|
1
|
Lazaridis KN and Gores GJ:
Cholangiocarcinoma. Gastroenterology. 128:1655–1667. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
West J, Wood H, Logan RF, Quinn M and
Aithal GP: Trends in the incidence of primary liver and biliary
tract cancers in England and Wales 1971–2001. Br J Cancer.
94:1751–1758. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Anderson CD, Pinson CW, Berlin J and Chari
RS: Diagnosis and treatment of cholangiocarcinoma. Oncologist.
9:43–57. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sirica AE: Cholangiocarcinoma: Molecular
targeting strategies for chemoprevention and therapy. Hepatology.
41:5–15. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fulda S, Gorman AM, Hori O and Samali A:
Cellular stress responses: Cell survival and cell death. Int J Cell
Biol. 2010:2140742010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fabregat I, Roncero C and Fernández M:
Survival and apoptosis: A dysregulated balance in liver cancer.
Liver Int. 27:155–162. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ferreira CG, Epping M, Kruyt FA and
Giaccone G: Apoptosis: Target of cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res.
8:2024–2034. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim ND, Im E, Yoo YH and Choi YH:
Modulation of the cell cycle and induction of apoptosis in human
cancer cells by synthetic bile acids. Curr Cancer Drug Targets.
6:681–689. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gujral ML, Sareen K, Tangri KK, Amma MK
and Roy AK: Antiarthritic and anti-inflammatory activity of gum
guggul (Balsamodendron mukul Hook). Indian J Physiol
Pharmacol. 4:267–273. 1960.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sharma JN and Sharma JN: Comparison of the
anti-inflammatory activity of Commiphora mukul (an indigenous
drug) with those of phenylbutazone and ibuprofen in experimental
arthritis induced by mycobacterial adjuvant. Arzneimittelforschung.
27:1455–1457. 1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Urizar NL and Moore DD: GUGULIPID: A
natural cholesterol-lowering agent. Annu Rev Nutr. 23:303–313.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Urizar NL, Liverman AB, Dodds DT, Silva
FV, Ordentlich P, Yan Y, Gonzalez FJ, Heyman RA, Mangelsdorf DJ and
Moore DD: A natural product that lowers cholesterol as an
antagonist ligand for FXR. Science. 296:1703–1706. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Singh SV, Choi S, Zeng Y, Hahm ER and Xiao
D: Guggulsterone-induced apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells
is caused by reactive oxygen intermediate dependent activation of
c-Jun NH2 -terminal kinase. Cancer Res. 67:7439–7449.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shishodia S, Sethi G, Ahn KS and Aggarwal
BB: Guggulsterone inhibits tumor cell proliferation, induces
S-phase arrest, and promotes apoptosis through activation of c-Jun
N-terminal kinase, suppression of Akt pathway, and downregulation
of antiapoptotic gene products. Biochem Pharmacol. 74:118–130.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Samudio I, Konopleva M, Safe S, McQueen T
and Andreeff M: Guggulsterones induce apoptosis and differentiation
in acute myeloid leukemia: Identification of isomer-specific
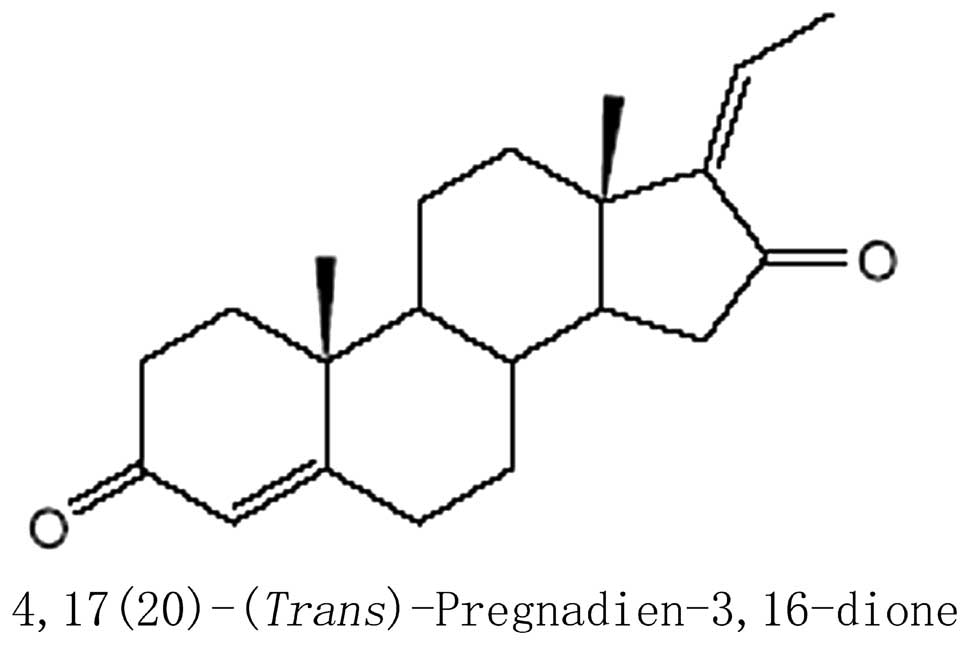
antileukemic activities of the pregnadienedione structure. Mol
Cancer Ther. 4:1982–1992. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
An MJ, Cheon JH, Kim SW, Kim ES, Kim TI
and Kim WH: Guggulsterone induces apoptosis in colon cancer cells
and inhibits tumor growth in murine colorectal cancer xenografts.
