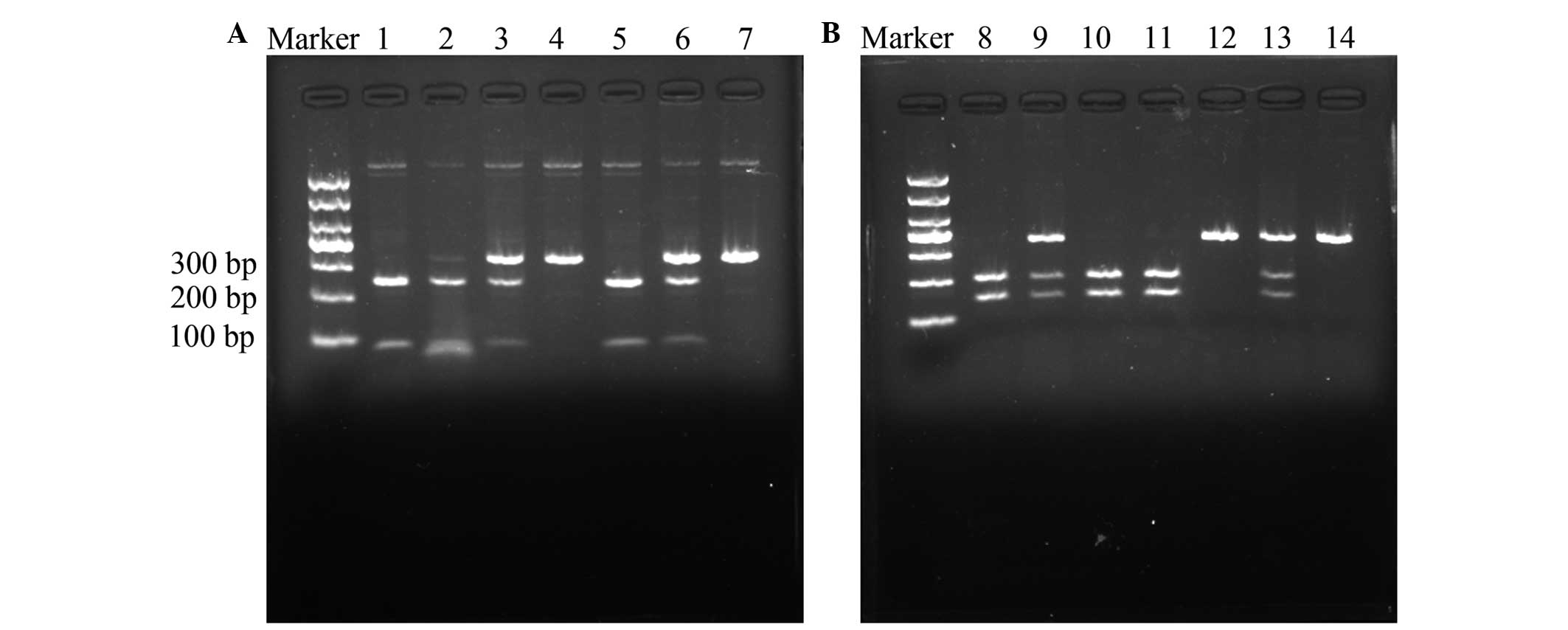
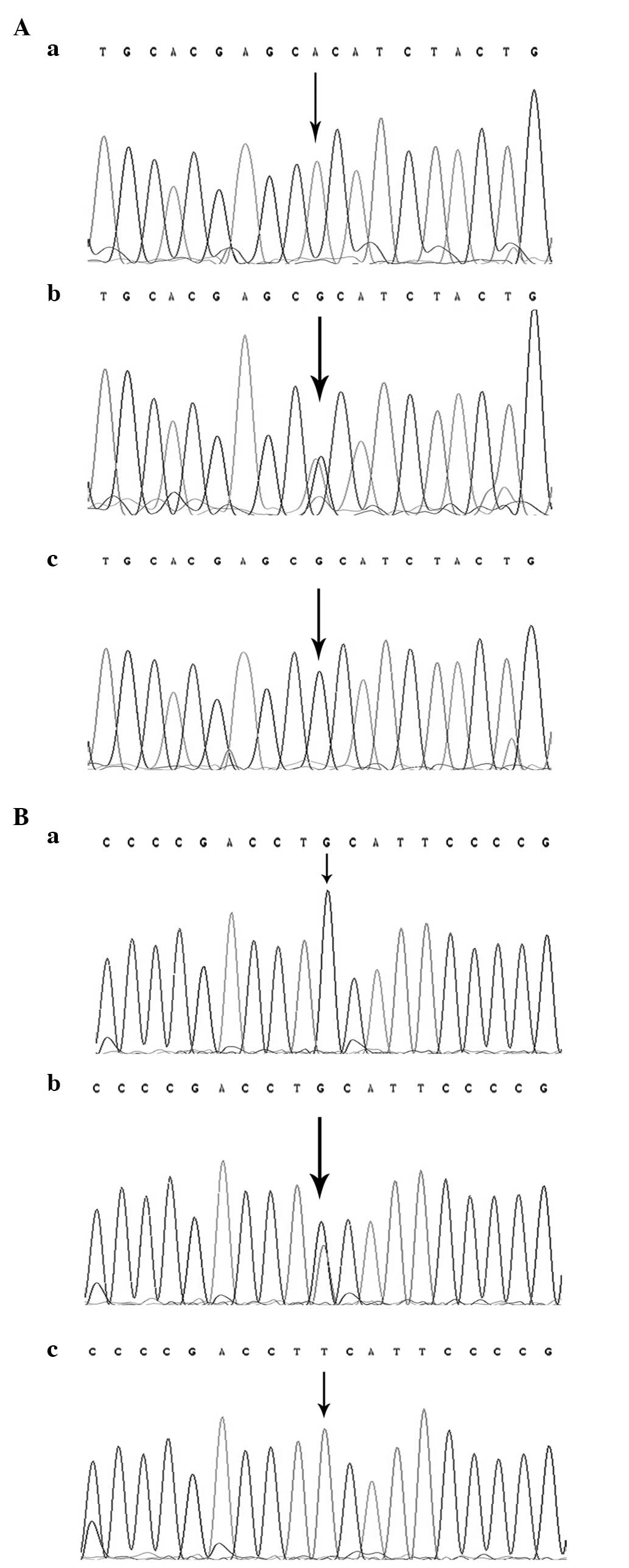
|
1
|
Danaei G, Vander Hoorn S, Lopez AD, Murray
CJ and Ezzati M: Comparative Risk Assessment collaborating group
(Cancers): Causes of cancer in the world: Comparative risk
assessment of nine behavioural and environmental risk factors.
Lancet. 366:1784–1793. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pisani P, Parkin DM, Bray F and Ferlay J:
Erratum: Estimates of the worldwide mortality from 25 cancers in
1990. Int. J. Cancer. 83:18–29. 1999.
Int J Cancer. 83:870–873. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Parkin DM: International variation.
Oncogene. 23:6329–6340. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu MS, Chen CJ and Lin JT:
Host-environment interactions: Their impact on progression from
gastric inflammation to carcinogenesis and on development of new
approaches to prevent and treat gastric cancer. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 14:1878–1882. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhu H, Yang L, Zhou B, Yu R, Tang N and
Wang B: Myeloperoxidase G-463A polymorphism and the risk of gastric
cancer: A case-control study. Carcinogenesis. 27:2491–2496. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sun Q, Gu H, Zeng Y, Xia Y, Wang Y, Jing
Y, Yang L and Wang B: Hsa-mir-27a genetic variant contributes to
gastric cancer susceptibility through affecting miR-27a and target
