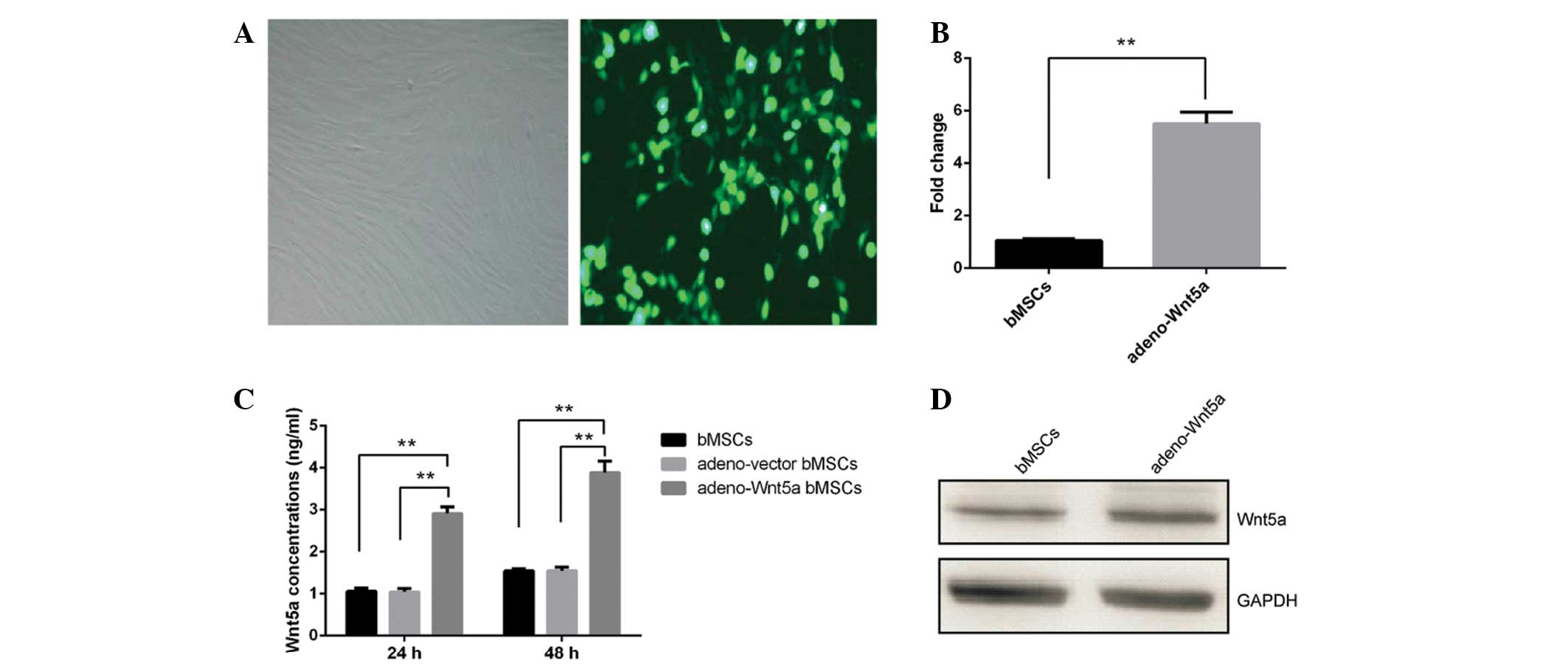
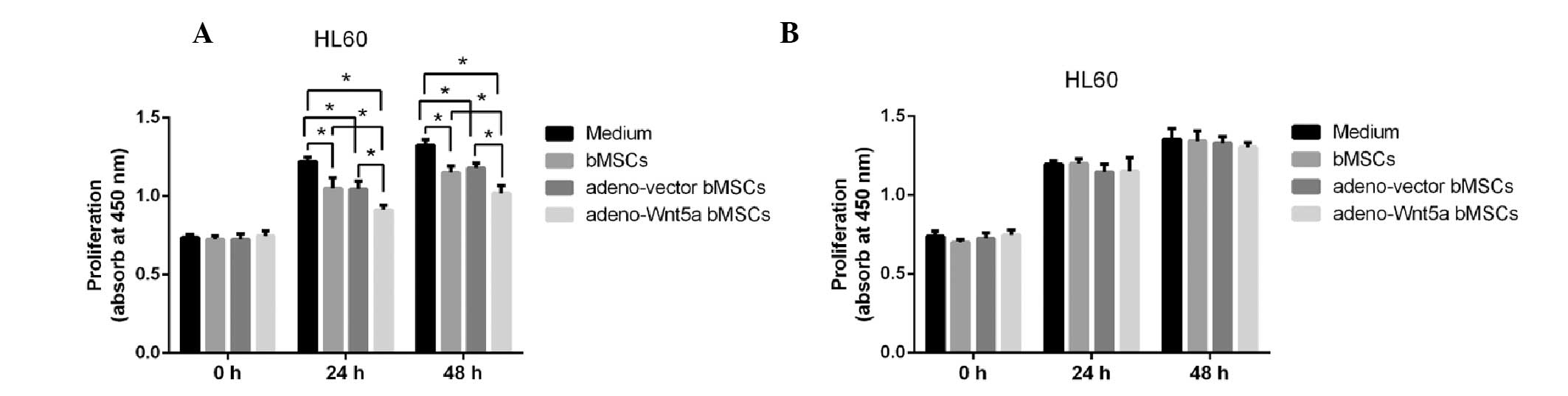
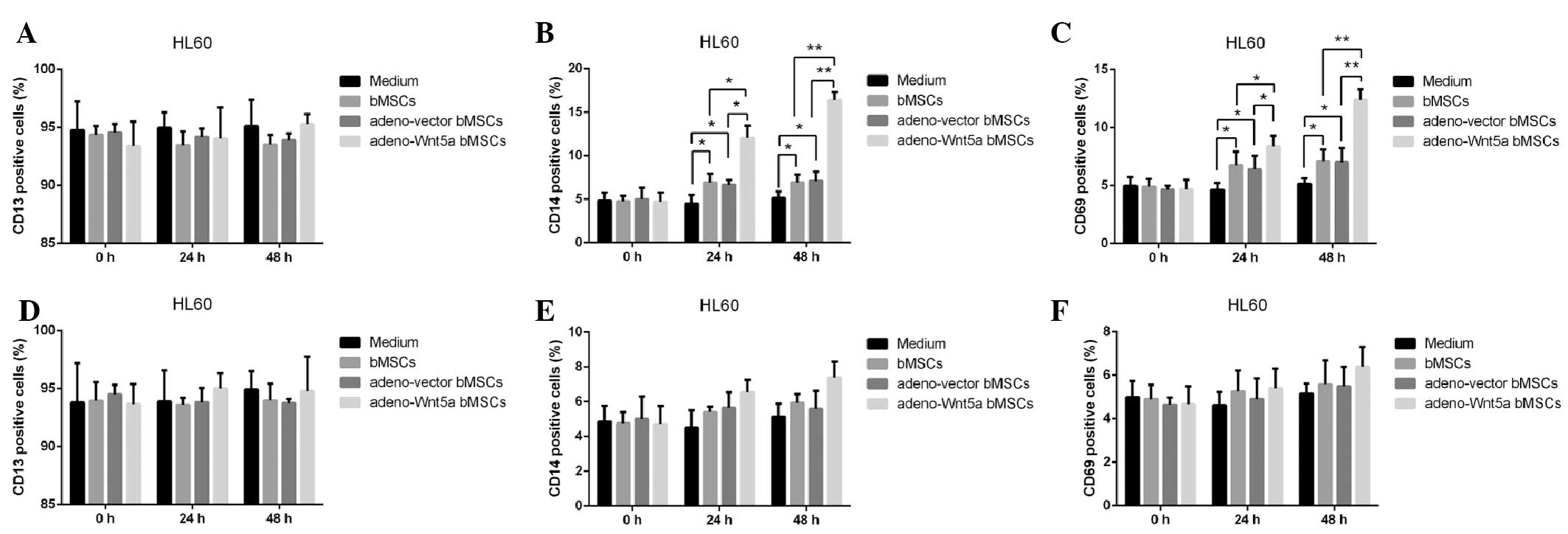
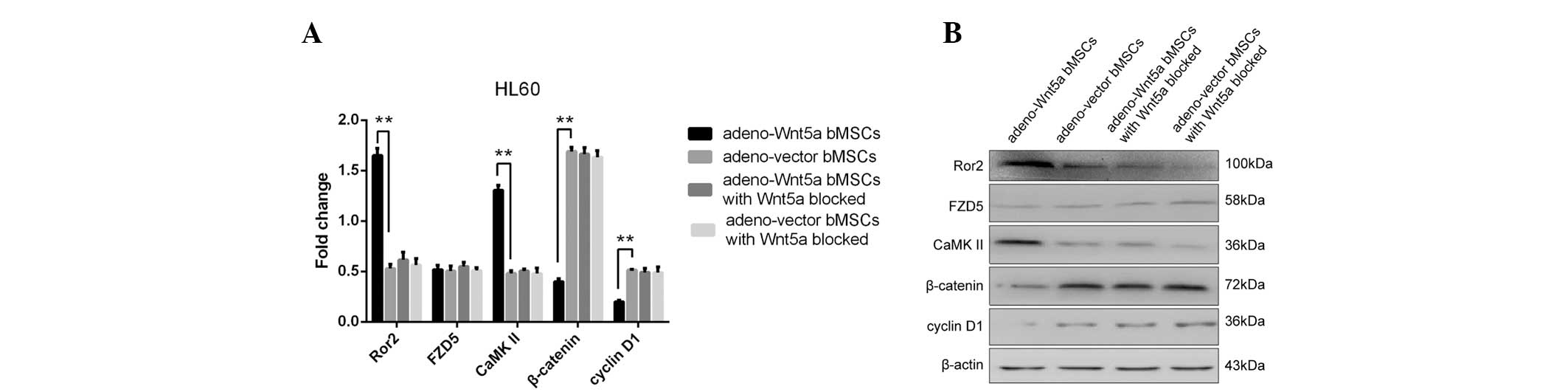
|
1
|
Gilliland DG, Jordan CT and Felix CA: The
molecular basis of leukemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ
Program. 1:80–97. 2004.
|
|
2
|
Arai KI, Lee F, Miyajima A, Miyatake S,
Arai N and Yokota T: Cytokines: coordinators of immune and
inflammatory responses. Annu Rev Biochem. 59:783–836. 1990.
|
|
3
|
Ploemacher RE, Mayen AE, De Koning AE, et
al: Hematopoiesis: gap junction intercellular communication is
likely to be involved in regulation of stroma-dependent
proliferation of hemopoietic stem cells. Hematology. 5:133–147.
2000.
|
|
4
|
Reya T and Clevers H: Wnt signalling in
stem cells and cancer. Nature. 434:843–850. 2005.
|
|
5
|
Taketo MM: Shutting down Wnt
signal-activated cancer. Nat Genet. 36:320–322. 2004.
|
|
6
|
McDonald SL and Silver A: The opposing
roles of Wnt-5a in cancer. Br J Cancer. 101:209–214. 2009.
|
|
7
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012.
|
|
8
|
Kikuchi A, Yamamoto H, Sato A and
Matsumoto S: Wnt5a: its signalling, functions and implication in
diseases. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 204:17–33. 2012.
|
|
9
|
Shen YL, Xu YH, Luo Q, Guo ZH, Zheng GH
and Guo YX: Growth and differentiation effect on HL60 cells by
adenovirus-mediated exogenous wnt5a gene modification on human bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.