Cancer Letters. 279:93–100. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Macha MA, Rachagani S, Gupta S, Pai P,
Ponnusamy MP, Batra SK and Jain M: Guggulsterone decreases
proliferation and metastatic behavior of pancreatic cancer cells by
modulating JAK/STAT and Src/FAK signaling. Cancer Lett.
341:166–177. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guan B, Li H, Yang Z, Hoque A and Xu X:
Inhibition of farnesoid X receptor controls esophageal cancer cell
growth in vitro and in nude mouse xenografts. Cancer.
119:1321–1329. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Herrmann M, Lorenz HM, Voll R, Grünke M,
Woith W and Kalden JR: A rapid and simple method for the isolation
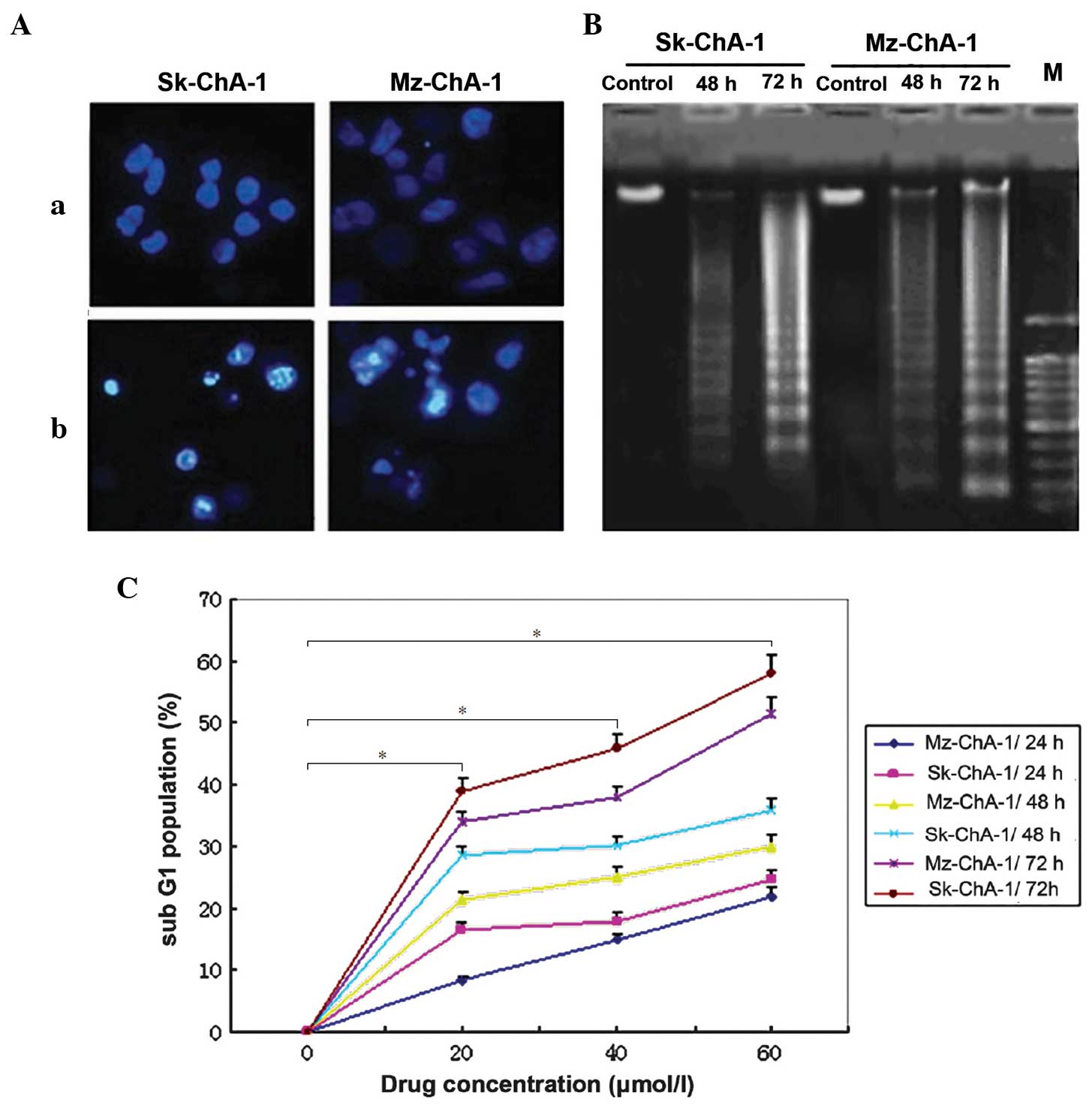
of apoptotic DNA fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 22:5506–5507. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kanjeekal S, Chambers A, Fung MF and Verma
S: Systemic therapy for advanced uterine sarcoma: A systematic
review of the literature. Gynecol Oncol. 97:624–637. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wiseman LR and Spencer CM: Paclitaxel. An
update of its use in the treatment of metastatic breast cancer and
ovarian and other gynaecological cancers. Drugs Aging. 12:305–334.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang J, Liang X, Zhou X, Huang L, Huang
R, Chu Z and Zhan Q: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled
trials comparing irinotecan/platinum with etoposide/platinum in
patients with previously untreated extensive-stage small cell lung
cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 5:867–873. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Karikas GA: Anticancer and chemopreventing
natural products: Some biochemical and therapeutic aspects. J BUON.
15:627–638. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Reed JC: Apoptosis-regulating proteins as
targets for drug discovery. Trends Mol Med. 7:314–319. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Desagher S and Martinou JC: Mitochondria
as the central control point of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol.
10:369–377. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Van Loo G, Saelens X, Van Gurp M,
MacFarlane M, Martin SJ and Vandenabeele P: The role of
mitochondrial factors in apoptosis: A Russian roulette with more
than one bullet. Cell Death Differ. 9:1031–1042. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
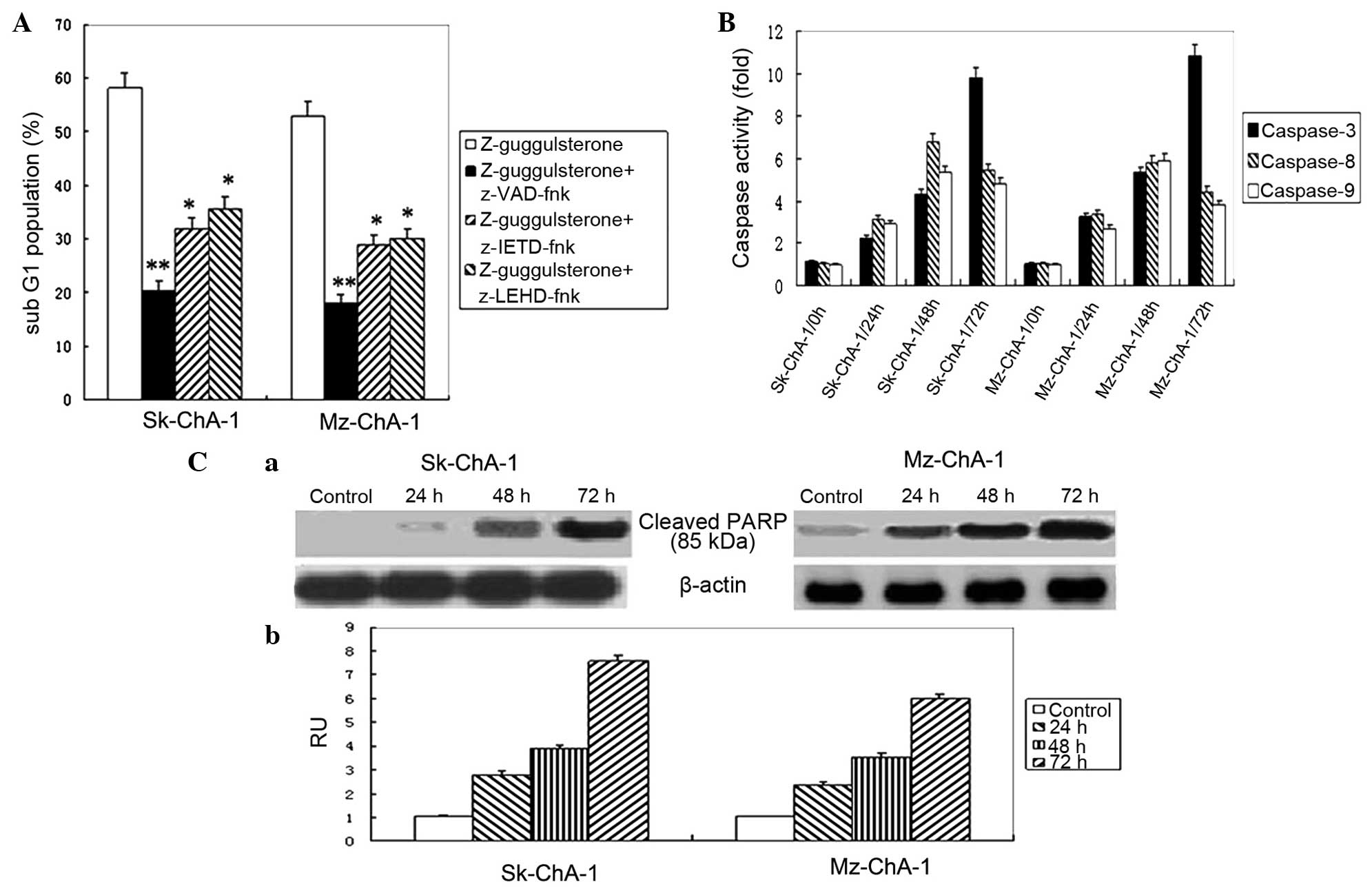
Thornberry NA and Lazebnik Y: Caspases:
Enemies within. Science. 281:1312–1316. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fulda S: Targeting extrinsic apoptosis in
cancer: Challenges and opportunities. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
39:20–25. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liang Q, Li W and Zhou B:
Caspase-independent apoptosis in yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1783:1311–1319. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzami N, Marzo I,
Snow BE, Brothers GM, Mangion J, Jacotot E, Costantini P, Loeffler
