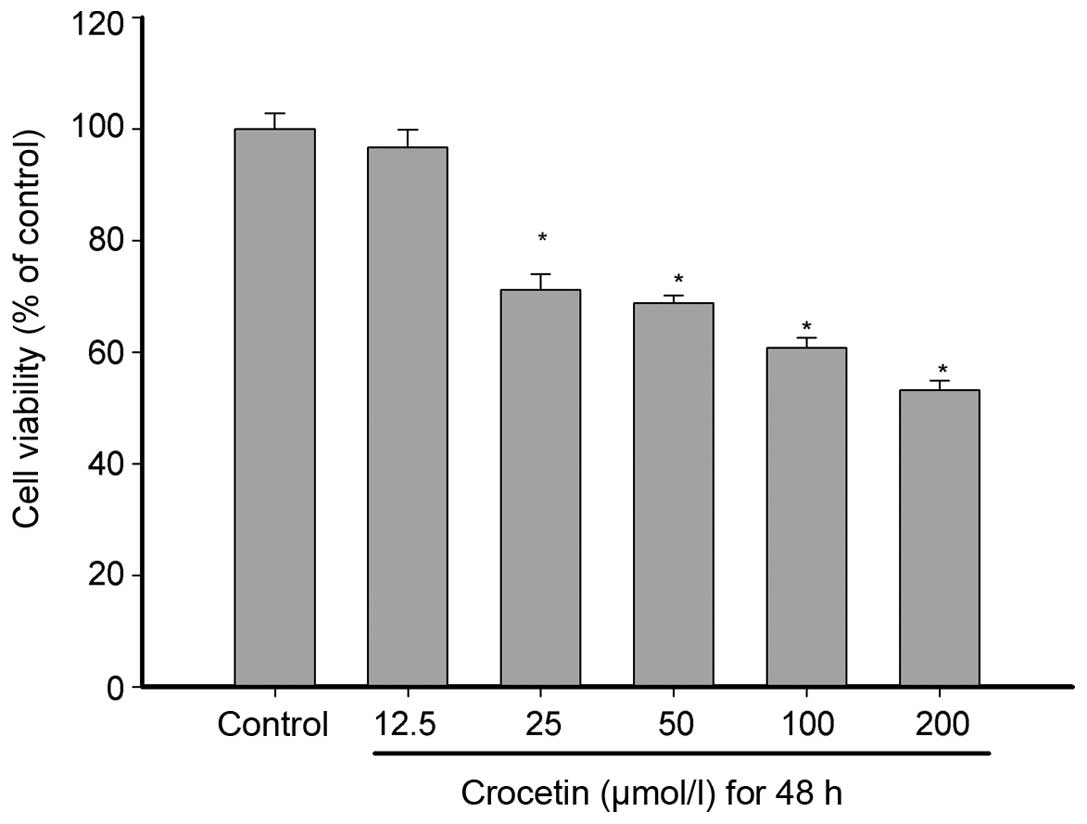
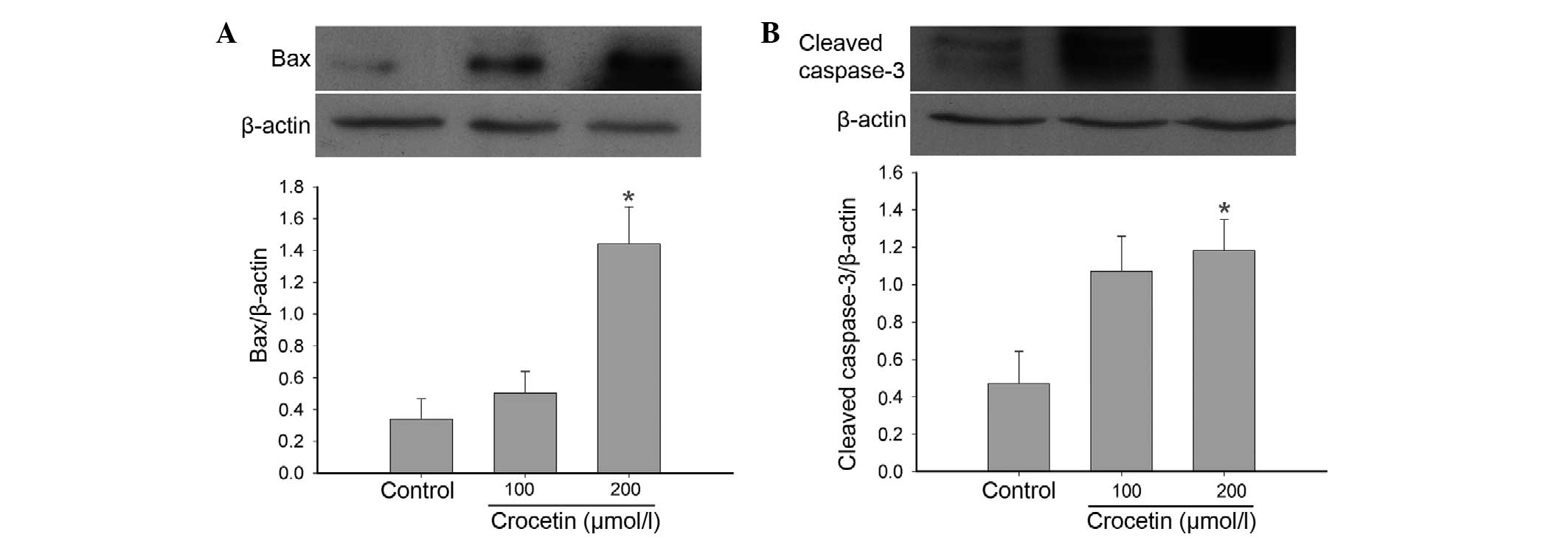
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al: Global
cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cook MB, Chow WH and Devesa SS:
Oesophageal cancer incidence in the United States by race, sex, and
histologic type, 1977–2005. Br J Cancer. 101:855–859. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Szumiło J: Epidemiology and risk factors
of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Pol Merkur Lekarski.
26:82–85. 2009.(In Polish).
|
|
4
|
Rubenstein JH and Chen JW: Epidemiology of
gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterol Clin North Am.
43:1–14. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gaur P, Kim MP and Dunkin BJ: Esophageal
cancer: Recent advances in screening, targeted therapy, and
management. J Carcinog. 13:112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Smith TJ, Ryan LM, Douglass HO Jr, et al:
Combined chemoradiotherapy vs. radiotherapy alone for early stage
squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: a study of the Eastern
Cooperative Oncology Group. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
42:269–276. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tepper J, Krasna MJ, Niedzwiecki D, et al:
Phase III trial of trimodality therapy with cisplatin,
fluorouracil, radiotherapy, and surgery compared with surgery alone
for esophageal cancer: CALGB 9781. J Clin Oncol. 26:1086–1092.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Blazeby JM, Farndon JR, Donovan J and
Alderson D: A prospective longitudinal study examining the quality
of life of patients with eso-phageal carcinoma. Cancer.
88:1781–1787. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Blazeby JM, Williams MH, Brookes ST, et
al: Quality of life measurement in patients with oesophageal
cancer. Gut. 37:505–508. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim T, Grobmyer SR, Smith R, et al:
Esophageal cancer - the five year survivors. J Surg Oncol.
103:179–183. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lin Y, Peng N, Li J, et al: Herbal
compound triptolide synergistically enhanced antitumor activity of
amino-terminal fragment of urokinase. Mol Cancer. 12:542013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang L, Lu A, Meng F, et al: Inhibitory
