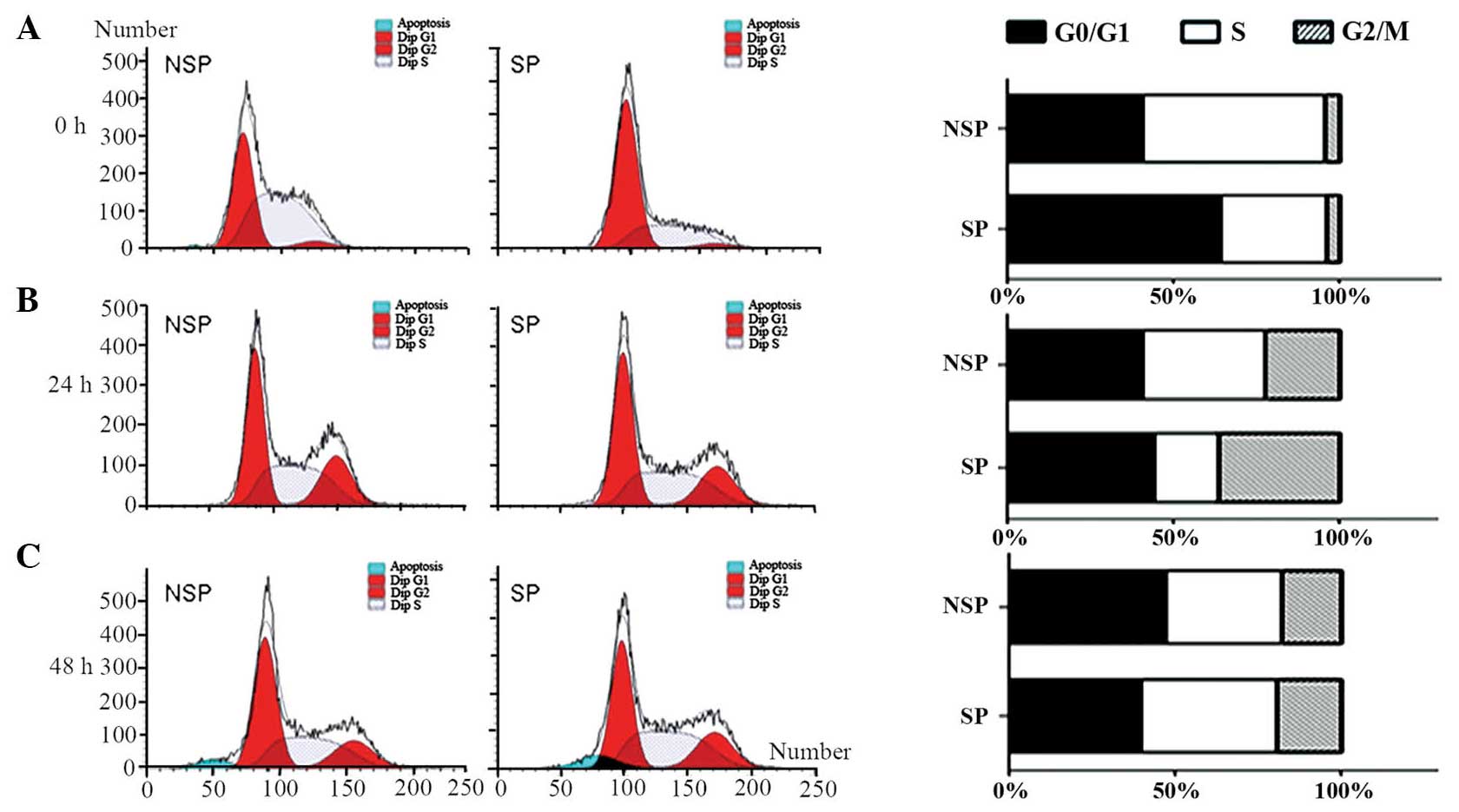
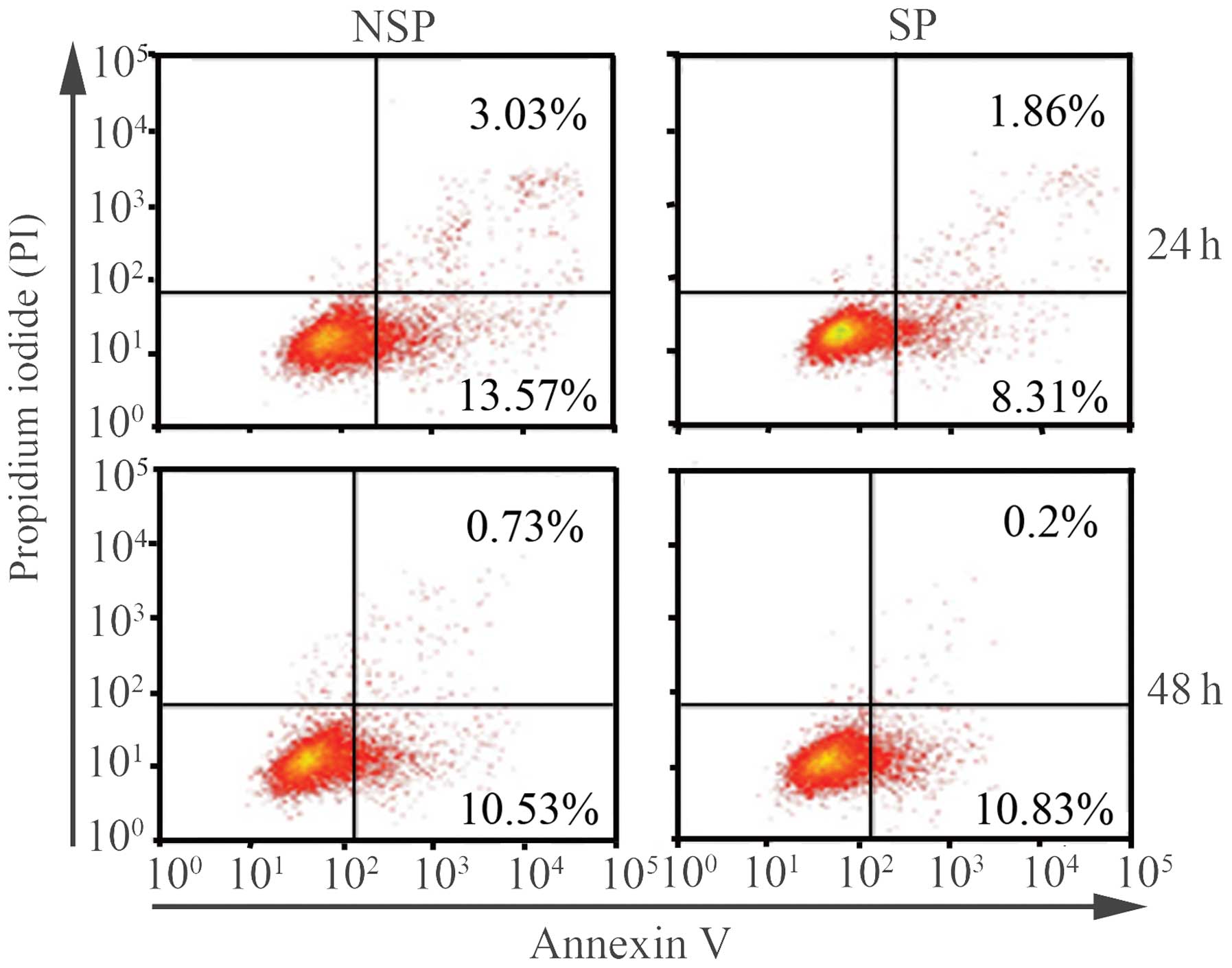
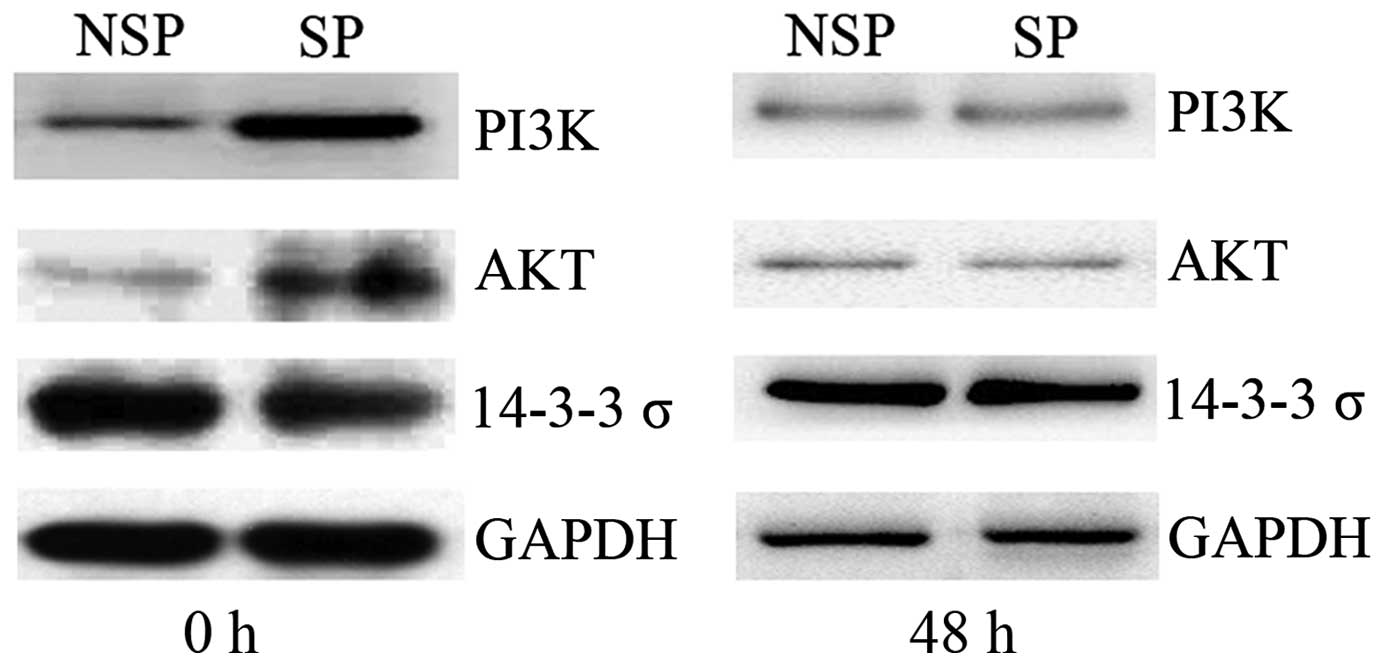
|
1
|
Kristoffersen K, Villingshøj M, Poulsen HS
and Stockhausen MT: Level of Notch activation determines the effect
on growth and stem cell-like features in glioblastoma multiforme
neurosphere cultures. Cancer Biol Ther. 14:625–637. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cetin I and Topcul M: Cancer stem cells in
oncology. J BUON. 17:644–648. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Muñoz P, Iliou MS and Esteller M:
Epigenetic alterations involved in cancer stem cell reprogramming.
Mol Oncol. 6:620–636. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mitsutake N, Iwao A, Nagai K, et al:
Characterization of side population in thyroid cancer cell lines:
Cancer stem-like cells are enriched partly but not exclusively.
Endocrinology. 148:1797–1803. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cao JX, Cui YX, Long ZJ, et al:
Pluripotency-associated genes in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma
CNE-2 cells are reactivated by a unique epigenetic
sub-microenvironment. BMC Cancer. 10:682010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hiraga T, Ito S and Nakamura H: Side
population in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells exhibits cancer
stem cell-like properties without higher bone-metastatic potential.
