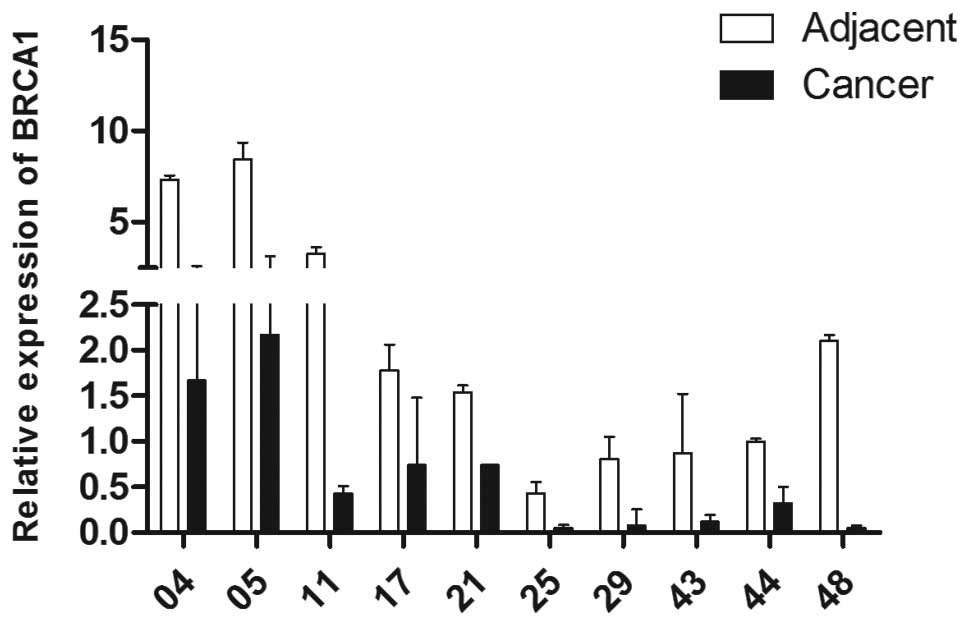
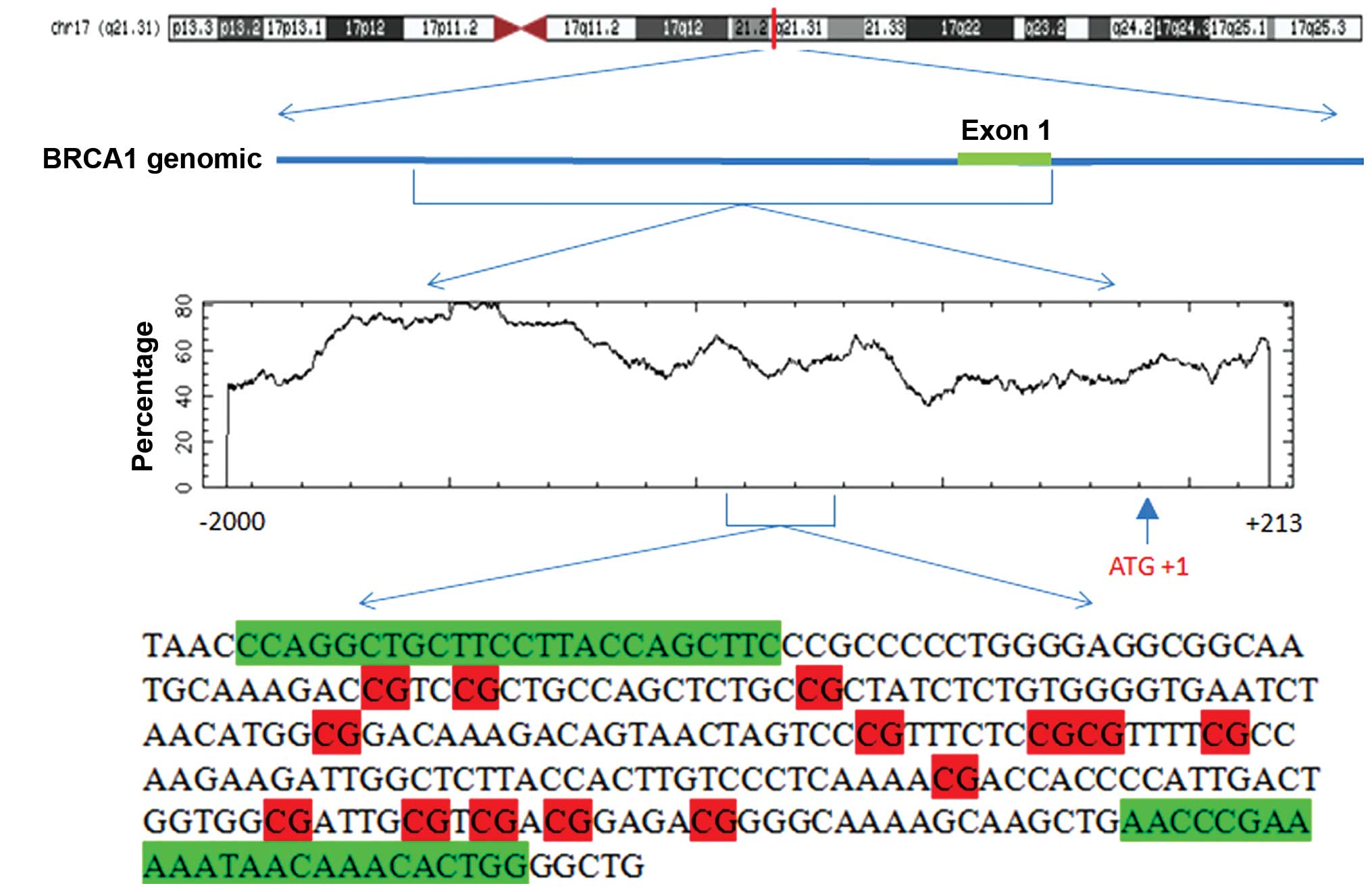
|
1
|
Hall JM, Lee MK, Newman B, et al: Linkage
of early-onset familial breast cancer to chromosome 17q21. Science.
250:1684–1689. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Deng CX and Wang RH: Roles of BRCA1 in DNA
damage repair: a link between development and cancer. Hum Mol
Genet. 12(Spec No 1): R113–R123. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xu B, St K and Kastan MB: Involvement of
BRCA1 in S-phase and G(2)-phase checkpoints after ionizing
irradiation. Mol Cell Biol. 21:3445–3450. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ralhan R, Kaur J, Kreienberg R and
Wiesmüller L: Links between DNA double strand break repair and
breast cancer: accumulating evidence from both familial and
nonfamilial cases. Cancer Lett. 248:1–17. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Miki Y, Swensen J, Shattuck-Eidens D, et
al: A strong candidate for the breast and ovarian cancer
susceptibility gene BRCA1. Science. 266:66–71. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Easton DF, Bishop DT, Ford D and Crockford
GP: Genetic linkage analysis in familial breast and ovarian cancer:
results from 214 families. The Breast Cancer Linkage Consortium. Am
J Hum Genet. 52:678–701. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Narod SA, Ford D, Devilee P, et al: An
evaluation of genetic heterogeneity in 145 breast-ovarian cancer
families. Breast Cancer Linkage Consortium. Am J Hum Genet.
56:254–264. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ford D, Easton DF, Stratton M, et al:
Genetic heterogeneity and penetrance analysis of the BRCA1 and