M, et al: Molecular characterization of mitochondrial
apoptosis-inducing factor. Nature. 397:441–446. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li F: Survivin study: What is the next
wave? J Cell Physiol. 197:8–29. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li F, Ambrosini G, Chu EY, Plescia J,
Tognin S, Marchisio PC and Altieri DC: Control of apoptosis and
mitotic spindle checkpoint by survivin. Nature. 396:580–584. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mirza A, McGuirk M, Hockenberry TN, Wu Q,
Ashar H, Black S, Wen SF, Wang L, Kirschmeier P, Bishop WR, et al:
Human survivin is negatively regulated by wild-type p53 and
participates in p53-dependent apoptotic pathway. Oncogene.
21:2613–2622. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Beltrami E, Plescia J, Wilkinson JC,
Duckett CS and Altieri DC: Acute ablation of survivin uncovers
p53-dependent mitotic checkpoint functions and control of
mitochondrial apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 279:2077–2084. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chang Q, Liu ZR, Wang DY, Kumar M, Chen YB
and Qin RY: Survivin expression induced by doxorubicin in
cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 10:415–418.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Javle MM, Tan D, Yu J, LeVea CM, Li F,
Kuvshinoff BW and Gibbs JF: Nuclear survivin expression predicts
poor outcome in cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatogastroenterol.
51:1653–1657. 2004.
