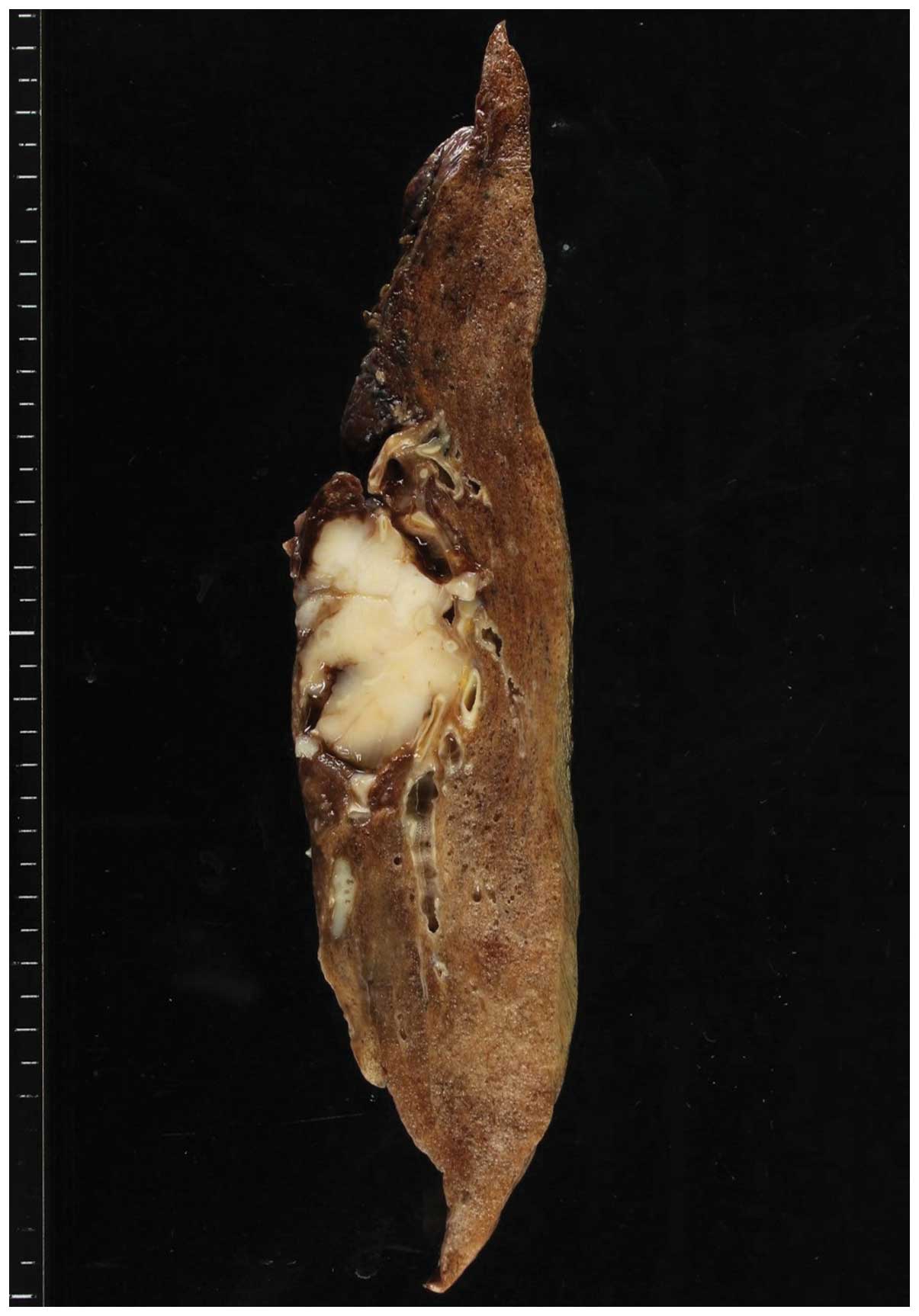
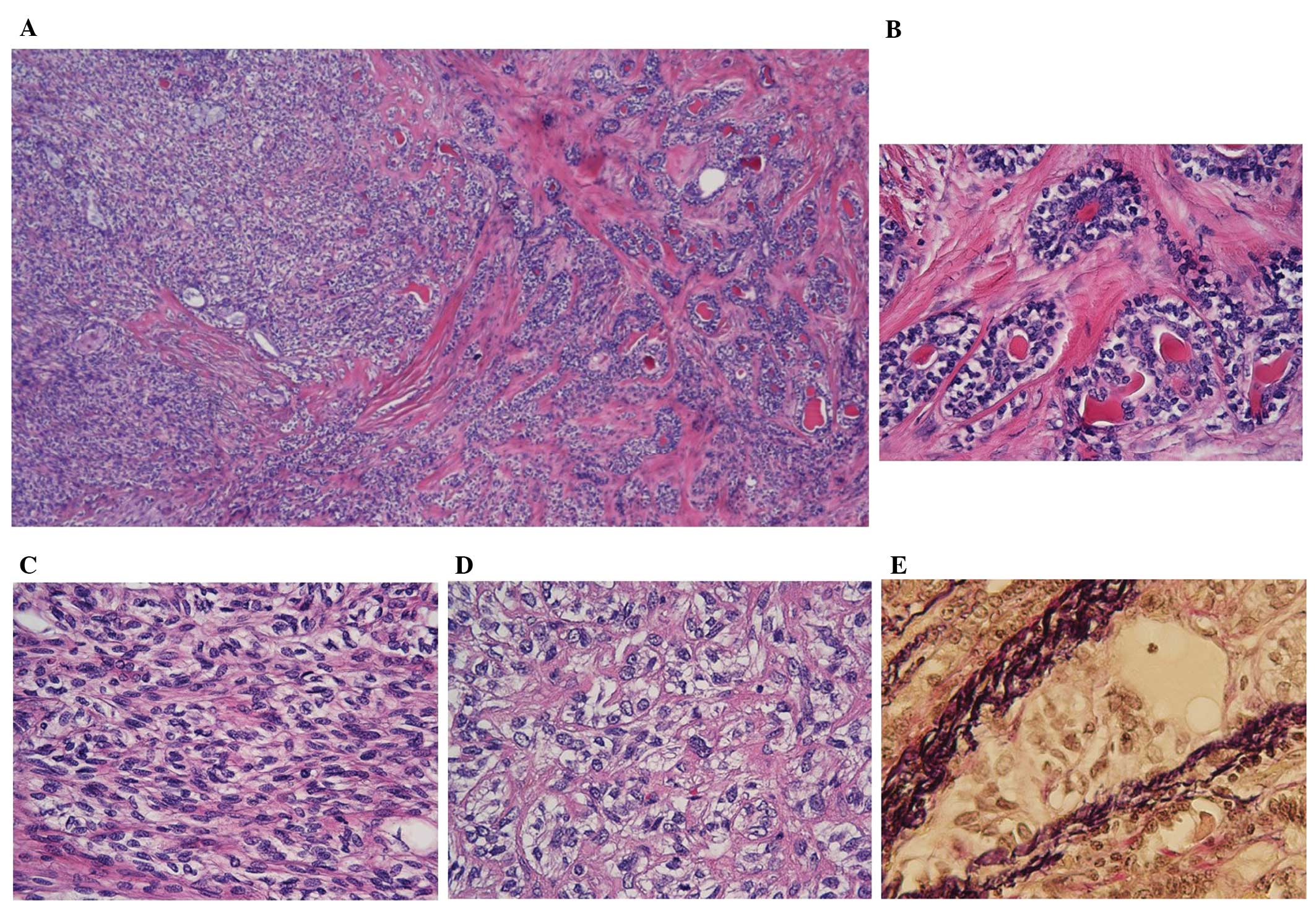
|
1
|
Kang DY, Yoon YS, Kim HK, et al: Primary
salivary gland-type lung cancer: surgical outcomes. Lung Cancer.
