|
1
|
Bohme E and Schmidt HH: Nitric oxide and
cytosolic guanylate cyclase: components of an intercellular
signalling system. Z Kardiol 78 Suppl. 6:75–79. 1989.
|
|
2
|
Orstavik S, Natarajan V, Tasken K, Jahnsen
T and Sandberg M: Characterization of the human gene encoding the
type I alpha and type I beta cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PRKG1).
Genomics. 42:311–318. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Orstavik S, Solberg R, Taskén K, et al:
Molecular cloning, cDNA structure and chromosomal localization of
the human type II cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 220:759–765. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wells A: EGF receptor. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 31:637–643. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jiang H, Grenley MO, Bravo MJ, Blumhagen
RZ and Edgar BA: EGFR/Ras/MAPK signaling mediates adult midgut
epithelial homeostasis and regeneration in Drosophila. Cell Stem
Cell. 8:84–95. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
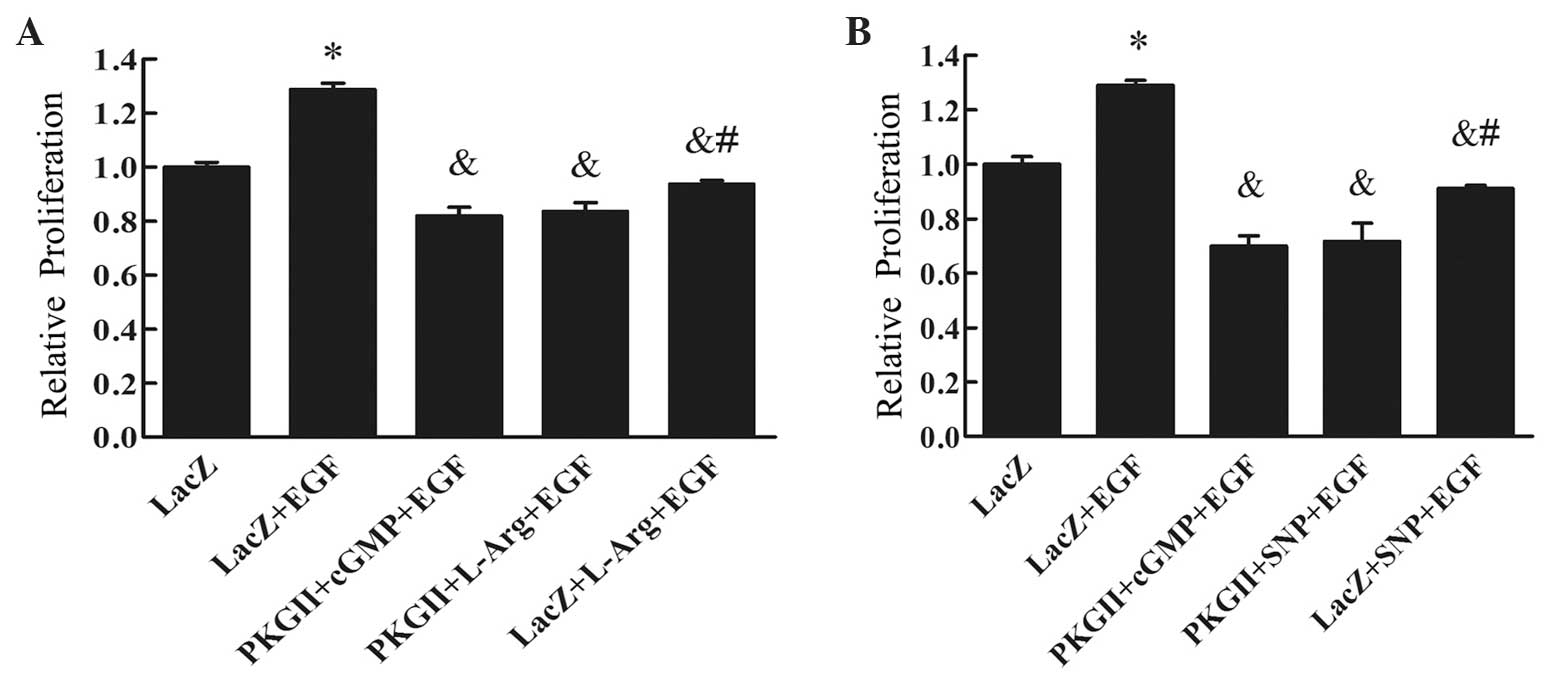
Chen YC, Ren F, Sang JR, Tao Y and Xu WR:
Type II cGMP-dependent protein kinase inhibits proliferation of the
gastric cancer cell line BGC-823. Mol Med Rep. 3:361–366. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
