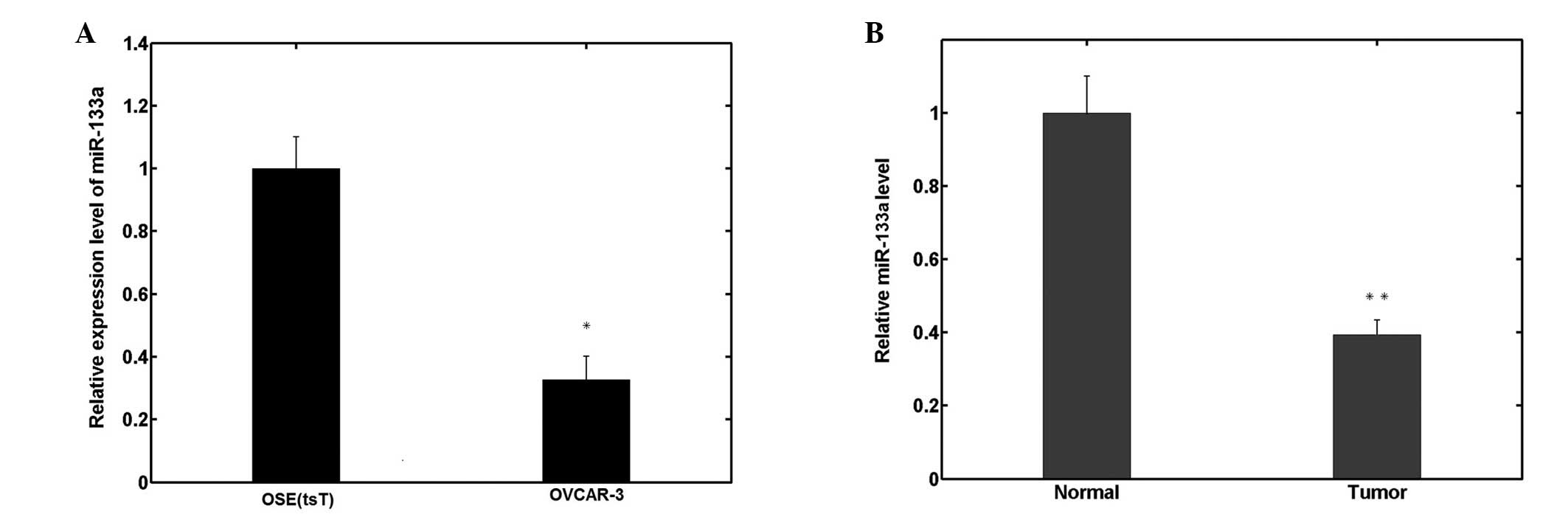
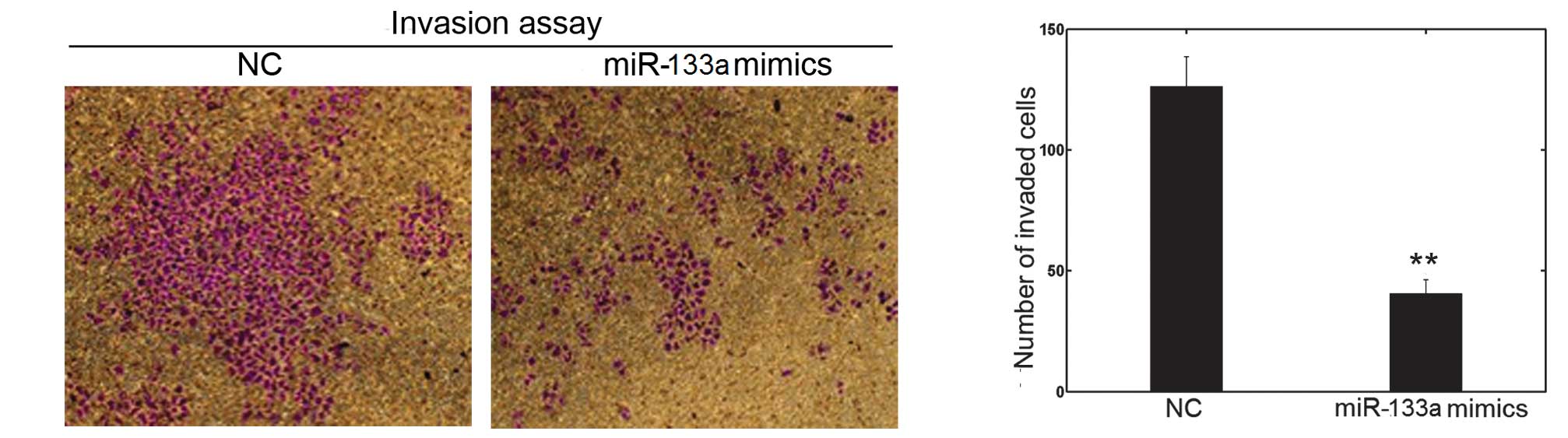
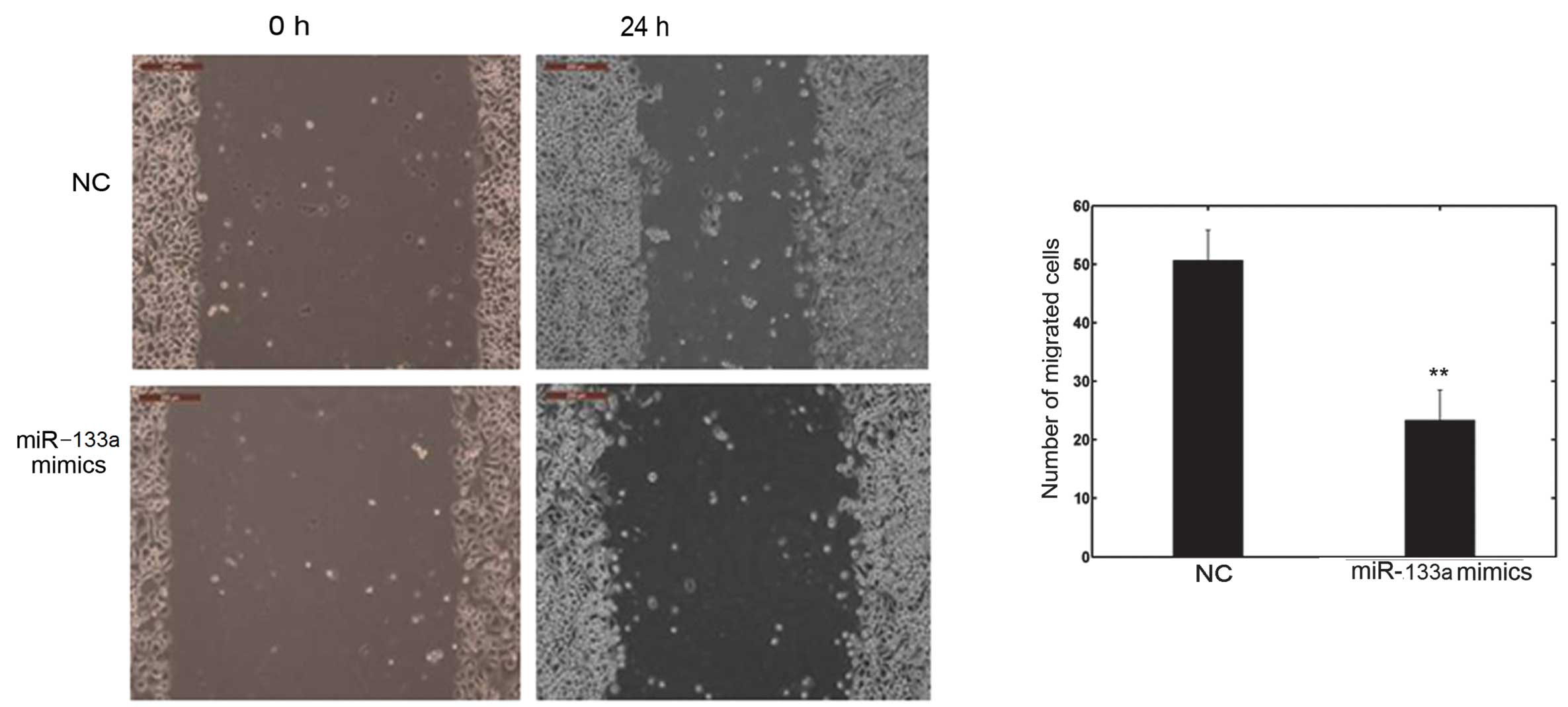
|
1
|
Hoskins WJ: Prospective on ovarian cancer:
why prevent? J Cell Biochem Suppl. 23:189–199. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Clarke-Pearson DL: Clinical practice.
Screening for ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 361:170–177. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ambros V: MicroRNA pathways in flies and
worms: growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell. 113:673–676.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, et al:
Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15
and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 99:15524–15529. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Song T, Xia W, Shao N, et al: Differential
miRNA expression profiles in bladder urothelial carcinomas. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 11:905–911. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, et al:
Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and
genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:2999–3004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Liu ZY, Zhang GL, Wang MM, Xiong YN and
Cui HQ: MicroRNA-663 targets TGFB1 and regulates lung cancer
proliferation. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:2819–2823.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fabian MR and Sonenberg N: The mechanics
of miRNA-mediated gene silencing: a look under the hood of miRISC.