gene expression. Cancer Sci. 101:2241–2247. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang L, Gu HJ, Zhu HJ, Sun QM, Cong RH,
Zhou B, Tang NP and Wang B: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2
G-418C polymorphism is associated with an increased risk of gastric
cancer in a Chinese population. Eur J Surg Oncol. 34:636–641. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang L, Zhu H, Zhou B, Gu H, Yan H, Tang
N, Dong H, Sun Q, Cong R, Chen G, et al: The association between
the survivin C-31G polymorphism and gastric cancer risk in a
Chinese population. Dig Dis Sci. 54:1021–1028. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Suzuki K, Sahara H, Okada Y, Yasoshima T,
Hirohashi Y, Nabeta Y, Hirai I, Torigoe T, Takahashi S, Matsuura A,
et al: Identification of natural antigenic peptides of a human
gastric signet ring cell carcinoma recognized by HLA-A31-restricted
cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 163:2783–2791. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ishigami S, Natsugoe S, Nakajo A, Arigami
T, Kitazono M, Okumura H, Matsumoto M, Uchikado Y, Setoyama T, et
al: HLA-class I expression in gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol.
97:605–608. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ferris RL, Hunt JL and Ferrone S: Human
leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I defects in head and neck cancer:
Molecular mechanisms and clinical significance. Immunol Res.