BRCA2 genes in breast cancer families. The Breast Cancer Linkage
Consortium. Am J Hum Genet. 62:676–689. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hedenfalk I, Ringner M, Ben-Dor A, et al:
Molecular classification of familial non-BRCA1/BRCA2 breast cancer.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:2532–2537. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Thompson ME, Jensen RA, Obermiller PS,
Page DL and Holt JT: Decreased expression of BRCA1 accelerates
growth and is often present during sporadic breast cancer
progression. Nat Genet. 9:444–450. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Magdinier F, Ribieras S, Lenoir GM,
Frappart L and Dante R: Down-regulation of BRCA1 in human sporadic
breast cancer; analysis of DNA methylation patterns of the putative
promoter region. Oncogene. 17:3169–3176. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bianco T, Chenevix-Trench G, Walsh DC,
Cooper JE and Dobrovic A: Tumour-specific distribution of BRCA1
promoter region methylation supports a pathogenetic role in breast
and ovarian cancer. Carcinogenesis. 21:147–151. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jones PA and Baylin SB: The fundamental
role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 3:415–428.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Franco R, Schoneveld O, Georgakilas AG and
Panayiotidis MI: Oxidative stress, DNA methylation and
carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 266:6–11. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Herman JG and Baylin SB: Gene silencing in
cancer in association with promoter hypermethylation. N Engl J Med.
