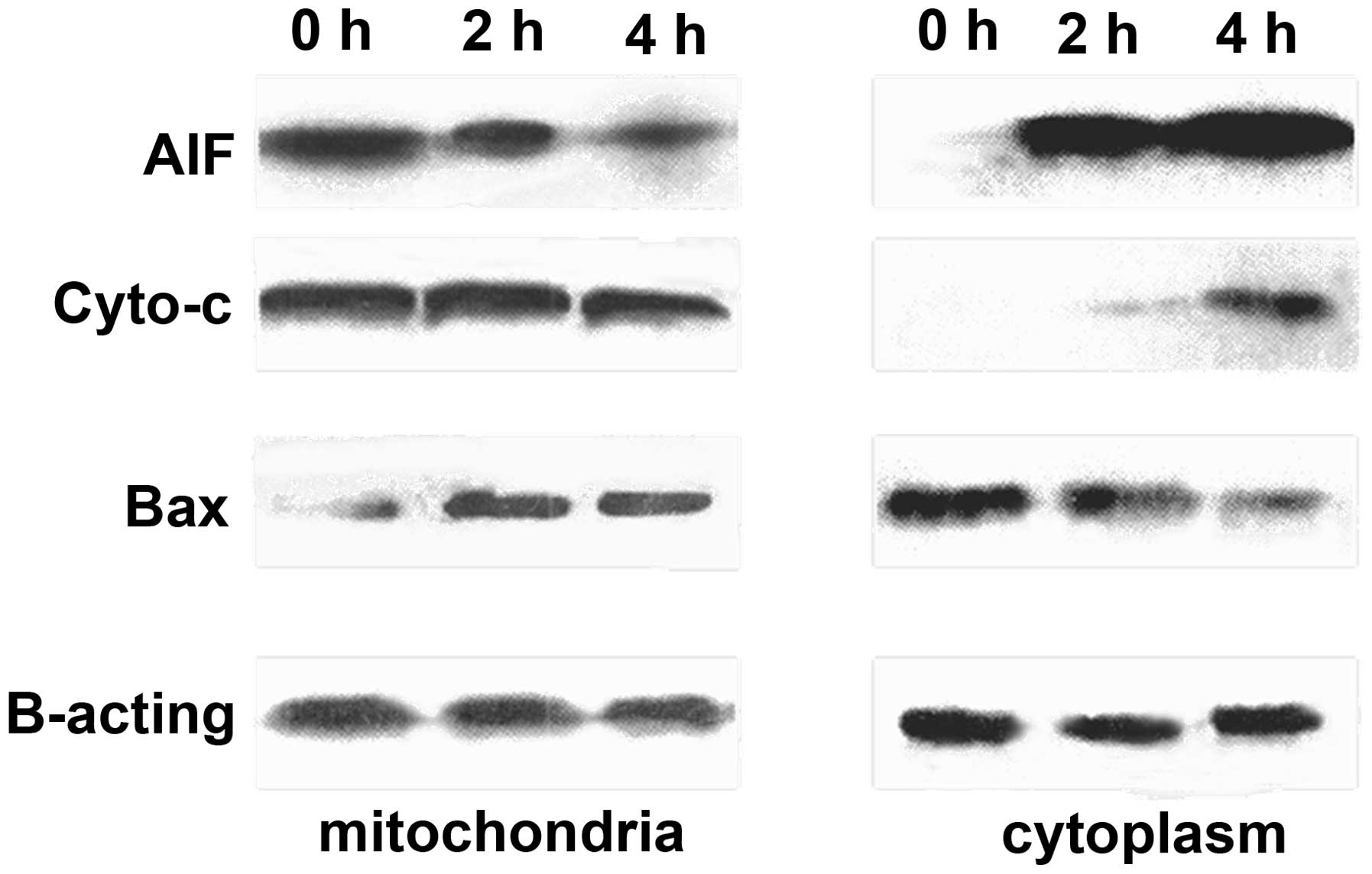
|
1
|
Koul D, Shen R, Bergh S, Sheng X,
Shishodia S, Lafortune TA, Lu Y, de Groot JF, Mills GB and Yung WK:
Inhibition of Akt survival pathway by a small-molecule inhibitor in
human glioblastoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:637–644. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Harikumar KB and Aggarwal BB: Resveratrol:
a multitargeted agent for age-associated chronic diseases. Cell
Cycle. 7:1020–1035. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Delmas D, Lançon A, Colin D, Jannin B and
Latruffe N: Resveratrol as a chemopreventive agent: a promising
molecule for fighting cancer. Curr Drug Targets. 7:423–442. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kundu JK and Surh YJ: Cancer
chemopreventive and therapeutic potential of resveratrol:
mechanistic perspectives. Cancer Lett. 269:243–261. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang CS, Landau JM, Huang MT and Newmark
HL: Inhibition of carcinogenesis by dietary polyphenolic compounds.