33:113–133. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Grommé M and Neefjes J: Antigen
degradation or presentation by MHC class I molecules via classical
and non-classical pathways. Mol Immunol. 39:181–202. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Song L, Ma N, Han L, Yan H, Yan B, Yuan Z
and Cao B: Association between LMP2/LMP7 genetic variability and
the metastasis risk of ovarian cancer in Chinese women in Beijing.
Hum Immunol. 75:239–244. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fellerhoff B, Gu S, Laumbacher B, Nerlich
AG, Weiss EH, Glas J, Kopp R, Johnson JP and Wank R: The LMP7-K
allele of the immunoproteasome exhibits reduced transcript
stability and predicts high risk of colon cancer. Cancer Res.
71:7145–7154. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cao B, Tian X, Li Y, Jiang P, Ning T, Xing
H, Zhao Y, Zhang C, Shi X, Chen D, et al: LMP7/TAP2 gene
polymorphisms and HPV infection in esophageal carcinoma patients
from a high incidence area in China. Carcinogenesis. 26:1280–1284.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu H, Yang L, Zhou B, Yu R, Tang N and
Wang B: Myeloperoxidase G-463A polymorphism and the risk of gastric
cancer: A case-control study. Carcinogenesis. 27:2491–2496. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Stephens M and Donnelly P: A comparison of
bayesian methods for haplotype reconstruction from population
genotype data. Am J Hum Genet. 73:1162–1169. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hemminki K, Försti A and Bermejo JL:
Gene-environment interactions in cancer: do they exist? Ann NY Acad
Sci. 1076:137–148. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Basler M, Kirk CJ and Groettrup M: The
immunoproteasome in antigen processing and other immunological
functions. Curr Opin Immunol. 25:74–80. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hussong SA, Roehrich H, Kapphahn RJ,
Maldonado M, Pardue MT and Ferrington DA: A novel role for the
immunoproteasome in retinal function. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
52:714–723. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee YM, Leu SY, Chiang H, Fung CP and Liu
WT: Human papillomavirus type 18 in colorectal cancer. J Microbiol
Immunol Infect. 34:87–91. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lv Y, Yan B, Yang H, Liu J, Zhong W, Li K,
Chen Z and Xu C: LMP2/LMP7 gene variant: A risk factor for
intestinal Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in the Chinese
population. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:1145–1150. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Camarena A, Aquino-Galvez A,
Falfán-Valencia R, Sánchez G, Montaño M, Ramos C, Juárez A,
García-de-Alba C, Granados J and Selman M: PSMB8 (LMP7) but not
PSMB9 (LMP2) gene polymorphisms are associated to pigeon breeder's
hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Respir Med. 104:889–894. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ozbas-Gerceker F, Bozman N, Kok S,
Pehlivan M, Yilmaz M, Pehlivan S and Oguzkan-Balci S: Association
of an LMP2 polymorphism with acute myeloid leukemia and multiple
myeloma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:6399–6402. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yu Z, Liu Q, Huang C, Wu M and Li G: The
interleukin 10 −819C/T polymorphism and cancer risk: A HuGE review
and meta-analysis of 73 studies including 15,942 cases and 22,336
controls. OMICS. 17:200–214. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang YM, Zhou XC, Xu Z and Tang CJ:
Meta-analysis of epidemiological studies of association of two
polymorphisms in the interleukin-10 gene promoter and colorectal
cancer risk. Genet Mol Res. 11:3389–3397. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kang JK, Yoon SJ, Kim NK and Heo DS: The
expression of MHC class I, TAP1/2, and LMP2/7 gene in human gastric
cancer cell lines. Int J Oncol. 16:1159–1163. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Milne AN, Carvalho R, Morsink FM, Musler
AR, de Leng WW, Ristimäki A and Offerhaus GJ: Early-onset gastric
cancers have a different molecular expression profile than
conventional gastric cancers. Mod Pathol. 19:564–572. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kelley JR and Duggan JM: Gastric cancer
epidemiology and risk factors. J Clin Epidemiol. 56:1–9. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gu H, Yang L, Sun Q, Zhou B, Tang N, Cong
R, Zeng Y and Wang B: Gly82Ser polymorphism of the receptor for
advanced glycation end products is associated with an increased
risk of gastric cancer in a Chinese population. Clin Cancer Res.
14:3627–3632. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lauren P: The two histological main types
of gastric carcinoma: Diffuse and so-called intestinal-type
carcinoma An attempt at a histo-clinical classification. Acta
Pathol Microbiol Scand. 64:31–49. 1965.PubMed/NCBI
|