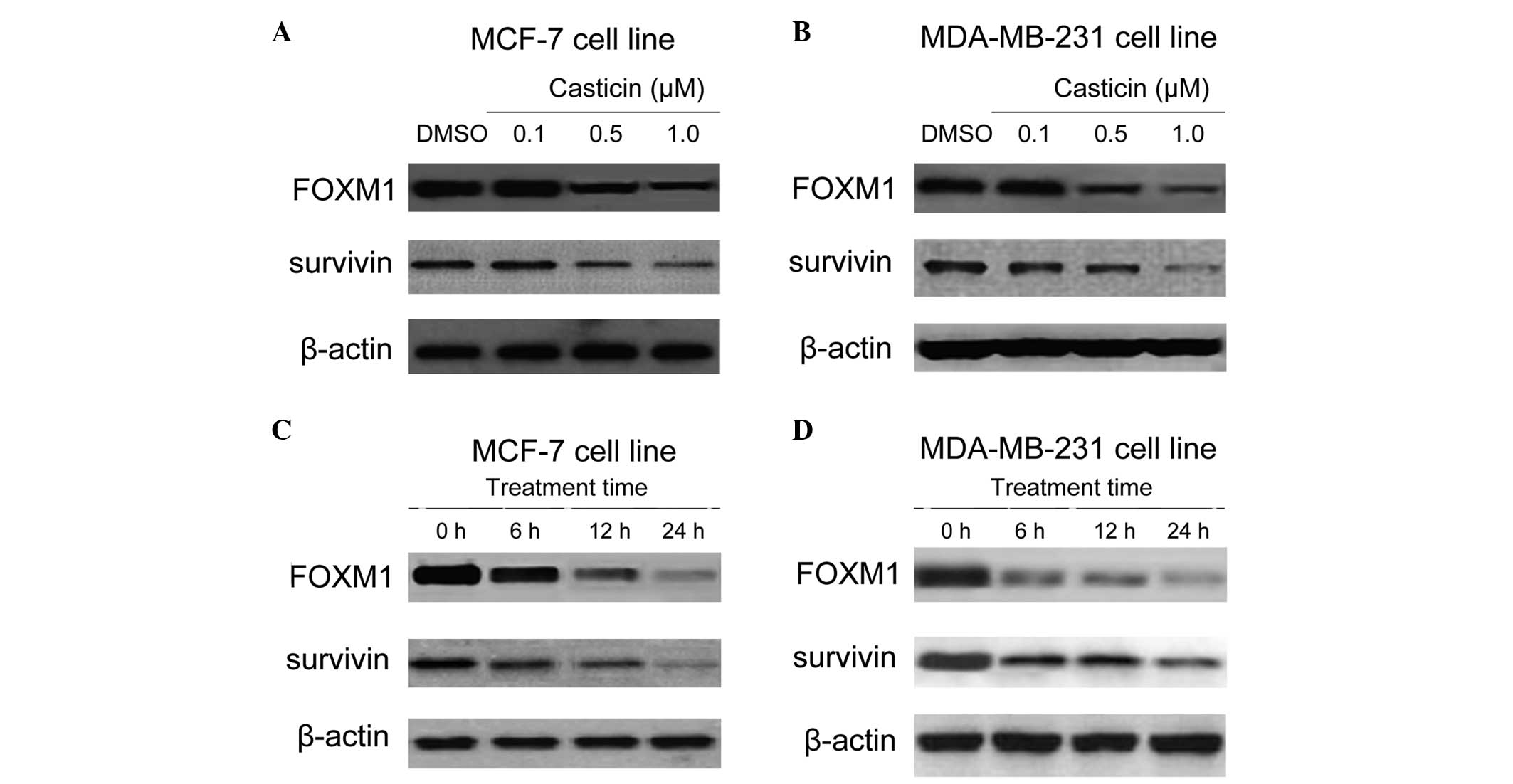
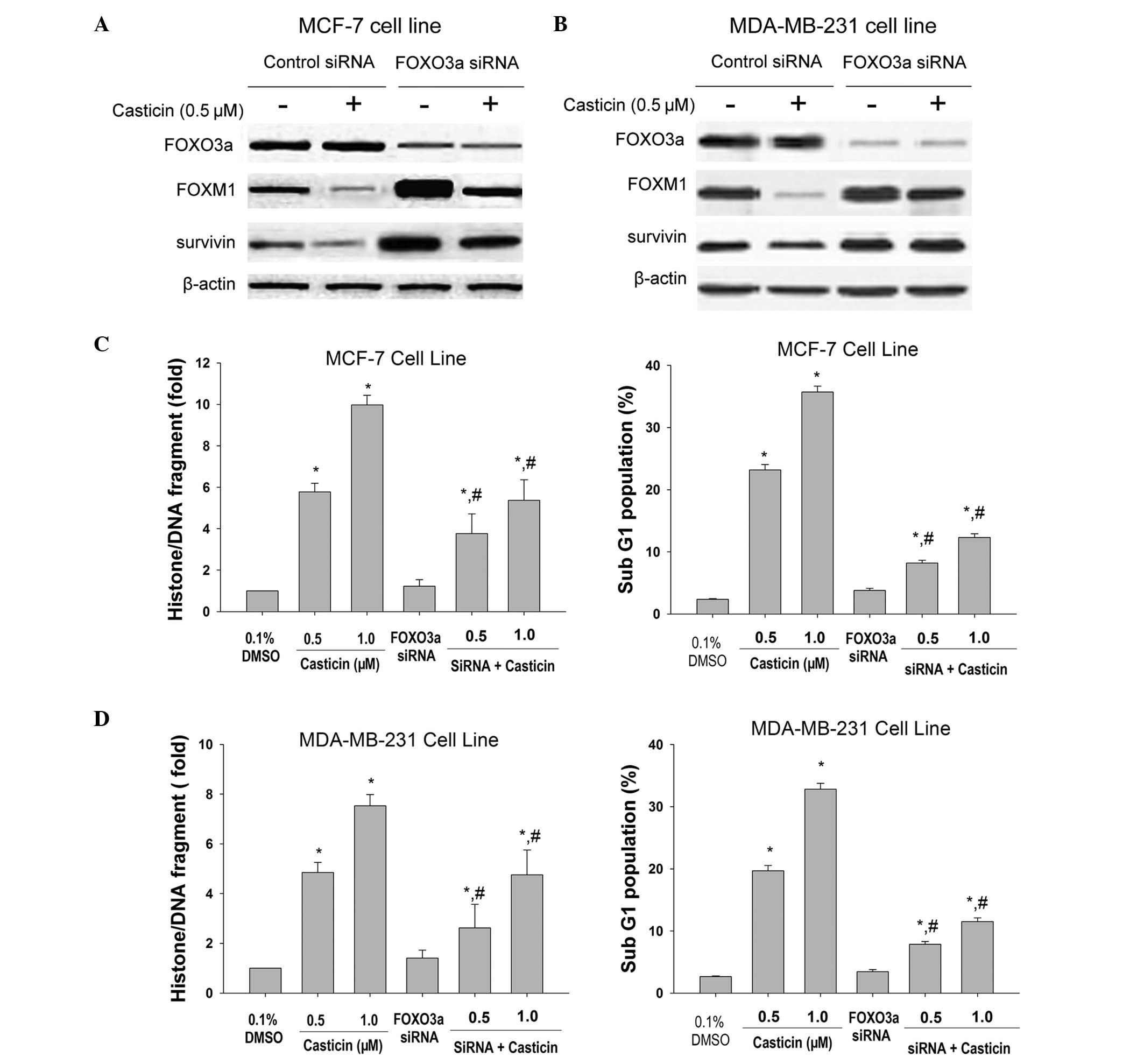
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al: Cancer
statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin. 56:106–130. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kelsey JL, Gammon MD and John EM:
Reproductive factors and breast cancer. Epidemiol Rev. 15:36–47.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hulka BS and Stark AT: Breast cancer:
cause and prevention. Lancet. 346:883–887. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kelsey JL and Bernstein L: Epidemiology
and prevention of breast cancer. Annu Rev Public Health. 17:47–67.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fisher B, Costantino JP, Wickerham DL, et
al: Tamoxifen for prevention of breast cancer: report of the
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project P-1 Study. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 90:1371–1388. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Cuzick J, Forbes J, Edwards R, et al:
First results from the International Breast Cancer Intervention
Study (IBIS-I): a randomised prevention trial. Lancet. 360:817–824.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Newman DJ, Cragg GM and Snader KM: Natural
products as sources of new drugs over the period 1981–2002. J Nat
Prod. 66:1022–1037. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zeng X, Fang Z, Wu Y and Zhang H: Chemical
constituents of the fruits of Vitex trifolia L. Zhongguo
Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 21:167–168. 1911996.(In Chinese).
|
|
9
|
Haïdara K, Zamir L, Shi QW and Batist G:
The flavonoid Casticin has multiple mechanisms of tumor
cytotoxicity action. Cancer Lett. 242:180–190. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Weisskopf M, Schaffner W, Jundt G, Sulser
T, Wyler S and Tullberg-Reinert H: A Vitex agnus-castus
extract inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in prostate
epithelial cell lines. Planta Med. 71:910–916. 2005.
|
|
11
|
Koh DJ, Ahn HS, Chung HS, et al:
Inhibitory effects of casticin on migration of eosinophil and
expression of chemokines and adhesion molecules in A549 lung
epithelial cells via NF-kappaB inactivation. J Ethnopharmacol.
