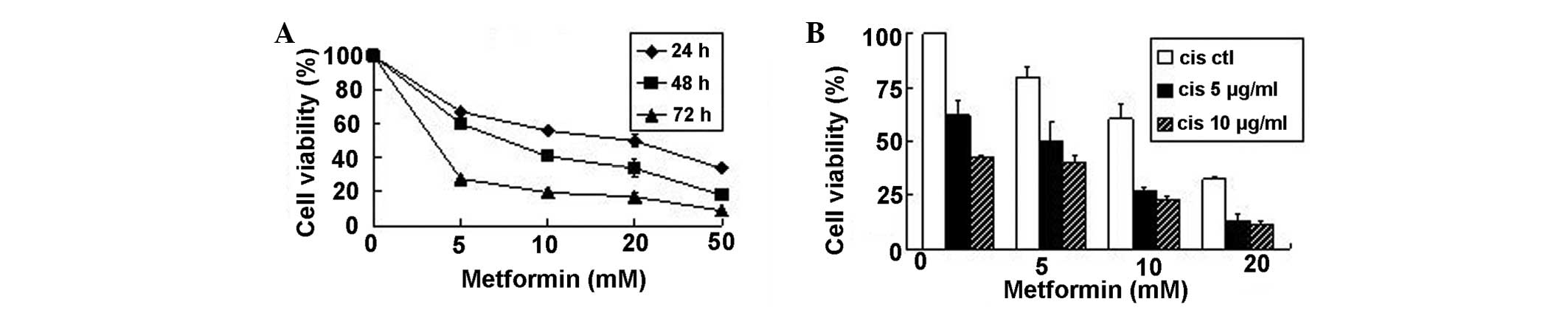
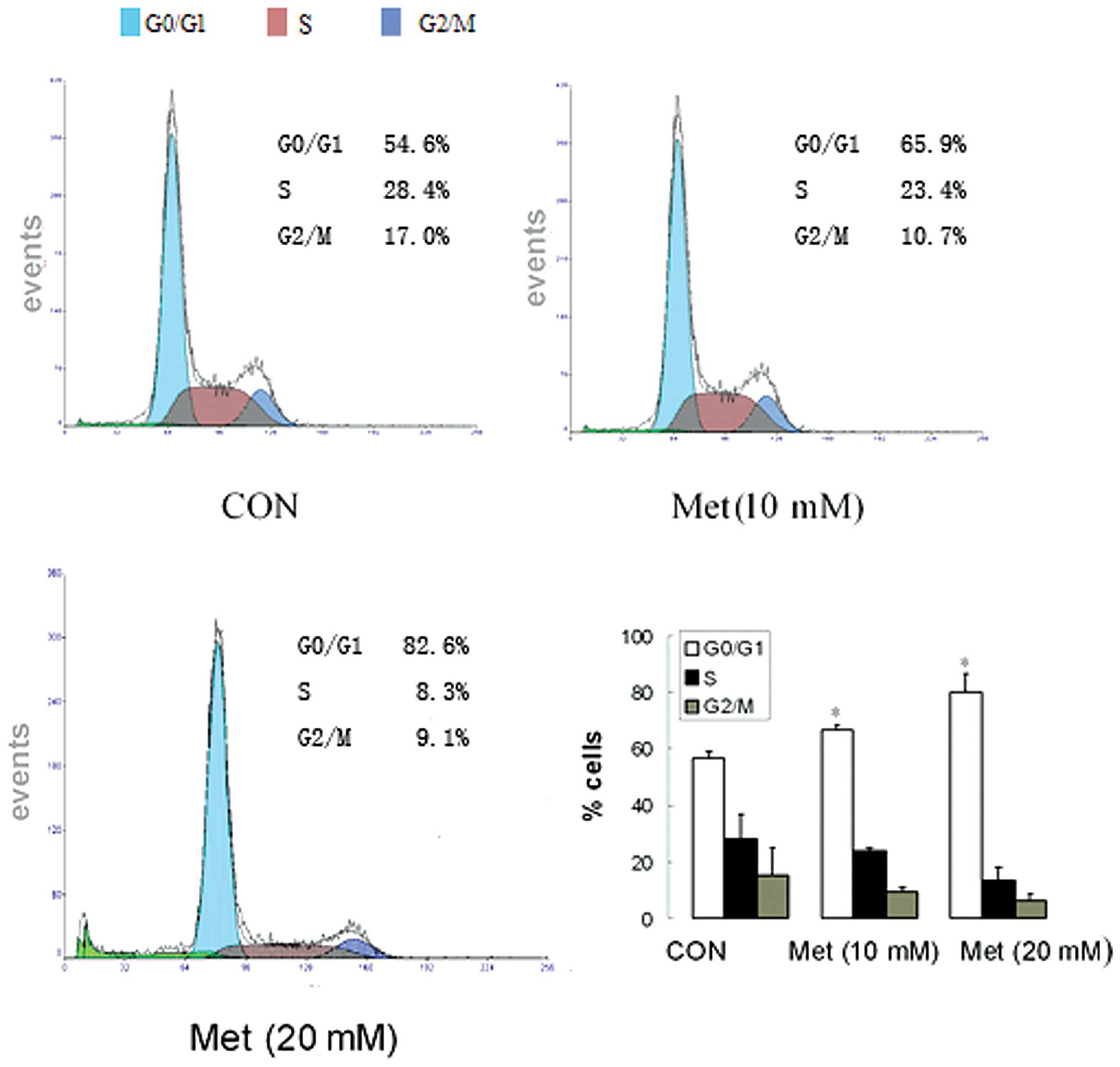
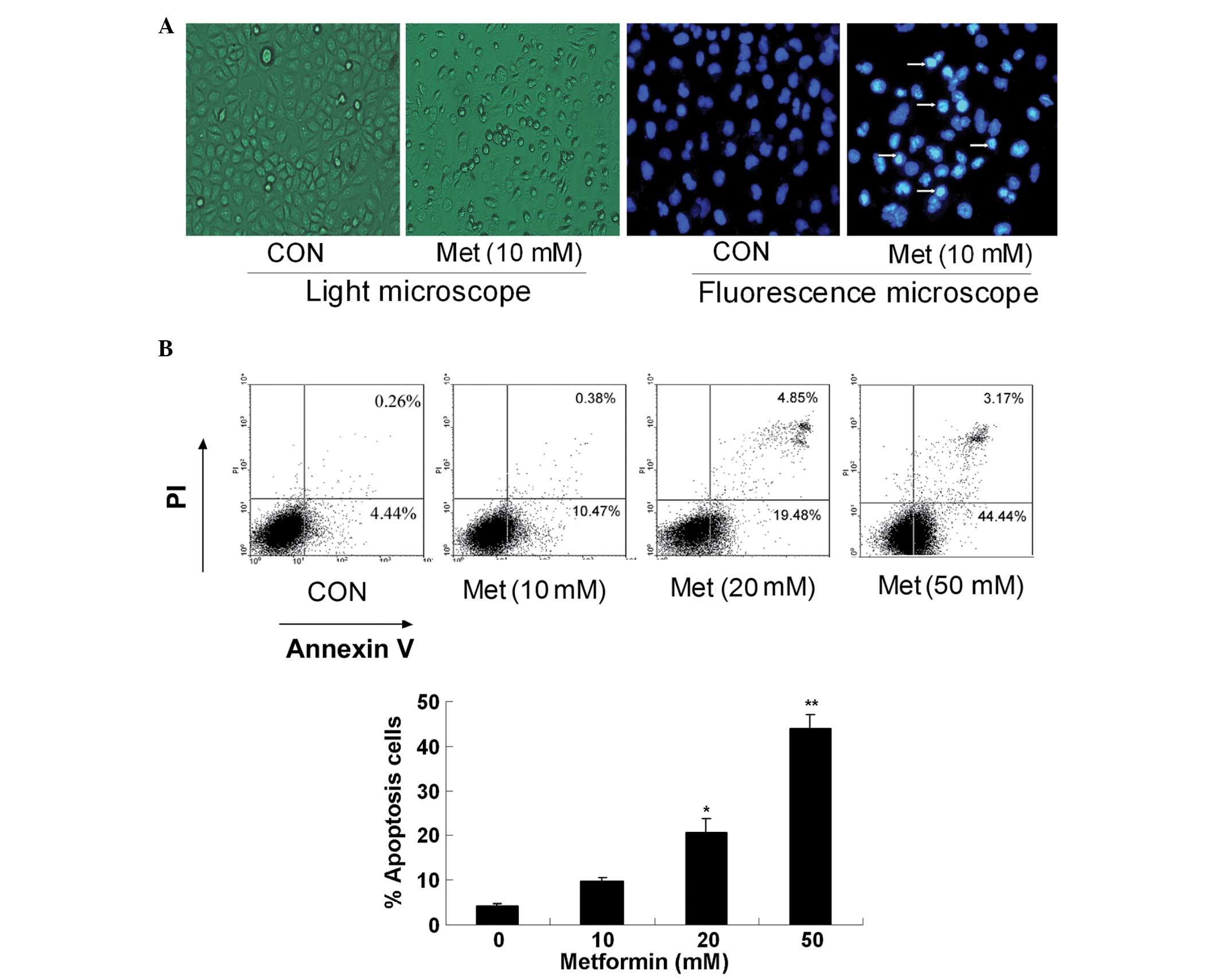
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mulshine JL and Sullivan DC: Clinical
practice. Lung cancer screening. N Engl J Med. 352:2714–2720. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dowling RJ, Goodwin PJ and Stambolic V:
Understanding the benefit of metformin use in cancer treatment. BMC
Med. 9:332011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Evans JM, Donnelly LA, Emslie-Smith AM, et
al: Metformin and reduced risk of cancer in diabetic patients. BMJ.