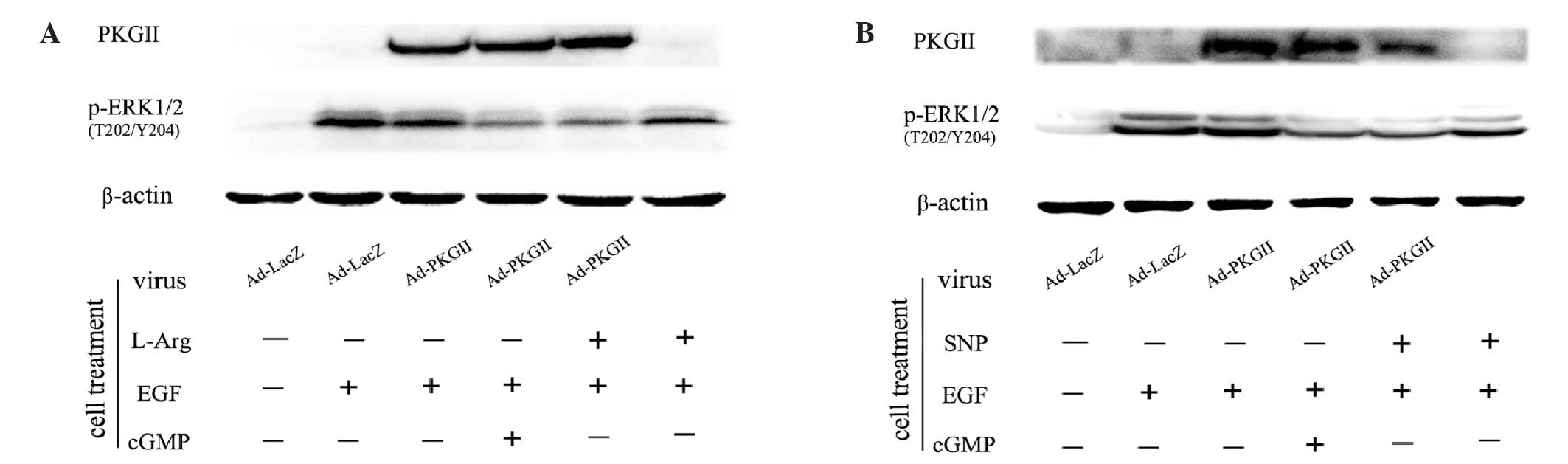
Wu Y, Chen Y, Qu R, Lan T and Sang J: Type
II cGMP-dependent protein kinase inhibits EGF-triggered signal
transduction of the MAPK/ERK-mediated pathway in gastric cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 27:553–558. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lan T, Chen Y, Sang J, et al: Type II
cGMP-dependent protein kinase inhibits EGF-induced MAPK/JNK signal
transduction in breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 27:2039–2044.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jiang L, Lan T, Chen Y, et al: PKG II
inhibits EGF/EGFR-induced migration of gastric cancer cells. PLoS
One. 8:e616742013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Medeiros JV, Gadelha GG, Lima SJ, et al:
Role of the NO/cGMP/K (ATP) pathway in the protective effects of
sildenafil against ethanol-induced gastric damage in rats. Br J
Pharmacol. 153:721–727. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Russo I, Doronzo G, Mattiello L, De Salve
A, Trovati M and Anfossi G: The activity of constitutive nitric
oxide synthase is increased by the pathway cAMP/cAMP-activated
protein kinase in human platelets. New insights into the
antiaggregating effects of cAMP-elevating agents. Thromb Res.