136:399–405. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Imai M, Kikuchi H, Denda T, Ohyama K,
Hirobe C and Toyoda H: Cytotoxic effects of flavonoids against a
human colon cancer derived cell line, COLO 201: a potential natural
anti-cancer substance. Cancer Lett. 276:74–80. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Shen JK, Du HP, Yang M, Wang YG and Jin J:
Casticin induces leukemic cell death through apoptosis and mitotic
catastrophe. Ann Hematol. 88:743–752. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen D, Cao J, Tian L, Liu F and Sheng X:
Induction of apoptosis by casticin in cervical cancer cells through
reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial signaling pathways.
Oncol Rep. 26:1287–1294. 2011.
|
|
15
|
Zeng F, Tian L, Liu F, Cao J, Quan M and
Sheng X: Induction of apoptosis by casticin in cervical cancer
cells: reactive oxygen species-dependent sustained activation of
Jun N-terminal kinase. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
44:442–449. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yang J, Yang Y, Tian L, Sheng XF, Liu F
and Cao JG: Casticin-induced apoptosis involves death receptor 5
upregulation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J
Gastroenterol. 17:4298–4307. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Myatt SS and Lam EW: The emerging roles of
forkhead box (Fox) proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:847–859.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kops GJ, Medema RH, Glassford J, et al:
Control of cell cycle exit and entry by protein kinase B-regulated
forkhead transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 22:2025–2036. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sunters A, Fernández de Mattos S, Stahl M,
et al: FoxO3a transcriptional regulation of Bim controls apoptosis
in paclitaxel-treated breast cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem.
278:49795–49805. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Krol J, Francis RE, Albergaria A, et al:
The transcription factor FOXO3a is a crucial cellular target of
gefitinib (Iressa) in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
6:3169–3179. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Essafi A, Fernández de Mattos S, Hassen
YA, et al: Direct transcriptional regulation of Bim by FoxO3a
mediates STI571-induced apoptosis in Bcr-Abl-expressing cells.
Oncogene. 24:2317–2329. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang XH, Zheng X, Cao JG, Xiang HL, Liu F
and Lv Y: 8-Bromo-7-methoxychrysin-induced apoptosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells involves ROS and JNK. World J
Gastroenterol. 16:3385–3393. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hollestelle A, Elstrodt F, Nagel JH,
Kallemeijn WW and Schutte M: Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase or
RAS pathway mutations in human breast cancer cell lines. Mol Cancer
Res. 5:195–201. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang Z, Ahmad A, Li Y, Banerjee S, Kong D
and Sarkar FH: Forkhead box M1 transcription factor: a novel target
for cancer therapy. Cancer Treat Rev. 36:151–156. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Z, Banerjee S, Kong D, Li Y and
Sarkar FH: Down-regulation of Forkhead Box M1 transcription factor
leads to the inhibition of invasion and angiogenesis of pancreatic
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 67:8293–8300. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li Y, Wang Z, Kong D, Li R, Sarkar SH and
Sarkar FH: Regulation of Akt/FOXO3a/GSK-3beta/AR signaling network
by isoflavone in prostate cancer cells. J Biol Chem.
283:27707–27716. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen Q, Ganapathy S, Singh KP, Shankar S
and Srivastava RK: Resveratrol induces growth arrest and apoptosis
through activation of FOXO transcription factors in prostate cancer
cells. PloS One. 5:e152882010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Roy SK, Chen Q, Fu J, Shankar S and
Srivastava RK: Resveratrol inhibits growth of orthotopic pancreatic
tumors through activation of FOXO transcription factors. PloS One.
6:e251662011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kalinichenko VV, Major ML, Wang X, et al:
Foxm1b transcription factor is essential for development of
hepatocellular carcinomas and is negatively regulated by the p19ARF
tumor suppressor. Genes Dev. 18:830–850. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zanella F, Link W and Carnero A:
Understanding FOXO, new views on old transcription factors. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 10:135–146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun Y, Zhao S, Tian H, et al: Depletion of
PI3K p85alpha induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in colorectal
cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 22:1435–1441. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Barreyro FJ, Kobayashi S, Bronk SF,
Werneburg NW, Malhi H and Gores GJ: Transcriptional regulation of
Bim by FoxO3A mediates hepatocyte lipoapoptosis. J Biol Chem.
282:27141–27154. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lynch RL, Konicek BW, McNulty AM, et al:
The progression of LNCaP human prostate cancer cells to androgen
independence involves decreased FOXO3a expression and reduced
p27KIP1 promoter transactivation. Mol Cancer Res. 3:163–169. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Davis R, Singh KP, Kurzrock R and Shankar
S: Sulforaphane inhibits angiogenesis through activation of FOXO
transcription factors. Oncol Rep. 22:1473–1478. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shankar S, Chen Q and Srivastava RK:
Inhibition of PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK pathways act synergistically to
enhance antiangiogenic effects of EGCG through activation of FOXO
transcription factor. J Mol Signal. 3:72008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhao X, Ogunwobi OO and Liu C: Survivin
inhibition is critical for Bcl-2 inhibitor-induced apoptosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PloS One. 6:e219802011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Huang H and Tindall DJ: Dynamic FoxO
transcription factors. J Cell Sci. 120:2479–2487. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|