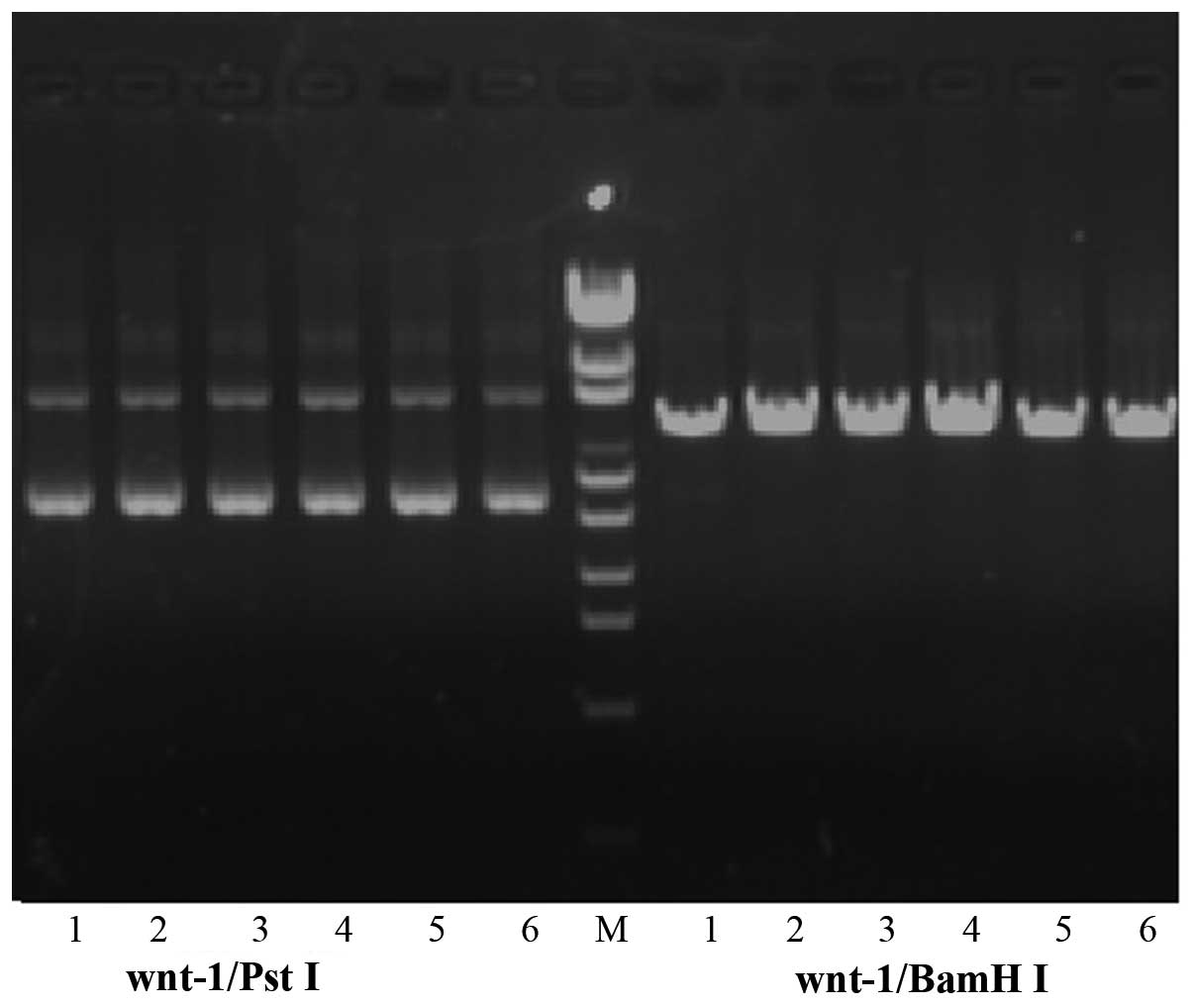
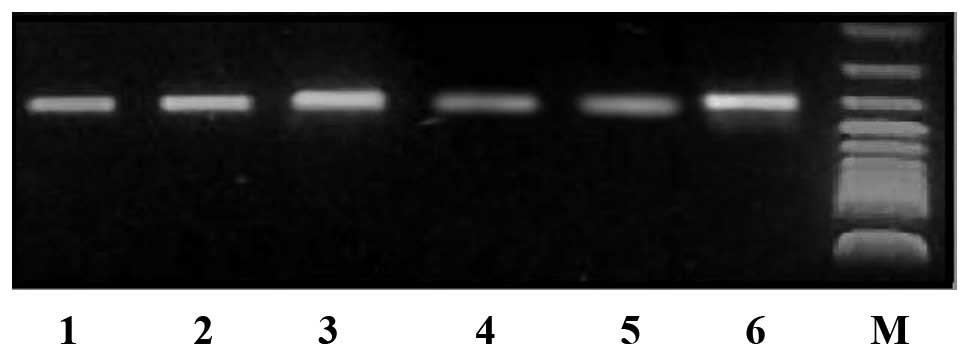
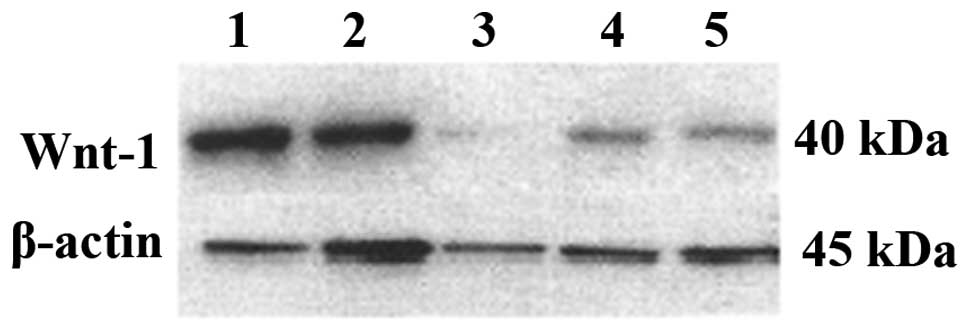
|
1
|
Benad P, Rauner M, Rachner TD and Hofbauer
LC: The anti-progestin RU-486 inhibits viability of MCF-7 breast
cancer cells by suppressing WNT1. Cancer Lett. 312:101–108. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Benchabane H, Xin N, Tian A, et al:
Jerky/Earthbound facilitates cell-specific Wnt/Wingless signalling
by modulating β-catenin-TCF activity. EMBO J. 30:1444–1458. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xu X, Sun PL, Li JZ, Jheon S, Lee CT and
Chung JH: Aberrant Wnt1/β-catenin expression is an independent poor
prognostic marker of non-small cell lung cancer after surgery. J
Thorac Oncol. 6:716–724. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nakashima N, Huang CL, Liu D, Ueno M and
Yokomise H: Intratumoral Wnt1 expression affects survivin gene
expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Oncol. 37:687–694.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Oguma K, Oshima H and Oshima M:
Inflammation, tumor necrosis factor and Wnt promotion in gastric
cancer development. Future Oncol. 6:515–526. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fracalossi AC, de Silva MS, Oshima CT and
Ribeiro DA: Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway following rat
tongue carcinogenesis induced by 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide. Exp Mol
Pathol. 88:176–183. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wang FL, Guo X, Yuan TZ, et al: Expression
and clinical significance of Wnt-1 and beta-catenin in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ai Zheng. 28:72–75. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
You L, Kim J, He B, Xu Z, McCormick F and
Jablons DM: Wnt-1 signal as a potential cancer therapeutic target.
Drug News Perspect. 19:27–31. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Augustin I, Goidts V, Bongers A, et al:
The Wnt secretion protein Evi/Gpr177 promotes glioma
tumourigenesis. EMBO Mol Med. 4:38–51. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Natsume A, Kinjo S, Yuki K, et al:
Glioma-initiating cells and molecular pathology: implications for
therapy. Brain Tumor Pathol. 28:1–12. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ille F and Sommer L: Wnt signaling:
multiple functions in neural development. Cell Mol Life Sci.
62:1100–1108. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Toledo EM, Colombres M and Inestrosa NC:
Wnt signaling in neuroprotection and stem cell differentiation.
Prog Neurobiol. 86:281–296. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Han L, Yang Y, Yue X, et al: Inactivation
of PI3K/AKT signaling inhibits glioma cell growth through
modulation of β-catenin-mediated transcription. Brain Res.
1366:9–17. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Reya T and Clevers H: Wnt signalling in
stem cells and cancer. Nature. 434:843–850. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
De Ferrari GV and Moon RT: The ups and
