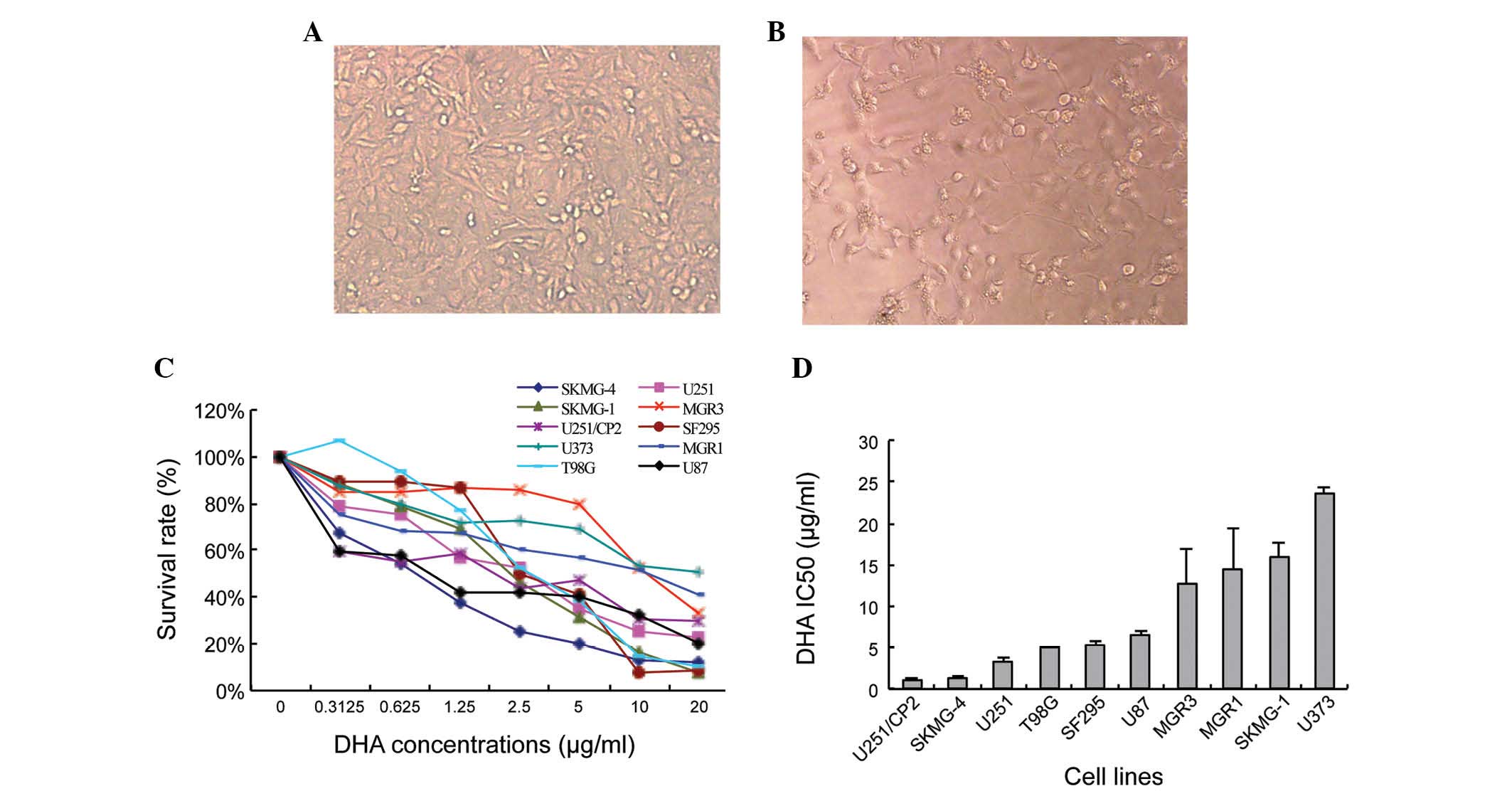
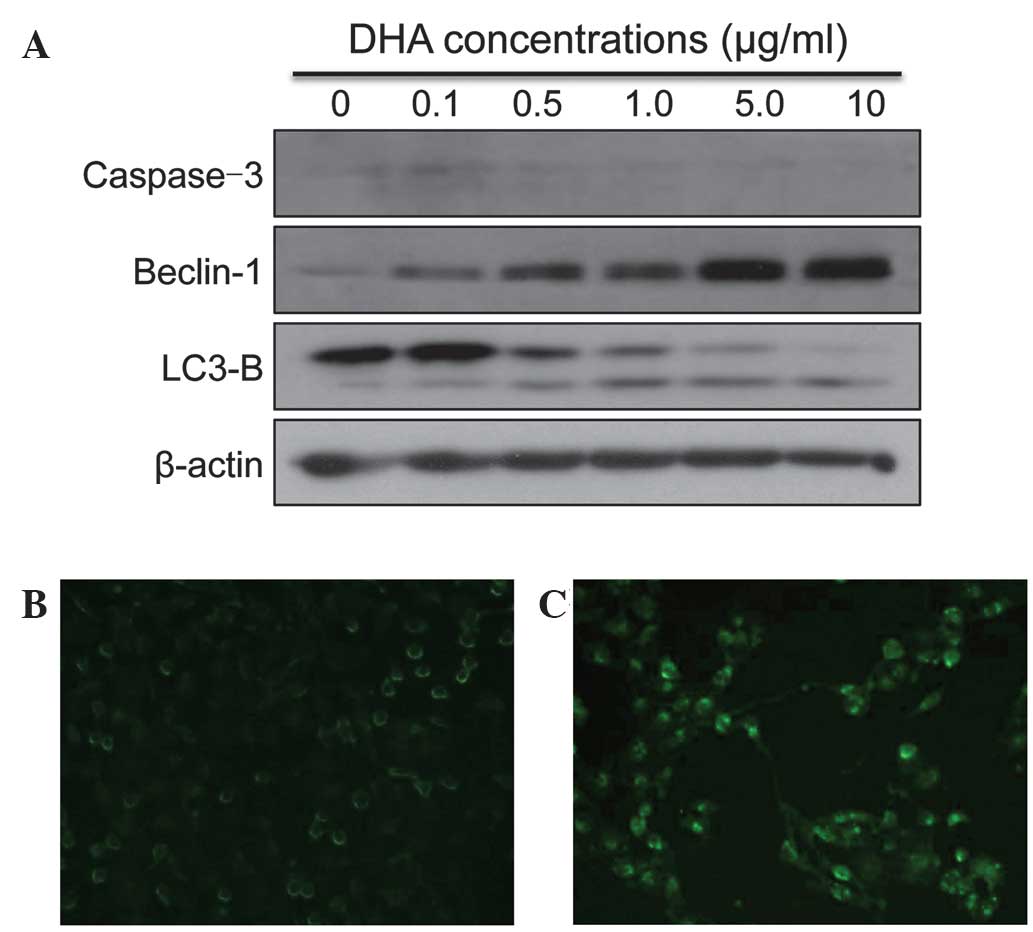
|
1
|
Smoll NR, Gautschi OP, Schatlo B, Schaller
K and Weber DC: Relative survival of patients with supratentorial
low-grade gliomas. Neuro Oncol. 14:1062–1069. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nakazato Y: The 4th edition of WHO
classification of tumours of the central nervous system published
in 2007. No Shinkei Geka. 36:473–491. 2008.(In Japanese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al:
National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group:
Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for
glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Davis FG, McCarthy BJ, Freels S, Kupelian
V and Bondy ML: The conditional probability of survival of patients
with primary malignant brain tumors: Surveillance, epidemiology and
end results (SEER) data. Cancer. 85:485–491. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Giese A, Bjerkvig R, Berens ME and
Westphal M: Cost of migration: Invasion of malignant gliomas and
implications for treatment. J Clin Oncol. 21:1624–1636. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, et al:
European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain
Tumour and Radiation Oncology Groups; National Cancer Institute of
Canada Clinical Trials Group: Effects of radiotherapy with
concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on
survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year
analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 10:459–466.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Klayman DL: Qinghaosu (artemisinin): An
antimalarial drug from China. Science. 228:1049–1055. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qaderi A, Dadgar N, Mansouri H, Alavi SE,
Esfahani MK and Akbarzadeh A: Modeling and prediction of
cytotoxicity of artemisinin for treatment of the breast cancer by
using artificial neural networks. Springerplus. 2:3402013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim SH, Chun SY and Kim TS:
Interferon-alpha enhances artemisinin-induced differentiation of
HL-60 leukemia cells via a PKC alpha/ERK pathway. Eur J Pharmacol.
