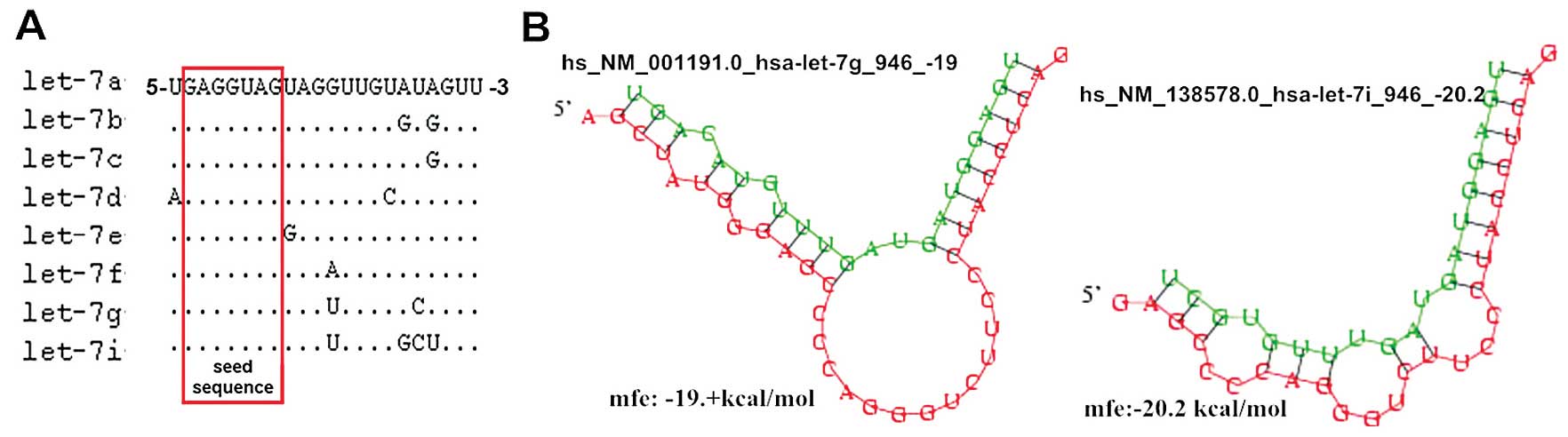
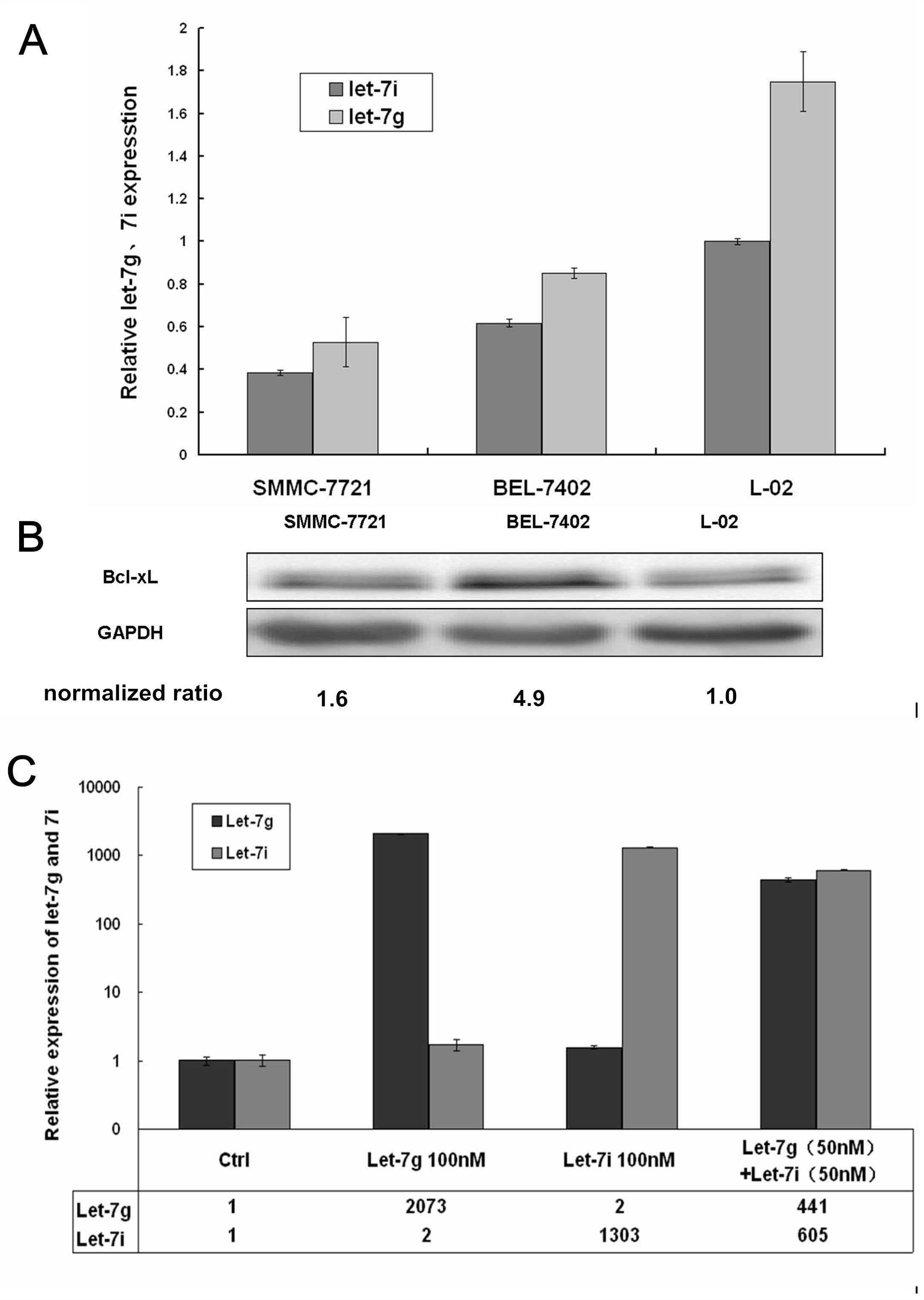
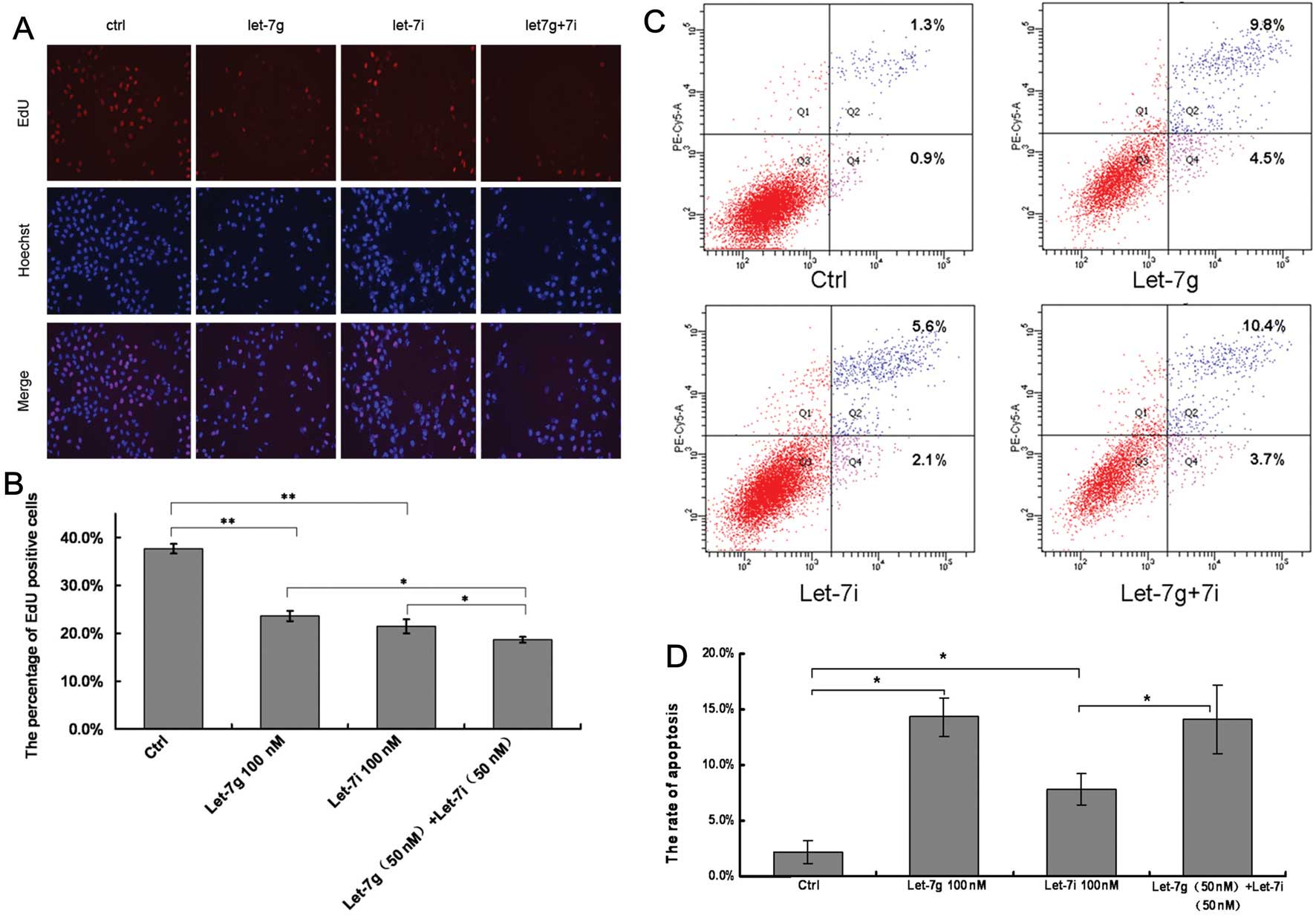
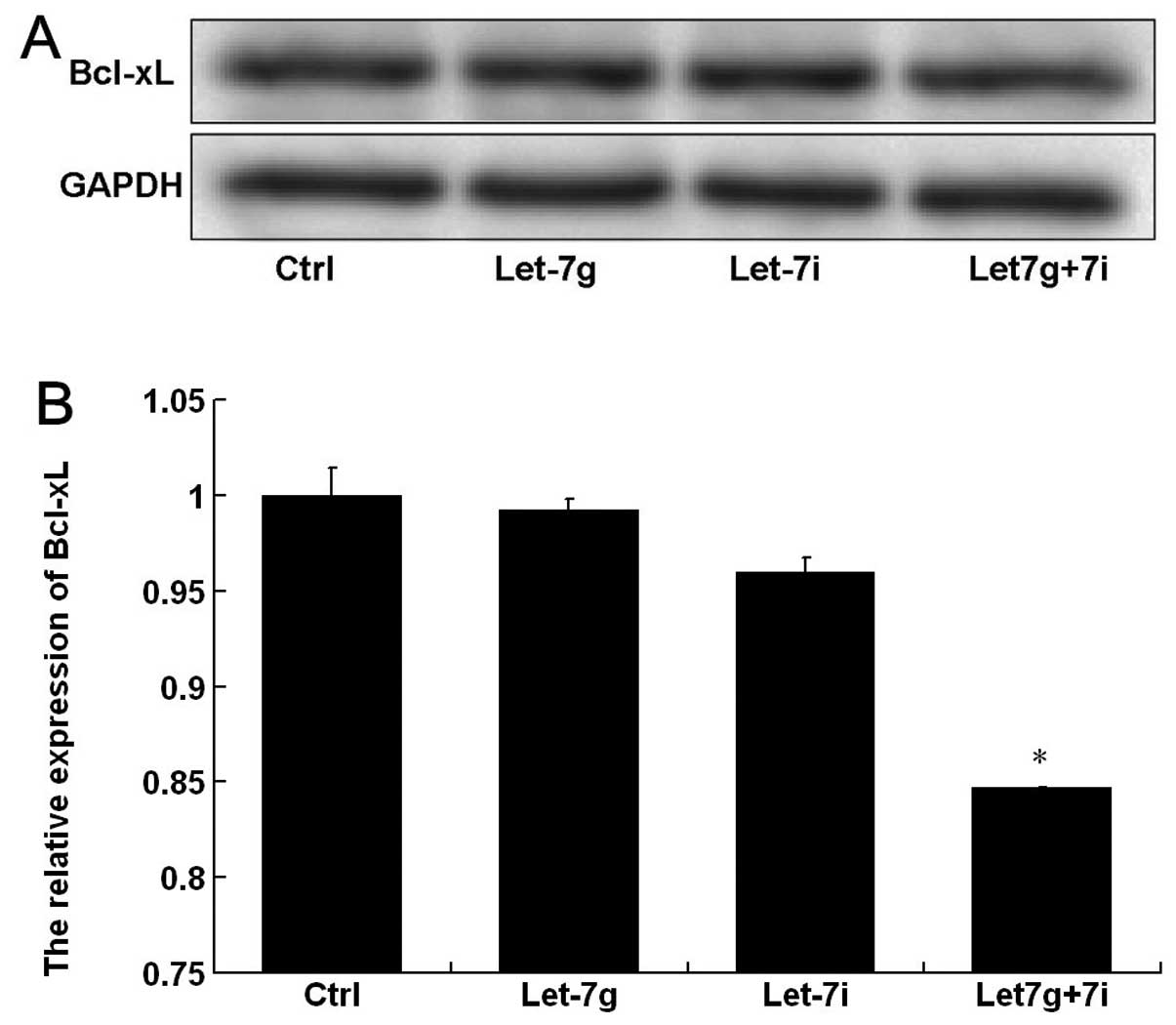
|
1
|
Lujambio A and Lowe SW: The microcosmos of
cancer. Nature. 482:347–355. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Roush S and Slack FJ: The let-7 family of
microRNAs. Trends Cell Biol. 18:505–516. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gregory RI and Shiekhattar R: MicroRNA
biogenesis and cancer. Cancer Res. 65:3509–3512. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hou J, Lin L, Zhou W, et al:
Identification of miRNomes in human liver and hepatocellular
carcinoma reveals miR-199a/b-3p as therapeutic target for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 19:232–243. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, et al:
Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and
prognosis. Cancer Cell. 9:189–198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Akao Y, Nakagawa Y and Naoe T: let-7
microRNA functions as a potential growth suppressor in human colon
cancer cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 29:903–906. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nam EJ, Yoon H, Kim SW, et al: MicroRNA
