|
1
|
Jemal A, Clegg LX, Ward E, et al: Annual
report to the nation on the status of cancer. 1975–2001, with a
special feature regarding survival. Cancer. 101:3–27. 2004.
|
|
2
|
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Díaz M and Cléries R:
Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends.
Gastroenterology. 127(5 Suppl 1): S5–S16. 2004.
|
|
3
|
Parkin DM, Bray FI and Devesa S: Cancer
burden in the year 2000. The global picture. Eur J Cancer.
37:S4–S66. 2001.
|
|
4
|
Hu Z and Zhao W: Novel insights into the
molecular mechanisms of α-fetoprotein expression and malignant
phenotypes of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Mol Immunol. 9:7–8.
2012.
|
|
5
|
Karabork A, Kaygusuz G and Ekinci C: The
best immunohistochemical panel for differentiating hepatocellular
carcinoma from metastatic adenocarcinoma. Pathol Res Pract.
206:572–577. 2010.
|
|
6
|
Yang M, Chen G, Dang Y and Luo D:
Significance of decoy receptor 3 in sera of hepatocellular
carcinoma patients. Ups J Med Sci. 115:232–237. 2010.
|
|
7
|
Thompson LH, Bachinski LL, Stallings RL,
et al: Complementation of repair gene mutations on the hemizygous
chromosome 9 in CHO: a third repair gene on human chromosome 19.
Genomics. 5:670–679. 1989.
|
|
8
|
Poehlmann A and Roessner A: Importance of
DNA damage checkpoints in the pathogenesis of human cancers. Pathol
Res Pract. 206:591–601. 2010.
|
|
9
|
Whitehouse CJ, Taylor RM, Thistlethwaite
A, et al: XRCC1 stimulates human polynucleotide kinase activity at
damaged DNA termini and accelerates DNA single-strand break repair.
