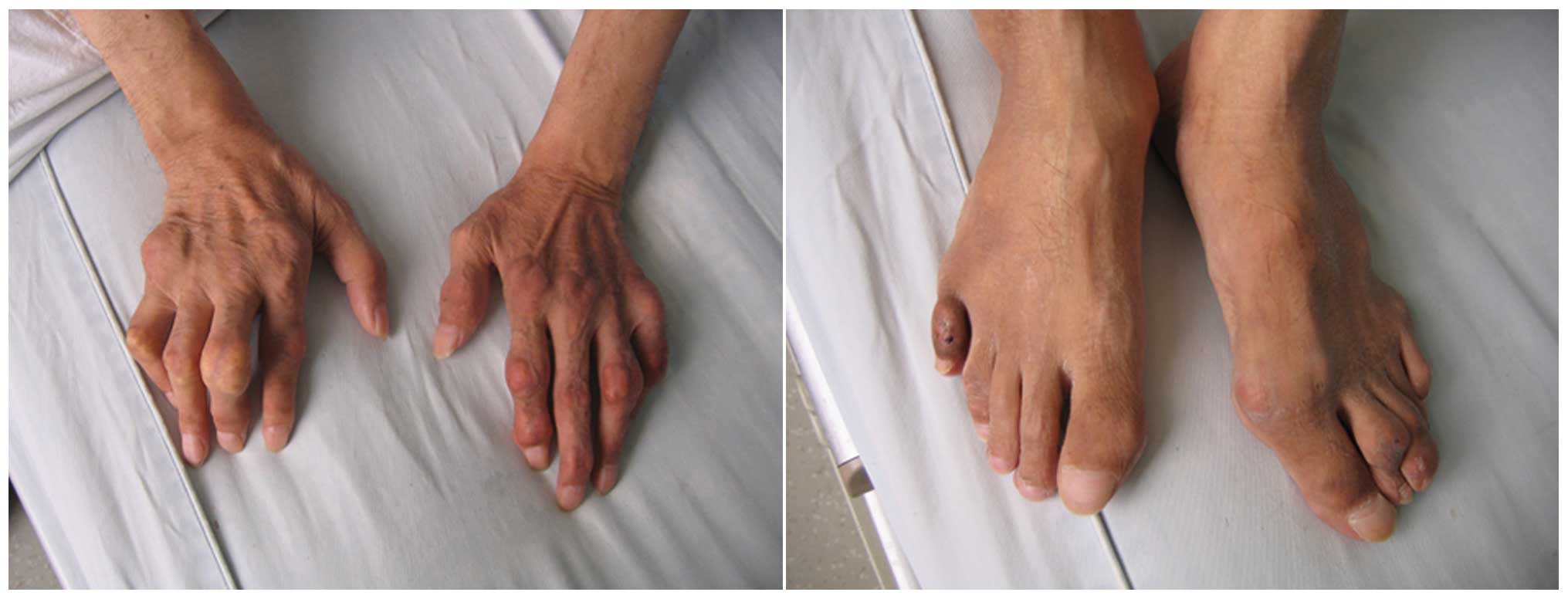
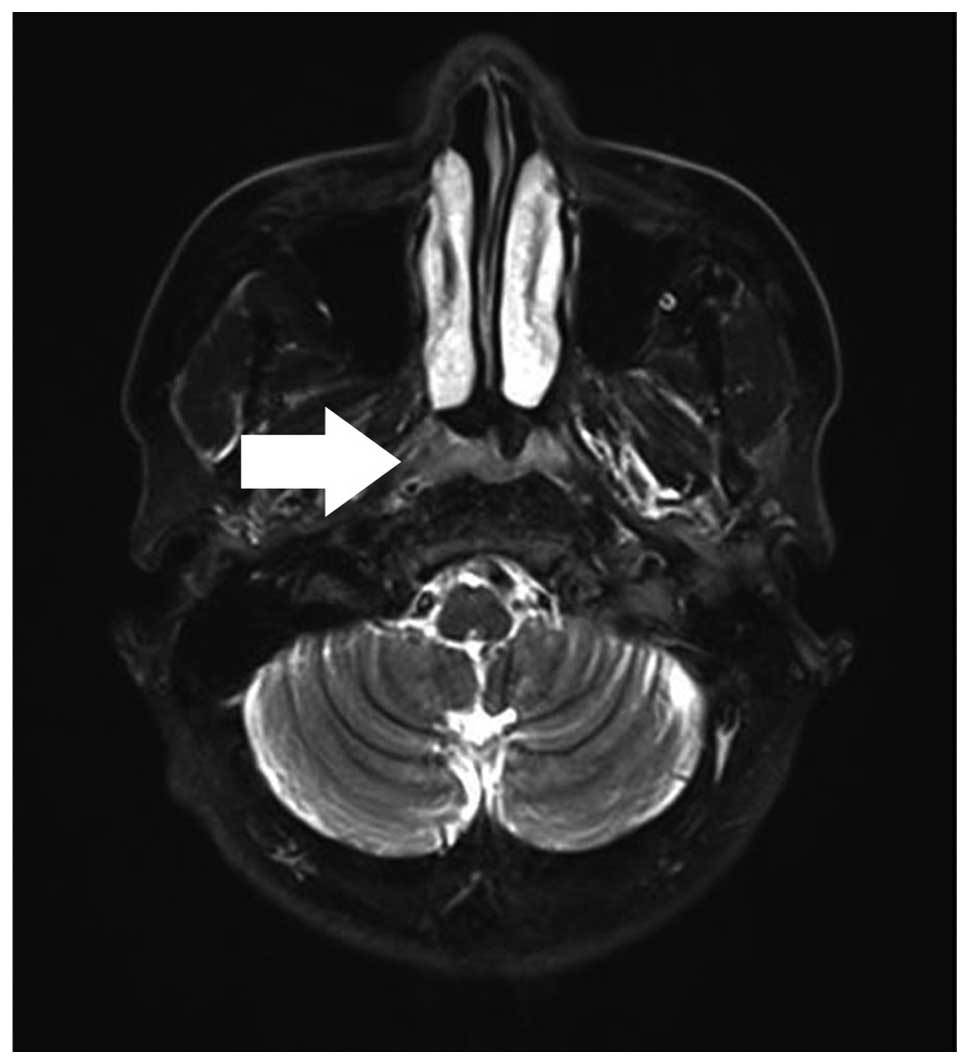
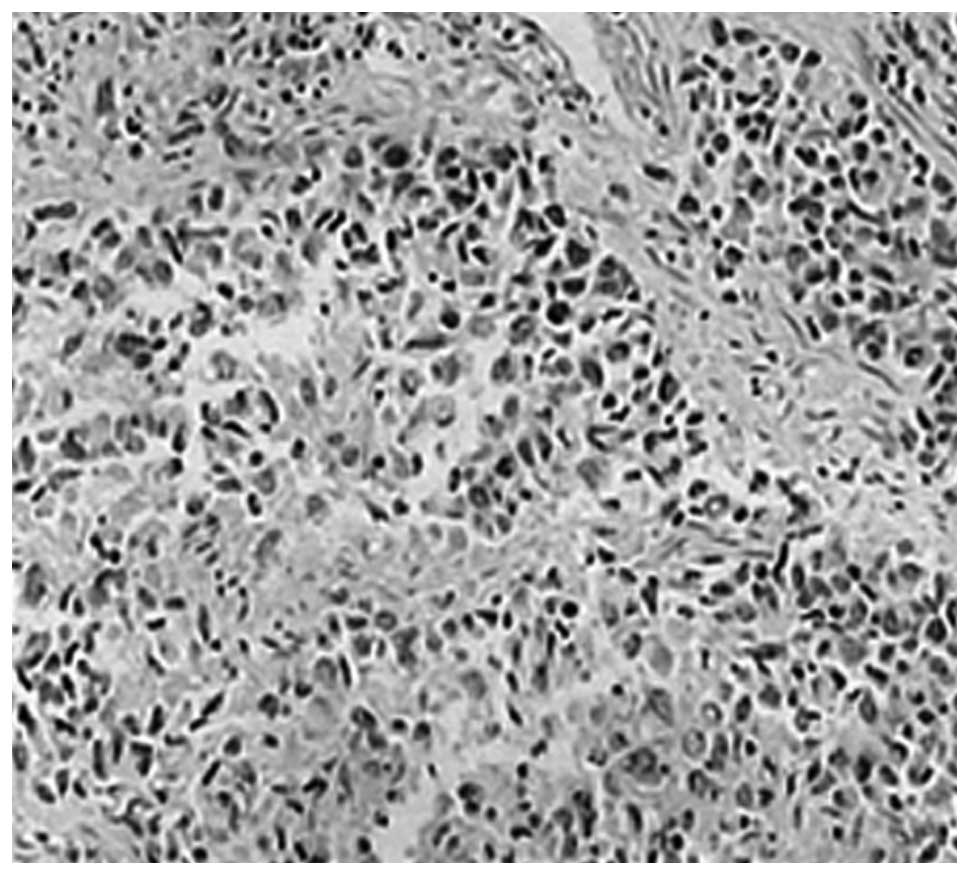
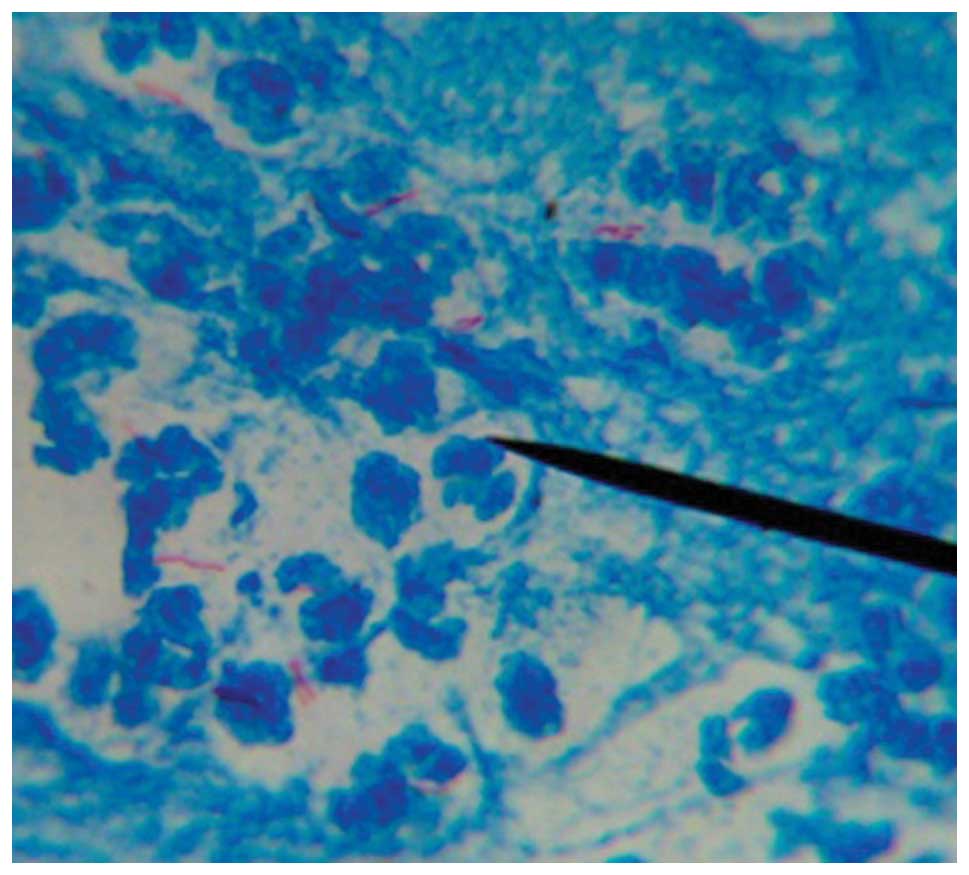
|
1
|
Trejaut J, Lee CL, Yen JC, Loo JH and Lin
M: Ancient migration routes of Austronesian-speaking populations in
oceanic Southeast Asia and Melanesia might mimic the spread of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chin J Cancer. 30:96–105. 2011.
|
|
2
|
Wee JT, Ha TC, Loong SL and Qian CN: Is
nasopharyngeal carcinoma really a ‘Cantonese Cancer’? Chin J
Cancer. 29:517–526. 2010.
|
|
3
|
He GX, van denHof S, van der Werf MJ, et
al: Infection control and the burden of tuberculosis infection and
disease in health care workers in china: a cross-sectional study.
BMC Infect Dis. 10:3132010.
|
|
4
|
Sun GM, Gao Q and Peng WX: Progress on
spatial epidemiology of tuberculosis. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za
Zhi. 31:1188–1191. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
5
|
Miao Z, Li C, Chen Y, et al: Dietary and
lifestyle changes associated with high prevalence of hyperuricemia
and gout in the Shandong coastal cities of Eastern China. J
Rheumatol. 35:1859–1864. 2008.
|
|
6
|
Li R, Sun J, Ren LM, et al: Epidemiology
of eight common rheumatic diseases in China: a large-scale
cross-sectional survey in Beijing. Rheumatology (Oxford).
