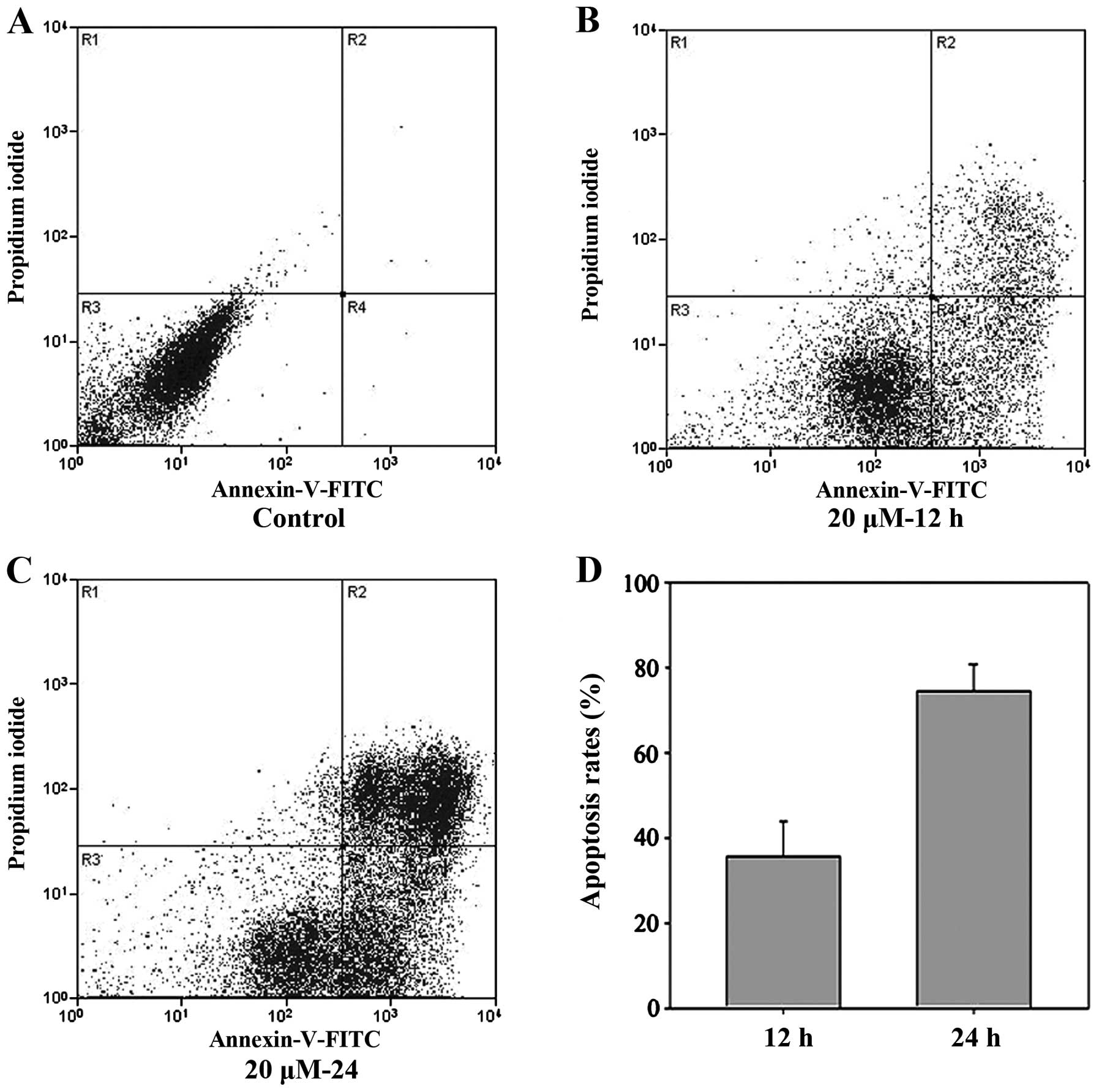
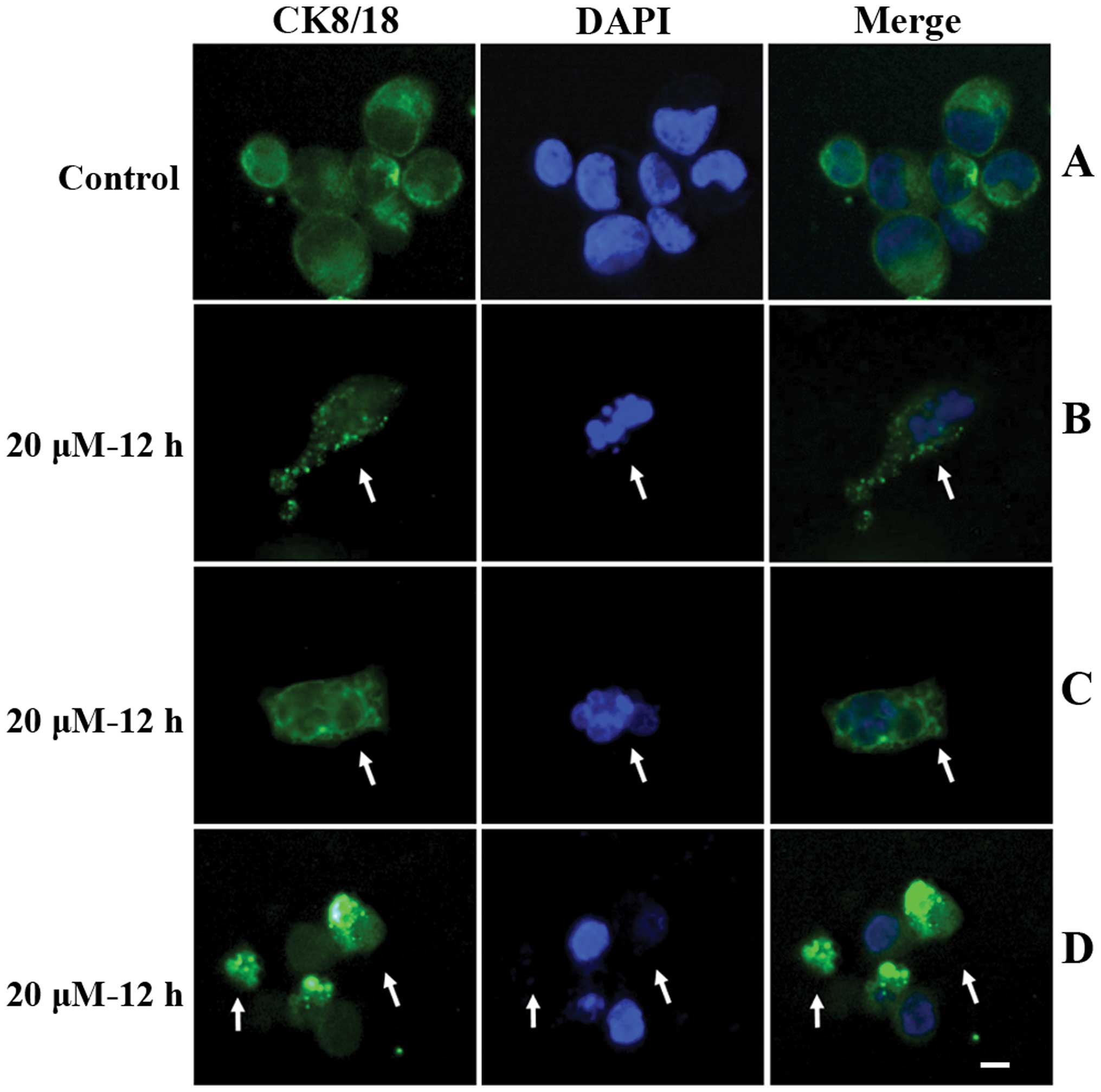
|
1
|
Burikhanov R, Shrestha-Bhattarai T, Qiu S,
et al: Novel mechanism of apoptosis resistance in cancer mediated
by extracellular PAR-4. Cancer Res. 73:1011–1019. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Li J, Quan H, Liu Q, et al: Alterations of
axis inhibition protein 1 (AXIN1) in hepatitis B virus-related
hepatocellular carcinoma and overexpression of AXIN1 induces
apoptosis in hepatocellular cancer cells. Oncol Res. 20:281–288.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fuchs Y, Brown S, Gorenc T, et al:
Sept4/ARTS regulates stem cell apoptosis and skin regeneration.
