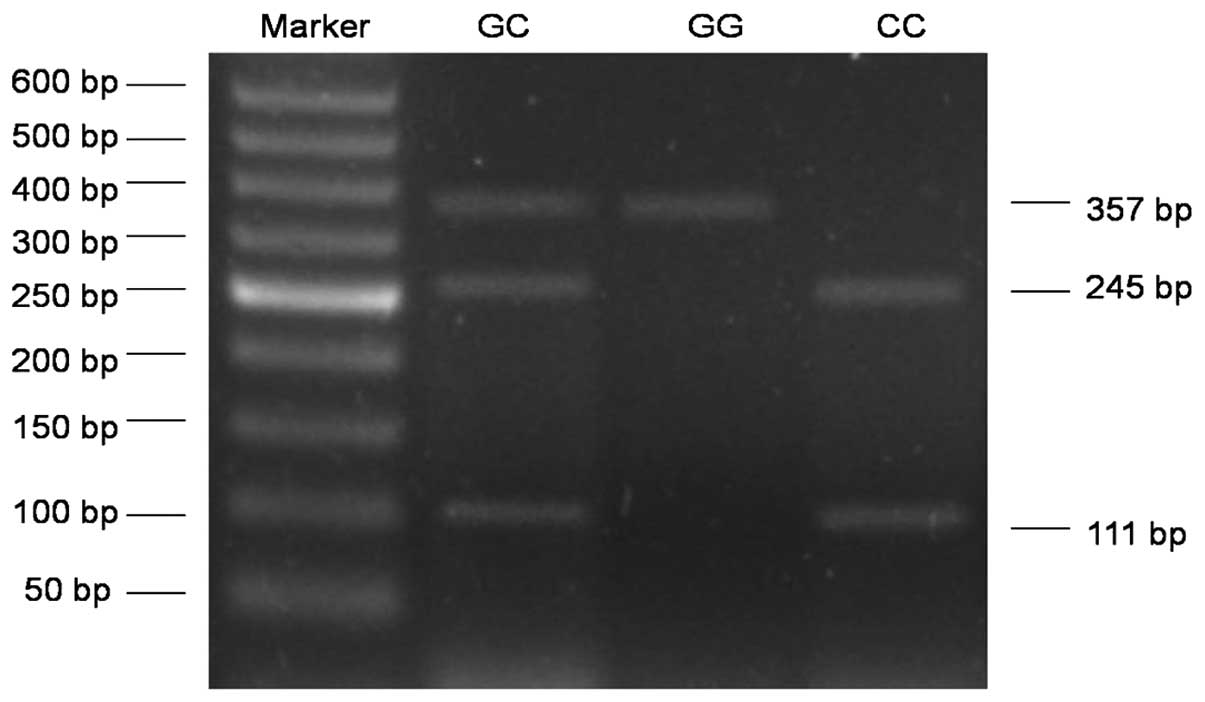
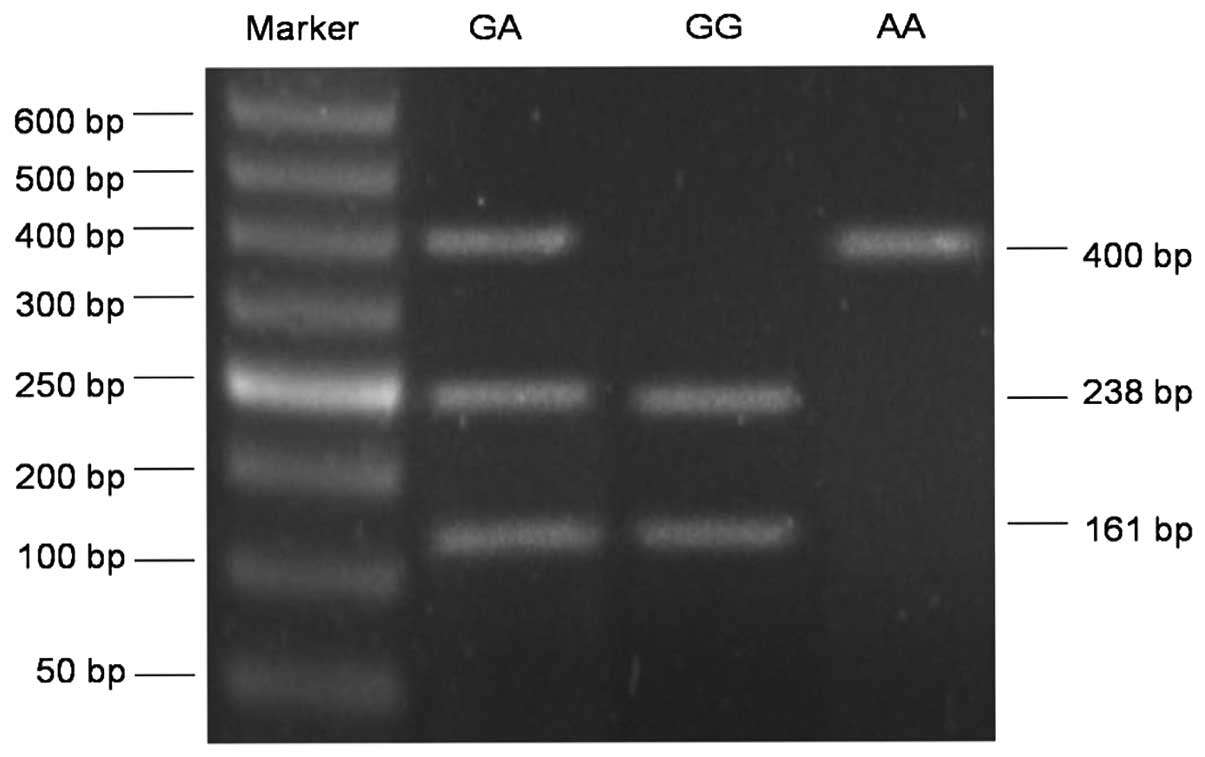
|
1
|
Lashner BA, Silverstein MD and Hanauer SB:
Hazard rates for dysplasia and cancer in ulcerative colitis.
Results from a surveillance program. Dig Dis Sci. 34:1536–1541.
1989.
|
|
2
|
Lennard-Jones JE, Morson BC, Ritchie JK,
et al: Cancer in colitis: Assessment of the individual risk by
clinical and histological criteria. Gastroenterology. 73:1280–1289.
1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rhodes JM and Campbell BJ: Inflammation
and colorectal cancer: IBD associated and sporadic cancer compared.
Trends Mol Med. 8:10–16. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Romano M and Claria J: Cyclooxygenase-2
and 5-lipoxygenase converging functions on cell proliferation and
tumor angiogenesis: Implications for cancer therapy. FASEB J.
17:1986–1995. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Simmons DL, Botting RM and Hla T:
Cyclooxygenase isozymes: The biology of prostaglandin synthesis and
inhibition. Pharmacol Rev. 56:387–437. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tsujii M, Kawano S, Tsuji S, et al:
Cyclooxygenase regulates angiogenesis induced by colon cancer
cells. Cell. 93:705–716. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ranger GS, Thomas V, Jewell A and Mokbel
K: Elevated cyclooxygenase-2 expression correlates with distant
metastases in breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 24:2349–2351.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Eberhart CE, Coffey RJ, Radhika A, et al:
Up-regulation of cyclooxygenase 2 gene expression in human
colorectal adenomas and adenocarcinomas. Gastroenterology.