72:250–254. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhu F, Liu Z, Hou Y, et al: Primary
salivary gland-type lung cancer: clinicopathological analysis of 88
cases from China. J Thorac Oncol. 8:1578–1584. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Song DH, Choi IH, Ha SY, et al:
Epithelial-myoepthelial carcinoma of the tracheobronchial tree: the
prognostic role of myoepithelial cells. Lung Cancer. 83:416–419.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Donath K, Seifert G and Schmitz R:
Diagnosis and ultrastructure of the tubular carcinoma of salivary
gland ducts. Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma of the intercalated
ducts. Virchows Arch A Pathol Pathol Anat. 356:16–31. 1972.(In
German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fonseca I and Soares J:
Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinomaWorld Health Organization
Classification of Tumours: Pathology and Genetics of Head and Neck
Tumours. Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart P and Sidransky D: 3rd. IARC
Press; Lyon, France: pp. 225–226. 2005
|
|
6
|
Corio RL, Sciubba JJ, Brannon RB and
Batsakis JG: Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma of intercalated
duct origin. A clinicopathologic and ultrastructural assessment of
sixteen cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 53:280–287. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Moran CA: Primary salivary gland-type
tumors of the lung. Semin Diagn Pathol. 12:106–122. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pelosi G, Fraggetta F, Maffini F, Solli P,
Cavallon A and Viale G: Pulmonary epithelial-myoepithelial tumor of
unproven malignant potential: report of a case and review of the
literature. Mod Pathol. 14:521–526. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nguyen CV, Suster S and Moran CA:
Pulmonary epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma: a clinicopathologic
and immunohistochemical study of 5 cases. Hum Pathol. 40:366–373.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nagao T: “Dedifferentiation” and
high-grade transformation in salivary gland carcinomas. Head Neck
Pathol. 7:(Suppl 1). S37–S47. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Seethala RR, Barnes EL and Hunt JL:
Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma: a review of the
clinicopathologic spectrum and immunophenotypic characteristics in
61 tumors of the salivary glands and upper aerodigestive tract. Am
J Surg Pathol. 31:44–57. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Costa AF, Altemani A and Hermsen M:
Current concepts on dedifferentiation/high-grade transformation in
salivary gland tumors. Patholog Res Int. 2011:3259652011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Baker AR, Ohanessian SE, Adil E, Crist HS,
Goldenberg D and Mani H: Dedifferentiated epithelial-myoepithelial
carcinoma: analysis of a rare entity based on a case report and
literature review. Int J Surg Pathol. 21:514–519. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Arif F, Wu S, Andaz S and Fox S: Primary
epithelial myoepithelial carcinoma of lung, reporting of a rare
entity, its molecular histogenesis and review of the literature.
Rep pathol. 2012:3194342012.
|
|
15
|
Yang S and Chen X:
Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma with high grade transformation.
Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 41:810–813. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Henley JD, Geary WA, Jackson CL, Wu CD and
Gnepp DR: Dedifferentiated acinic cell carcinoma of the parotid
gland: A distinct rarely described entity. Hum Pathol. 28:869–873.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Di Palma S, Corletto V, Lavarino C,
Birindelli S and Pilotti S: Unilateral aneuploid dedifferentiated
acinic cell carcinoma associated with bilateral-low grade diploid
acinic cell carcinoma of the parotid gland. Virchows Arch.
434:361–365. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Casimiro MC and Pestell RG: Cyclin d1
induces chromosomal instability. Oncotarget. 3:224–225.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Casimiro MC, Crosariol M, Loro E, et al:
ChIP sequencing of cyclin D1 reveals a transcriptional role in
chromosomal instability in mice. J Clin Invest. 122:833–843. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Roy P, Bullock MJ, Perez-Ordoñez B,
Dardick I and Weinreb I: Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma with
high grade transformation. Am J Surg Pathol. 34:1258–1265. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cheuk W and Chan JK: Advances in salivary
gland pathology. Histopathology. 51:1–20. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cho KJ, el-Naggar AK, Ordonez NG, Luna MA,
Austin J and Batsakis JG: Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma of
salivary glands. A clinicopathologic, DNA flow cytometric, and
immunohistochemical study of Ki-67 and HER-2/neu oncogene. Am J
Clin Pathol. 103:432–437. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Luna MA, Ordonez NG, Mackay B, Batsakis JG
and Guillamondegui O: Salivary epithelial-myoepithelial carcinomas
of intercalated ducts: a clinical, electron microscopic, and
immunocytochemical study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol.
59:482–490. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|