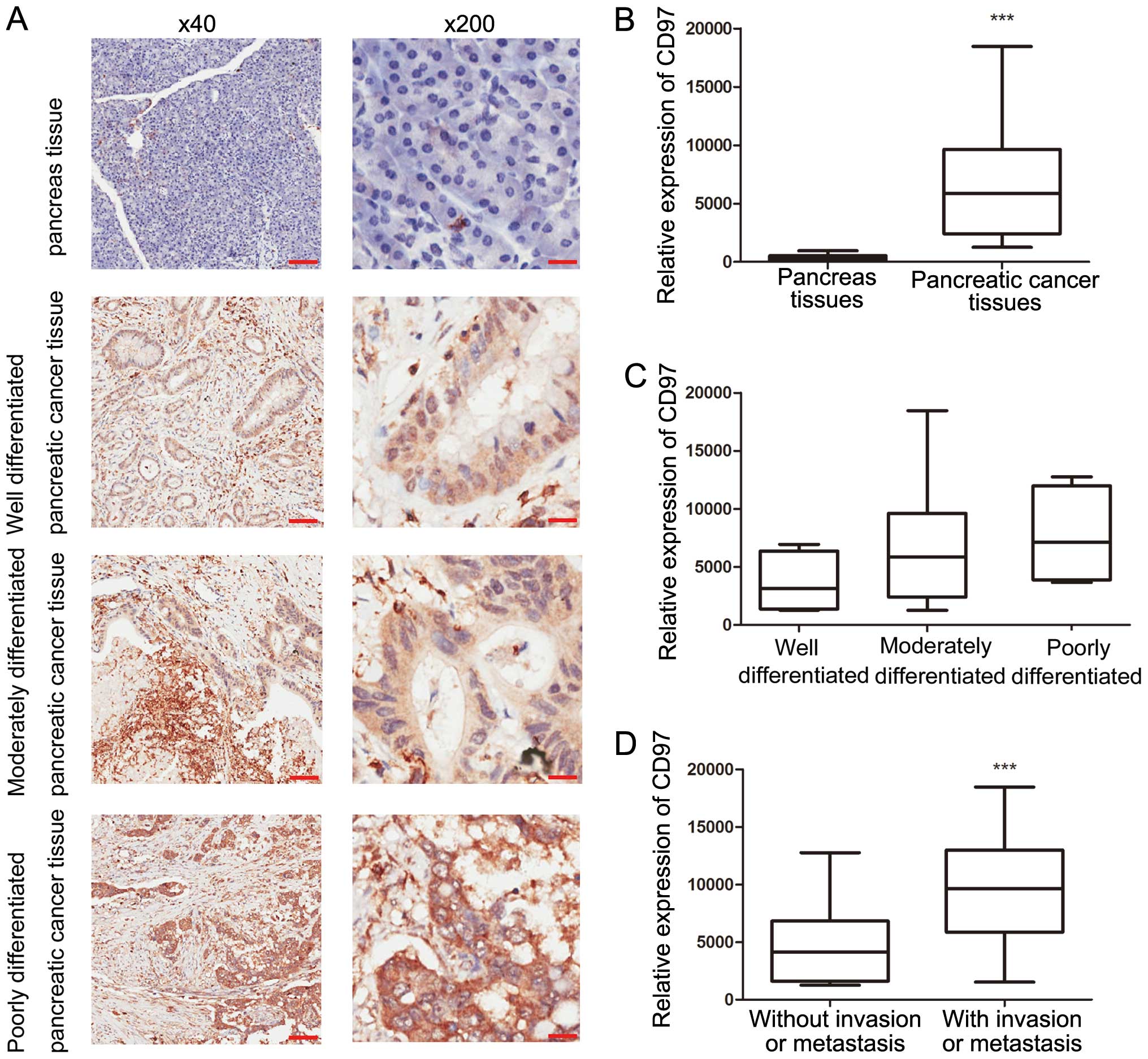
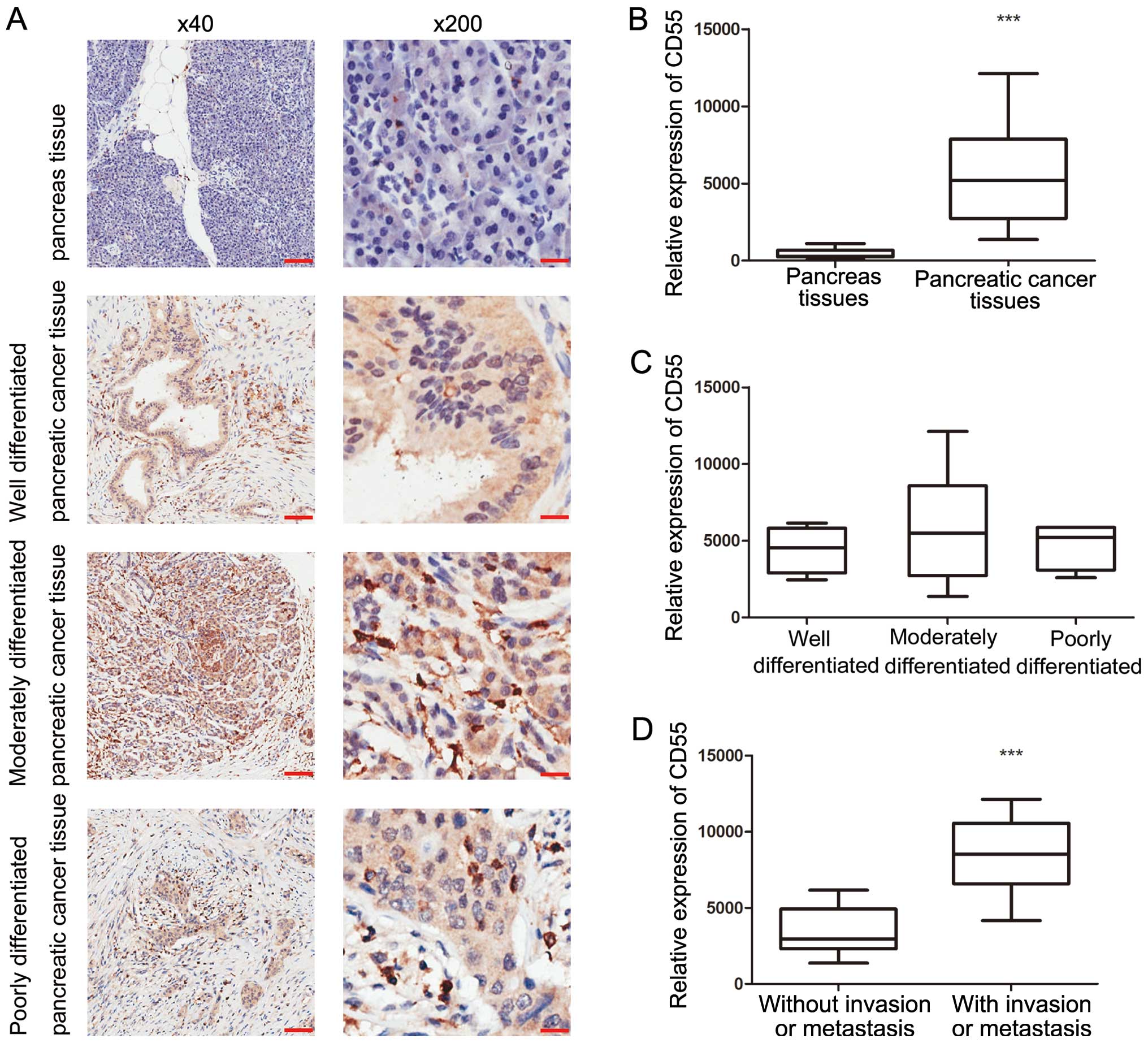
|
1
|
Ma C, Jiang YX, Liu SZ, et al: Trend and
prediction on the incidence of pancreatic cancer in China. Zhonghua
Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 34:160–163. 2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ji BT, Silverman DT, Dosemeci M, et al:
Occupation and pancreatic cancer risk in Shanghai, China. Am J Ind
Med. 35:76–81. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wolfgang CL, Herman JM, Laheru DA, et al:
Recent progress in pancreatic cancer. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:318–348.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hamann J, Vogel B, van Schijndel GM and
van Lier RA: The seven-span transmembrane receptor CD97 has a
cellular ligand (CD55, DAF). J Exp Med. 184:1185–1189. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
McKnight AJ and Gordon S: The EGF-TM7
family: unusual structures at the leukocyte surface. J Leukoc Biol.