Annu Rev Nutr. 21:381–406. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jang M, Cai L, Udeani GO, Slowing KV,
Thomas CF, Beecher CW, Fong HH, Farnsworth NR, Kinghorn AD, Mehta
RG, et al: Cancer chemopreventive activity of resveratrol, a
natural product derived from grapes. Science. 275:218–220. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tessitore L, Davit A, Sarotto I and
Caderni G: Resveratrol depresses the growth of colorectal aberrant
crypt foci by affecting bax and p21(CIP) expression.
Carcinogenesis. 21:1619–1622. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hebbar V, Shen G, Hu R, Kim BR, Chen C,
Korytko PJ, Crowell JA, Levine BS and Kong AN: Toxicogenomics of
resveratrol in rat liver. Life Sci. 76:2299–2314. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Soleas GJ, Angelini M, Grass L, Diamandis
EP and Goldberg DM: Absorption of trans-resveratrol in rats.
Methods Enzymol. 335:145–154. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Singh G and Pai RS: In-vitro/in-vivo
characterization of trans-resveratrol-loaded nanoparticulate drug
delivery system for oral administration. J Pharm Pharmacol.
66:1062–1076. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Croy SR and Kwon GS: Polymeric micelles
for drug delivery. Curr Pharm Des. 12:4669–4684. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Escorcia FE, McDevitt MR, Villa CH and
Scheinberg DA: Targeted nanomaterials for radiotherapy.
Nanomedicine (Lond). 2:805–815. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Li F, Zhang X, Li H, Xiang L and Chen Y:
Preparation of self-assembled nanoparticles of chitosan
oligosaccharide-graft-polycaprolactone as a carrier of bovine serum
albumin drug. Biomed Mater Eng. 24:2041–2048. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu Z, Yu M, Zhang Z, Hong G and Xiong Q:
Bovine serum albumin nanoparticles as controlled release carrier
for local drug delivery to the inner ear. Nanoscale Res Lett.
9:3432014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guo LY, Yao JP and Sui LH: Preparation and
Effects of Resveratrol-Bovine Serum Albumin Nanoparticles on
Proliferation of Human Ovarian Carcinoma Cell SKOV3. Chemical
Journal of Chinese Universities. 30:474–477. 2009.
|
|
16
|
Guo LY, Peng Y, Li YL, Yao JP, Wang J,
Zhang GM, Chen J and Sui LH: Mechanisms of resveratrol-bovine serum
albumin nanoparticle-induced cell death in human ovarian cancer
SKOV3 cells. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 30:2440–2442. 2010.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guo L, Peng Y, Yao J, Sui L, Gu A and Wang
J: Anticancer activity and molecular mechanism of
resveratrol-bovine serum albumin nanoparticles on subcutaneously
implanted human primary ovarian carcinoma cells in nude mice.
Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 25:471–477. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Anastasiadis PZ, Jiang H, Bezin L, Kuhn DM
and Levine RA: Tetrahydrobiopterin enhances apoptotic PC12 cell
death following withdrawal of trophic support. J Biol Chem.
276:9050–9058. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jäättelä M: Programmed cell death: many
ways for cells to die decently. Ann Med. 34:480–488. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Jäättelä M and Tschopp J:
Caspase-independent cell death in T lymphocytes. Nat Immunol.