Cell. 104:107–117. 2001.
|
|
10
|
Lee SG, Kim B, Choi J, et al: Genetic
polymorphisms of XRCC1 and risk of gastric cancer. Cancer Lett.
187:53–60. 2012.
|
|
11
|
Park JY, Lee SY, Jeon HS, et al:
Polymorphism of the DNA repair gene XRCC1 and risk of primary lung
cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 11:23–27. 2002.
|
|
12
|
Kim SU, Park SK, Yoo KY, et al: XRCC1
genetic polymorphism and breast cancer risk. Pharmacogenetics.
12:335–338. 2002.
|
|
13
|
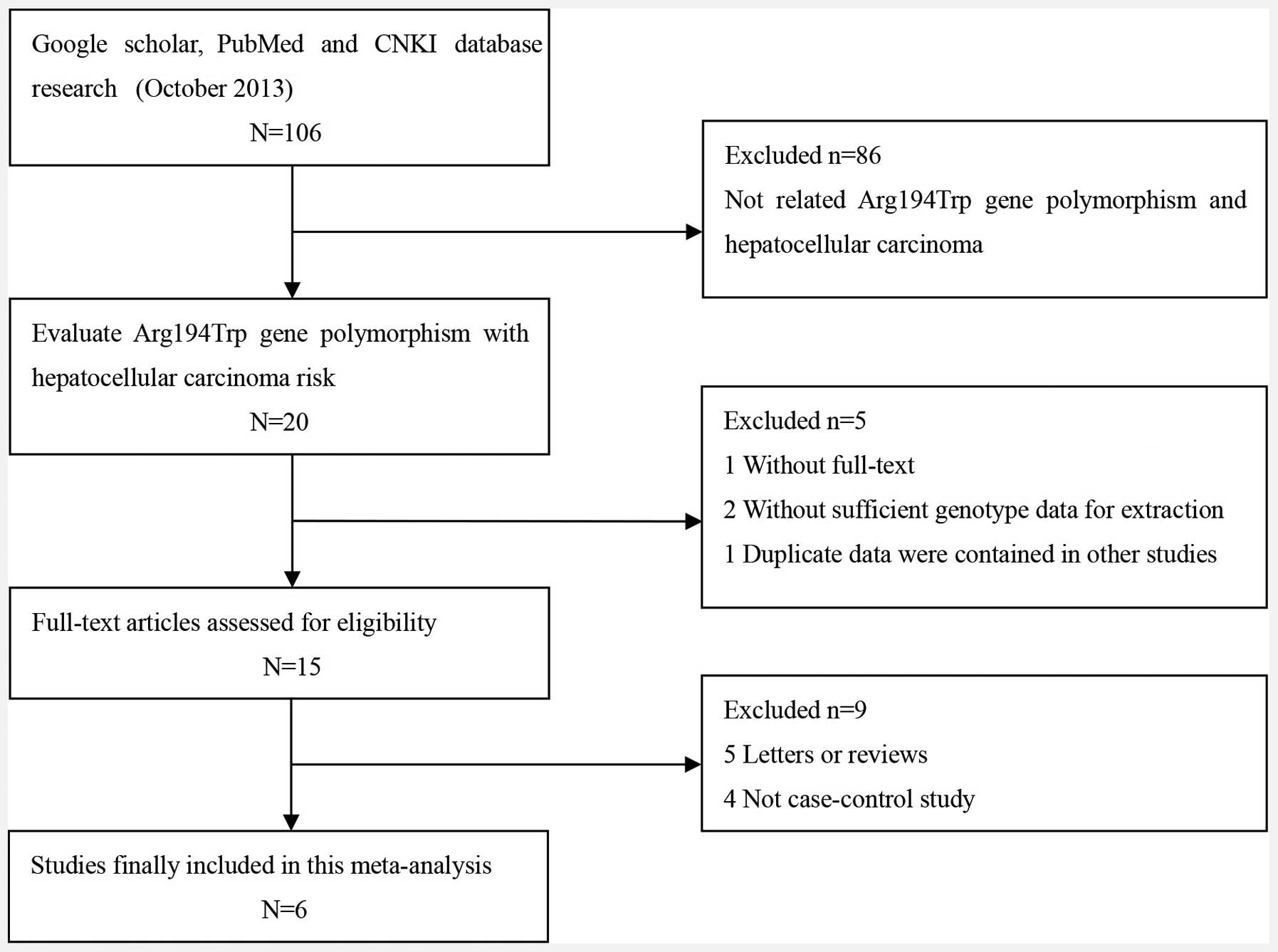
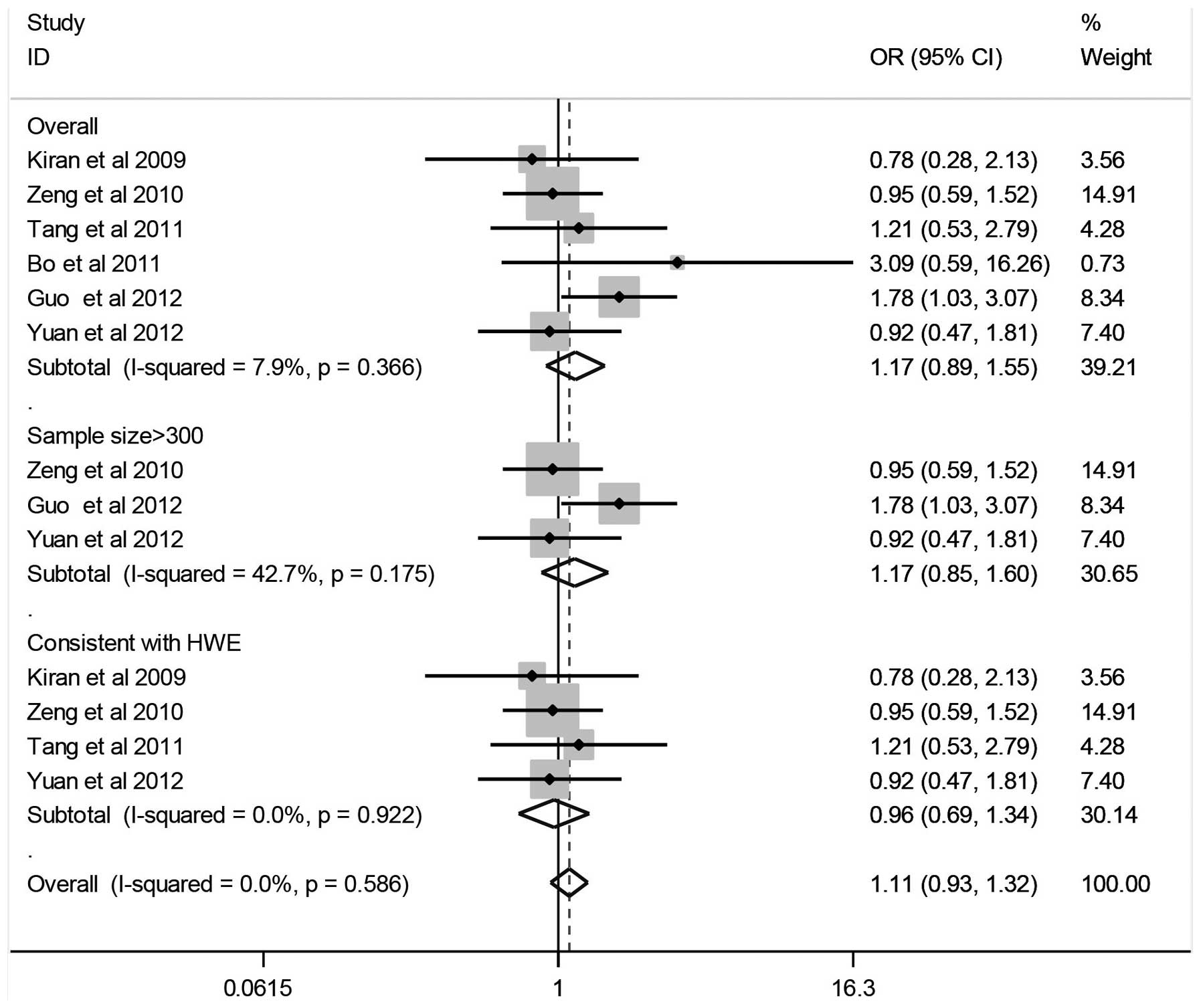
Kiran M, Saxena R, Chawla YK, et al:
Polymorphism of DNA repair gene XRCC1 and hepatitis-related
hepatocellular carcinoma risk in Indian population. Mol Cell
Biochem. 7–13. 2009.
|
|
14
|
Zeng X, Yu H and Qiu X: A case-control
study of polymorphism of XRCC1 gene and the risk of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Zhongguo Jibing Kongzhi Zazhi. 14:760–763. 2010.
|
|
15
|
Tang Y, Li X, Liu T, et al: Genetic
polymorphisms of DNA repair genes in patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma. Shandong Yiyao. 51:19–20. 2011.
|
|
16
|
Bo W, Zhang G, Li D, et al: Polymorphisms
of DNA repair gene XRCC1 and susceptibility to hepatic cancer.
Xiandai Zhongliu Yixue. 19:1724–1726. 2011.
|
|
17
|
Guo LY, Jin XP, Niu W, et al: Association
of XPD and XRCC1 genetic polymorphisms with hepatocellular
carcinoma risk. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:4423–4426. 2012.
|
|
18
|
Yuan T, Deng S, Liu H, et al: Relationship
between XRCC1 and XPD polymorphisms and the risk of the development
