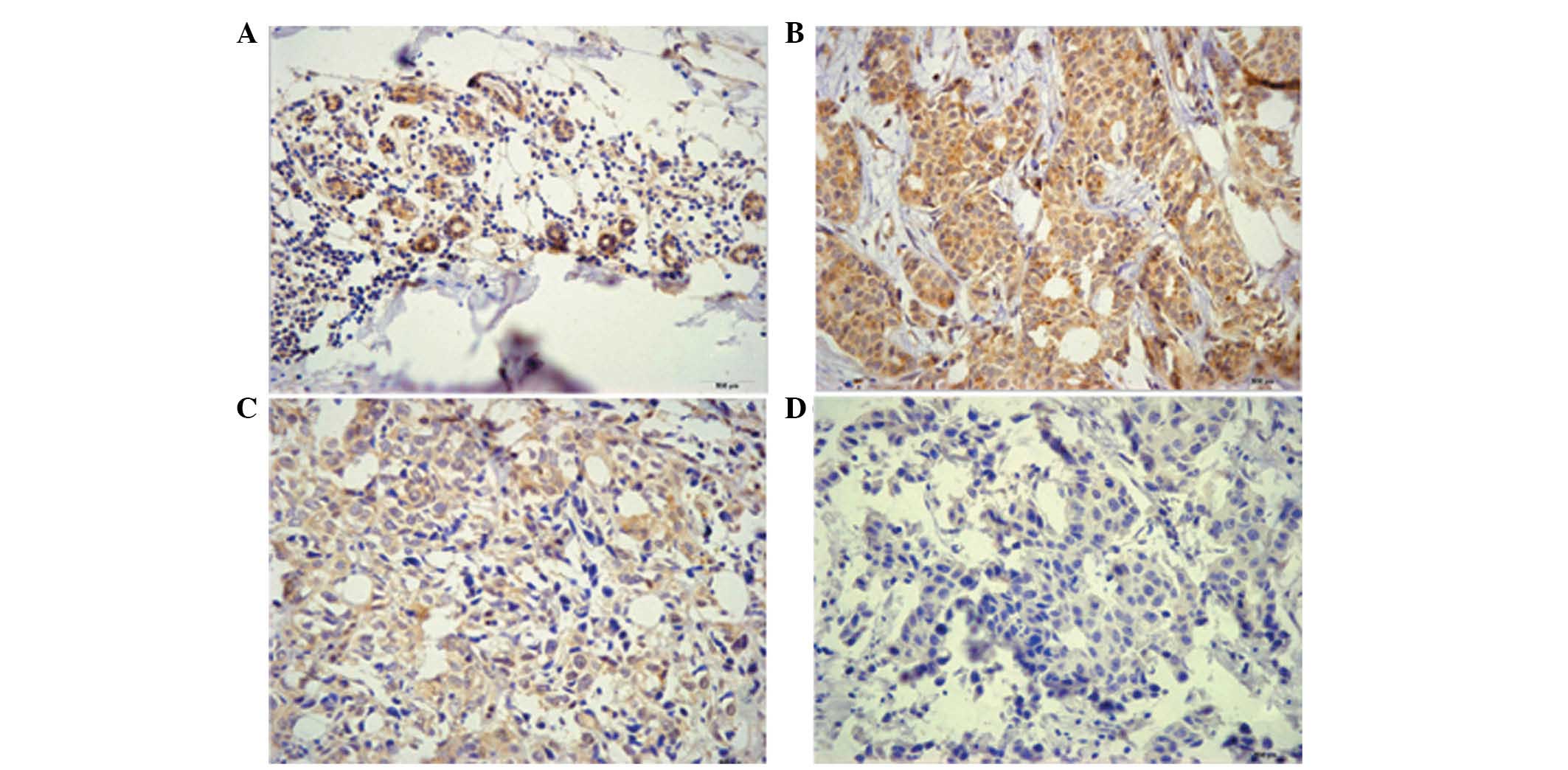
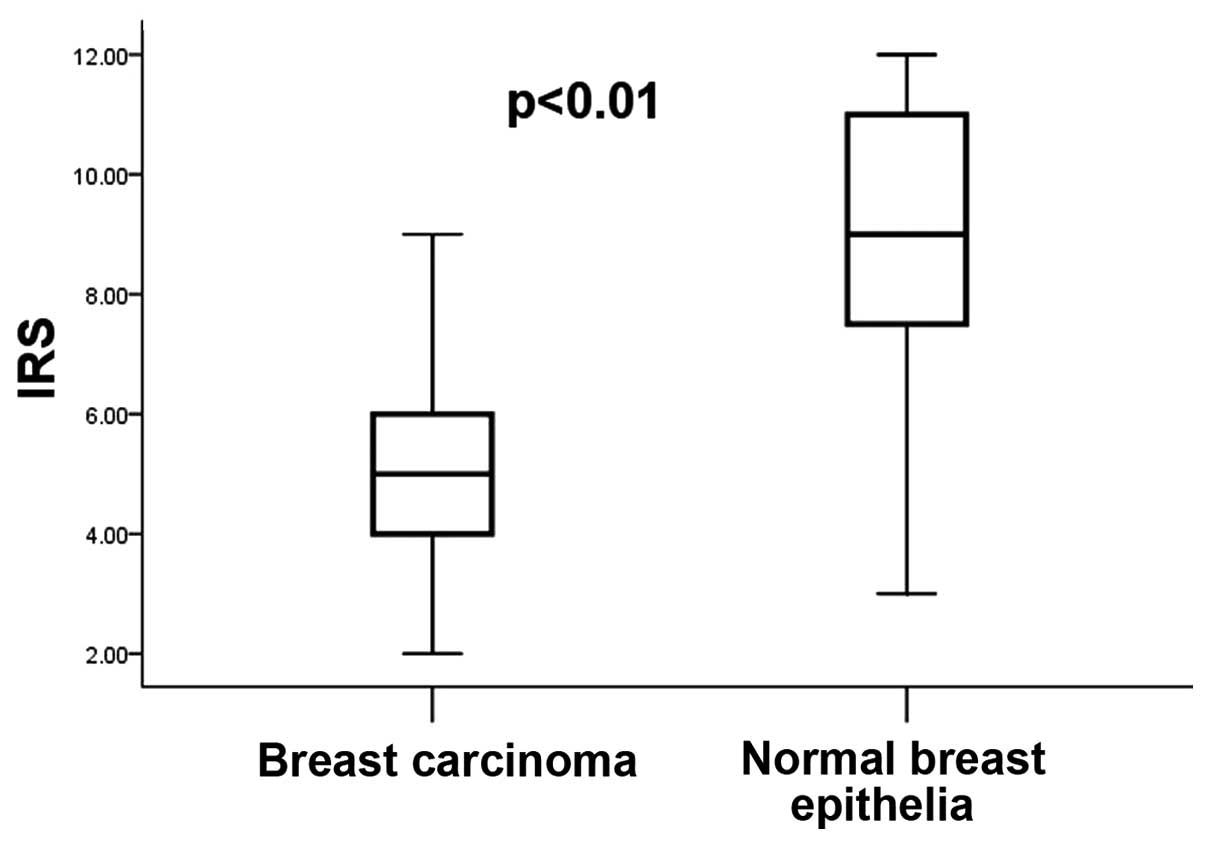
|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. Int J Cancer.
94:153–156. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Center MM, Desantis C and Ward
EM: Global patterns of cancer incidence and mortality rates and
trends. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 19:1893–1907. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Althuis MD, Dozier JM, Anderson WF, Devesa
SS and Brinton LA: Global trends in breast cancer incidence and
mortality 1973–1997. Int J Epidemiol. 34:405–412. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Autier P, Boniol M, La Vecchia C, Vatten
L, Gavin A, Héry C and Heanue M: Disparities in breast cancer
mortality trends between 30 European countries: Retrospective trend
analysis of WHO mortality database. BMJ. 341:c36202010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers CD and Parkin D: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bombonati A and Sgroi DC: The molecular
pathology of breast cancer progression. J Pathol. 223:307–317.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rakha EA, Putti TC, Abd El-Rehim DM, Paish
C, Green AR, Powe DG, Lee AH, Robertson JF and Ellis IO:
Morphological and immunophenotypic analysis of breast carcinomas
with basal and myoepithelial differentiation. J Pathol.
208:495–506. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Linjawi A, Kontogiannea M, Halwani F,
Edwardes M and Meterissian S: Prognostic significance of p53, bcl-2
and Bax expression in early breast cancer. J Am Coll Surg.