effects of lupeal acetate of Cortex periplocae on
N-nitrosomethylbenzylamine-induced rat esophageal tumorigenesis.
Oncol Lett. 4:231–236. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rasul A, Yu B, Khan M, et al: Magnolol, a
natural compound, induces apoptosis of SGC-7901 human gastric
adenocarcinoma cells via themitochondrial and PI3K/Akt signaling
pathways. Int J Oncol. 40:1153–1161. 2012.
|
|
14
|
Bolhassani A, Khavari A and Bathaie SZ:
Saffron and natural carotenoids: Biochemical activities and
anti-tumor effects. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1845:20–30. 2014.
|
|
15
|
Ordoudi SA, Befani CD, Nenadis N, et al:
Further examination of antiradical properties of Crocus sativus
stigmas extract rich in crocins. J Agric Food Chem. 57:3080–3086.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Higashino S, Sasaki Y, Giddings JC, et al:
Crocetin, a carotenoid from Gardenia jasminoides Ellis, protects
against hypertension and cerebral thrombogenesis in stroke-prone
spontaneously hypertensive rats. Phytother Res. 28:1315–1319. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tsantarliotou MP, Poutahidis T, Markala D,
et al: Crocetin administration ameliorates endotoxin-induced
disseminated intravascular coagulation in rabbits. Blood Coagul
Fibrinolysis. 24:305–310. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nam KN, Park YM, Jung HJ, et al:
Anti-inflammatory effects of crocin and crocetin in rat brain
microglial cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 648:110–116. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cai J, Yi FF, Bian ZY, et al: Crocetin
protects against cardiac hypertrophy by blocking MEK-ERK1/2
signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 13:909–925. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang R, Vernon K, Thomas A, et al:
Crocetin reduces activation of hepatic apoptotic pathways and
improves survival in experimental hemorrhagic shock. JPEN J
Parenter Enteral Nutr. 35:107–113. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Khan MB, Hoda MN, Ishrat T, et al:
Neuroprotective efficacy of Nardostachys jatamansi and crocetin in
conjunction with selenium in cognitive impairment. Neurol Sci.