41:931–935. 2010.
|
|
10
|
Liang H, Chen Q, Coles AH, et al: Wnt5a
inhibits B cell proliferation and functions as a tumor suppressor
in hematopoietic tissue. Cancer Cell. 4:349–360. 2003.
|
|
11
|
Shrivastava A, Radziejewski C, Campbell E,
et al: An orphan receptor tyrosine kinase family whose members
serve as nonintegrin collagen receptors. Mol Cell. 1:25–34.
1997.
|
|
12
|
Pan Z, Sun X, Shan H, et al: MicroRNA-101
inhibited postinfarct cardiac fibrosis and improved left
ventricular compliance via the FBJ osteosarcoma
oncogene/transforming growth factor-beta1 pathway. Circulation.
126:840–850. 2012.
|
|
13
|
Luo J, Deng ZL, Luo X, et al: A protocol
for rapid generation of recombinant adenoviruses using the AdEasy
system. Nat Protoc. 2:1236–1247. 2007.
|
|
14
|
van Amerongen R, Fuerer C, Mizutani M and
Nusse R: Wnt5a can both activate and repress Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling during mouse embryonic development. Dev Biol.
369:101–114. 2012.
|
|
15
|
Nemeth MJ, Topol L, Anderson SM, Yang Y
and Bodine DM: Wnt5a inhibits canonical Wnt signaling in
hematopoietic stem cells and enhances repopulation. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 104:15436–15441. 2007.
|
|
16
|
Cheng CW, Yeh JC, Fan TP, Smith SK and
Charnock-Jones DS: Wnt5a-mediated non-canonical Wnt signalling
regulates human endothelial cell proliferation and migration.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 365:285–290. 2008.
|
|
17
|
Koehler A, Schlupf J, Schneider M, Kraft
B, Winter C and Kashef J: Loss of Xenopus cadherin-11 leads to
increased Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and up-regulation of target
genes c-myc and cyclin D1 in neural crest. Dev Biol. 383:132–145.
2013.
|
|
18
|
Kühl M and Pandur P: Measuring CamKII
activity in Xenopus embryos as a read-out for non-canonical Wnt
signaling. Methods Mol Biol. 468:173–86. 2008.
|
|
19
|
Xin H, Xin F, Zhou S and Guan S: The
Wnt5a/Ror2 pathway is associated with determination of the
differentiation fate of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in
vascular calcification. Int J Mol Med. 31:583–588. 2013.
|
|
20
|
Baksh D and Tuan RS: Canonical and
non-canonical Wnts differentially affect the development potential
of primary isolate of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J
Cell Physiol. 212:817–826. 2007.
|
|
21
|
de Barros AP, Takiya CM, Garzoni LR, et
al: Osteoblasts and bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells control
hematopoietic stem cell migration and proliferation in 3D in vitro
model. PLoS One. 5:e90932010.
|
|
22
|
Takada R, Hijikata H, Kondoh H and Takada
S: Analysis of combinatorial effects of Wnts and Frizzleds on
beta-catenin/armadillo stabilization and Dishevelled
phosphorylation. Genes Cells. 10:919–928. 2005.
|
|
23
|
Cong F, Schweizer L and Varmus H: Wnt
signals across the plasma membrane to activate the beta-catenin
pathway by forming oligomers containing its receptors, frizzled and
LRP. Development. 131:5103–5115. 2004.
|
|
24
|
Yamamoto H, Sakane H, Yamamoto H, Michiue
T and Kikuchi A: Wnt3a and Dkk1 regulate distinct internalization
pathways of LRP6 to tune the activation of beta-catenin signaling.
Dev Cell. 15:37–48. 2008.
|
|
25
|
Torres MA, Yang-Snyder JA, Purcell SM,
DeMarais AA, McGrew LL and Moon RT: Activities of the Wnt-1 class
of secreted signaling factors are antagonized by the Wnt-5A class
and by a dominant negative cadherin in early Xenopus development. J
Cell Biol. 133:1123–1137. 1996.
|
|
26
|
Umbhauer M, Djiane A, Goisset C, et al:
The C-terminal cytoplasmic Lys-thr-X-X-X-Trp motif in frizzled
receptors mediates Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. EMBO J.
19:4944–4954. 2000.
|