198:83–90. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rohan TE, Li SQ, Hartwick R and Kandel RA:
p53 Alterations and protein accumulation in benign breast tissue
and breast cancer risk: A cohort study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 15:1316–1323. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tsutsui S, Inoue H, Yasuda K, Suzuki K,
Higashi H, Era S and Mori M: Reduced expression of PTEN protein and
its prognostic implications in invasive ductal carcinoma of the
breast. Oncology. 68:398–404. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wolff TA and Wilson JE: Genetic risk
assessment and BRCA mutation testing for breast and ovarian cancer
susceptibility. Am Fam Physician. 74:1759–1760. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Greggi S, Scala F and Laurelli G:
Hereditery breast and ovarian cancer. Curr Probl Cancer. 27:24–28.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gatalica Z, Lele SM, Rampy BA and Norris
BA: The expression of Fhit protein is related inversely to disease
progression in patients with breast carcinoma. Cancer.
88:1378–1383. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Allred DC, Clark GM, Tandon AK, Molina R,
Tormey DC, Osborne CK, Gilchrist KW, Mansour EG, Abeloff M and
Eudey L: Her-2/neu in node-negative breast cancer: Prognostic
significance of overexpression influenced by the presence of in
situ carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 10:599–605. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Muss HB, Thor AD, Berry DA, Kute T, Liu
ET, Koerner F, Cirrincione CT, Budman DR, Wood WC and Barcos M:
C-erbB-2 expression and response to adjuvant therapy in women with
node-positive early breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 330:1260–1266.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Paik S, Bryant J, Park C, Fisher B,
Tan-Chiu E, Hyams D, Fisher ER, Lippman ME, Wickerham DL and
Wolmark N: ErbB-2 and response to doxorubicin in patients with
axillary lymph node-positive, hormone receptor-negative breast
cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 90:1361–1370. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Veronese SM, Gambacorta M, Gottardi O,
Scanzi F, Ferrari M and Lampertico P: Proliferation index as a
prognostic marker in breast cancer. Cancer. 71:3926–3931. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Van Poznak C, Tan L, Panageas KS, Arroyo
CD, Hudis C, Norton L and Seidman AD: Assessment of molecular
markers of clinical sensitivity to single-agent taxane therapy for
metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 20:2319–2326. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
De Placido S, De Laurentiis M, Carlomagno
C, Gallo C, Perrone F, Pepe S, Ruggiero A, Marinelli A, Pagliarulo
C, Panico L, et al: Twenty-year results of the Naples GUN
randomized trial: Predictive factors of adjuvant tamoxifen efficacy
in early breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 9:1039–1046.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
de Winter JP, Roelen BA, ten Dijke P, van
der Burg B and van den Eijnden-van Raaij AJ: DPC4 (SMAD4) mediates
transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) induced growth
inhibition and transcriptional response in breast tumour cells.
Oncogene. 14:1891–1899. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ali NA, McKay MJ and Molloy MP: Proteomics
of Smad4 regulated transforming growth factor-beta signalling in
colon cancer cells. Mol Biosyst. 6:2332–2338. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
de Caestecker MP, Piek E and Roberts AB:
Role of transforming growth factor-beta signaling in cancer. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 92:1388–1402. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Morén A, Itoh S, Moustakas A, Dijke P and
Heldin CH: Functional consequences of tumorigenic missense
mutations in the amino-terminal domain of Smad4. Oncogene.
19:4396–4404. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li Q, Wu L, Oelschlager DK, Wan M,
Stockard CR, Grizzle WE, Wang N, Chen H, Sun Y and Cao X: Smad4
inhibits tumor growth by inducing apoptosis in estrogen
receptor-positive breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem.
280:27022–27028. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ren Y, Wu L, Frost AR, Grizzle W, Cao X
and Wan M: Dual effects of TGF-beta on ERalpha-mediated estrogenic
transcriptional activity in breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 8:1112009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Deckers M, van Dinther M, Buijs J, Que I,
Löwik C, van der Pluijm G and ten Dijke P: The tumor suppressor
Smad4 is required for transforming growth factor beta-induced
epithelial to mesenchymal transition and bone metastasis of breast
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 66:2202–2209. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wiercinska E, Naber HP, Pardali E, van der
Pluijm G, van Dam H and ten Dijke P: The TGF-β/Smad pathway induces
breast cancer cell invasion through the up-regulation of matrix
metalloproteinase 2 and 9 in a spheroid invasion model system.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 128:657–666. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang LH, Kim SH, Lee JH, Choi YL, Kim YC,
Park TS, Hong YC, Wu CF and Shin YK: Inactivation of SMAD4 tumor
suppressor gene during gastric carcinoma progression. Clin Cancer
Res. 13:102–110. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kojima K, Vickers SM, Adsay NV, Jhala NC,
Kim HG, Schoeb TR, Grizzle WE and Klug CA: Inactivation of Smad4
accelerates Kras (G12D)-mediated pancreatic neoplasia. Cancer Res.