33:1011–1020. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Bathaie SZ, Hoshyar R, Miri H and
Sadeghizadeh M: Anticancer effects of crocetin in both human
adenocarcinoma gastric cancer cells and rat model of gastric
cancer. Biochem Cell Biol. 91:397–403. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li CY, Huang WF, Wang QL, et al: Crocetin
induces cytotoxicity in colon cancer cells via p53-independent
mechanisms. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:3757–3761. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chryssanthi DG, Dedes PG, Karamanos NK, et
al: Crocetin inhibits invasiveness of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer
cells via downregulation of matrix metalloproteinases. Planta Med.
77:146–151. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Magesh V, DurgaBhavani K, Senthilnathan P,
et al: In vivo protective effect of crocetin on
benzo(a)pyrene-induced lung cancer in Swiss albino mice. Phytother
Res. 23:533–539. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Song EL, Hou YP, Yu SP, et al: EFEMP1
expression promotes angiogenesis and accelerates the growth of
cervical cancer in vivo. Gynecol Oncol. 121:174–180. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Gutheil WG, Reed G, Ray A, et al:
Crocetin: an agent derived from saffron for prevention and therapy
for cancer. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 13:173–179. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Dhar A, Mehta S, Dhar G, et al: Crocetin
inhibits pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and tumor progression
in a xenograft mouse model. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:315–323. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhong YJ, Shi F, Zheng XL, et al: Crocetin
induces cytotoxicity and enhances vincristine-induced cancer cell
death via p53-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Acta Pharmacol
Sin. 32:1529–1536. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nurse P: A long twentieth century of the
cell cycle and beyond. Cell. 100:71–78. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nurse P, Masui Y and Hartwell L:
Understanding the cell cycle. Nat Med. 4:1103–1106. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dehay C and Kennedy H: Cell-cycle control
and cortical development. Nat Rev Neurosci. 8:438–450. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kastan MB and Bartek J: Cell-cycle
checkpoints and cancer. Nature. 432:316–323. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chu G: Cellular responses to cisplatin.
The roles of DNA-binding proteins and DNA repair. J Biol Chem.
269:787–790. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Warner TF: Apoptosis. Lancet. 2:12521972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wyllie AH: The biology of cell death in
tumours. Anticancer Res. 5:131–136. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Amin A, Hamza AA, Bajbouj K, et al:
Saffron: a potential candidate for a novel anticancer drug against
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 54:857–867. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, et al: Bid, a
Bcl2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome c release from
mitochondria in response to activation of cell surface death
receptors. Cell. 94:481–490. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li P, Nijhawan D and Wang X: Mitochondrial
activation of apoptosis. Cell. 116(Suppl 2): S57–S59. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Porter AG and Jänicke RU: Emerging roles
of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 6:99–104. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Napier KJ, Scheerer M and Misra S:
Esophageal cancer: A review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, staging
workup and treatment modalities. World J Gastrointest Oncol.
6:112–120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Javle M, Ailawadhi S, Yang GY, et al:
Palliation of malignant dysphagia in esophageal cancer: a
literature-based review. J Support Oncol. 4:365–373.
3792006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Martin TA: The role of tight junctions in
cancer metastasis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 36C:224–231. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Liotta LA, Rao CN and Barsky SH: Tumor
invasion and the extracellular matrix. Lab Invest. 49:636–649.
1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Mahadevan V and Hart IR: Metastasis and
angiogenesis. Acta Oncol. 29:97–103. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Xiang M, Qian ZY, Zhou CH, et al: Crocetin
inhibits leukocyte adherence to vascular endothelial cells induced
by AGEs. J Ethnopharmacol. 107:25–31. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Umigai N, Tanaka J, Tsuruma K, et al:
Crocetin, a carotenoid derivative, inhibits VEGF-induced
angiogenesis via suppression of p38 phosphorylation. Curr Neurovasc
Res. 9:102–109. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|