Nat Struct Mol Biol. 19:586–593. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lou Y, Cui Z, Wang F, Yang X and Qian J:
miR-21 down-regulation promotes apoptosis and inhibits invasion and
migration abilities of OVCAR3 cells. Clin Invest Med.
34:E2812011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kan CW, Hahn MA, Gard GB, et al: Elevated
levels of circulating microRNA-200 family members correlate with
serous epithelial ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer. 12:6272012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Flavin R, Smyth P, Barrett C, et al:
miR-29b expression is associated with disease-free survival in
patients with ovarian serous carcinoma. Int J Gynecol Cancer.
19:641–647. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lou Y, Yang X, Wang F, Cui Z and Huang Y:
MicroRNA-21 promotes the cell proliferation, invasion and migration
abilities in ovarian epithelial carcinomas through inhibiting the
expression of PTEN protein. Int J Mol Med. 26:819–827.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yeh YM, Chuang CM, Chao KC and Wang LH:
MicroRNA-138 suppresses ovarian cancer cell invasion and metastasis
by targeting SOX4 and HIF-1α. Int J Cancer. 15:867–878.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nohata N, Hanazawa T, Kikkawa N, et al:
Caveolin-1 mediates tumor cell migration and invasion and its
regulation by miR-133a in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Int J Oncol. 38:209–217. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rao PK, Missiaglia E, Shields L, et al:
Distinct roles for miR-1 and miR-133a in the proliferation and
differentiation of rhabdomyosarcoma cells. FASEB J. 24:3427–3437.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kano M, Seki N, Kikkawa N, et al: miR-145,
miR-133a and miR-133b: Tumor-suppressive miRNAs target FSCN1 in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 127:2804–2814.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sarver AL, French AJ, Borralho PM, et al:
Human colon cancer profiles show differential microRNA expression
depending on mismatch repair status and are characteristic of
undifferentiated proliferative states. BMC Cancer. 9:4012009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wong TS, Liu XB, Chung-Wai Ho A, Po-Wing
Yuen A, Wai-Man Ng R and Ignace Wei W: Identification of pyruvate
kinase type M2 as potential oncoprotein in squamous cell carcinoma
of tongue through microRNA profiling. Int J Cancer. 123:251–257.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kawakami K, Enokida H, Chiyomaru T, et al:
The functional significance of miR-1 and miR-133a in renal cell
carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 48:827–836. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Karseladze AI: WHO histological
classification of ovarian tumors. Geneva: 1999, Scully RE and Sobin
LH: Arkh Patol Suppl. pp. 1–64. 2005, (In Russian).
|
|
21
|
Odicino F, Pecorelli S, Zigliani L and
Creasman WT: History of the FIGO cancer staging system. Int J
Gynaecol Obstet. 101:205–210. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Alley MC, Scudiero DA, Monks A, et al:
Feasibility of drug screening with panels of human tumor cell lines
using a microculture tetrazolium assay. Cancer Res. 48:589–601.
1988.
|
|
24
|
Jovanovic M and Hengartner MO: miRNAs and
apoptosis: RNAs to die for. Oncogene. 25:6176–6187. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Casalini P and Iorio MV: MicroRNAs and
future therapeutic applications in cancer. J BUON. 14(Suppl 1):
S17–S22. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Moriya Y, Nohata N, Kinoshita T, et al:
Tumor suppressive microRNA-133a regulates novel molecular networks
in lung squamous cell carcinoma. J Hum Genet. 57:38–45. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nohata N, Hanazawa T, Kikkawa N, et al:
Identification of novel molecular targets regulated by tumor
suppressive miR-1/miR-133a in maxillary sinus squamous cell
carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 39:1099–1107. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kojima S, Chiyomaru T, Kawakami K, et al:
Tumour suppressors miR-1 and miR-133a target the oncogenic function
of purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) in prostate cancer. Br J
Cancer. 106:405–413. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yoshino H, Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, et al:
The tumour-suppressive function of miR-1 and miR-133a targeting
TAGLN2 in bladder cancer. Br J Cancer. 104:808–818. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu ZS, Wang CQ, Xiang R, et al: Loss of
miR-133a expression associated with poor survival of breast cancer
and restoration of miR-133a expression inhibited breast cancer cell
growth and invasion. BMC Cancer. 12:512012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Tatarano S, et al:
miR-145 and miR-133a function as tumour suppressors and directly
regulate FSCN1 expression in bladder cancer. Br J Cancer.
102:883–891. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Kawakami K, et al:
Functional role of LASP1 in cell viability and its regulation by
microRNAs in bladder cancer. Urol Oncol. 30:434–443. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|