downs of Wnt signaling in prevalent neurological disorders.
Oncogene. 25:7545–7553. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu C, Tu Y, Sun X, et al:
Wnt/beta-Catenin pathway in human glioma: expression pattern and
clinical/prognostic correlations. Clin Exp Med. 11:105–112. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kamino M, Kishida M, Kibe T, et al: Wnt-5a
signaling is correlated with infiltrative activity in human glioma
by inducing cellular migration and MMP-2. Cancer Sci. 102:540–548.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Thiele S, Rauner M, Goettsch C, et al:
Expression profile of WNT molecules in prostate cancer and its
regulation by aminobisphosphonates. J Cell Biochem. 112:1593–1600.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sharma V, Dixit D, Koul N, Mehta VS and
Sen E: Ras regulates interleukin-1β-induced HIF-1α transcriptional
activity in glioblastoma. J Mol Med (Berl). 89:123–136. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chen L, Huang K, Han L, et al:
β-catenin/Tcf-4 complex transcriptionally regulates AKT1 in glioma.
Int J Oncol. 39:883–890. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wei W, Chua MS, Grepper S and So SK:
Blockade of Wnt-1 signaling leads to anti-tumor effects in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer. 24:762009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sareddy GR, Challa S, Panigrahi M and Babu
PP: Wnt/beta-catenin/Tcf signaling pathway activation in malignant
progression of rat gliomas induced by transplacental
N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea exposure. Neurochem Res. 34:1278–1288. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Whangbo JS and Hunter CP: Environmental
RNA interference. Trends Genet. 24:297–305. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dillin A: The specifics of interfering RNA
specificity. Proc Nat Acd Sci USA. 100:6289–6291. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mikami I, You L, He B, et al: Efficacy of
Wnt-1 monoclonal antibody in sarcoma cells. BMC Cancer. 5:532005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wieczorek M, Paczkowska A, Guzenda P,
Majorek M, Bednarek AK and Lamparska-Przybysz M: Silencing of Wnt-1
by siRNA induces apoptosis of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells.
Cancer Biol Ther. 7:268–274. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Polanec J, Pavelic ZP and Myers WL: Effect
of Wnt-1 antisense RNA on the outgrowth of a mammary adenocarcinoma
cell line expressing that oncogene. Clin Mol Pathol. 49:M166–M169.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang L, Li K, Lv Z, Xiao X and Zheng J:
The effect on cell growth by Wnt1 RNAi in human neuroblastoma
SH-SY5Y cell line. Pediatr Surg Int. 25:1065–1071. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Takahashi-Yanaga F and Sasaguri T: The
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway as a target in drug discovery. J
Pharmacol Sci. 104:293–302. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|