Oncol Rep. 25:289–296. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang J, Guo LP, Chen LZ, Zeng YX and Lu
SH: Identification of cancer stem cell-like side population cells
in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line. Cancer Res.
67:3716–3724. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kong QL, Hu LJ, Cao JY, et al:
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded LMP2A induces an epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and increases the number of side population stem-like
cancer cells in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS Pathog.
6:e10009402010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liang Y, Zhong Z, Huang Y, Deng W, Cao J,
Tsao G, Liu Q, Pei D, Kang T and Zeng YX: Stem-like cancer cells
are inducible by increasing genomic instability in cancer cells. J
Biol Chem. 285:4931–4940. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang HB, Ren CP, Yang XY, Wang L, Li H,
Zhao M, Yang H and Yao KT: Identification of label-retaining cells
in nasopharyngeal epithelia and nasopharyngeal carcinoma tissues.
Histochem Cell Biol. 127:347–354. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Y, Peng J, Zhang H, Zhu Y, Wan L,
Chen J, Chen X, Lin R, Li H, Mao X and Jin K: Notch1 signaling is
activated in cells expressing embryonic stem cell proteins in human
primary nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.
39:157–166. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xia H, Cheung WK, Sze J, Lu G, Jiang S,
Yao H, Bian XW, Poon WS, Kung HF and Lin MC: miR-200a regulates
epithelial-mesenchymal to stem-like transition via ZEB2 and
beta-catenin signaling. J Biol Chem. 285:36995–37004. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Diaz-Moralli S, Tarrado-Castellarnau M,
Miranda A and Cascante M: Targeting cell cycle regulation in cancer
therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 138:255–271. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Williams GH and Stoeber K: The cell cycle
and cancer. J Pathol. 226:352–364. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Aarts M, Linardopoulos S and Turner NC:
Tumour selective targeting of cell cycle kinases for cancer
treatment. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 13:529–535. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sankari SL, Masthan KM, Babu NA,
Bhattacharjee T and Elumalai M: Apoptosis in cancer - an update.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:4873–4878. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zielinski RR, Eigl BJ and Chi KN:
Targeting the apoptosis pathway in prostate cancer. Cancer J.
19:79–89. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Beesoo R, Neergheen-Bhujun V, Bhagooli R
and Bahorun T: Apoptosis inducing lead compounds isolated from
marine organisms of potential relevance in cancer treatment. Mutat
Res Fundam Mol Mech Mutagen. 768:84–97. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jia LT, Chen SY and Yang AG: Cancer gene
therapy targeting cellular apoptosis machinery. Cancer Treat Rev.
38:868–876. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Qiao M, Sheng S and Pardee AB: Metastasis
and AKT activation. Cell Cycle. 7:2991–2996. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wagner EF and Nebreda AR: Signal
integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:537–549. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ho JH: An epidemiologic and clinical study
of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
4:182–198. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou Y, Wang W, Zheng D, Peng S, Xiong W,
Ma J, Zeng Z, Wu M, Zhou M, Xiang J, et al: Risk of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma associated with polymorphic lactotransferrin haplotypes.
Med Oncol. 29:1456–1462. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhou Y, Zeng Z, Zhang W, Xiong W, Wu M,
Tan Y, Yi W, Xiao L, Li X, Huang C, et al: Lactotransferrin, a
candidate tumor suppressor, deficient expression in human
nasopharyngeal carcinoma and inhibits NPC cell proliferation by
modulating the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Int J
Cancer. 123:2065–2072. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou Y, Zeng Z, Zhang W, Xiong W, Li X,
Zhang B, Yi W, Xiao L, Wu M, Shen S, et al: Identification of
candidate molecular markers of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by
microarray analysis of subtracted cDNA libraries constructed by
suppression subtractive hybridization. Eur J Cancer Prev.