63:271–280. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wobus M, Vogel B, Schmucking E, Hamann J
and Aust G: N-glycosylation of CD97 within the EGF domains is
crucial for epitope accessibility in normal and malignant cells as
well as CD55 ligand binding. Int J Cancer. 112:815–822. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lin HH, Stacey M, Saxby C, et al:
Molecular analysis of the epidermal growth factor-like short
consensus repeat domain-mediated protein-protein interactions:
dissection of the CD97-CD55 complex. J Biol Chem. 276:24160–24169.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Han SL, Xu C, Wu XL, et al: The impact of
expressions of CD97 and its ligand CD55 at the invasion front on
prognosis of rectal adenocarcinoma. Int J Colorectal Dis.
25:695–702. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mustafa T, Eckert A, Klonisch T, et al:
Expression of the epidermal growth factor seven-transmembrane
member CD97 correlates with grading and staging in human oral
squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
14:108–119. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Abbott RJ, Spendlove I, Roversi P, et al:
Structural and functional characterization of a novel T cell
receptor co-regulatory protein complex, CD97-CD55. J Biol Chem.
282:22023–22032. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hamann J, Stortelers C, Kiss-Toth E, et
al: Characterization of the CD55 (DAF)-binding site on the
seven-span transmembrane receptor CD97. Eur J Immunol.
28:1701–1707. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hamann J, Wishaupt JO, van Lier RA, et al:
Expression of the activation antigen CD97 and its ligand CD55 in
rheumatoid synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 42:650–658. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Qian YM, Haino M, Kelly K and Song WC:
Structural characterization of mouse CD97 and study of its specific
interaction with the murine decay-accelerating factor (DAF, CD55).
Immunology. 98:303–311. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Karpus ON, Veninga H, Hoek RM, et al:
Shear stress-dependent downregulation of the adhesion-G
protein-coupled receptor CD97 on circulating leukocytes upon
contact with its ligand CD55. J Immunol. 190:3740–3748. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, et al:
Exocrine and endocrine pancreas. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th
edition. Springer; New York, NY: pp. 241–249. 2010
|
|
16
|
Tempero MA, Behrman S, Ben-Josef E, et al:
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Clinical Practice Guidelines in
Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 3:598–626. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Barton MK: Thromboembolism is common and
influences prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer, study
reports. CA Cancer J Clin. Jan 18–2012.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yang GY, Wagner TD, Fuss M and Thomas CJ:
Multimodality approaches for pancreatic cancer. CA Cancer J Clin.
55:352–367. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mustafa T, Klonisch T, Hombach-Klonisch S,
et al: Expression of CD97 and CD55 in human medullary thyroid
carcinomas. Int J Oncol. 24:285–294. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sutavani RV, Bradley RG, Ramage JM, et al:
CD55 costimulation induces differentiation of a discrete T
regulatory type 1 cell population with a stable phenotype. J
Immunol. 191:5895–5903. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Durrant LG, Chapman MA, Buckley DJ, et al:
Enhanced expression of the complement regulatory protein CD55
predicts a poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 52:638–642. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu Y, Chen L, Peng SY, Chen ZX and
Hoang-Vu C: Role of CD97 (stalk) and CD55 as molecular markers for
prognosis and therapy of gastric carcinoma patients. J Zhejiang
Univ Sci B. 6:913–918. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Loberg RD, Wojno KJ, Day LL and Pienta KJ:
Analysis of membrane-bound complement regulatory proteins in
prostate cancer. Urology. 66:1321–1326. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu J, Lei L, Wang S, Gu D and Zhang J:
Immunohistochemical expression and prognostic value of CD97 and its
ligand CD55 in primary gallbladder carcinoma. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2012:5876722012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|