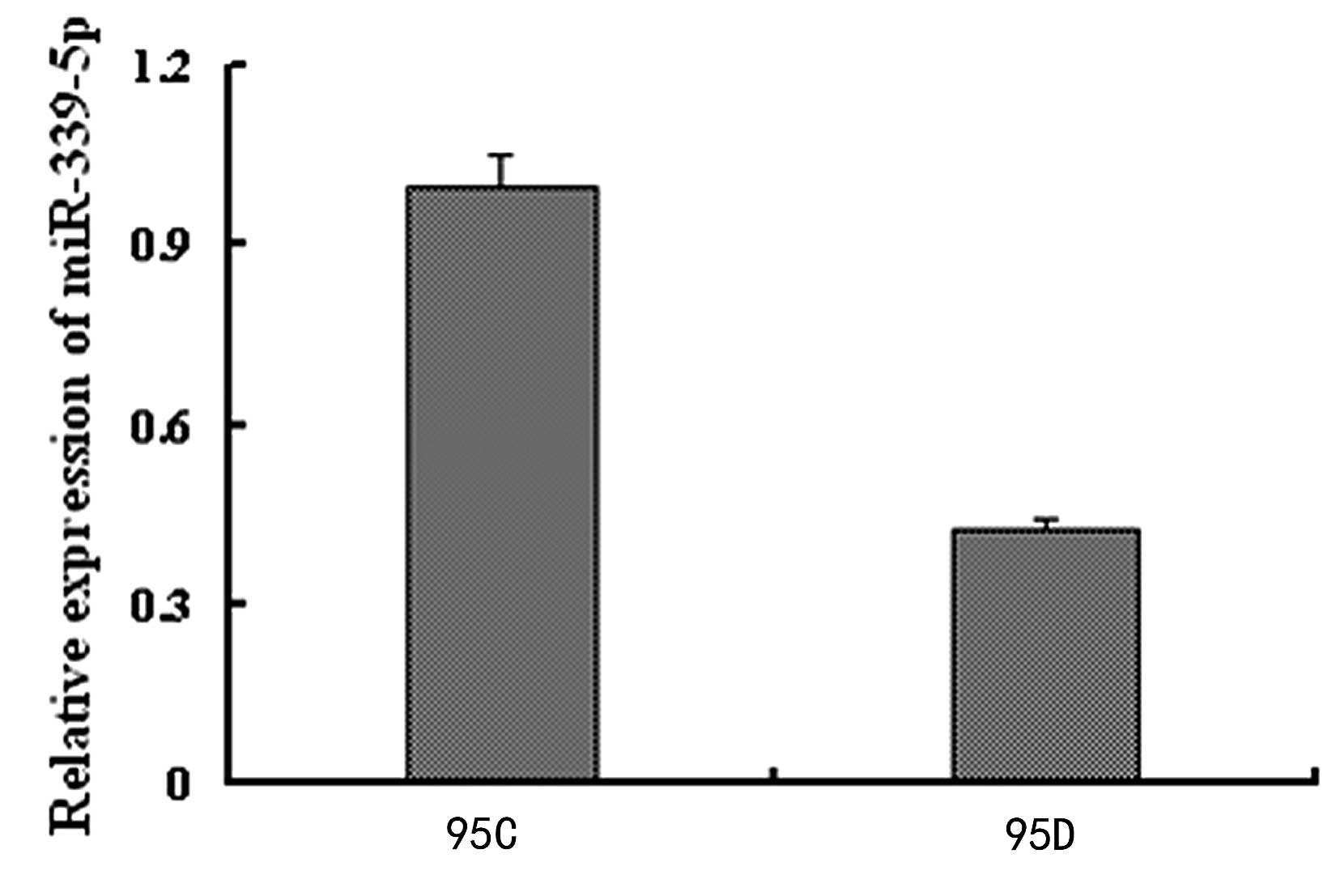
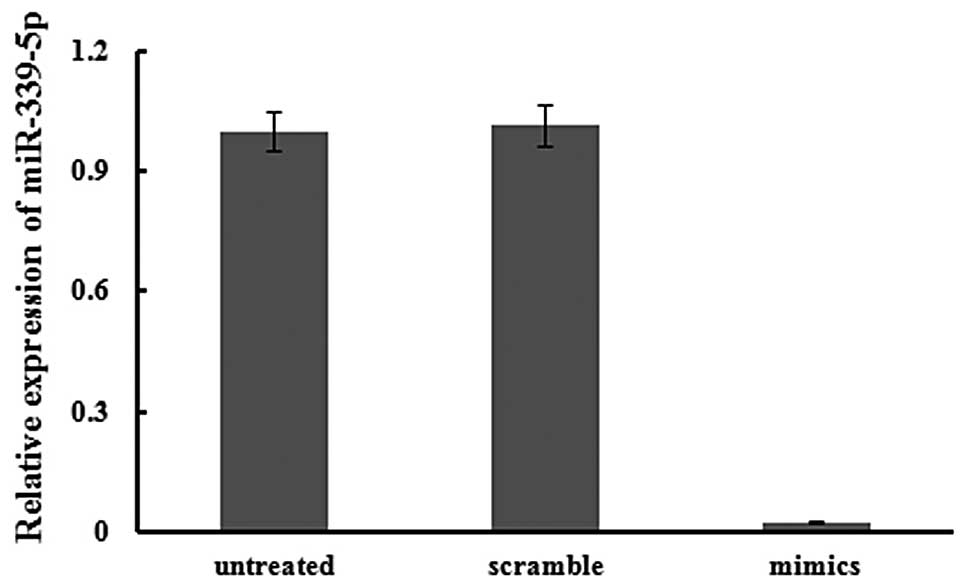
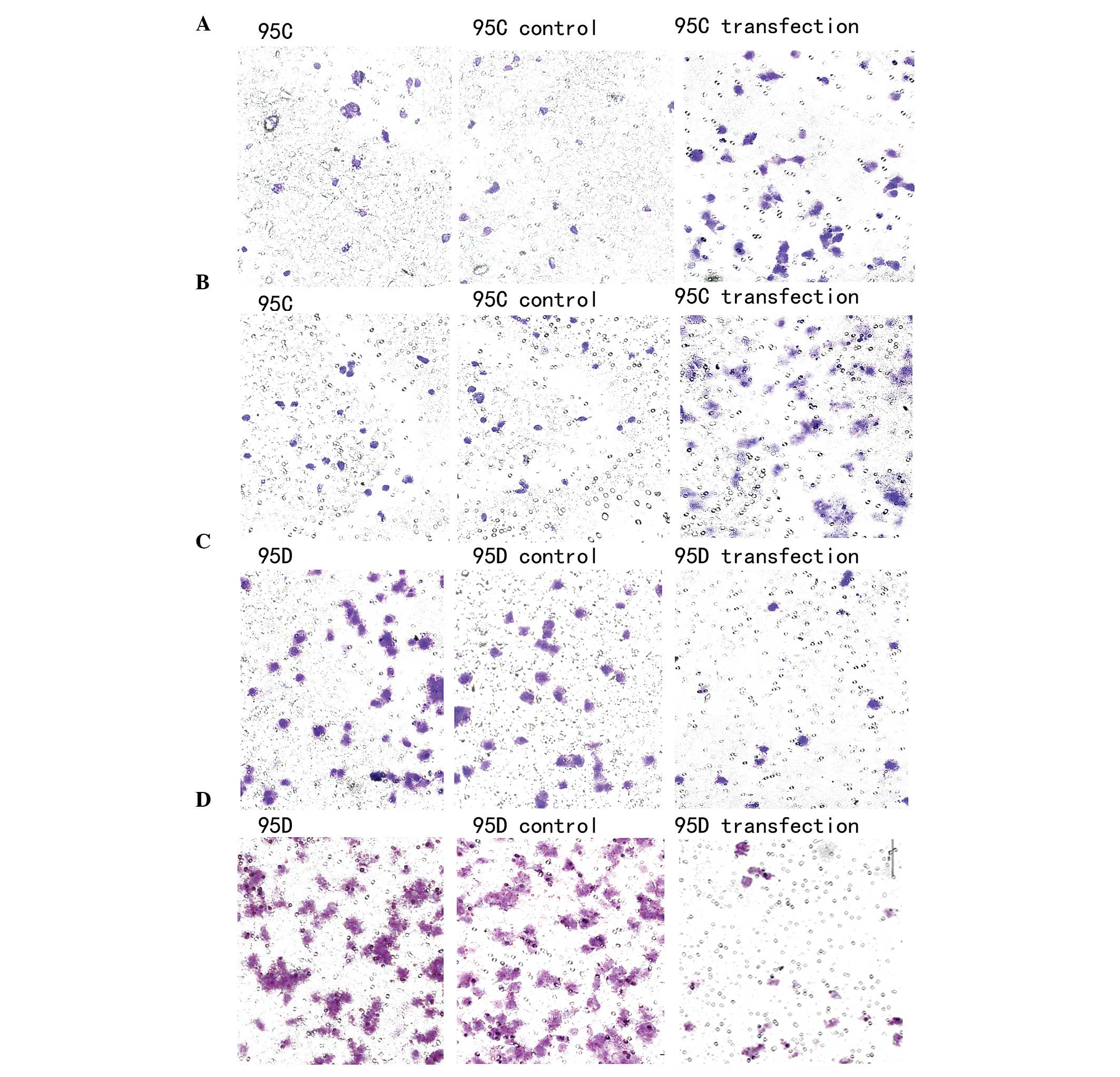
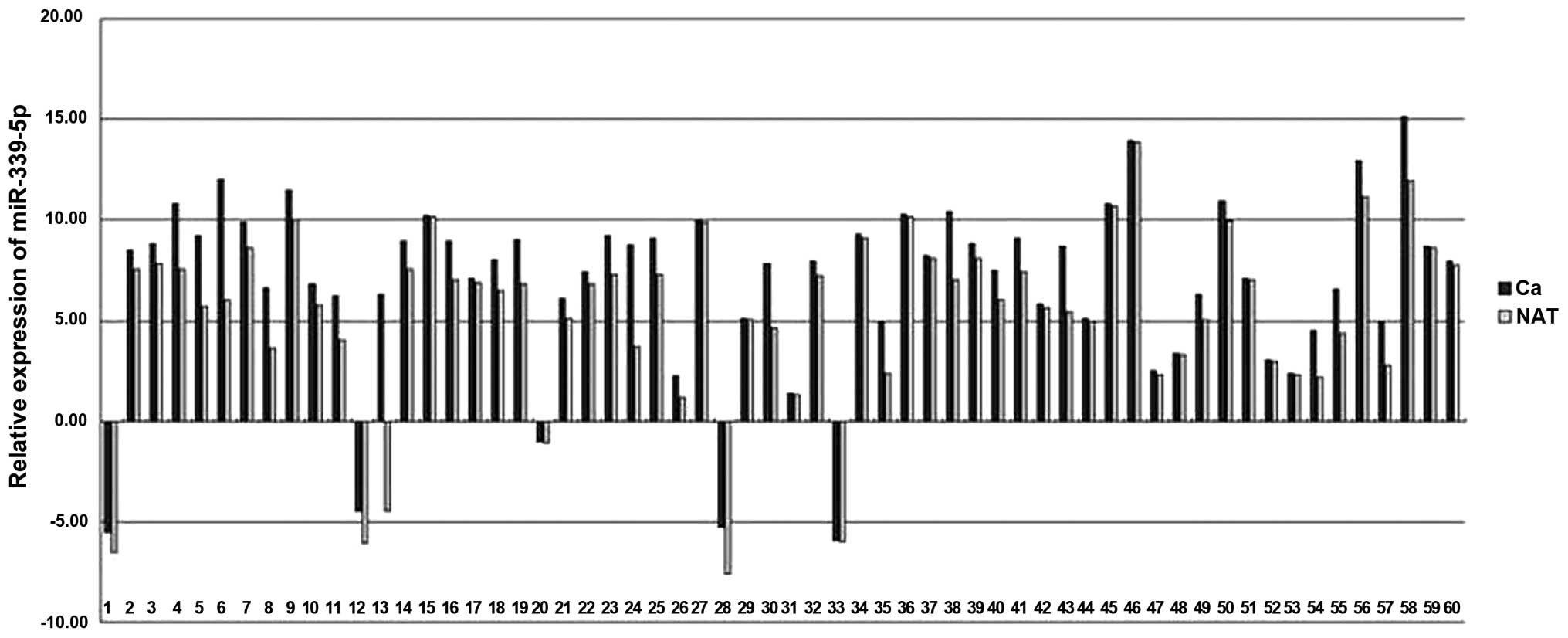
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012.
|
|
2
|
Lee Y, Ahn C, Han J, et al: The nuclear
RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature.
425:415–419. 2003.
|
|
3
|
Lund E, Güttinger S, Calado A, et al:
Nuclear export of microRNA precursors. Science. 303:95–98.