107:1183–1188. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ristimäki A, Honkanen N, Jänkälä H, et al:
Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human gastric carcinoma. Cancer
Res. 57:1276–1280. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu X, Li P, Zhang ST, et al: COX-2 mRNA
expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and effect
by NSAID. Dis Esophagus. 21:9–14. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Brosens LA, Donahue CA, Keller JJ, et al:
Increased cyclooxygenase-2 expression in duodenal compared with
colonic tissues in familial adenomatous polyposis and relationship
to the −765 G/C COX-2 polymorphism. Clin Cancer Res. 11:4090–4096.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fritsche E, Baek SJ, King LM, Zeldin DC,
Eling TE and Bell DA: Functional characterization of
cyclooxygenase-2 polymorphisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 299:468–476.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Papafili A, Hill MR, Brull DJ, et al:
Common promoter variant in cyclooxygenase-2 represses gene
expression: Evidence of role in acute-phase inflammatory response.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 22:1631–1636. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hamajima N, Takezaki T, Matsuo K, et al:
Genotype frequencies of cyclooxygenease 2 (COX2) rare polymorphisms
for Japanese with and without colorectal cancer. Asian Pac. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 2:57–62. 2001.
|
|
15
|
Lee TS, Jeon YT, Kim JW, et al: Lack of
association of the cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide
synthase gene polymorphism with risk of cervical cancer in Korean
population. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1095:134–142. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang X, Miao X, Tan W, et al:
Identification of functional genetic variants in cyclooxygenase-2
and their association with risk of esophageal cancer.
Gastroenterology. 129:565–576. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Szczeklik W, Sanak M, Szczeklik A, et al:
Functional effects and gender association of COX-2 gene
polymorphism G-765C in bronchial asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
114:248–253. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hermanek P, Scheibe O, Spiessl B and
Wagner G: TNM classification of malignant tumors: The new 1987
edition. Rontgenblatter. 40:2001987.(In German). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hamilton SR, Bosman FT, Boffetta P, et al:
Tumours of the colon and rectumWHO Classification of Tumours of the
Digestive System. Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH and Theise ND:
IARC Press; Lyon: pp. 131–181. 2010
|
|
20
|
Koh WP, Yuan JM, Van Den Berg D, et al:
Interaction between cyclooxygenase-2 gene polymorphism and dietary
n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids on colon cancer risk: The Singapore
Chinese Health Study. Br J Cancer. 90:1760–1764. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ulrich CM, Whitton J, Yu JH, et al: PTGS2
(COX-2) −765G>C promoter variant reduces risk of colorectal
adenoma among nonusers of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 14:616–619. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lin HJ, Keku TO, Reddy ST, et al:
Prostaglandin H synthase 2 variant (Val511Ala) in African Americans
may reduce the risk for colorectal neoplasia. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 11:1305–1315. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sansbury LB, Millikan RC, Schroeder JC, et
al: COX-2 polymorphism, use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
and risk of colon cancer in African Americans (United States).
Cancer Causes Control. 17:257–266. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Goodman JE, Bowman ED, Chanock SJ, et al:
Arachidonate lipoxygenase (ALOX) and cyclooxygenase (COX)
polymorphisms and colon cancer risk. Carcinogenesis. 25:2467–2472.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cox DG, Pontes C, Guino E, Navarro M,
Osorio A, Canzian F and Moreno V: Bellvitge Colorectal Cancer Study
Group: Polymorphisms in prostaglandin synthase 2/cyclooxygenase 2
(PTGS2/COX2) and risk of colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer.
91:339–343. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tomozawa S, Tsuno NH, Sunami E, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression correlates with tumour recurrence,
especially haematogenous metastasis, of colorectal cancer. Br J
Cancer. 83:324–328. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang H and Sun XF: Overexpression of
cyclooxygenase-2 correlates with advanced stages of colorectal
cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 97:1037–1041. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Konno H, Baba M, Shoji T, Ohta M, Suzuki S
and Nakamura S: Cyclooxygenase-2 expression correlates with uPAR
levels and is responsible for poor prognosis of colorectal cancer.
Clin Exp Metastasis. 19:527–534. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yao M, Lam EC, Kelly CR, Zhou W and Wolfe
MM: Cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibition with NS-398 suppresses
proliferation and invasiveness and delays liver metastasis in
colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 90:712–719. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tsujii M, Kawano S and DuBois RN:
Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human colon cancer cells increase
metastatic potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:3336–3340. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|