114:265–273. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kwiatkowski AV, Gertler FB and Loureiro
JJ: Function and regulation of Ena/VASP proteins. Trends Cell Biol.
13:386–392. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
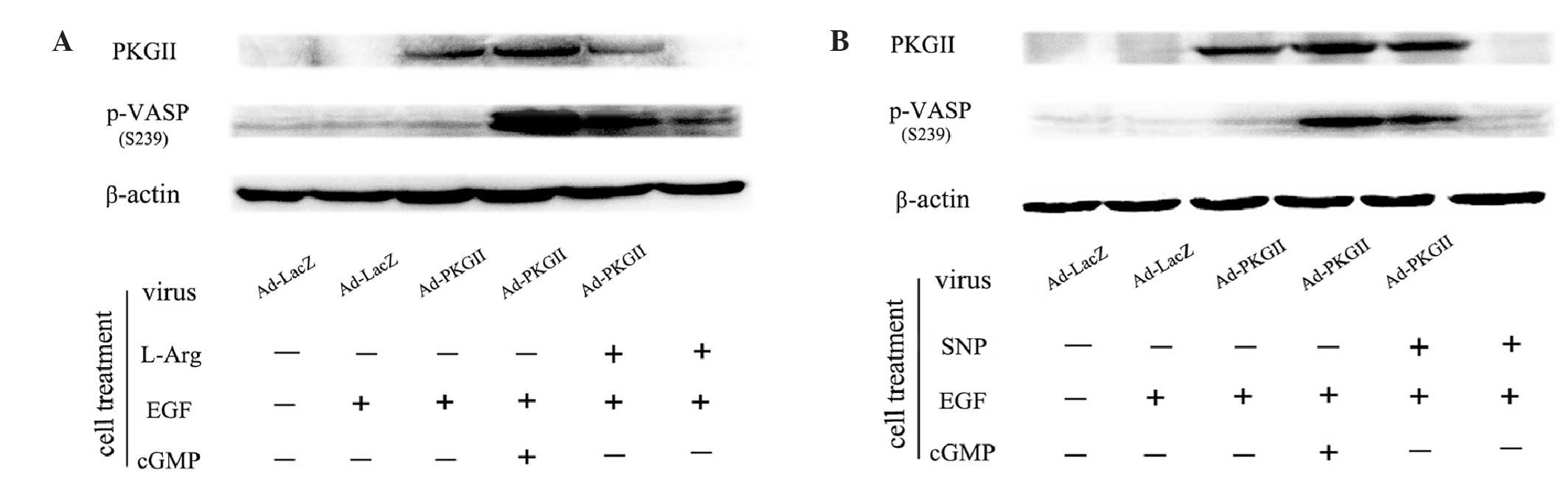
Tao Y, Gu YJ, Cao ZH, et al: Endogenous
cGMP-dependent protein kinase reverses EGF-induced MAPK/ERK signal
transduction through phosphorylation of VASP at Ser239. Oncol Lett.