17:561–571. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zeng Z, Zhou Y, Xiong W, Luo X, Zhang W,
Li X, Fan S, Cao L, Tang K, Wu M and Li G: Analysis of gene
expression identifies candidate molecular markers in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma using microdissection and cDNA microarray. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 133:71–81. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zeng ZY, Zhou YH, Zhang WL, Xiong W, Fan
SQ, Li XL, Luo XM, Wu MH, Yang YX, Huang C, et al: Gene expression
profiling of nasopharyngeal carcinoma reveals the abnormally
regulated WNT signaling pathway. Hum Pathol. 38:120–133. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zeng Z, Zhou Y, Zhang W, Li X, Xiong W,
Liu H, Fan S, Qian J, Wang L, Li Z, et al: Family-based association
analysis validates chromosome 3p21 as a putative nasopharyngeal
carcinoma susceptibility locus. Genet Med. 8:156–160. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Szafarowski T and Szczepanski MJ: Cancer
stem cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Otolaryngol
Pol. 68:105–111. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Qian X, Wagner S, Ma C, Coordes A, Gekeler
J, Klussmann JP, Hummel M, Kaufmann AM and Albers AE: Prognostic
significance of ALDH1A1-positive cancer stem cells in patients with
locally advanced, metastasized head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 140:1151–1158. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Han J, Fujisawa T, Husain SR and Puri RK:
Identification and characterization of cancer stem cells in human
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 14:1732014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, Bonn VE,
Hawkins C, Squire J and Dirks PB: Identification of a cancer stem
cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 63:5821–5828.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ricci-Vitiani L, Lombardi DG, Pilozzi E,
Biffoni M, Todaro M, Peschle C and De Maria R: Identification and
expansion of human colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature.
445:111–115. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu A, Luo W, Zhang Q, Yang Z, Zhang G, Li
S and Yao K: Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1, a functional marker for
identifying cancer stem cells in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Cancer Lett. 330:181–189. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pollard SM, Yoshikawa K, Clarke ID, Danovi
D, Stricker S, Russell R, Bayani J, Head R, Lee M, Bernstein M, et
al: Glioma stem cell lines expanded in adherent culture have
tumor-specific phenotypes and are suitable for chemical and genetic
Screens. Cell Stem Cell. 4:568–580. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Han ME, Jeon TY, Hwang SH, Lee YS, Kim HJ,
Shim HE, Yoon S, Baek SY, Kim BS, Kang CD and Oh SO: Cancer spheres
from gastric cancer patients provide an ideal model system for
cancer stem cell research. Cell Mol Life Sci. 68:3589–3605. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Singh S, Trevino J, Bora-Singhal N,
Coppola D, Haura E, Altiok S and Chellappan SP: EGFR/Src/Akt
signaling modulates Sox2 expression and self-renewal of stem-like
side-population cells in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer.
11:732012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Orford KW and Scadden DT: Deconstructing
stem cell self-renewal: Genetic insights into cell-cycle
regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 9:115–128. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Horsley V, Aliprantis AO, Polak L,
Glimcher LH and Fuchs E: NFATc1 balances quiescence and
proliferation of skin stem cells. Cell. 132:299–310. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Malumbres M: Physiological relevance of
cell cycle kinases. Physiol Rev. 91:973–1007. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mhawech P: 14-3-3 proteins - an update.
Cell Res. 15:228–236. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Laronga C, Yang HY, Neal C and Lee MH:
Association of the cyclin-dependent kinases and 14-3-3σ negatively
regulates cell cycle progression. J Biol Chem. 275:23106–23112.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yang HY, Wen YY, Chen CH, Lozano G and Lee
MH: 14-3-3σ positively regulates p53 and suppresses tumor growth.
Mol Cell Biol. 23:7096–7107. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gudkov AV and Komarova EA: The role of p53
in determining sensitivity to radiotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer.
3:117–129. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|