Science. 341:286–289. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cavallo F, Feldman DR and Barchi M:
Revisiting DNA damage repair, p53-mediated apoptosis and cisplatin
sensitivity in germ cell tumors. Int J Dev Biol. 57:273–280. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huang AC, Lien JC, Lin MW, et al:
Tetrandrine induces cell death in SAS human oral cancer cells
through caspase activation-dependent apoptosis and LC3-I and LC3-II
activation-dependent autophagy. Int J Oncol. 43:485–494.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Daniel B and DeCoster MA: Quantification
of sPLA2-induced early and late apoptosis changes in neuronal cell
cultures using combined TUNEL and DAPI staining. Brain Res Brain
Res Protoc. 13:144–150. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Grzanka D, Marszałek A, Izdebska M, et al:
Actin cytoskeleton reorganization correlates with cofilin nuclear
expression and ultrastructural changes in cho aa8 cell line after
apoptosis and mitotic catastrophe induction by doxorubicin.
Ultrastruct Pathol. 35:130–138. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ndozangue-Touriguine O, Hamelin J and
Bréard J: Cytoskeleton and apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol. 76:11–18.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schietke R, Bröhl D, Wedig T, et al:
Mutations in vimentin disrupt the cytoskeleton in fibroblasts and
delay execution of apoptosis. Eur J Cell Biol. 85:1–10. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Dong Q, Zhang J, Hendricks DT and Zhao X:
GROβ and its downstream effector EGR1 regulate cisplatin-induced
apoptosis in WHCO1 cells. Oncol Rep. 25:1031–1037. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang B, Hendricks DT, Wamunyokoli F and
Parker MI: A growth-related oncogene/CXC chemokine receptor 2
autocrine loop contributes to cellular proliferation in esophageal
cancer. Cancer Res. 66:3071–3077. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nguyen TT, Kreisel FH, Frater JL and
Bartlett NL: Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma with aberrant
expression of multiple cytokeratins masquerading as metastatic
carcinoma of unknown primary. J Clin Oncol. 31:e443–e445. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yilmaz Y: Cytokeratins in hepatitis. Clin
Chim Acta. 412:2031–2036. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Weng YR, Cui Y and Fang JY: Biological
functions of cytokeratin 18 in cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 10:485–493.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Heo CK, Hwang HM, Ruem A, et al:
Identification of a mimotope for circulating anti-cytokeratin 8/18
antibody and its usage for the diagnosis of breast cancer. Int J
Oncol. 42:65–74. 2013.
|
|
16
|
Wang Y, Zhu JF, Liu YY and Han GP: An
analysis of cyclin D1, cytokeratin 5/6 and cytokeratin 8/18
expression in breast papillomas and papillary carcinomas. Diagn
Pathol. 8:82013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Song DG, Kim YS, Jung BC, et al: Parkin
induces upregulation of 40S ribosomal protein SA and
posttranslational modification of cytokeratins 8 and 18 in human
cervical cancer cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 171:1630–1638.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ekman S, Eriksson P, Bergström S, et al:
Clinical value of using serological cytokeratins as therapeutic
markers in thoracic malignancies. Anticancer Res. 27:3545–3553.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Szturmowicz M: Cytokeratins - tissue and
biochemical markers of non-small cell lung cancer. Pneumonol
Alergol Pol. 75:315–316. 2007.(In Polish).
|
|
20
|
Makino T, Yamasaki M, Takeno A, et al:
Cytokeratins 18 and 8 are poor prognostic markers in patients with
squamous cell carcinoma of the oesophagus. Br J Cancer.
101:1298–1306. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fillies T, Werkmeister R, Packeisen J, et
al: Cytokeratin 8/18 expression indicates a poor prognosis in
squamous cell carcinomas of the oral cavity. BMC Cancer. 6:102006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nagashio R, Sato Y, Matsumoto T, et al:
Significant high expression of cytokeratins 7, 8, 18, 19 in
pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinomas, compared to small
cell lung carcinomas. Pathol Int. 60:71–77. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH and Currie AR:
Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging
implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 26:239–257. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lukamowicz M, Kirsch-Volders M, Suter W
and Elhajouji A: In vitro primary human lymphocyte flow cytometry
based micronucleus assay: simultaneous assessment of cell
proliferation, apoptosis and MN frequency. Mutagenesis. 26:763–770.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|