4:1104–1108. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
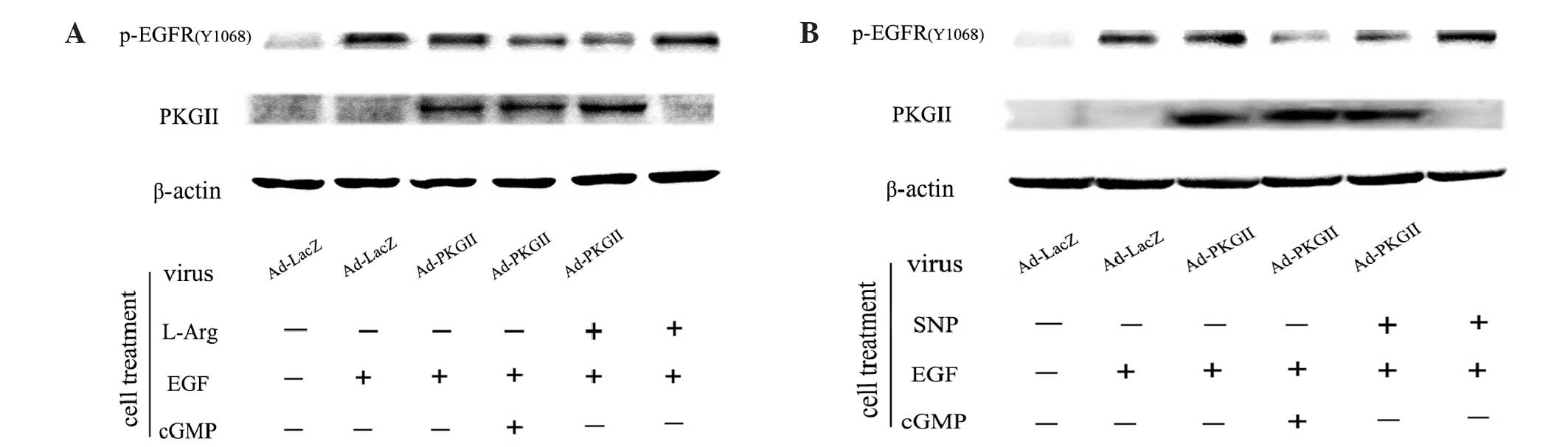
Wheeler S, Siwak DR, Chai R, et al: Tumor
epidermal growth factor receptor and EGFR PY1068 are independent
prognostic indicators for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Clin Cancer Res. 18:2278–2289. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yamazaki T, Zaal K, Hailey D, Presley J,
Lippincott-Schwartz J and Samelson LE: Role of Grb2 in
EGF-stimulated EGFR internalization. J Cell Sci. 115:1791–1802.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rojas M, Yao S and Lin YZ: Controlling
epidermal growth factor (EGF)-stimulated Ras activation in intact
cells by a cell-permeable peptide mimicking phosphorylated EGF
receptor. J Biol Chem. 271:27456–27461. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Saito T, Okada S, Ohshima K, et al:
Differential activation of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor
downstream signaling pathways by betacellulin and EGF.
Endocrinology. 145:4232–4243. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kolch W: Meaningful relationships: the
regulation of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway by protein interactions.
Biochem J. 351:289–305. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dumitrescu C, Biondi R, Xia Y, et al:
Myocardial ischemia results in tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) oxidation
with impaired endothelial function ameliorated by BH4. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 104:15081–15086. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Knowles RG and Moncada S: Nitric oxide
synthases in mammals. Biochem J. 298:249–258. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Koesling D, Russwurm M, Mergia E,
Mullershausen F and Friebe A: Nitric oxide-sensitive guanylyl
cyclase: structure and regulation. Neurochem Int. 45:813–819. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bruckdorfer R: The basics about nitric
oxide. Mol Aspects Med. 26:3–31. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Madhusoodanan KS and Murad F: NO-cGMP
signaling and regenerative medicine involving stem cells. Neurochem
Res. 32:681–694. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Russo I, Viretto M, Doronzo G, et al: A
short-term incubation with high glucose impairs VASP
phosphorylation at serine 239 in response to the nitric oxide/cGMP
pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells: role of oxidative stress.
Biomed Res Int. 2014:3289592014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lambrechts A, Kwiatkowski AV, Lanier LM,
et al: cAMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation of EVL, a
Mena/VASP relative, regulates its interaction with actin and SH3
domains. J Biol Chem. 275:36143–36151. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Butt E, Abel K, Krieger M, et al: cAMP-
and cGMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation sites of the
focal adhesion vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) in
vitro and in intact human platelets. J Biol Chem. 269:14509–14517.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tao Y, Chen YC, Sang JR and Xu WR:
Phosphorylation of vasodilator stimulated phosphoprotein is
correlated with cell cycle progression in HeLa cells. Mol Med Rep.
3:657–662. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Roux PP and Blenis J: ERK and p38
MAPK-activated protein kinases: a family of protein kinases with
diverse biological functions. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 68:320–344.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sang JR, Chen YC and Tao Y: Nitric oxide
inhibits gastric cancer cell growth through the modulation of the
Akt pathway. Mol Med Rep. 4:1163–1167. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|