587:65–72. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sadava D, Phillips T, Lin C and Kane SE:
Transferrin overcomes drug resistance to artemisinin in human
small-cell lung carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 179:151–156. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schmuck G and Haynes RK: Establishment of
an in vitro screening model for neurodegeneration induced by
antimalarial drugs of the artemisinin-type. Neurotox Res. 2:37–49.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ontikatze T, Rudner J, Handrick R, Belka C
and Jendrossek V: Dihydroartemisinin is a hypoxia-active
anti-cancer drug in colorectal carcinoma cells. Front Oncol.
4:1162014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li YJ, Zhou JH, Du XX, et al:
Dihydroartemisinin accentuates the anti-tumor effects of
photodynamic therapy via inactivation of NF-κB in Eca109 and Ec9706
esophageal cancer cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 33:1527–1536. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Park J, Lai HC, Singh M, Sasaki T and
Singh NP: Development of a dihydroartemisinin-resistant Molt-4
leukemia cell line. Anticancer Res. 34:2807–2810. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gu HM, Warhurst DC and Peters W: Uptake of
[3H] dihydroartemisinine by erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium
falciparum in vitro. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 78:265–270. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xie LH, Li Q, Zhang J and Weina PJ:
Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and mass balance of
radiolabeled dihydroartemisinin in male rats. Malar J. 8:1122009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim SJ, Kim MS, Lee JW, et al:
Dihydroartemisinin enhances radiosensitivity of human glioma cells
in vitro. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 132:129–135. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang XJ, Li CT, Zhang WP, Lu YB, Fang SH
and Wei EQ: Dihydroartemisinin potentiates the cytotoxic effect of
temozolomide in rat C6 glioma cells. Pharmacology. 82:1–9. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun YC, Wang J, Guo CC, et al: MiR-181b
sensitizes glioma cells to teniposide by targeting MDM2. BMC
Cancer. 14:6112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Naito S, von Eschenbach AC, Giavazzi R and
Fidler IJ: Growth and metastasis of tumor cells isolated from a
human renal cell carcinoma implanted into different organs of nude
mice. Cancer Res. 46:4109–4115. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Buckner JC: Factors influencing survival
in high-grade gliomas. Semin Oncol. 30(Suppl 19): S10–S14.
2003.
|
|
22
|
Curran WJ Jr, Scott CB, Horton J, et al:
Recursive partitioning analysis of prognostic factors in three
Radiation Therapy Oncology Group malignant glioma trials. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 85:704–710. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
De Angelis LM: Brain tumors. N Engl J Med.
344:114–123. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sai K, Li WY, Chen YS, et al: Triptolide
synergistically enhances temozolomide-induced apoptosis and
potentiates inhibition of NF-κB signaling in glioma initiating
cells. Am J Chin Med. 42:485–503. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fu J, Yang QY, Sai K, et al: TGM2
inhibition attenuates ID1 expression in CD44-high glioma-initiating
cells. Neuro Oncol. 15:1353–1365. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li Y and Wu YL: An over four millennium
story behind qinghaosu (artemisinin) - a fantastic antimalarial
drug from a traditional Chinese herb. Curr Med Chem. 10:2197–2230.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rasheed SA, Efferth T, Asangani IA and
Allgayer H: First evidence that the antimalarial drug artesunate
inhibits invasion and in vivo metastasis in lung cancer by
targeting essential extracellular proteases. Int J Cancer.
127:1475–1485. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Efferth T, Sauerbrey A, Olbrich A, et al:
Molecular modes of action of artesunate in tumor cell lines. Mol
Pharmacol. 64:382–394. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Stockwin LH, Han B, Yu SX, et al:
Artemisinin dimer anticancer activity correlates with
heme-catalyzed reactive oxygen species generation and endoplasmic
reticulum stress induction. Int J Cancer. 125:1266–1275. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Scherz-Shouval R and Elazar Z: ROS,
mitochondria and the regulation of autophagy. Trends Cell Biol.
17:422–427. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Z, Hu W, Zhang JL, Wu XH and Zhou HJ:
Dihydroartemisinin induces autophagy and inhibits the growth of
iron-loaded human myeloid leukemia K562 cells via ROS toxicity.
FEBS Open Bio. 2:103–112. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Efferth T, Briehl MM and Tome ME: Role of
antioxidant genes for the activity of artesunate against tumor
cells. Int J Oncol. 23:1231–1235. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kanzawa T, Germano IM, Komata T, Ito H,
Kondo Y and Kondo S: Role of autophagy in temozolomide-induced
cytotoxicity for malignant glioma cells. Cell Death Differ.
11:448–457. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|