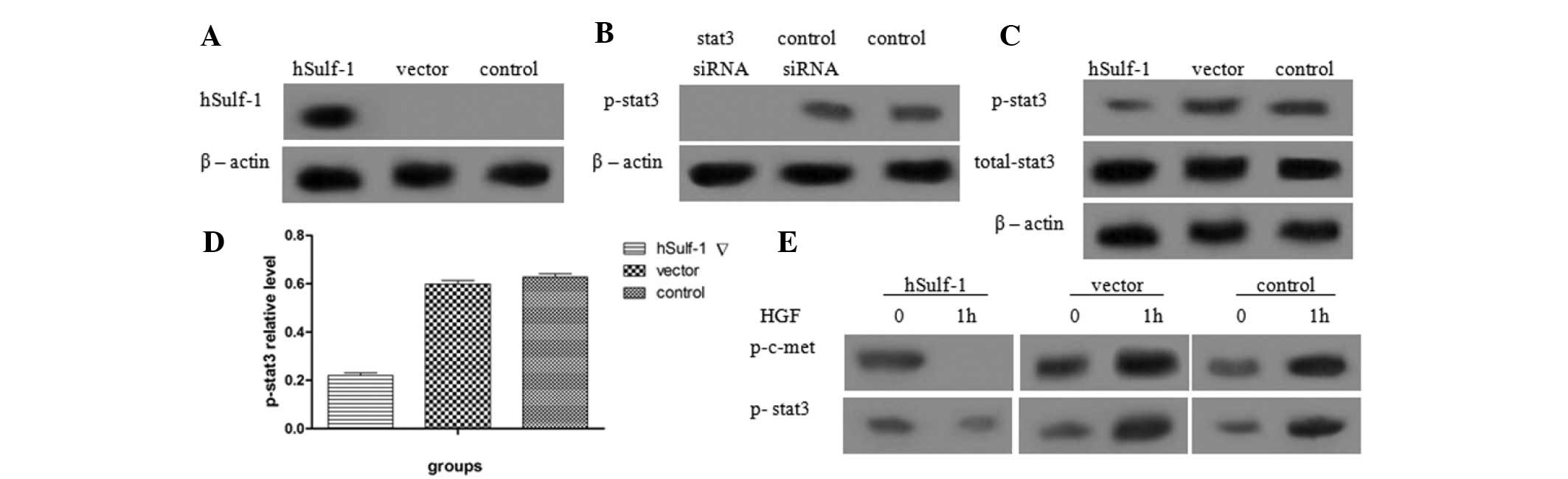
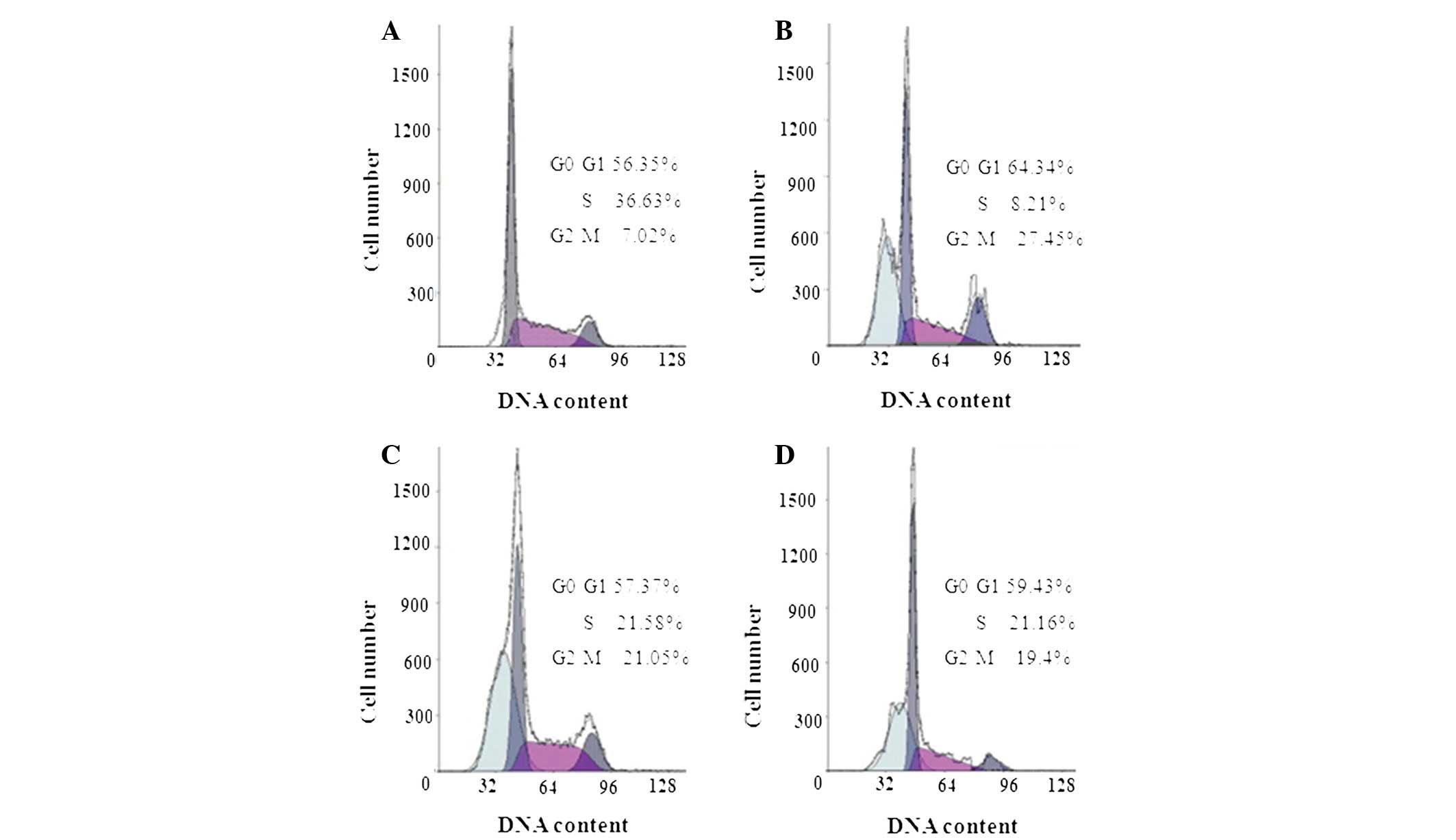
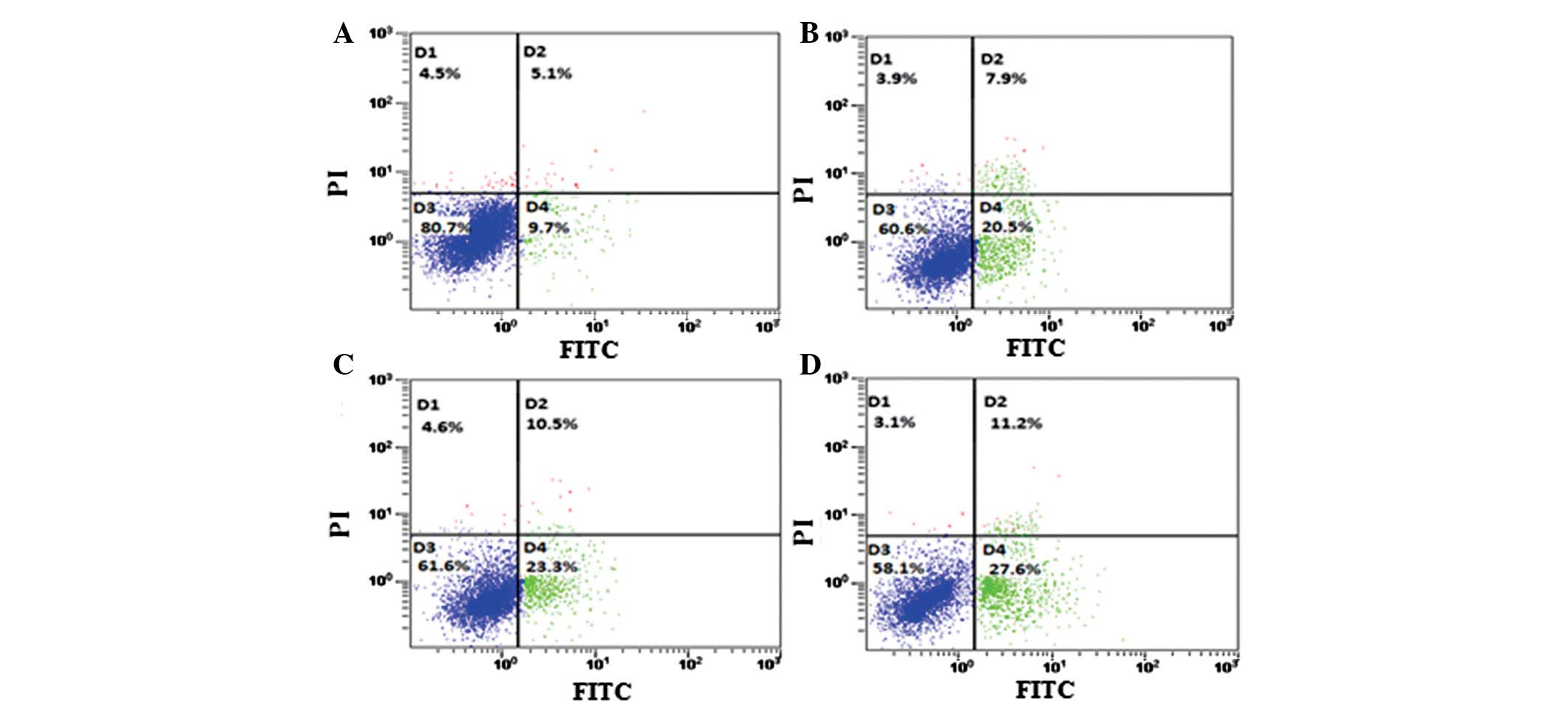
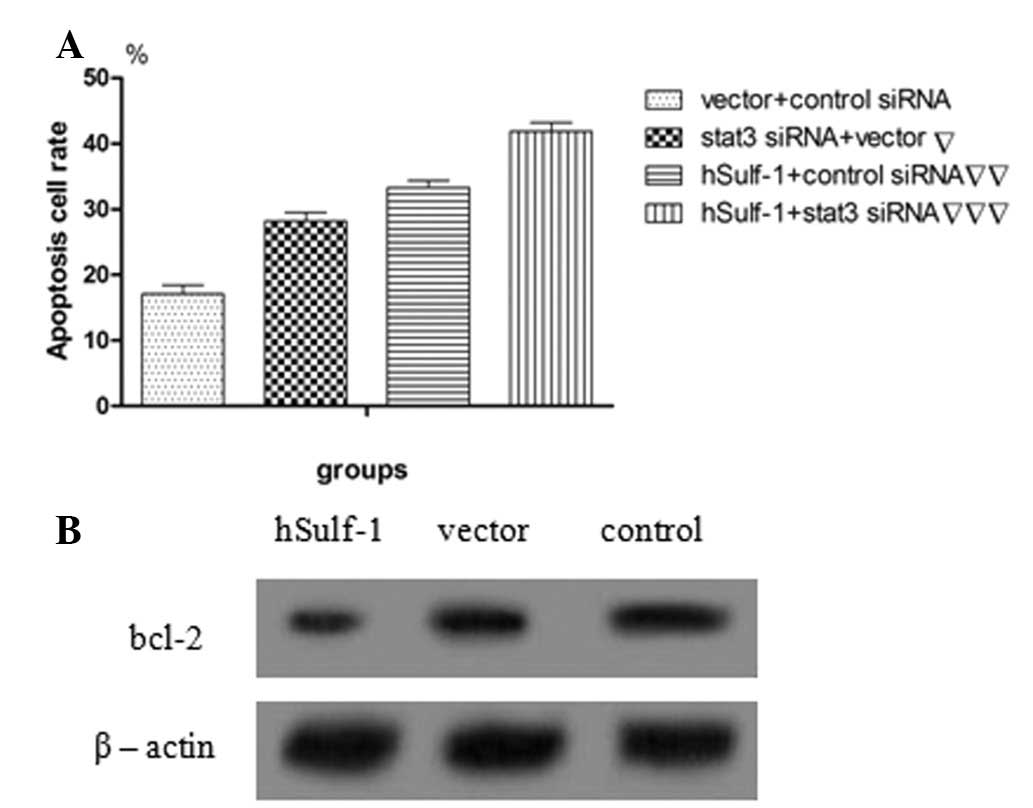
|
1
|
el-Serag HB: Epidemiology of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Liver Dis. 5:87–107. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
He J, Gu D, Wu X, et al: Major causes of
death among men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 353:1124–1134.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lin X: Functions of heparan sulfate
proteoglycans in cell signaling during development. Development.
131:6009–6021. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Park PW, Reizes O and Bernfield M: Cell
surface heparan sulfate proteo-glycans: selective regulators of
ligand-receptor encounters. J Biol Chem. 275:29923–29926. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kirkpatrick CA and Selleck SB: Heparan
sulfate proteoglycans at a glance. J Cell Sci. 120:1829–1832. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kikuchi A and Yamamoto H: Regulation of
Wnt signalling by receptor-mediated endocytosis. J Biochem.
