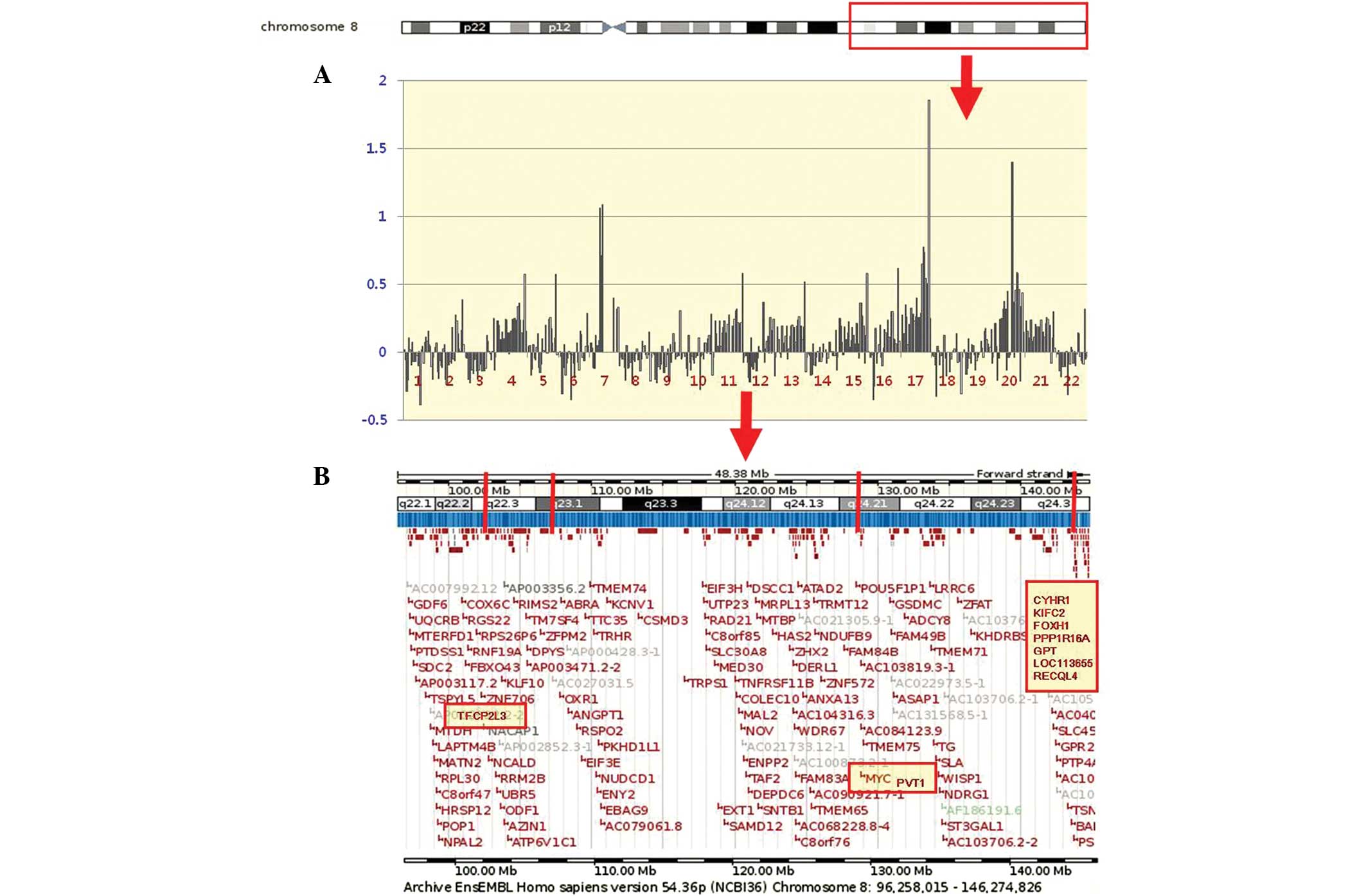
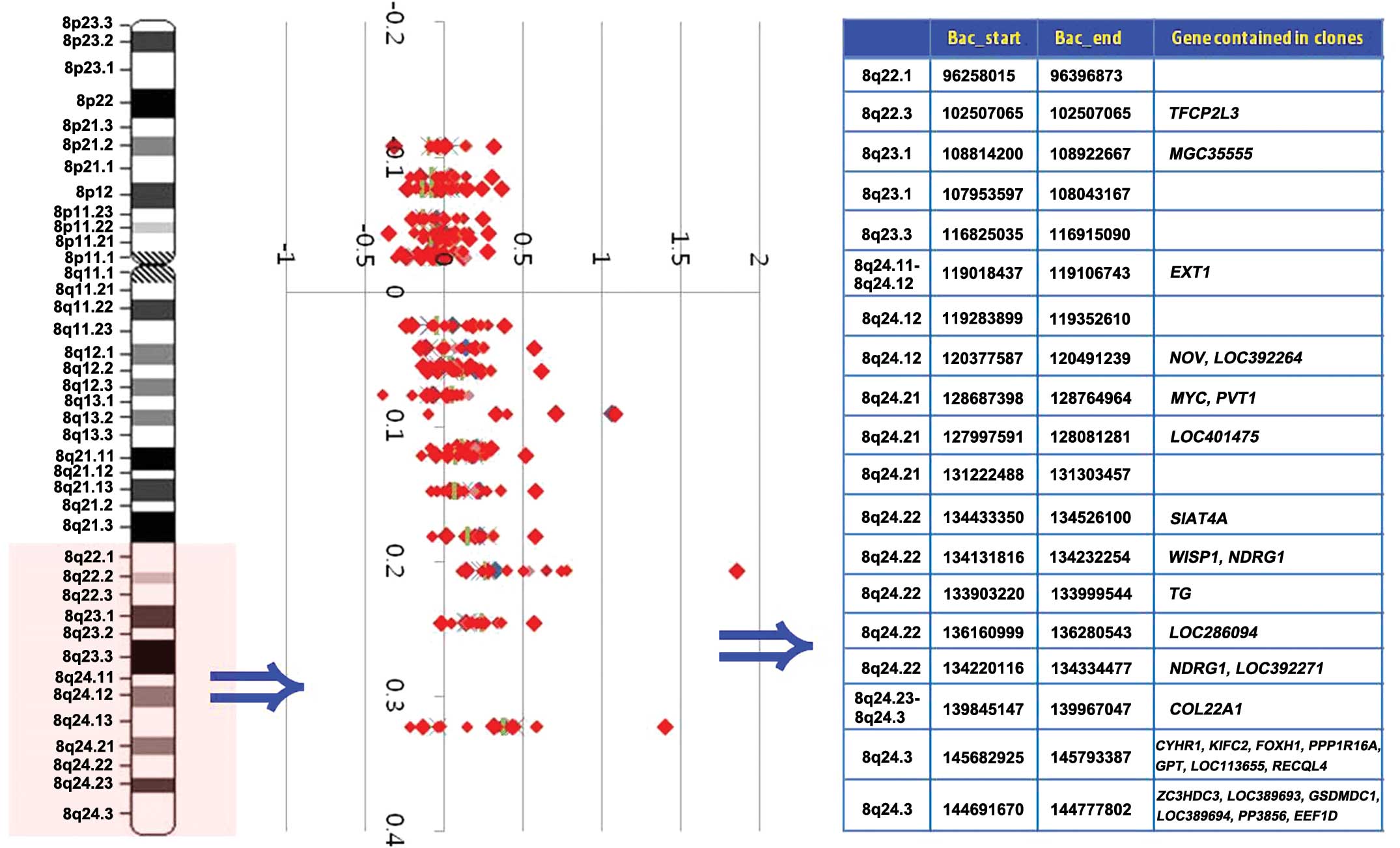
|
1
|
Nakayama T, Ling ZQ, Mukaisho K, Hattori T
and Sugihara H: Lineage analysis of early and advanced tubular
adenocarcinomas of the stomach: continuous or discontinuous? BMC
Cancer. 10:3112010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Cheng L, Wang P, Yang S, et al:
Identification of genes with a correlation between copy number and
expression in gastric cancer. BMC Med Genomics. 5:142012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brenner H, Rothenbacher D and Arndt V:
Epidemiology of stomach cancer. Methods Mol Biol. 472:467–477.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Gümüs-Akay G, Unal AE, Elhan AH, et al:
DNA copy number changes in gastric adenocarcinomas: high
resolution-comparative genomic hybridization study in Turkey. Arch
Med Res. 40:551–560. 2009.
|
|
5
|
Cheng L and Zhang Q, Yang S, Yang Y, Zhang
W, Gao H, Deng X and Zhang Q: A 4-gene panel as a marker at
chromosome 8q in Asian gastric cancer patients. Genomics.
102:323–330. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mihailovici MS, Danciu M, Teleman S,
Stanciu C, Stan M, Bălan G and Potoroacă A: Diagnosis of gastric
cancer on endobiopsies using the WHO classification. Rev Med Chir
Soc Med Nat Iasi. 106:725–729. 2002.(In Romanian).
|
|
7
|
Sun YN and Li Y: Expression of mRNA for
membrane-type 1, 2, and 3 matrix metalloproteinases in human
laryngeal cancer. Chin Med Sci J. 19:170–173. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lowy AM, Clements WM, Bishop J, et al:
beta-Catenin/Wnt signaling regulates expression of the membrane
type 3 matrix metalloproteinase in gastric cancer. Cancer Res.
