellacosa A: AKT plays a
central role in tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:10983–10985. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Simon D, Herva ME, Benitez MJ, Garrido JJ,
Rojo AI, Cuadrado A, Torres JM and Wandosell F: Dysfunction of the
PI3K-Akt-GSK-3 pathway is a common feature in cell culture and in
vivo models of prion disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. Jun
6–2013.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Arafa el SA, Zhu Q, Barakat BM, Wani G,
Zhao Q, El-Mahdy MA and Wani AA: Tangeretin sensitizes
cisplatin-resistant human ovarian cancer cells through
downregulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway.
Cancer Res. 69:8910–8917. 2009.
|
|
31
|
Chen R, Yang Q and Lee JD: BMK1 kinase
suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the Akt/GSK3β
signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 72:1579–1587. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Maseki S, Ijichi K, Tanaka H, Fujii M,
Hasegawa Y, Ogawa T, Murakami S, Kondo E and Nakanishi H:
Acquisition of EMT phenotype in the gefitinib-resistant cells of a
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell line through
Akt/GSK-3β/snail signalling pathway. Br J Cancer. 106:1196–1204.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|