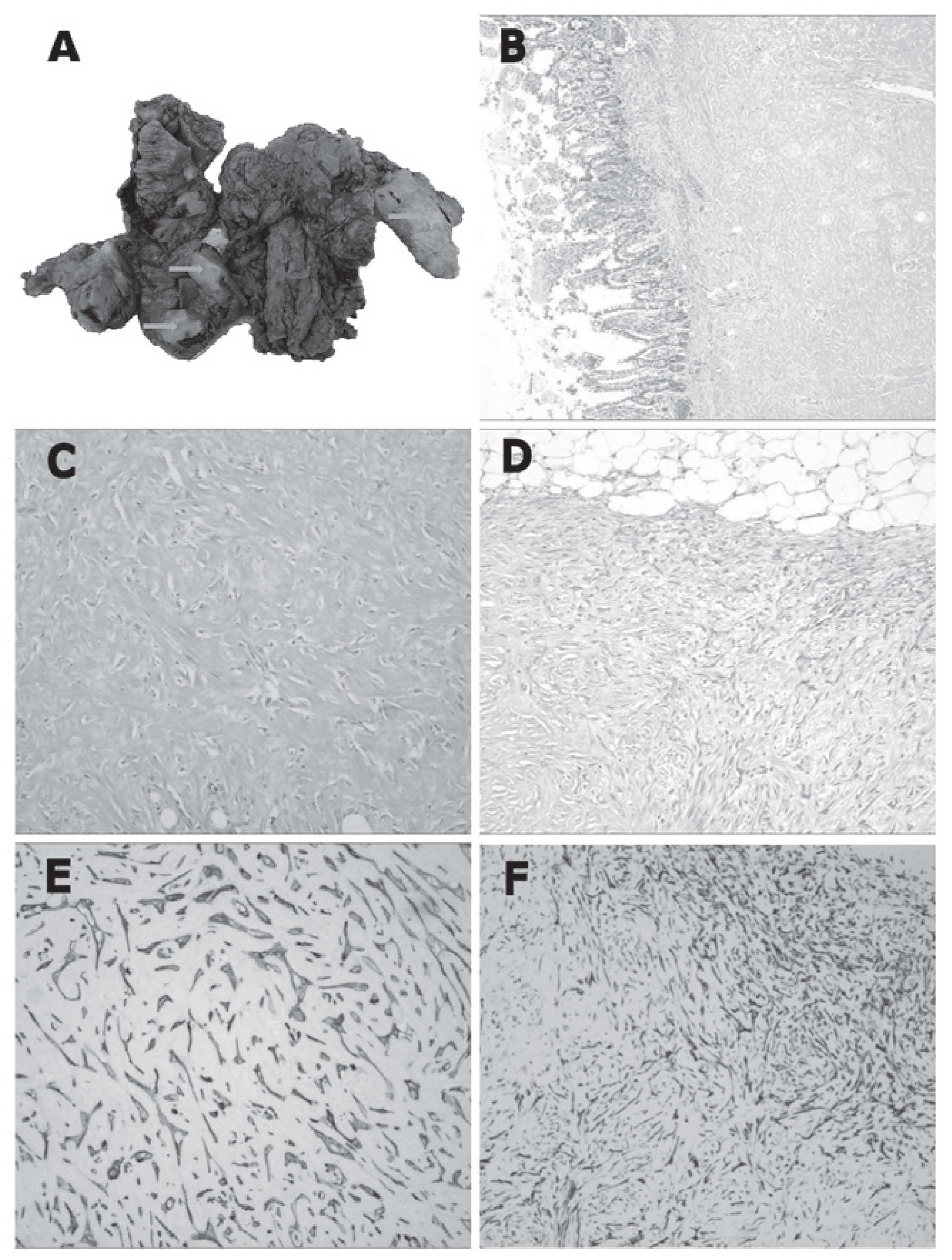
|
1
|
Yantiss RK, Nielsen GP, Lauwers GY and
Rosenberg AE: Reactive nodular fibrous pseudotumor of the
gastrointestinal tract and mesentery: a clinicopathologic study of
five cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 27:532–540. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Saglam EA, Usubütün A, Kart C, Ayhan A and
Küçükali T: Reactive nodular fibrous pseudotumor involving the
pelvic and abdominal cavity: a case report and review of
literature. Virchows Arch. 447:879–882. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yin SS, Zhang L, Cziffer-Paul A, Divino CM
and Chin E: Reactive nodular fibrous pseudotumor presenting as a
small bowel obstruction. Am Surg. 77:790–791. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Daum O, Vanecek T, Sima R, et al: Reactive
nodular fibrous pseudotumors of the gastrointestinal tract: report
of 8 cases. Int J Surg Pathol. 12:365–374. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Barak S, Wang Z and Miettinen M:
Immunoreactivity for calretinin and keratins in desmoid
fibromatosis and other myofibroblastic tumors: a diagnostic
pitfall. Am J Surg Pathol. 36:1404–1409. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
McAteer J, Huaco JC, Deutsch GH and Gow
KW: Torsed reactive nodular fibrous pseudotumor in an adolescent:
case report and review of the literature. J Pediatr Surg.
