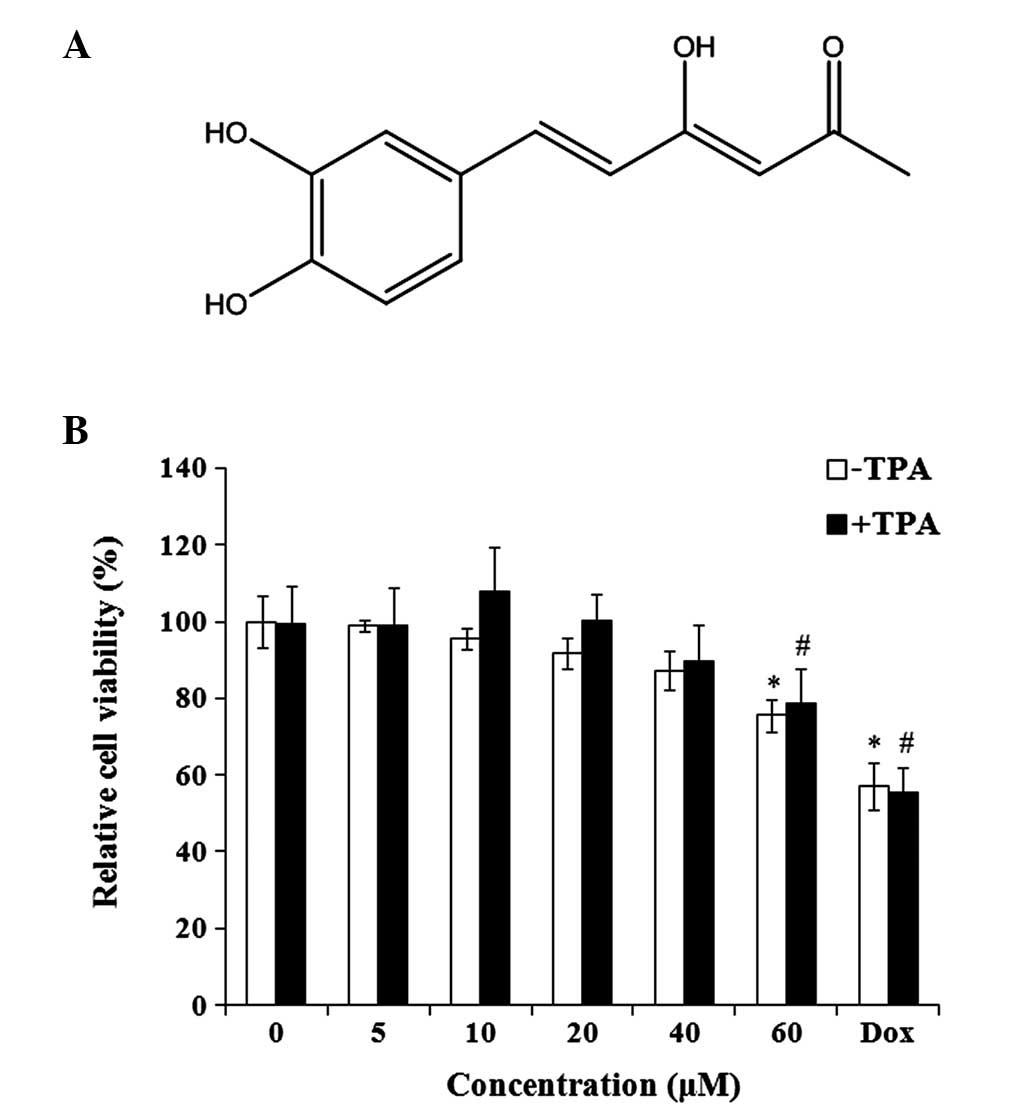
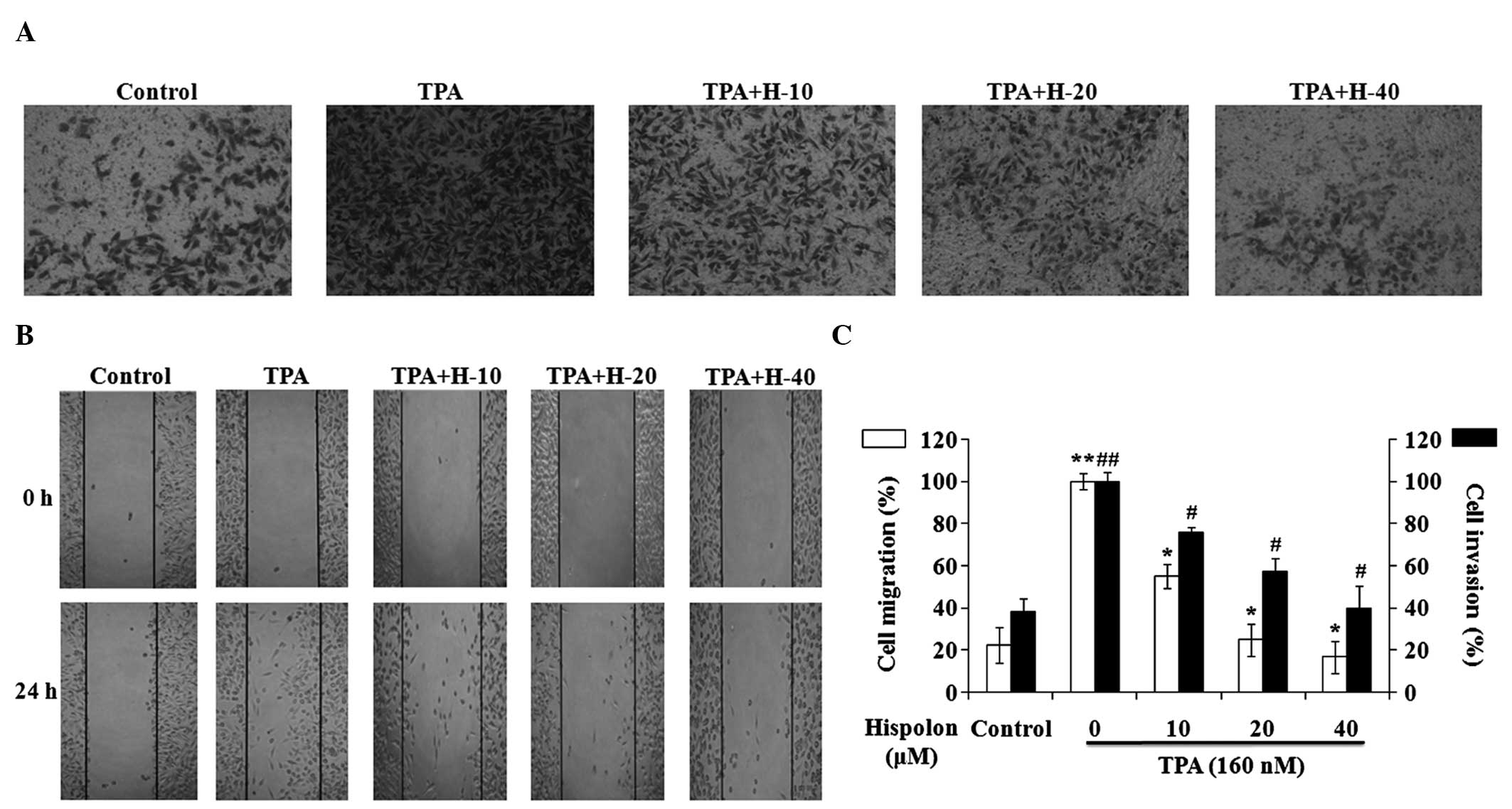
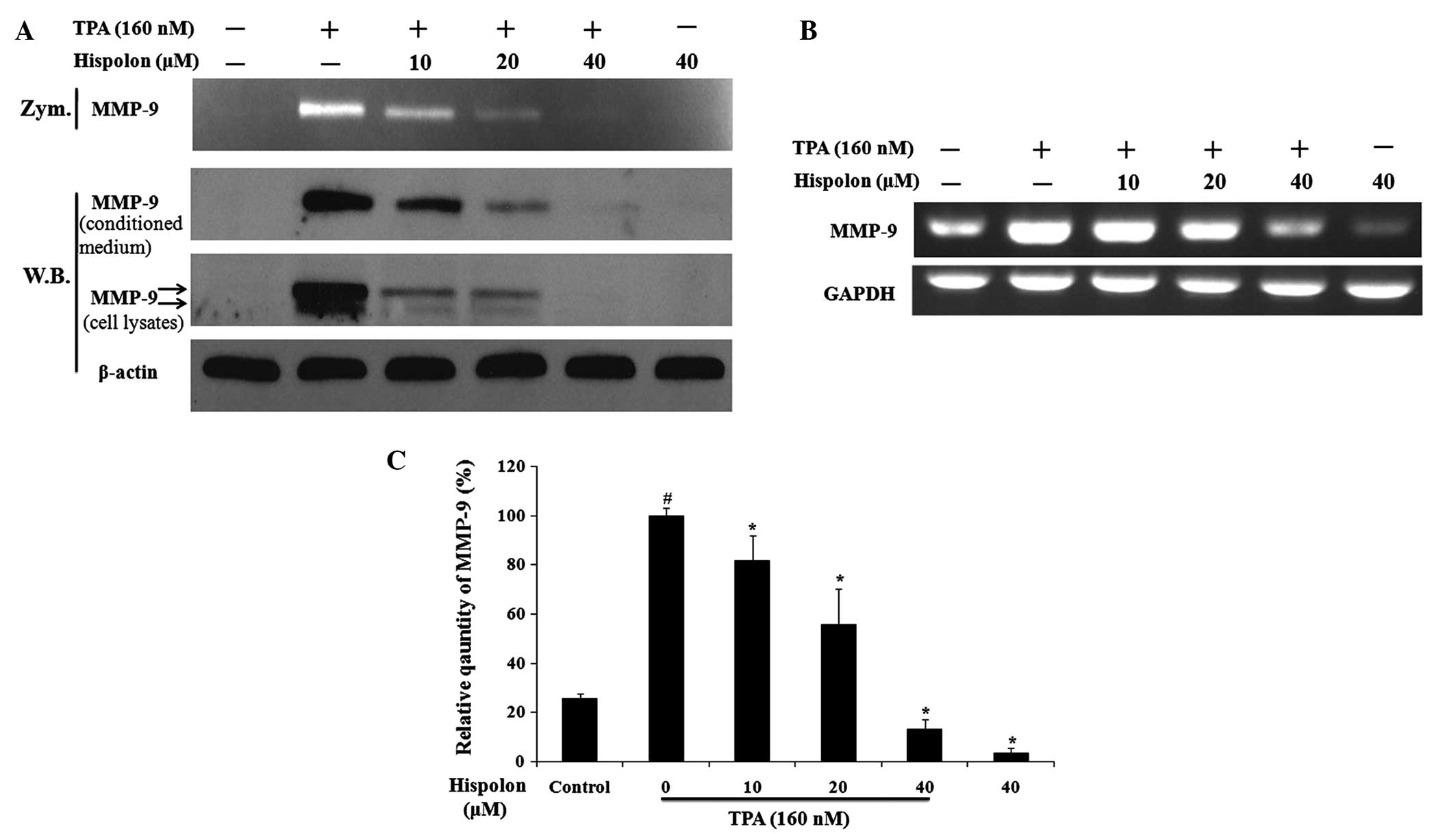
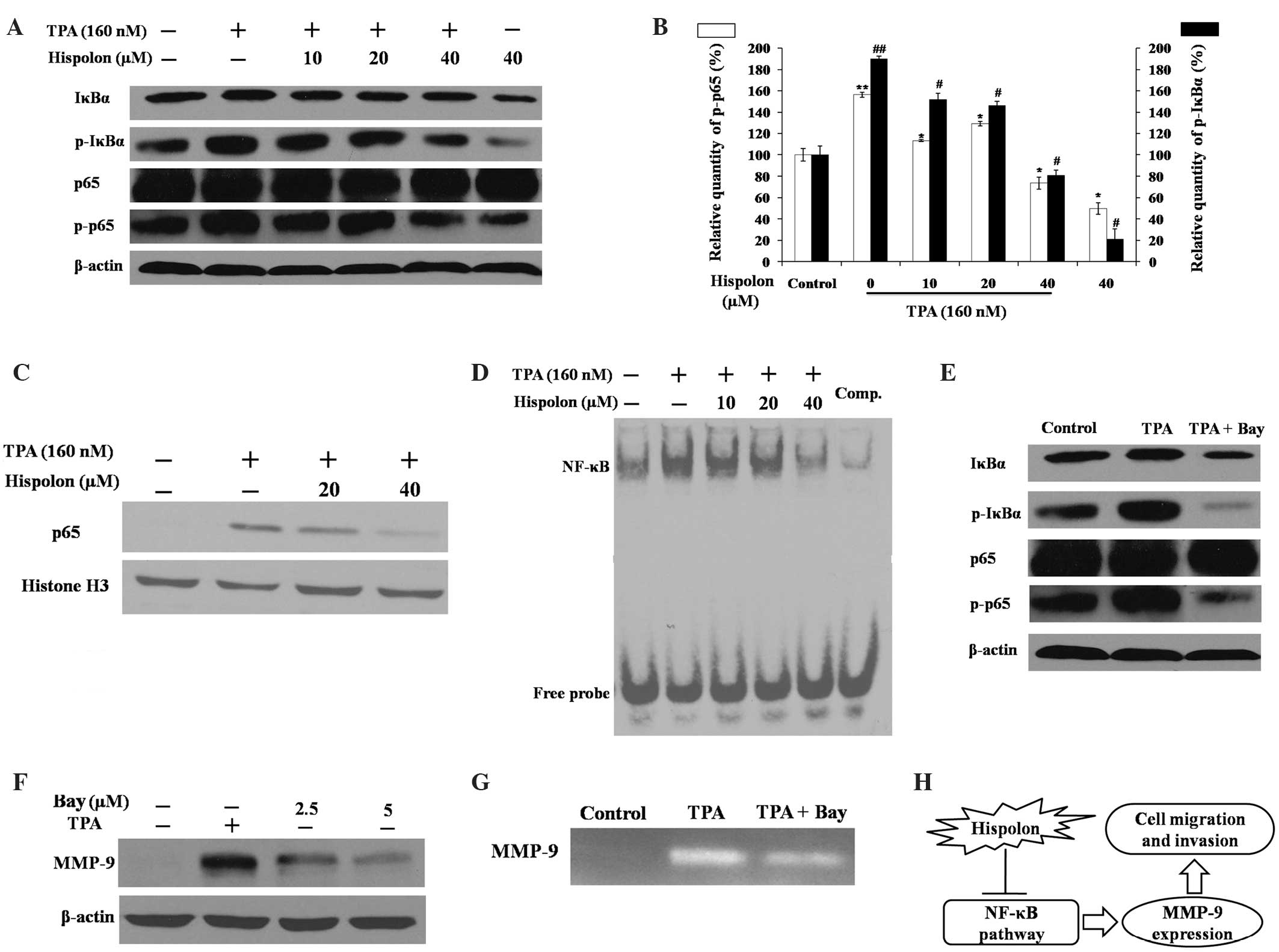
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Valastyan S and Weinberg RA: Tumor
metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell.
147:275–292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lin CW, Hou WC, Shen SC, et al: Quercetin
inhibition of tumor invasion via suppressing PKC
delta/ERK/AP-1-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation in
breast carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis. 29:1807–1815. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pellikainen JM, Ropponen KM, Kataja VV, et
al: Expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 in
breast cancer with a special reference to activator protein-2,
HER2, and prognosis. Clin Cancer Res. 10:7621–7628. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Laulan NB and St-Pierre Y: Bone
morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP-4) and epidermal growth factor (EGF)
inhibit metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) expression in cancer cells.
Oncoscience. 2:309–316. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Roomi MW, Monterrey JC, Kalinovsky T, Rath
M and Niedzwiecki A: Patterns of MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression in
human cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep. 21:1323–1333. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Han H, Du B, Pan X, et al: CADPE inhibits
PMA-stimulated gastric carcinoma cell invasion and matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression by FAK/MEK/ERK-mediated AP-1
activation. Mol Cancer Res. 8:1477–1488. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Park SK, Hwang YS, Park KK, et al:
Kalopanaxsaponin A inhibits PMA-induced invasion by reducing matrix
metalloproteinase-9 via PI3K/Akt- and PKCdelta-mediated signaling
in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 30:1225–1233.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ali NAA, Pilgrim H, Liberra K, Lindequist
U and Jansen R: Hispolon, a yellow pigment from Inonotus hispidus.