of hepatocellular carcinoma: A case-control study. Exp Ther Med.
4:285–290. 2012.
|
|
19
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al: Global
cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 61:69–90. 2011.
|
|
20
|
Nordenstedt H, White DL and El-Serag HB:
The changing pattern of epidemiology in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Dig Liver Dis. 3:S206–S214. 2010.
|
|
21
|
Cochran WG: The combination of estimates
from different experiments. Biometrics. 10:101–129. 1954.
|
|
22
|
Higgins JP and Thompson SG: Quantifying
heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 21:1539–1558. 2002.
|
|
23
|
Kirk GD, Lesi OA, Mendy M, et al: 249(ser)
TP53 mutation in plasma DNA, hepatitis B viral infection, and risk
of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 24:5858–5867. 2005.
|
|
24
|
Thompson LH, Brookman KW, Jones NJ, et al:
Molecular cloning of the human XRCC1 gene, which corrects defective
DNA strand break repair and sister chromatid exchange. Mol Cell
Biol. 10:6160–6171. 1990.
|
|
25
|
Zhong H, Feng Y, Zheng GX, et al: A
meta-analysis of the association between glutathione S-transferase
P1 gene polymorphism and the risk of adenocarcinomas of lung
cancer. Cancer Biomark. 13:29–35. 2013.
|
|
26
|
Pakiz M, Potocnik U, But I and Mujezinovic
F: A CYP17A1 gene polymorphism in association with multiple uterine
leimyomas; a meta-analysis. Cancer Biomark. 8:29–34. 2011.
|
|
27
|
Sato K and Mori M: Evolving molecular
mechanism-based strategies for control of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Curr Med Chem. 18:4375–4388. 2011.
|