141:443–451. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Staub J, Chien J, Pan Y, et al: Epigenetic
silencing of HSulf-1 in ovarian cancer: implications
inchemoresistance. Oncogene. 26:4969–4978. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lai J, Chien J, Staub J, et al: Loss of
HSulf-1 up-regulates heparin-binding growth factor signaling in
cancer. J Biol Chem. 278:23107–23117. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Chen Z, Fan JQ, Li J, et al: Promoter
hypermethylation correlates with the HSulf-1 silencing in human
breast and gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 124:739–744. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Monneret C: Histone deacetylase
inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem. 40:1–13. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Pye DA, Vives RR, Turnbull JE, Hyde P and
Gallagher JT: Heparan sulfate oligosaccharides require
6-O-sulfation for promotion of basic fibroblast growth factor
mitogenic activity. J Biol Chem. 273:22936–22942. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lai JP, Chien J, Strome SE, et al: HSulf-1
modulates HGF-mediated tumor cell invasion and signaling in head
and neck squamous carcinoma. Oncogene. 23:1439–1447. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lai JP, Chien JR, Moser DR, et al: hSulf-1
sulfatase promotes apoptosis of hepatocellular cancer cells by
decreasing heparin-binding growth factor signaling.
Gastroenterology. 126:231–248. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li J, Kleeff J, Abiatari I, et al:
Enhanced levels of Hsulf-1 interfere with heparin-binding growth
factor signaling in pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer. 4:142005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dai Y, Yang Y, MacLeod V, et al: HSulf-1
and HSulf-2 are potent inhibitors of myeloma tumor growth in vivo.
J Biol Chem. 280:40066–40073. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lai JP, Sandhu DS, Shire AM and Roberts
LR: The tumor suppressor function of human sulfatase 1 (SULF1) in
carcinogenesis. J Gastrointest Cancer. 39:149–158. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Narita K, Staub J, Chien J, et al: HSulf-1
inhibits angiogenesis and tumorigenesis in vivo. Cancer Res.
66:6025–6032. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ji W, Yang J, Wang D, et al: hSulf-1 gene
exhibits anticancer efficacy through negatively regulating VEGFR-2
signaling in human cancers. PLoS ONE. 6:e232742011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bowman T, Garcia R, Turkson J and Jove R:
STATs in oncogenesis. Oncogene. 19:2474–2788. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rahaman SO and Harbor PC: Inhibition of
constitutively active Stat3 suppresses proliferation and induces
apoptosis in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Oncogene. 21:8404–8413.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Iwamaru A, Szymanski S, Iwado E, et al: A
novel inhibitor of the stat3 pathway induces apoptosis in malignant
glioma cells both in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 26:2435–2444.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jacoby JJ, Kalinowski A, Liu MG, et al:
Cardiomyocyte restricted knockout of stat3 results in higher
sensitivity to inflammation, cardiac fibrosis, and heart failure
with advanced age. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:12929–12934. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kurdi M and Booz GW: Can the protective
actions of JAK-stat in the heart be exploited therapeutically?
Parsing the regulation of interleukin-6-type cytokine signaling. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 50:126–141. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Bores P and Miller CM: Hepatocyte growth
factor: a multifunctional cytokine. Lancet. 345:293–295. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee KH, Choi EY, Hyun MS, et al: Role of
hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met signaling in regulating urokinase
plasminogen activator on invasiveness in human hepatocellular
carcinoma: a potential therapeutic target. Clin Exp Metastasis.
25:89–96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Moore AE, Greenhough A, Roberts HR, et al:
HGF/Met signaling promotes PGE2 biogenesis via regulation of COX-2
and 15-PGDH expression in colorectal cancer cells. Carcinogenesis.
30:1796–1804. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ai X, Do AT, Kusche-Gullberg M, Lindahl U,
Lu K and Emerson CP Jr: Substrate specificity and domain functions
of extracellular heparan sulfate 6-O-endosulfatases, QSulf1 and
QSulf2. J Biol Chem. 281:4969–4976. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Diez-Roux G and Ballabio A: Sulfatases and
human disease. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 6:355–379. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Forsten-Williams K, Chu CL, Fannon M,
Buczek-Thomas JA and Nugent MA: Control of growth factor networks
by heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Ann Biomed Eng. 36:2134–2148.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dhoot GK, Gustafsson MK, Ai X, Sun W,
Standiford DM and Emerson CP Jr: Regulation of Wnt signaling and
embryo patterning by an extracellular sulfatase. Science.
293:1663–1666. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ornitz DM: FGFs, heparan sulfate and
FGFRs: complex interactions essential for development. Bioessays.
22:108–112. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fletcher S, Turkson J and Gunning PT:
Molecular approaches towards the inhibition of the signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat3) protein.
ChemMedChem. 3:1159–1168. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen Z and Han ZC: STAT3: a critical
transcription activator in angiogenesis. Med Res Rev. 28:185–200.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Frank DA: STAT3 as a central mediator of
neoplastic cellular transformation. Cancer Lett. 251:199–210. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yu ZY, Huang R, Xiao H, et al:
Fluacrypyrim, a novel stat3 activation inhibitor, induces cell
cycle arrest and apoptosis in cancer cells harboring
constitutively-active stat3. Int J Cancer. 127:1259–1270. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|