330:1304–1305. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bowker SL, Majumdar SR, Veugelers P and
Johnson JA: Increased cancer-related mortality for patients with
type 2 diabetes who use sulfonylureas or insulin. Diabetes Care.
29:254–258. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee MS, Hsu CC, Wahlqvist ML, et al: Type
2 diabetes increases and metformin reduces total, colorectal, liver
and pancreatic cancer incidences in Taiwanese: a representative
population prospective cohort study of 800,000 individuals. BMC
Cancer. 11:202011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhu Z, Jiang W, Thompson MD, et al:
Metformin as an energy restriction mimetic agent for breast cancer
prevention. J Carcinog. 10:172011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schneider MB, Matsuzaki H, Haorah J, et
al: Prevention of pancreatic cancer induction in hamsters by
metformin. Gastroenterology. 120:1263–1270. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Buzzai M, Jones RG, Amaravadi RK, et al:
Systemic treatment with the antidiabetic drug metformin selectively
impairs p53-deficient tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. 67:6745–6752.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dowling RJ, Zakikhani M, Fantus IG, et al:
Metformin inhibits mammalian target of rapamycin dependent
translation initiation in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
67:10804–10812. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Noto H, Goto A, Tsujimoto T and Noda M:
Cancer risk in diabetic patients treated with metformin: a
systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 7:e334112012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shaw RJ, Lamia KA, Vasquez D, et al: The
kinase LKB1 mediates glucose homeostasis in liver and therapeutic
effects of metformin. Science. 310:1642–1646. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ben Sahra I, Laurent K, Loubat A, et al:
The antidiabetic drug metformin exerts an antitumoral effect in
vitro and in vivo through a decrease of cyclin D1 level. Oncogene.
27:3576–3586. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhuang Y and Miskimins WK: Cell cycle
arrest in Metformin treated breast cancer cells involves activation
of AMPK, downregulation of cyclin D1 and requires p27Kip1 or
p21Cip1. J Mol Signal. 3:182008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vazquez-Martin A, Oliveras-Ferraros C and
Menendez JA: The antidiabetic drug metformin suppresses HER2
(erbB-2)oncoprotein overexpression via inhibition of the mTOR
effector p70S6K1 in human breast carcinoma cells. Cell Cycle.
8:88–96. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bailey CJ and Turner RC: Metformin. N Engl
J Med. 334:574–579. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang LW, Li ZS, Zou DW, et al: Metformin
induces apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells. World J
Gastroenterol. 14:7192–7198. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hirsch HA, Iliopoulos D, Tsichlis PN and
Struhl K: Metformin selectively targets cancer stem cells and acts
together with chemotherapy to block tumor growth and prolong
remission. Cancer Res. 69:7507–7511. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cantrell LA, Zhou C, Mendivil A, et al:
Metformin is a potent inhibitor of endometrial cancer cell
proliferation - implications for a novel treatment strategy.
Gynecol Oncol. 116:92–98. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Goodwin PJ, Stambolic V, Lemieux J, et al:
Evaluation of metformin in early breast cancer: a modification of
the traditional paradigm for clinical testing of anti-cancer
agents. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 126:215–220. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xiong Y, Lu QJ, Zhao J and Wu GY:
Metformin inhibits growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by
inducing apoptosis via mitochondrion-mediated pathway. Asian
Pacific J Cancer Prev. 13:3275–3279. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Soranna D, Scotti L and Zambon A: Cancer
risk associated with use of metformin and sulfonylurea in type 2
diabetes: a meta-analysis. Oncologist. 17:813–822. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gotlieb WH, Saumet J, Beauchamp MC, et al:
In vitro metformin anti-neoplastic activity in epithelial ovarian
cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 110:246–250. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hanna RK, Zhou C, Malloy KM, et al:
Metformin potentiates the effects of paclitaxel in endometrial
cancer cells through inhibition of cell proliferation and
modulation of the mTOR pathway. Gynecol Oncol. 125:458–469. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
An D, Kewalramani G, Chan JK, et al:
Metformin influences cardiomyocyte cell death by pathways that are
dependent and independent of caspase-3. Diabetologia. 49:2174–2184.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang X, Wullschleger S, Shpiro N, et al:
Important role of the LKB1-AMPK pathway in suppressing
tumorigenesis in PTEN-deficient mice. Biochem J. 412:211–221. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ben Sahra I, Laurent K, Loubat A, et al:
The antidiabetic drug metformin exerts an antitumoral effect in
vitro and in vivo through a decrease of cyclin D1 level. Oncogene.
27:3576–3586. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|