66:4734–4741. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nanjundan M, Nakayama Y, Cheng KW, Lahad
J, Liu J, Lu K, Kuo WL, Smith-McCune K, Fishman D, Gray JW and
Mills GB: Amplification of MDS1/EVI1 and EVI1, located in the
3q26.2 amplicon, is associated with favorable patient prognosis in
ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 67:3074–3084. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kim KR, Oh SY, Park UC, et al: Gene
expression profiling using oligonucleotide microarray in atrophic
gastritis and intestinal metaplasia. Korean J Gastroenterol.
49:209–224. 2007.(In Korean).
|
|
11
|
Sanjmyatav J, Steiner T, Wunderlich H,
Diegmann J, Gajda M and Junker K: A specific gene expression
signature characterizes metastatic potential in clear cell renal
cell carcinoma. J Urol. 186:289–294. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hashimoto T, Kusakabe T, Watanabe K, et
al: Liver-type fatty acid-binding protein is highly expressed in
intestinal metaplasia and in a subset of carcinomas of the stomach
without association with the fatty acid synthase status in the
carcinoma. Pathobiology. 71:115–122. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hashimoto T, Kusakabe T, Sugino T, et al:
Expression of heart-type fatty acid-binding protein in human
gastric carcinoma and its association with tumor aggressiveness,
metastasis and poor prognosis. Pathobiology. 71:267–273. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Buffart TE, van Grieken NC, Tijssen M,
Coffa J, Ylstra B, Grabsch HI, van de Velde CJ, Carvalho B and
Meijer GA: High resolution analysis of DNA copy-number aberrations
of chromosomes 8, 13, and 20 in gastric cancers. Virchows Arch.
455:213–223. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Katoh M and Katoh M: Human FOX gene family
(Review). Int J Oncol. 25:1495–1500. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Abi-Ayad N, Couturier J,
Devouassoux-Shisheboran M, Grange JD, Kodjikian L and Calender A:
Genomic profiling by comparative genomic hybridization: analysis of
ten enucleated uveal melanoma cases. J Fr Ophtalmol. 34:17–23.
2011.(In French).
|
|
17
|
de Krijger RR, Claessen SM, van der Ham F,
van Unnik AJ, Hulsbergen-van de Kaa CA, van Leuven L, van Noesel M
and Speel EJ: Gain of chromosome 8q is a frequent finding in
pleuropulmonary blastoma. Mod Pathol. 20:1191–1199. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Costa Raiol LC, Figueira Silva EC, Mendes
da Fonseca D, et al: Interrelationship between MYC gene numerical
aberrations and protein expression in individuals from northern
Brazil with early gastric adenocarcinoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet.
181:31–35. 2008.
|
|
19
|
Calcagno DQ, Leal MF, Assumpcao PP, Smith
MA and Burbano RR: MYC and gastric adenocarcinoma carcinogenesis.
World J Gastroenterol. 14:5962–5968. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Onoda N, Maeda K, Chung YS, Yano Y,
Matsui-Yuasa I, Otani S and Sowa M: Overexpression of c-myc
messenger RNA in primary and metastatic lesions of carcinoma of the
stomach. J Am Coll Surg. 182:55–59. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ishii H, Gobé G, Kawakubo Y, Sato Y and
Ebihara Y: Interrelationship between Epstein-Barr virus infection
in gastric carcinomas and the expression of apoptosis-associated
proteins. Histopathology. 38:111–119. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Suzuki S, Tenjin T, Watanabe H, Matsushima
S, Shibuya T and Tanaka S: Low level c-myc gene amplification in
gastric cancer detected by dual color fluorescence in situ
hybridization analysis. J Surg Oncol. 66:173–178. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Meyer KB, Maia AT, O’Reilly M, et al: A
functional variant at a prostate cancer predisposition locus at
8q24 is associated with PVT1 expression. PLoS Genet.
7:e10021652011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nagoshi H, Taki T, Hanamura I, et al:
Frequent PVT1 rearrangement and novel chimeric genes PVT1-NBEA and
PVT1-WWOX occur in multiple myeloma with 8q24 abnormality. Cancer
Res. 72:4954–4962. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Jia L, Landan G, Pomerantz M, Jaschek R,
Herman P, Reich D, Yan C, Khalid O, Kantoff P, Oh W, Manak JR,
Berman BP, Henderson BE, Frenkel B, Haiman CA, Freedman M, Tanay A
and Coetzee GA: Functional enhancers at the gene-poor 8q24
cancer-linked locus. PLoS Genet. 5:e10005972009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Enciso-Mora V, Broderick P, Ma Y, et al: A
genome-wide association study of Hodgkin’s lymphoma identifies new
susceptibility loci at 2p16.1 (REL), 8q24.21 and 10p14 (GATA3). Nat
Genet. 42:1126–1130. 2010.
|