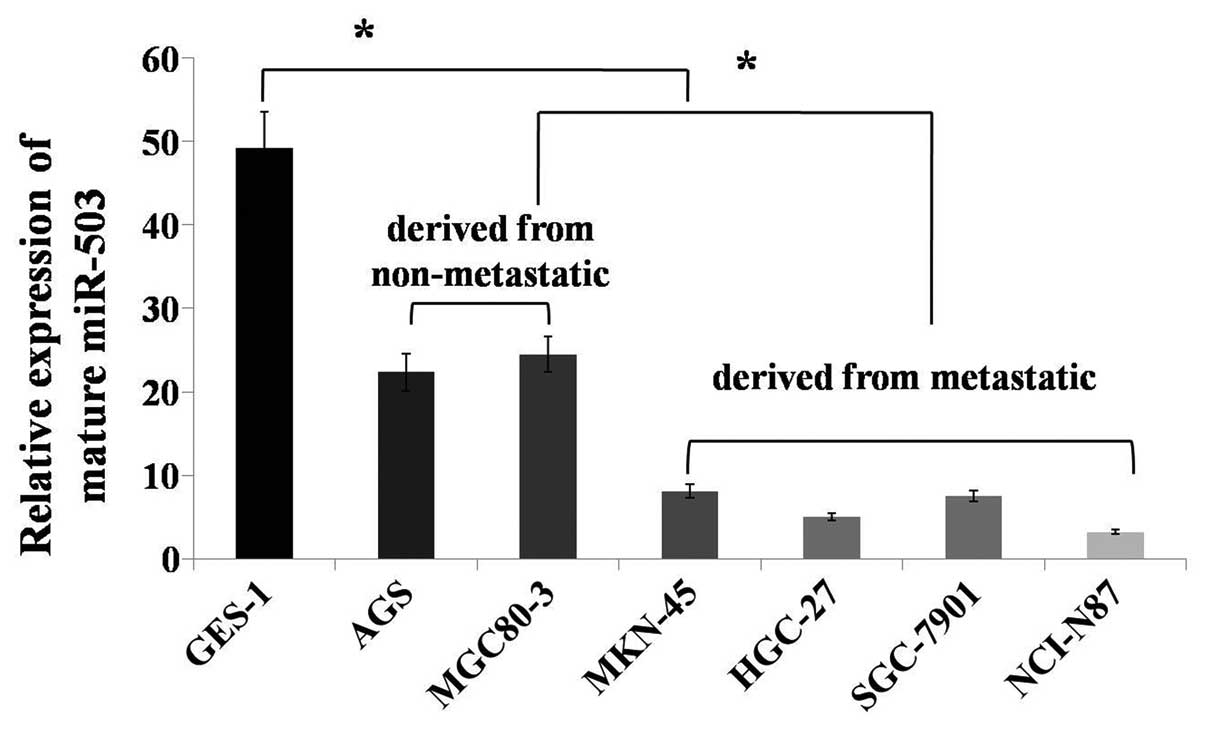
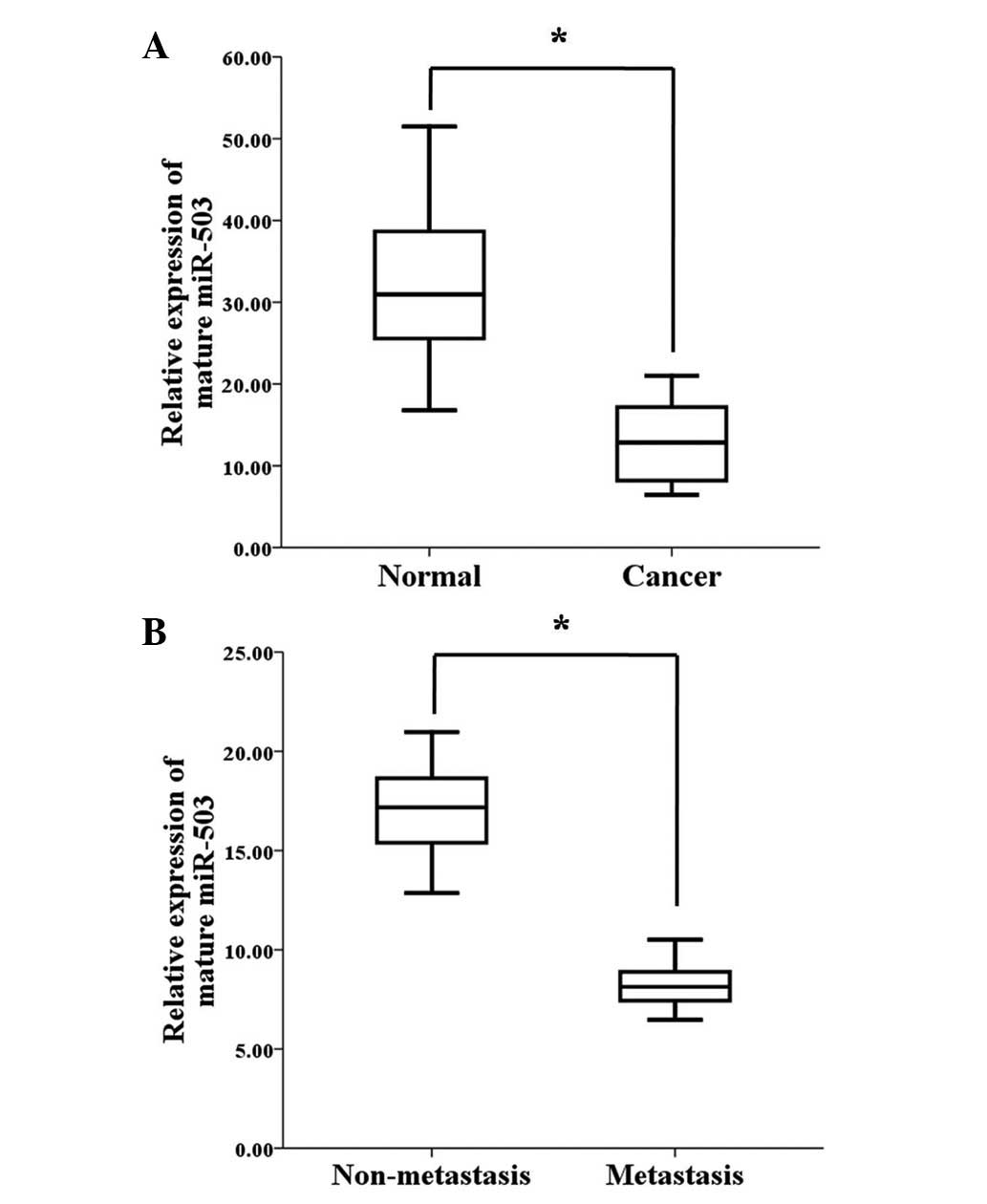
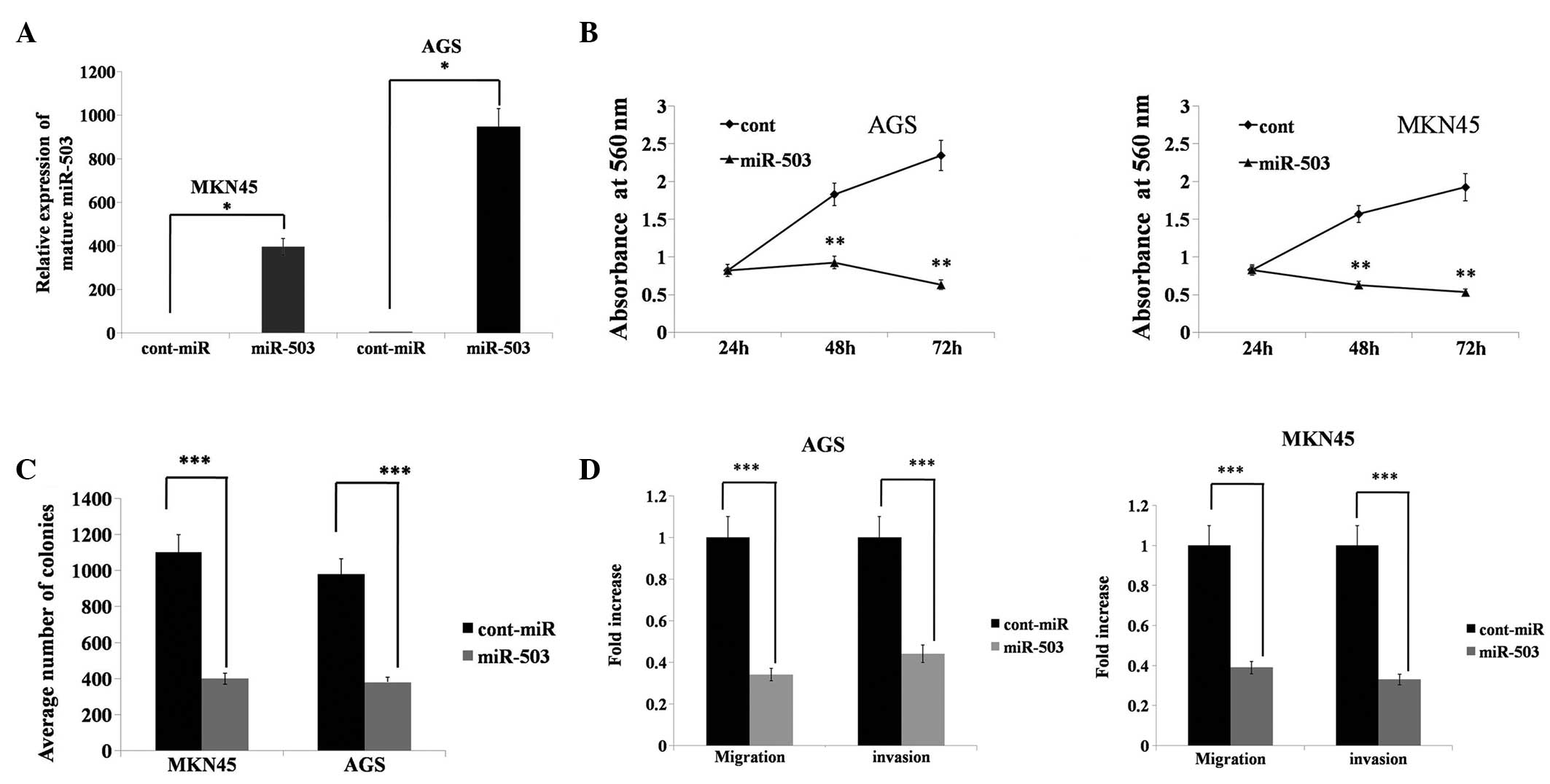
|
1
|
Rana TM: Illuminating the silence:
understanding the structure and function of small RNAs. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 8:23–36. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Valencia-Sanchez MA, Liu J, Hannon GJ and
Parker R: Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and
siRNAs. Genes Dev. 20:515–524. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pillai RS, Bhattacharyya SN and Filipowicz
W: Repression of protein synthesis by miRNAs: how many mechanisms?
Trends Cell Biol. 17:118–126. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, et al: MicroRNA
expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 435:834–838.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thomson JM, Newman M, Parker JS,
Morin-Kensicki EM, Wright T and Hammond SM: Extensive
post-transcriptional regulation of microRNAs and its implications
for cancer. Genes Dev. 20:2202–2207. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, et al:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gibbons DL, Lin W, Creighton CJ, et al:
Contextual extracellular cues promote tumor cell EMT and metastasis
by regulating miR-200 family expression. Genes Dev. 23:2140–2151.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao X, Dou W, He L, et al: MicroRNA-7
functions as an anti-metastatic microRNA in gastric cancer by
targeting insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor. Oncogene.