expression profiles in serous ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
14:2690–2695. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Peng Y, Laser J, Shi G, et al:
Antiproliferative effects by Let-7 repression of high-mobility
group A2 in uterine leiomyoma. Mol Cancer Res. 6:663–673. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shimizu S, Takehara T, Hikita H, et al:
The let-7 family of microRNAs inhibits Bcl-xL expression and
potentiates sorafenib-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Hepatol. 52:698–704. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhu XM, Wu LJ, Xu J, Yang R and Wu FS:
Let-7c microRNA expression and clinical significance in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Int Med Res. 39:2323–2329. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hu X, Guo J, Zheng L, et al: The
heterochronic microRNA let-7 inhibits cell motility by regulating
the genes in the actin cytoskeleton pathway in breast cancer. Mol
Cancer Res. 11:240–250. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Doench JG and Sharp PA: Specificity of
microRNA target selection in translational repression. Genes Dev.
18:504–511. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brennecke J, Stark A, Russell RB and Cohen
SM: Principles of microRNA-target recognition. PLoS Biol.
3:e852005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Abbott AL, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Miska EA,
et al: The let-7 MicroRNA family members mir-48, mir-84, and
mir-241 function together to regulate developmental timing in
Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Cell. 9:403–414. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Johnson CD, Esquela-Kerscher A, Stefani G,
et al: The let-7 microRNA represses cell proliferation pathways in
human cells. Cancer Res. 67:7713–7722. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Inui M, Martello G and Piccolo S: MicroRNA
control of signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 11:252–263.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nicoloso MS, Spizzo R, Shimizu M, Rossi S
and Calin GA: MicroRNAs-the micro steering wheel of tumour
metastases. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:293–302. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hunter SE, Finnegan EF, Zisoulis DG, et
al: Functional genomic analysis of the let-7 regulatory network in
Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Genet. 9:e10033532013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Murray MJ, Saini HK, Siegler CA, et al:
LIN28 Expression in malignant germ cell tumors downregulates let-7
and increases oncogene levels. Cancer Res. 73:4872–4884. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bueno MJ, Gomez de Cedron M, Gomez-Lopez
G, et al: Combinatorial effects of microRNAs to suppress the Myc
oncogenic pathway. Blood. 117:6255–6266. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mayr C, Hemann MT and Bartel DP:
Disrupting the pairing between let-7 and Hmga2 enhances oncogenic
transformation. Science. 315:1576–1579. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, et
al: RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell.
120:635–647. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tsang WP and Kwok TT: Let-7a microRNA
suppresses therapeutics-induced cancer cell death by targeting
caspase-3. Apoptosis. 13:1215–1222. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Watanabe J, Kushihata F, Honda K, et al:
Prognostic significance of Bcl-xL in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Surgery. 135:604–612. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|