4:416–423. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lorenzo HK and Susin SA: Mitochondrial
effectors in caspase-independent cell death. FEBS Lett. 557:14–20.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Blagosklonny MV: Cell death beyond
apoptosis. Leukemia. 14:1502–1508. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Moubarak RS, Yuste VJ, Artus C, Bouharrour
A, Greer PA, Menissier-de Murcia J and Susin SA: Sequential
activation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1, calpains, and Bax is
essential in apoptosis-inducing factor-mediated programmed
necrosis. Mol Cell Biol. 27:4844–4862. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zanna C, Ghelli A, Porcelli AM, Martinuzzi
A, Carelli V and Rugolo M: Caspase-independent death of Leber’s
hereditary optic neuropathy cybrids is driven by energetic failure
and mediated by AIF and Endonuclease G. Apoptosis. 10:997–1007.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Miyake K, Bekisz J, Zhao T, Clark CR and
Zoon KC: Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) is targeted in
IFN-α2a-induced Bid-mediated apoptosis through Bak activation in
ovarian cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1823:1378–1388. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhan ZL and Chen LY: Changes in the
expression of the apoptosis of esophageal cancer EC9706 cells
during nuclear matrix proteins induced by curcumin. Zhong Guo Sheng
Wu Hua Xue Yu Fen Zi Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 546–555. 2010.
|
|
27
|
Wu B and Gao Q: Microscope laser
cytoskeleton changes in the process of cell apoptosis confocal.
Dian Zi Xian Wei Xue Bao. 361–366. 2010.
|
|
28
|
Byun HS, Song JK, Kim YR, Piao L, Won M,
Park KA, Choi BL, Lee H, Hong JH, Park J, et al: Caspase-8 has an
essential role in resveratrol-induced apoptosis of rheumatoid
fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford). 47:301–308.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Arnoult D, Parone P, Martinou JC,
Antonsson B, Estaquier J and Ameisen JC: Mitochondrial release of
apoptosis-inducing factor occurs downstream of cytochrome c release
in response to several proapoptotic stimuli. J Cell Biol.
159:923–929. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cregan SP, Fortin A, MacLaurin JG,
Callaghan SM, Cecconi F, Yu SW, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, Park DS,
Kroemer G and Slack RS: Apoptosis-inducing factor is involved in
the regulation of caspase-independent neuronal cell death. J Cell
Biol. 158:507–517. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bröker LE, Kruyt FA and Giaccone G: Cell
death independent of caspases: a review. Clin Cancer Res.
11:3155–3162. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hall JB, Dobrovolskaia MA, Patri AK and
McNeil SE: Characterization of nanoparticles for therapeutics.
Nanomedicine (Lond). 2:789–803. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Dorrie J, Gerauer H, Wachter Y and Zunino
SJ: Resveratrol induces extensive apoptosis by depolarizing
mitochondrial membranes and activating caspase-9 in acute
lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 61:4731–4739.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tinhofer I, Bernhard D, Senfter M, Anether
G, Loeffler M, Kroemer G, Kofler R, Csordas A and Greil R:
Resveratrol, a tumor-suppressive compound from grapes, induces
apoptosis via a novel mitochondrial pathway controlled by Bcl-2.
FASEB J. 15:1613–1615. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Howells LM, Moiseeva EP, Neal CP, Foreman
BE, Andreadi CK, Sun YY, Hudson EA and Manson MM: Predicting the
physiological relevance of in vitro cancer preventive activities of
phytochemicals. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 28:1274–1304. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Athar M, Back JH, Tang X, Kim KH,
Kopelovich L, Bickers DR and Kim AL: Resveratrol: a review of
preclinical studies for human cancer prevention. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 224:274–283. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pervaiz S: Chemotherapeutic potential of
the chemopreventive phytoalexin resveratrol. Drug Resist Updat.
7:333–344. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Signorelli P and Ghidoni R: Resveratrol as
an anticancer nutrient: molecular basis, open questions and
promises. J Nutr Biochem. 16:449–466. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Le Corre L, Chalabi N, Delort L, Bignon YJ
and Bernard-Gallon DJ: Resveratrol and breast cancer
chemoprevention: molecular mechanisms. Mol Nutr Food Res.
49:462–471. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sheridan C, Delivani P, Cullen SP and
Martin SJ: Bax- or Bak-induced mitochondrial fission can be
uncoupled from cytochrome C release. Mol Cell. 31:570–585. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|