2004.
|
|
4
|
Lee Y, Jeon K, Lee JT, et al: MicroRNA
maturation: stepwise processing and subcellular localization. EMBO
J. 21:4663–4670. 2002.
|
|
5
|
Rana TM: Illuminating the silence:
understanding the structure and function of small RNAs. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 8:23–36. 2007.
|
|
6
|
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, et al:
Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and
prognosis. Cancer Cell. 9:189–198. 2006.
|
|
7
|
Gibbons DL, Lin W, Creighton CJ, et al:
Contextual extracellular cues promote tumor cell EMT and metastasis
by regulating miR-200 family expression. Genes Dev. 23:2140–2151.
2009.
|
|
8
|
Ceppi P, Mudduluru G, Kumarswamy R, et al:
Loss of miR-200c expression induces an aggressive, invasive, and
chemoresistant phenotype in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer
Res. 8:1207–1216. 2010.
|
|
9
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
CH; International Union Against Cancer. TNM Classification of
Malignant Tumours. 7th edition. WileyBlackwell; New York, NY:
2010
|
|
10
|
Wu ZS, Wu Q, Wang CQ, et al: MiR-339-5p
inhibits breast cancer cell migration and invasion in vitro and may
be a potential biomarker for breast cancer prognosis. BMC Cancer.
10:5422010.
|
|
11
|
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J and Weinberg RA:
Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast
cancer. Nature. 449:682–688. 2007.
|
|
12
|
Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A,
et al: Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional
target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem.
283:1026–1033. 2008.
|
|
13
|
Edmonds MD, Hurst DR, Vaidya KS, et al:
Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 coordinately regulates
metastasis-associated microRNA expression. Int J Cancer.
125:1778–1785. 2009.
|
|
14
|
Dews M, Homayouni A, Yu D, et al:
Augmentation of tumor angiogenesis by a Myc-activated microRNA
cluster. Nat Genet. 38:1060–1065. 2006.
|
|
15
|
Foekens JA, Sieuwerts AM, Smid M, et al:
Four miRNAs associated with aggressiveness of lymph node-negative,
estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:13021–13026. 2008.
|
|
16
|
Song G, Zhang Y and Wang L: MicroRNA-206
targets notch3, activates apoptosis, and inhibits tumor cell
migration and focus formation. J Biol Chem. 284:31921–31927.
2009.
|
|
17
|
Yu F, Yao H, Zhu P, et al: let-7 regulates
self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. Cell.
131:1109–1123. 2007.
|
|
18
|
Xiao F, Zuo Z, Cai G, et al: miRecords: an
integrated resource for microRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids
Res. 37(Database issue): D105–D110. 2009.
|
|
19
|
Krek A, Grün D, Poy MN, et al:
Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet. 37:495–500.
2005.
|
|
20
|
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, et al: Human
microRNA targets. PLoS Biol. 2:e3632004.
|
|
21
|
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW, et
al: Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell. 115:787–798.
2003.
|
|
22
|
Phan RT, Saito M, Basso K, et al: BCL6
interacts with the transcription factor Miz-1 to suppress the
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 and cell cycle arrest in
germinal center B cells. Nat Immunol. 6:1054–1060. 2005.
|
|
23
|
Polo JM, Dell’Oso T, Ranuncolo SM, et al:
Specific peptide interference reveals BCL6 transcriptional and
oncogenic mechanisms in B-cell lymphoma cells. Nat Med.
10:1329–1335. 2004.
|
|
24
|
Pinto AE, André S, Silva G, et al: BCL-6
oncoprotein in breast cancer: loss of expression in disease
progression. Pathobiology. 76:235–242. 2009.
|
|
25
|
Yamamoto S, Tomita Y, Hoshida Y, et al:
Expression level of valosin-containing protein (p97) is correlated
with progression and prognosis of non-small-cell lung carcinoma.
Ann Surg Oncol. 11:697–704. 2004.
|
|
26
|
Yi P, Higa A, Taouji S, et al:
Sorafenib-mediated targeting of the AAA+ ATPase p97/VCP
leads to disruption of the secretory pathway, endoplasmic reticulum
stress, and hepatocellular cancer cell death. Mol Cancer Ther.
11:2610–2620. 2012.
|
|
27
|
Yamamoto S, Tomita Y, Hoshida Y, et al:
Expression level of valosin-containing protein is strongly
associated with progression and prognosis of gastriccarcinoma. J
Clin Oncol. 21:2537–2544
|
|
28
|
Yamamoto S, Tomita Y, Hoshida Y, et al:
Expression of valosin-containing protein in colorectal carcinomas
as a predictor for disease recurrence and prognosis. Clin Cancer
Res. 10:651–657. 2004.
|