349:2042–2054. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Das PM and Singal R: DNA methylation and
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 22:4632–4642. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Feinberg AP and Vogelstein B:
Hypomethylation distinguishes genes of some human cancers from
their normal counterparts. Nature. 301:89–92. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Choi JY, James SR, Link PA, et al:
Association between global DNA hypomethylation in leukocytes and
risk of breast cancer. Carcinogenesis. 30:1889–1897. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Robertson KD: DNA methylation and
chromatin-unraveling the tangled web. Oncogene. 21:5361–5379. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Baylin SB and Ohm JE: Epigenetic gene
silencing in cancer-a mechanism for early oncogenic pathway
addiction. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:107–116. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Esteller M, Silva JM, Dominguez G, et al:
Promoter hypermethylation and BRCA1 inactivation in sporadic breast
and ovarian tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 92:564–569. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Birgisdottir V, Stefansson OA,
Bodvarsdottir SK, Hilmarsdottir H, Jonasson JG and Eyfjord JE:
Epigenetic silencing and deletion of the BRCA1 gene in sporadic
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 8:R382006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rice JC, Massey-Brown KS and Futscher BW:
Aberrant methylation of the BRCA1 CpG island promoter is associated
with decreased BRCA1 mRNA in sporadic breast cancer cells.
Oncogene. 17:1807–1812. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Catteau A, Harris WH, Xu CF and Solomon E:
Methylation of the BRCA1 promoter region in sporadic breast and
ovarian cancer: correlation with disease characteristics. Oncogene.
18:1957–1965. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Turner N, Tutt A and Ashworth A: Hallmarks
of ‘BRCAness’ in sporadic cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:814–819. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chu D, Zhang Z, Li Y, et al: Prediction of
colorectal cancer relapse and prognosis by tissue mRNA levels of
NDRG2. Mol Cancer Ther. 10:47–56. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang J and Powell SN: The role of the
BRCA1 tumor suppressor in DNA double-strand break repair. Mol
Cancer Res. 3:531–539. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ting NS and Lee WH: The DNA double-strand
break response pathway: becoming more BRCAish than ever. DNA Repair
(Amst). 3:935–944. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
De Vargas Roditi L and Michor F:
Evolutionary dynamics of BRCA1 alterations in breast tumorigenesis.
J Theor Biol. 273:207–215. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Valentin MD, da Silva SD, Privat M,
Alaoui-Jamali M and Bignon YJ: Molecular insights on basal-like
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 134:21–30. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Warmoes M, Jaspers JE, Pham TV, et al:
Proteomics of mouse BRCA1-deficient mammary tumors identifies DNA
repair proteins with potential diagnostic and prognostic value in
human breast cancer. Mol Cell Proteomics. 11:M111.0133342012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Esteller M, Silva JM, Dominguez G, et al:
Promoter hypermethylation and BRCA1 inactivation in sporadic breast
and ovarian tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 92:564–569. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rice JC, Ozcelik H, Maxeiner P, Andrulis I
and Futscher BW: Methylation of the BRCA1 promoter is associated
with decreased BRCA1 mRNA levels in clinical breast cancer
specimens. Carcinogenesis. 21:1761–1765. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Krasteva ME, Bozhanov SS, Antov GG,
Gospodinova ZI and Angelov SG: Breast cancer patients with
hypermethylation in the promoter of BRCA1 gene exhibit favorable
clinical status. Neoplasma. 59:85–91. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Xu X, Gammon MD, Zhang Y, et al: BRCA1
promoter methylation is associated with increased mortality among
women with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 115:397–404.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Matros E, Wang ZC, Lodeiro G, Miron A,
Iglehart JD and Richardson AL: BRCA1 promoter methylation in
sporadic breast tumors: relationship to gene expression profiles.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 91:179–186. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li S, Rong M and Iacopetta B: DNA
hypermethylation in breast cancer and its association with
clinicopathological features. Cancer Lett. 237:272–280. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Krasteva ME, Bozhanov SS, Antov GG,
Gospodinova ZI and Angelov SG: Breast cancer patients with
hypermethylation in the promoter of BRCA1 gene exhibit favorable
clinical status. Neoplasma. 59:85–91. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|