Phytochemistry. 41:927–929. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chen W, Zhao Z, Li L, Wu B, Chen SF, Zhou
H, Wang Y and Li YQ: Hispolon induces apoptosis in human gastric
cancer cells through a ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway. Free
Radic Biol Med. 45:60–72. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mo S, Wang S, Zhou G, et al: Phelligridins
C-F: cytotoxic pyrano[4,3-c][2]benzopyran-1,6-dione and
furo[3,2-c]pyran-4-one derivatives from the fungus Phellinus
igniarius. J Nat Prod. 67:823–828. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chang HY, Sheu MJ, Yang CH, Lu TC, Chang
YS, Peng WH, Huang SS and Huang GJ: Analgesic effects and the
mechanisms of anti-inflammation of hispolon in mice. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2011:4782462011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang GJ, Deng JS, Huang SS, et al:
Hispolon induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of human
hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells by modulating ERK
phosphorylation. J Agric Food Chem. 59:7104–7113. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang GJ, Yang CM, Chang YS, et al:
Hispolon suppresses SK-Hep1 human hepatoma cell metastasis by
inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2/9 and urokinase-plasminogen
activator through the PI3K/Akt and ERK signaling pathways. J Agric
Food Chem. 58:9468–9475. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lu TL, Huang GJ, Lu TJ, et al: Hispolon
from Phellinus linteus has antiproliferative effects via
MDM2-recruited ERK1/2 activity in breast and bladder cancer cells.
Food Chem Toxicol. 47:2013–2021. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu TL, Huang GJ, Wang HJ, et al: Hispolon
promotes MDM2 downregulation through chaperone-mediated autophagy.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 398:26–31. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Venkateswarlu S, Ramachandra MS, Sethuramu
K and Subbaraju GV: Synthesis and antioxidant activity of hispolon,
a yellow pigment from Inonotus hispidius. J Chem Sect B.
41:875–877. 2002.
|
|
18
|
Helbig G, Christopherson KW II,
Bhat-Nakshatri P, et al: NF-kappaB promotes breast cancer cell
migration and metastasis by inducing the expression of the
chemokine receptor CXCR4. J Biol Chem. 278:21631–21638. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shin Y, Yoon SH, Choe EY, et al:
PMA-induced up-regulation of MMP-9 is regulated by a
PKCalpha-NF-kappaB cascade in human lung epithelial cells. Exp Mol
Med. 39:97–105. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim GY, Oh YH and Park YM: Acidic
polysaccharide isolated from Phellinus linteus induces nitric
oxide-mediated tumoricidal activity of macrophages through protein
tyrosine kinase and protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
309:399–407. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sliva D, Jedinak A, Kawasaki J, Harvey K
and Slivova V: Phellinus linteus suppresses growth, angiogenesis
and invasive behaviour of breast cancer cells through the
inhibition of AKT signalling. Br J Cancer. 98:1348–1356. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hsiao PC, Hsieh YH, Chow JM, et al:
Hispolon induces apoptosis through JNK1/2-mediated activation of a
caspase-8, -9, and -3-dependent pathway in acute myeloid leukemia
(AML) cells and inhibits AML xenograft tumor growth in vivo. J
Agric Food Chem. 61:10063–10073. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Scorilas A, Karameris A, Arnogiannaki N,
et al: Overexpression of matrix-metalloproteinase-9 in human breast
cancer: a potential favourable indicator in node-negative patients.
Br J Cancer. 84:1488–1496. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Toth M, Gervasi DC and Fridman R: Phorbol
ester-induced cell surface association of matrix
metalloproteinase-9 in human MCF10A breast epithelial cells. Cancer
Res. 57:3159–3167. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ling H, Yang H, Tan SH, Chui WK and Chew
EH: 6-Shogaol, an active constituent of ginger, inhibits breast
cancer cell invasion by reducing matrix metalloproteinase-9
expression via blockade of nuclear factor-κB activation. Br J
Pharmacol. 161:1763–1777. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jones CB, Sane DC and Herrington DM:
Matrix metalloproteinases: a review of their structure and role in
acute coronary syndrome. Cardiovasc Res. 59:812–823. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|