47:795–798. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gauchotte G, Bressenot A, Serradori T,
Boissel P, Plenat F and Montagne K: Reactive nodular fibrous
pseudotumor: a first report of gastric localization and
clinicopathologic review. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 33:1076–1081.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Carruthers MN, Stone JH and Khosroshahi A:
The latest on IgG4-RD: a rapidly emerging disease. Curr Opin
Rheumatol. 24:60–69. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Chetty R, Serra S, Gauchotte G, Märkl B
and Agaimy A: Sclerosing nodular lesions of the gastrointestinal
tract containing large numbers of IgG4 plasma cells. Pathology.
43:31–35. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu FY, Qi JP, Xu FL and Wu AP:
Clinicopathological and immunohistochemical analysis of
gastrointestinal stromal tumor. World J Gastroenterol.
12:4161–4165. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Novelli M, Rossi S, Rodriguez-Justo M, et
al: DOG1 and CD117 are the antibodies of choice in the diagnosis of
gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Histopathology. 57:259–270. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee CH, Liang CW and Espinosa I: The
utility of discovered on gastrointestinal stromal tumor 1 (DOG1)
antibody in surgical pathology - the GIST of it. Adv Anat Pathol.
17:222–232. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Espinosa I, Lee CH, Kim MK, et al: A novel
monoclonal antibody against DOG1 is a sensitive and specific marker
for gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 32:210–218.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hill KA, Gonzalez-Crussi F and Chou PM:
Calcifying fibrous pseudotumor versus inflammatory myofibroblastic
tumor: a histological and immunohistochemical comparison. Mod
Pathol. 14:784–790. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fetsch JF, Montgomery EA and Meis JM:
Calcifying fibrous pseudotumor. Am J Surg Pathol. 17:502–508. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Coffin CM, Watterson J, Priest JR and
Dehner LP: Extrapulmonary inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor
(inflammatory pseudotumor). A clinicopathologic and
immunohistochemical study of 84 cases. Am J Surg Pathol.
19:859–872. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shatzel J, Wooten K, Ankola A, Cheney RT,
Morrison CD and Skitzki JJ: Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of
the mesentery: a clinical dilemma. Int J Clin Oncol. 17:380–384.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Cook JR, Dehner LP, Collins MH, et al:
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) expression in the inflammatory
myofibroblastic tumor: a comparative immunohistochemical study. Am
J Surg Pathol. 25:1364–1371. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ferenc T, Wronski JW, Kopczyński J, et al:
Analysis of APC, alpha-, beta-catenins, and N-cadherin protein
expression in aggressive fibromatosis (desmoid tumor). Pathol Res
Pract. 205:311–324. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Montgomery EA and Meis JM: Nodular
fasciitis. Its morphologic spectrum and immunohistochemical
profile. Am J Surg Pathol. 15:942–948. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Montgomery E, Torbenson MS, Kaushal M,
Fisher C and Abraham SC: Beta-catenin immunohistochemistry
separates mesenteric fibromatosis from gastrointestinal stromal
tumor and sclerosing mesenteritis. Am J Surg Pathol. 26:1296–1301.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|