51:721–729. 2012.
|
|
7
|
Al-Sarraf M, LeBlanc M, Giri PG, et al:
Chemoradiotherapy versus radiotherapy in patients with advanced
nasopharyngeal cancer: phase III randomized Intergroup study 0099.
J Clin Oncol. 16:1310–1317. 1998.
|
|
8
|
Komatsu M, Tsukuda M, Matsuda H, et al:
Comparison of concurrent chemoradiotherapy versus induction
chemotherapy followed by radiation in patients with nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 32:681–686. 2012.
|
|
9
|
National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Head and Neck
Cancers. http://www.nccn.org/93c288ea1c3664690434dfff86acacfe/head-and-neck.pdf.
Accessed April 28, 2014
|
|
10
|
Lee NY, Zhang Q, Pfister DG, et al:
Addition of bevacizumab to standard chemoradiation for
locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma (RTOG 0615): a
phase 2 multi-institutional trial. Lancet Oncol. 13:172–180.
2012.
|
|
11
|
Lu T, Zhao C, Chen C, et al: An open,
muticenter clinical study on cetuximab combined with intensity
modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) plus concurrent chemotherapy in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC): A 2-year follow-up report. In:
2012; ASCO Annual Meeting; J Clin Oncol. 30(suppl): pp. abstr
55352012
|
|
12
|
Basavaraj C, Sierra P, Shivu J, Melarkode
R, Montero E and Nair P: Nimotuzumab with chemoradiation confers a
survival advantage in treatment-naïve head and neck tumors over
expressing EGFR. Cancer Biol Ther. 10:673–681. 2010.
|
|
13
|
Rodríguez MO, Rivero TC, del Castillo Bahi
R, et al: Nimotuzumab plus radiotherapy for unresectable
squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer Biol Ther.
9:343–349. 2010.
|
|
14
|
Huang XD, Yi JL, Gao L, et al:
Multi-center phase II clinical trial of humanized anti-epidermal
factor receptor monoclonal antibody h-R3 combined with radiotherapy
for Iocoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Zhonghua
Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 29:197–201. 2007.
|
|
15
|
Huncharek M and Kupelnick B: Combined
chemoradiation versus radiation therapy alone in locally advanced
nasopharyngeal carcinoma: results of a meta-analysis of 1,528
patients from six randomized trials. Am J Clin Oncol. 25:219–223.
2002.
|
|
16
|
Thephamongkhol K, Zhou J, Browman G, et
al: Chemoradiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for nasopharyngeal
carcinoma: A meta-analysis of 78 randomized controlled trials
(RCTs) from English and non-English databases. In: 2004; ASCO
Annual Meeting; J Clin Oncol. 22(suppl 14): pp. abstr 55222004
|
|
17
|
Shao-jun C, Hai-xin H and Gui-sheng L:
Different dosage cisplatin based concurrent radiochemotherapy in
the treatment for locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Zhong
Guo Zhong Liu. 18:597–599. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
18
|
Dong-ning H, Hai-xin H and Shao-jun C:
Different administration regimens of cisplatin combined with
concurrent radiotherapy for 65 cases with locally advanced
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Zhong Liu Xue Za Zhi. 15:836–838.
2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
19
|
Shi W, Zhou Q and Ju W: Observation on
therapeutic effects of chemotherapy involving oxaliplatin in
treatment of advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Zhong Guo Yao Fang.
16:1886–1888. 2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
20
|
World Health Organization (WHO). global
tuberculosis control report. 2010, http://reliefweb.int/sites/reliefweb.int/files/resour-ces/F530290AD0279399C12577D8003E9D65-Full_Report.pdf.
Accessed April 28, 2014
|
|
21
|
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
(CDC). Recommendations for use of an isoniazid-rifapentine regimen
with direct observation to treat latent Mycobacterium
tuberculosis infection. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep.
60:1650–1653. 2011.
|
|
22
|
Sterling TR, Villarino ME, Borisov AS, et
al; TB Trials Consortium PREVENT TB Study Team. Three months of
rifapentine and isoniazid for latent tuberculosis infection. N Engl
J Med. 365:2155–2166. 2011.
|