32:1363–1372. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kong W, Yang H, He L, et al: MicroRNA-155
is regulated by the transforming growth factor beta/Smad pathway
and contributes to epithelial cell plasticity by targeting RhoA.
Mol Cell Biol. 28:6773–6784. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Korpal M, Lee ES, Hu G and Kang Y: The
miR-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
cancer cell migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin
transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Biol Chem.
283:14910–14914. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Gebeshuber CA, Zatloukal K and Martinez J:
miR-29a suppresses tristetraprolin, which is a regulator of
epithelial polarity and metastasis. EMBO Rep. 10:400–405. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Cottonham CL, Kaneko S and Xu L: miR-21
and miR-31 converge on TIAM1 to regulate migration and invasion of
colon carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 285:35293–35302. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Eades G, Yao Y, Yang M, Zhang Y, Chumsri S
and Zhou Q: miR-200a regulates SIRT1 expression and epithelial to
mesenchymal transition (EMT)-like transformation in mammary
epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 286:25992–26002. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, et al:
The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 10:593–601.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Du R, Sun W, Xia L, et al: Hypoxia-induced
down-regulation of microRNA-34a promotes EMT by targeting the Notch
signaling pathway in tubular epithelial cells. PLoS One.
7:e307712012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Xu YY, Wu HJ, Ma HD, Xu LP, Huo Y and Yin
LR: MicroRNA-503 suppresses proliferation and cell cycle
progression of endometrioid endometrial cancer via negatively
regulating cyclin D1. FEBS J. 280:3768–3779. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Luo HC, Zhang ZZ, Zhang X, Ning B, Guo JJ,
Nie N, Liu B and Wu XL: microRNA expression signature in gastric
cancer. Chin J Cancer Res. 21:74–80. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang Y, Chen X, Lian H, et al:
MicroRNA-503 acts as a tumor suppressor in glioblastoma for
multiple antitumor effects by targeting IGF-1R. Oncol Rep.
31:1445–1452. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao JJ, Yang J, Lin J, et al:
Identification of miRNAs associated with tumorigenesis of
retinoblastoma by miRNA microarray analysis. Childs Nerv Syst.
25:13–20. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Corbetta S, Vaira V, Guarnieri V, et al:
Differential expression of microRNAs in human parathyroid
carcinomas compared with normal parathyroid tissue. Endocr Relat
Cancer. 17:135–146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Özata DM, Caramuta S, Velázquez-Fernández
D, et al: The role of microRNA deregulation in the pathogenesis of
adrenocortical carcinoma. Endocr Relat Cancer. 18:643–655.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lu YC, Chen YJ, Wang HM, et al: Oncogenic
function and early detection potential of miRNA-10b in oral cancer
as identified by microRNA profiling. Cancer Prev Res (Phila).
5:665–674. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Watahiki A, Wang Y, Morris J, et al:
MicroRNAs associated with metastatic prostate cancer. PLoS One.
6:e249502011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiang Q, Feng MG and Mo YY: Systematic
validation of predicted microRNAs for cyclin D1. BMC Cancer.
9:1942009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Caporali A, Meloni M, Völlenkle C, et al:
Deregulation of microRNA-503 contributes to diabetes
mellitus-induced impairment of endothelial function and reparative
angiogenesis after limb ischemia. Circulation. 123:282–291. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhou B, Ma R, Si W, et al: MicroRNA-503
targets FGF2 and VEGFA and inhibits tumor angiogenesis and growth.
Cancer Lett. 333:159–169. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou J and Wang W: Analysis of microRNA
expression profiling identifies microRNA-503 regulates metastatic
function in hepatocellular cancer cell. J Surg Oncol. 104:278–283.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kurashige J, Kamohara H, Watanabe M, et
al: MicroRNA-200b regulates cell proliferation, invasion, and
migration by directly targeting ZEB2 in gastric carcinoma. Ann Surg
Oncol. 19(Suppl 3): S656–S664. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhang Z, Liu S, Shi R and Zhao G: miR-27
promotes human gastric cancer cell metastasis by inducing
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Genet. 204:486–491.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|