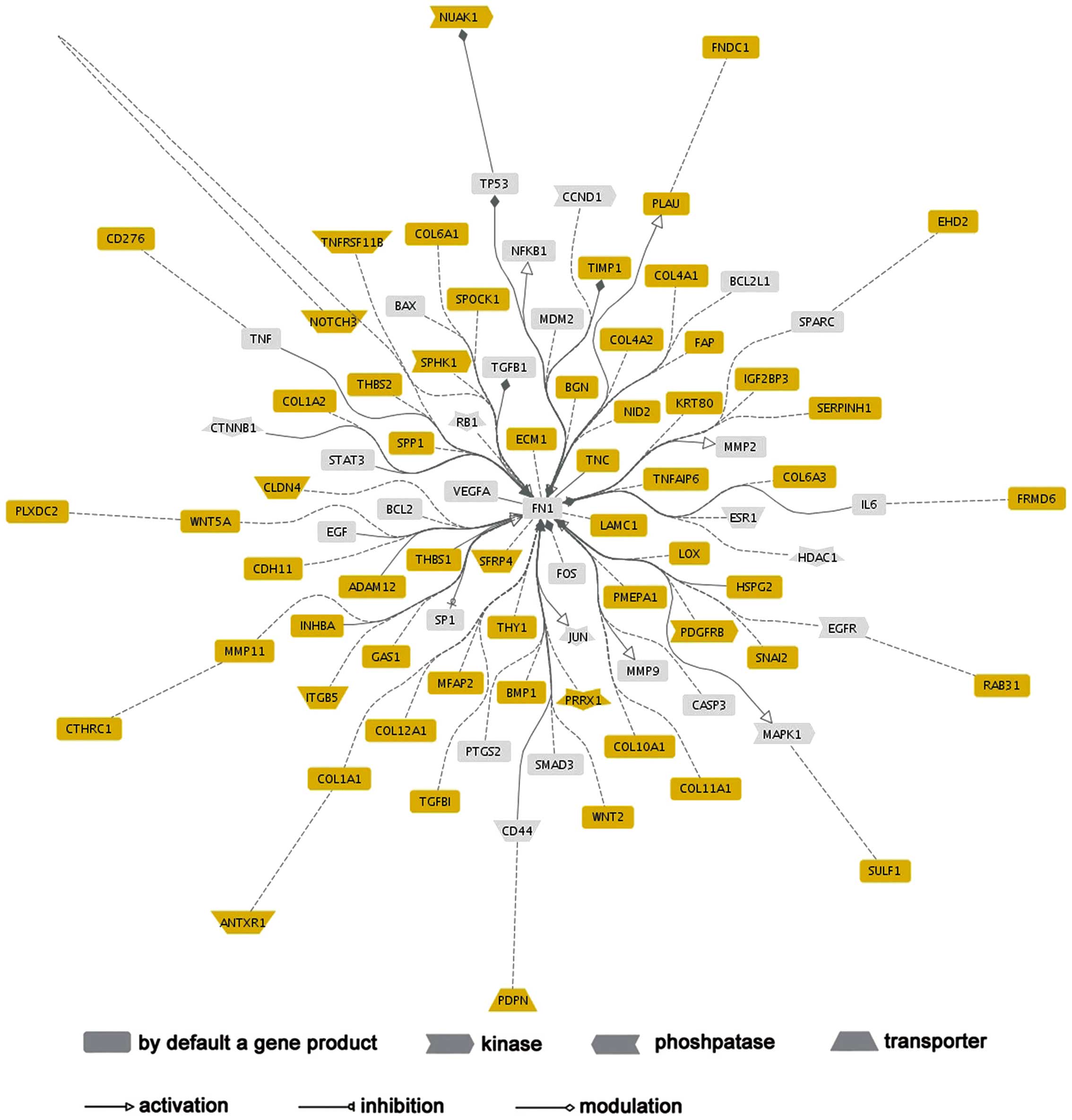
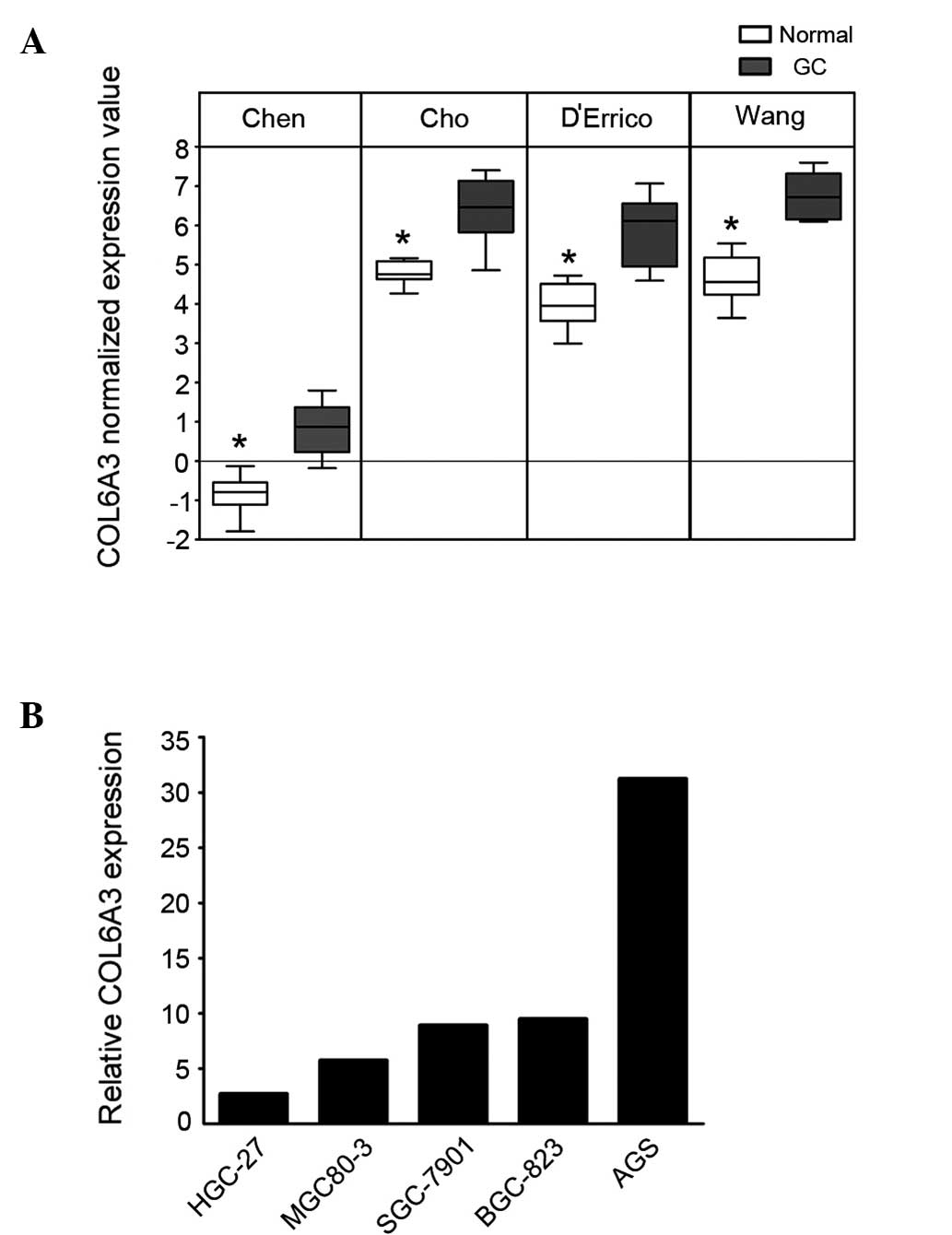
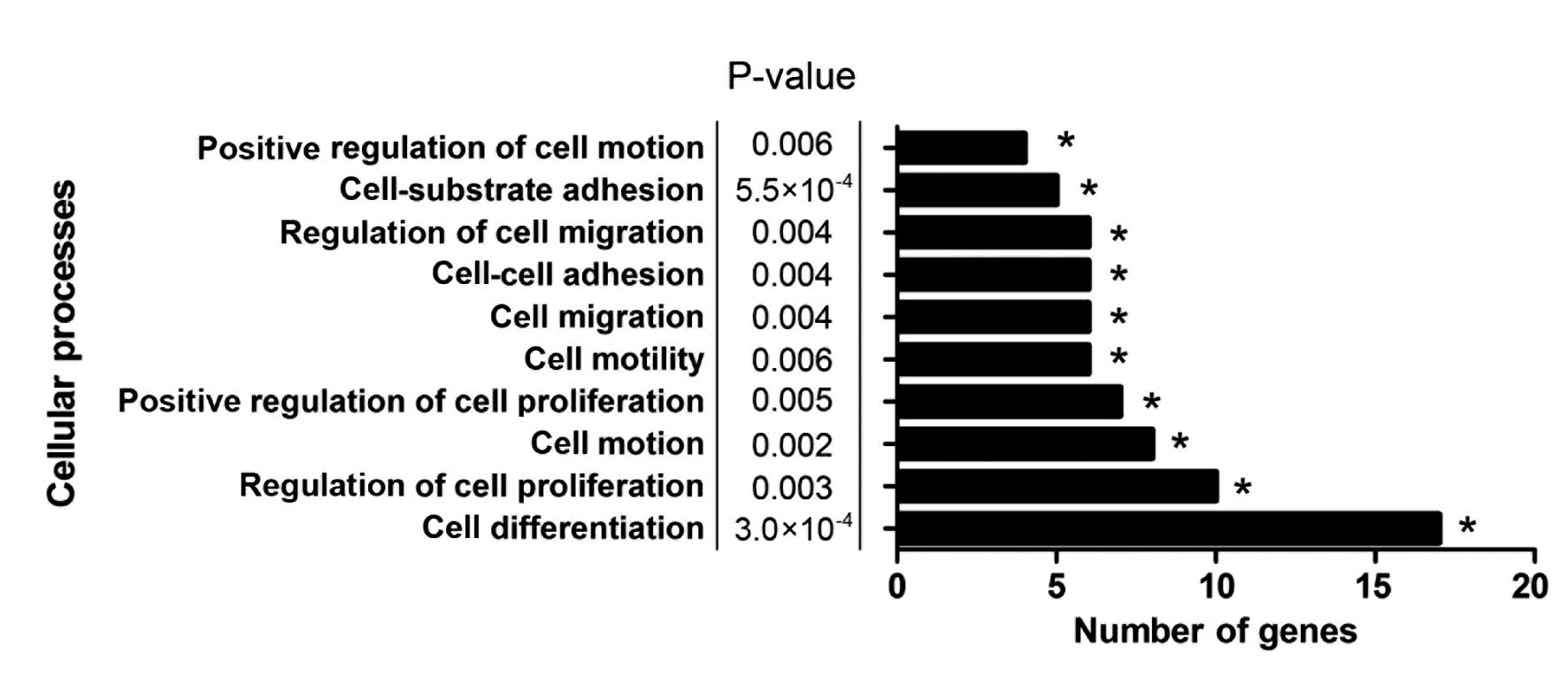
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bönnemann CG: The collagen VI-related
myopathies: muscle meets its matrix. Nat Rev Neurol. 7:379–390.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Iyengar P, Espina V, Williams TW, et al:
Adipocyte-derived collagen VI affects early mammary tumor
progression in vivo, demonstrating a critical interaction in the
tumor/stroma microenvironment. J Clin Invest. 115:1163–1176. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Schäffler A, Schölmerich J and Buechler C:
Mechanisms of disease: adipokines and breast cancer - endocrine and
paracrine mechanisms that connect adiposity and breast cancer. Nat
Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 3:345–354. 2007.
|
|
5
|
Sherman-Baust CA, Weeraratna AT, Rangel
LB, et al: Remodeling of the extracellular matrix through
overexpression of collagen VI contributes to cisplatin resistance
in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Cell. 3:377–386. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Aumailley M, Mann K, von der Mark H and
Timpl R: Cell attachment properties of collagen type VI and
Arg-Gly-Asp dependent binding to its alpha 2(VI) and alpha 3(VI)
chains. Exp Cell Res. 181:463–474. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ismail RS, Baldwin RL, Fang J, Browning D,
Karlan BY, Gasson JC and Chang DD: Differential gene expression
between normal and tumor-derived ovarian epithelial cells. Cancer
Res. 60:6744–6749. 2000.
|
|
8
|
Thorsen K, Sørensen KD, Brems-Eskildsen
AS, et al: Alternative splicing in colon, bladder, and prostate
cancer identified by exon array analysis. Mol Cell Proteomics.