|
|
37
|
Obama K, Ura K, Li M, Katagiri T, Tsunoda
T, Nomura A, Satoh S, Nakamura Y and Furukawa Y: Genome-wide
analysis of gene expression in human intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology. 41:1339–1348. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
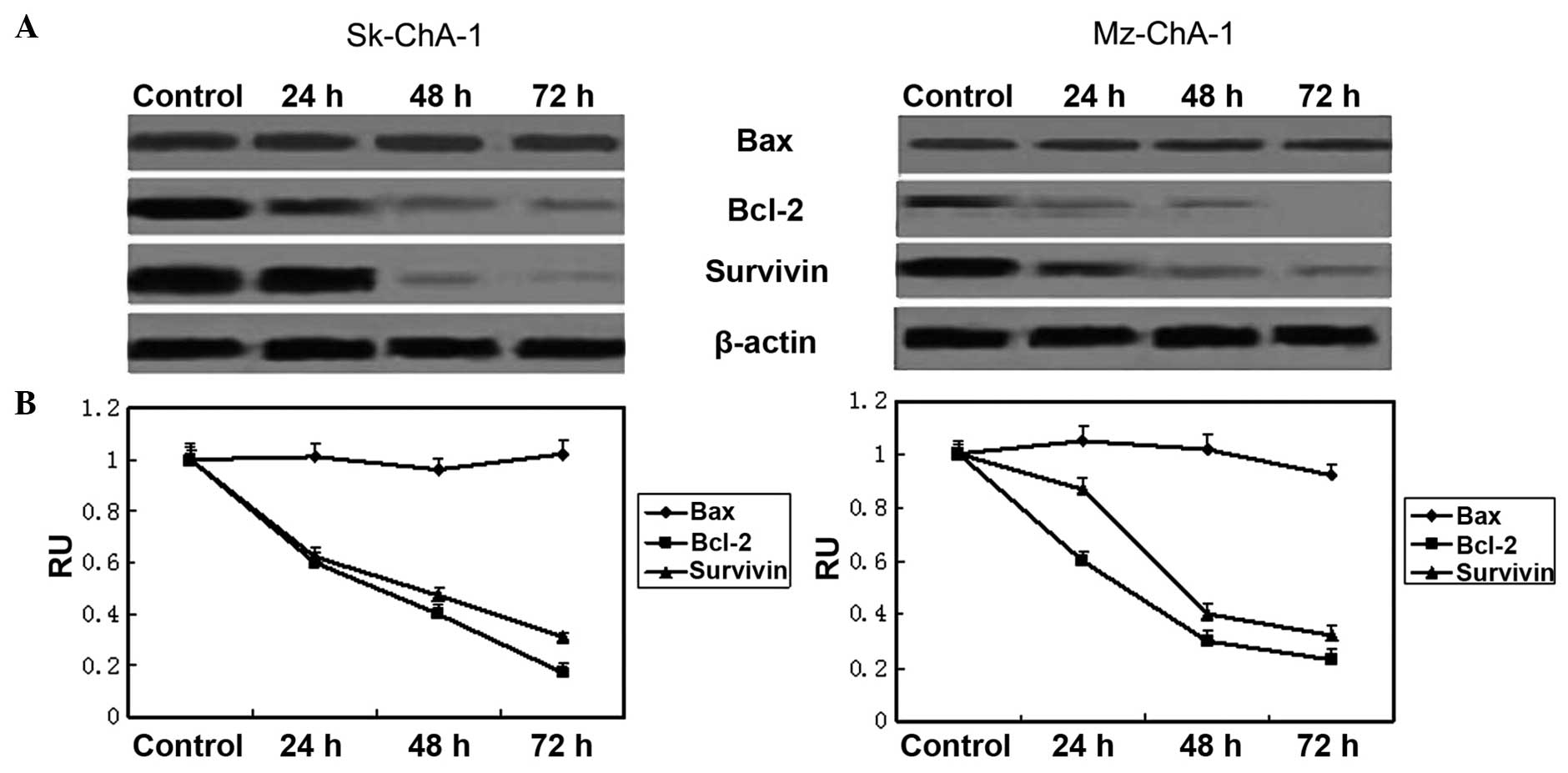
Antonsson B: Mitochondria and the Bcl-2
family proteins in apoptosis signaling pathways. Mol Cell Biochem.
256–257:141–155. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Nascimento Pde S, Ornellas AA, Campos MM,
Scheiner MA, Fiedler W and Alves G: Bax and bcl-2 imbalance and HPB
infection in penile tumors and adjacent tissues. Prog Urol.
14:353–359. 2004.(In French). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Reed JC: Double identity for proteins of
the Bcl-2 family. Nature. 387:773–776. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EH, Lindsten T,
Panoutsakopoulou V, Ross AJ, MacGregor GR, Thompson CB and
Korsmeyer SJ: Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: A requisite gateway to
mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Science. 292:727–730. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang CL, Wu LJ, Tashiro S, Onodera S and
Ikejima T: Oridonin induces apoptosis of HeLa cells via altering
expression of Bcl-2/Bax and activating caspase-3/ICAD pathway. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 25:691–698. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Manion MK and Hockenbery DM: Targeting
BCL-2-related proteins in cancer therapy. Cancer Biol Ther. 2((Sul
1)): S105–S114. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kanwar JR, Kamalapuram SK and Kanwar RK:
Targeting survivin in cancer: The cell-signalling perspective. Drug
Discov Today. 16:485–494. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|