67:8121–8130. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kitamura T, Kometani K, Hashida H,
Matsunaga A, Miyoshi H, Hosogi H, Aoki M, Oshima M, Hattori M,
Takabayashi A, et al: SMAD4-deficient intestinal tumors recruit
CCR1+ myeloid cells that promote invasion. Nat Genet. 39:467–475.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang L, Mao C, Teng Y, Li W, Zhang J,
Cheng X, Li X, Han X, Xia Z, Deng H, et al: Targeted disruption of
Smad4 in mouse epidermis results in failure of hair follicle
cycling and formation of skin tumors. Cancer Res. 65:8671–8678.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Edge S, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG,
Greene FL and Trotti A: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th. Springer;
New York, NY: pp. 347–376. 2010
|
|
33
|
Taubert H, Heidenreich C, Holzhausen HJ,
Schulz A, Bache M, Kappler M, Eckert AW, Würl P, Melcher I,
Hauptmann K, et al: Expression of survivin detected by
immunohistochemistry in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus is
associated with prognosis of leiomyosarcoma and synovial sarcoma
patients. BMC Cancer. 10:652010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mantel N and Haenszel W: Statistical
aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of
disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 22:719–748. 1959.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cox DR: Regression models and life tables.
J Roy Statist Soc. 34:187–220. 1972.
|
|
37
|
Stuelten CH, Buck MB, Dippon J, Roberts
AB, Fritz P and Knabbe C: Smad4-expression is decreased in breast
cancer tissues: A retrospective study. BMC Cancer. 6:252006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Miller DV, Leontovich AA, Lingle WL, Suman
VJ, Mertens ML, Lillie J, Ingalls KA, Perez EA, Ingle JN, Couch FJ,
et al: Utilizing nottingham prognostic index in microarray gene
expression profiling of breast carcinomas. Mod Pathol. 17:756–764.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xie W, Mertens JC, Reiss DJ, Rimm DL, Camp
RL, Haffty BG and Reiss M: Alterations of Smad signaling in human
breast carcinoma are associated with poor outcome: A tissue
microarray study. Cancer Res. 62:497–505. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhong D, Morikawa A, Guo L, Colpaert C,
Xiong L, Nassar A, Chen C, Lamb N, Dong JT and Zhou W: Homozygous
deletion of SMAD4 in breast cancer cell lines and invasive ductal
carcinomas. Cancer Biol Ther. 5:601–607. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jakob J, Nagase S, Gazdar A, Chien M,
Morozova I, Russo JJ, Nandula SV, Murty VV, Li CM, Tycko B, et al:
Two somatic biallelic lesions within and near SMAD4 in a human
breast cancer cell line. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 42:372–383.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mesker WE, Liefers GJ, Junggeburt JM, van
Pelt GW, Alberici P, Kuppen PJ, Miranda NF, van Leeuwen KA, Morreau
H, Szuhai K, et al: Presence of a high amount of stroma and
downregulation of SMAD4 predict for worse survival for stage I–II
colon cancer patients. Cell Oncol. 31:169–178. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fink SP, Swinler SE, Lutterbaugh JD,
Massagué J, Thiagalingam S, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Willson JK
and Markowitz S: Transforming growth factor-beta-induced growth
inhibition in a Smad4 mutant colon adenoma cell line. Cancer Res.
61:256–260. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
de Jong JS, van Diest PJ, van der Valk P
and Baak JP: Expression of growth factors, growth inhibiting
factors and their receptors in invasive breast cancer. I: An
inventory in search of autocrine and paracrine loops. J Pathol.
184:44–52. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gobbi H, Dupont WD, Simpson JF, Plummer WD
Jr, Schuyler PA, Olson SJ, Arteaga CL and Page DL: Transforming
growth factor-beta and breast cancer risk in women with mammary
epithelial hyperplasia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 91:2096–2101. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|