7:1214–1224. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K, et al:
Large-scale meta-analysis of cancer microarray data identifies
common transcriptional profiles of neoplastic transformation and
progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:9309–9314. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Xing C, Zhou W, Ding S, et al: Reversing
effect of ring finger protein 43 inhibition on malignant phenotypes
of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:94–103.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chen X, Leung SY, Yuen ST, et al:
Variation in gene expression patterns in human gastric cancers. Mol
Biol Cell. 14:3208–3215. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cho JY, Lim JY, Cheong JH, et al: Gene
expression signature-based prognostic risk score in gastric cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 17:1850–1857. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
D’Errico M, de Rinaldis E, Blasi MF, et
al: Genome-wide expression profile of sporadic gastric cancers with
microsatellite instability. Eur J Cancer. 45:461–469.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Q, Wen YG, Li DP, et al: Upregulated
INHBA expression is associated with poor survival in gastric
cancer. Med Oncol. 29:77–83. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fierro AC, Vandenbussche F, Engelen K, Van
de Peer Y and Marchal K: Meta analysis of gene expression data
within and across species. Curr Genomics. 9:525–534. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pfaff M, Aumailley M, Specks U, Knolle J,
Zerwes HG and Timpl R: Integrin and Arg-Gly-Asp dependence of cell
adhesion to the native and unfolded triple helix of collagen type
VI. Exp Cell Res. 206:167–176. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Burg MA, Tillet E, Timpl R and Stallcup
WB: Binding of the NG2 proteoglycan to type VI collagen and other
extracellular matrix molecules. J Biol Chem. 271:26110–26116. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Perris R, Kuo HJ, Glanville RW and
Bronner-Fraser M: Collagen type VI in neural crest development:
distribution in situ and interaction with cells in vitro. Dev Dyn.
198:135–149. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gardina PJ, Clark TA, Shimada B, et al:
Alternative splicing and differential gene expression in colon
cancer detected by a whole genome exon array. BMC Genomics.
7:3252006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Arafat H, Lazar M, Salem K, et al:
Tumor-specific expression and alternative splicing of the COL6A3
gene in pancreatic cancer. Surgery. 150:306–315. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Smith DD, Saetrom P, Snøve O Jr, Lundberg
C, Rivas GE, Glackin C and Larson GP: Meta-analysis of breast
cancer microarray studies in conjunction with conserved
cis-elements suggest patterns for coordinate regulation. BMC
Bioinformatics. 9:632008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Rybaczyk LA, Bashaw MJ, Pathak DR and
Huang K: An indicator of cancer: downregulation of monoamine
oxidase-A in multiple organs and species. BMC Genomics. 9:1342008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Verrecchia F, Chu ML and Mauviel A:
Identification of novel TGF-beta/Smad gene targets in dermal
fibroblasts using a combined cDNA microarray/promoter
transactivation approach. J Biol Chem. 276:17058–17062. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Torbenson M, Wang J, Choti M, Ashfaq R,
Maitra A, Wilentz RE and Boitnott J: Hepatocellular carcinomas show
abnormal expression of fibronectin protein. Mod Pathol. 15:826–830.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Warawdekar UM, Zingde SM, Iyer KS,
Jagannath P, Mehta AR and Mehta NG: Elevated levels and fragmented
nature of cellular fibronectin in the plasma of gastrointestinal
and head and neck cancer patients. Clin Chim Acta. 372:83–93. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Waalkes S, Atschekzei F, Kramer MW, et al:
Fibronectin 1 mRNA expression correlates with advanced disease in
renal cancer. BMC Cancer. 10:5032010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|