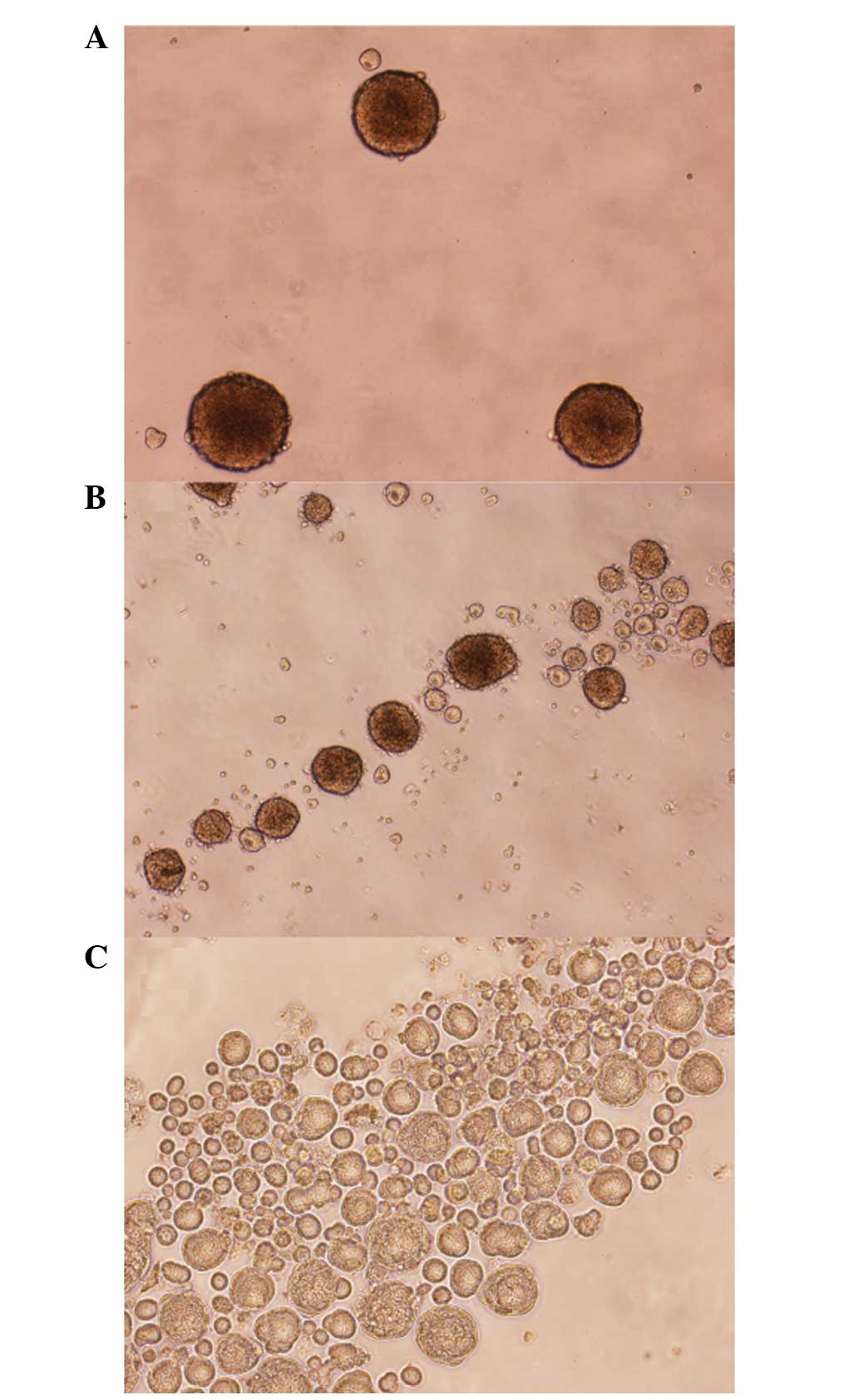
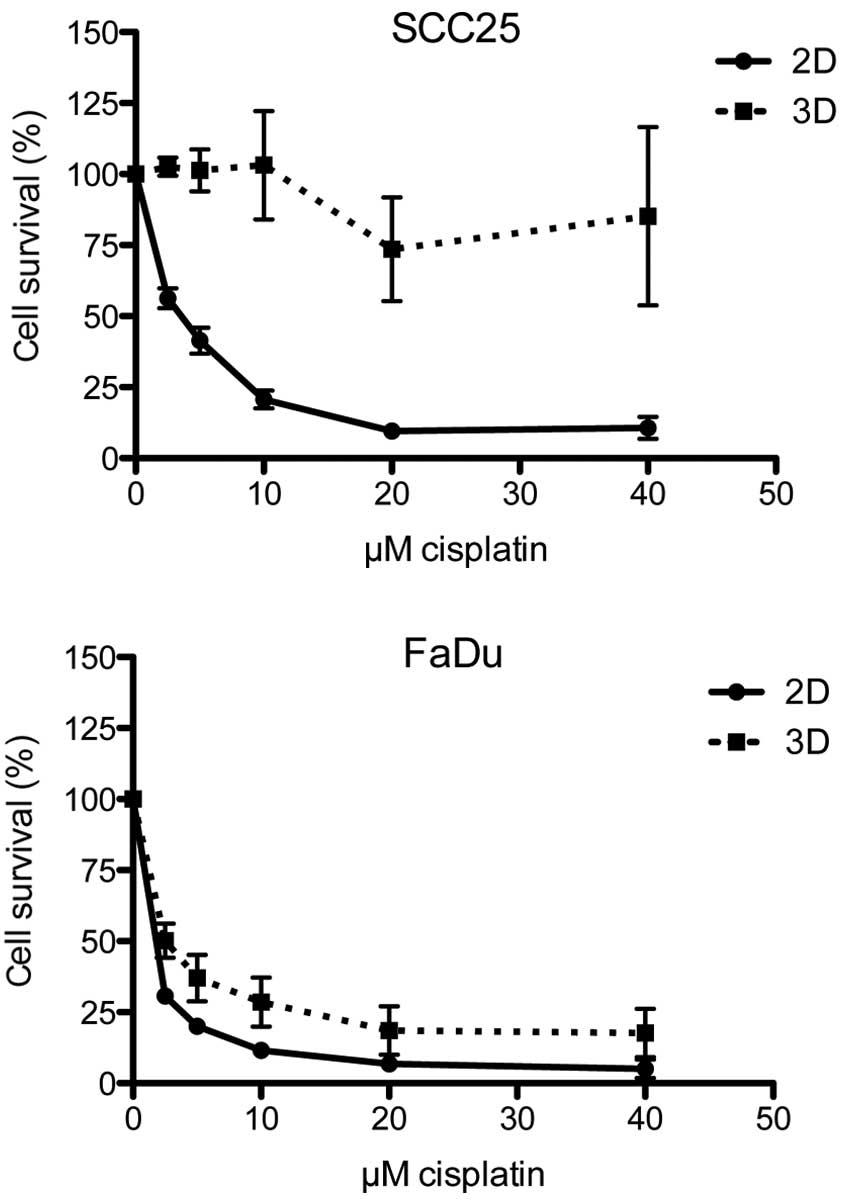
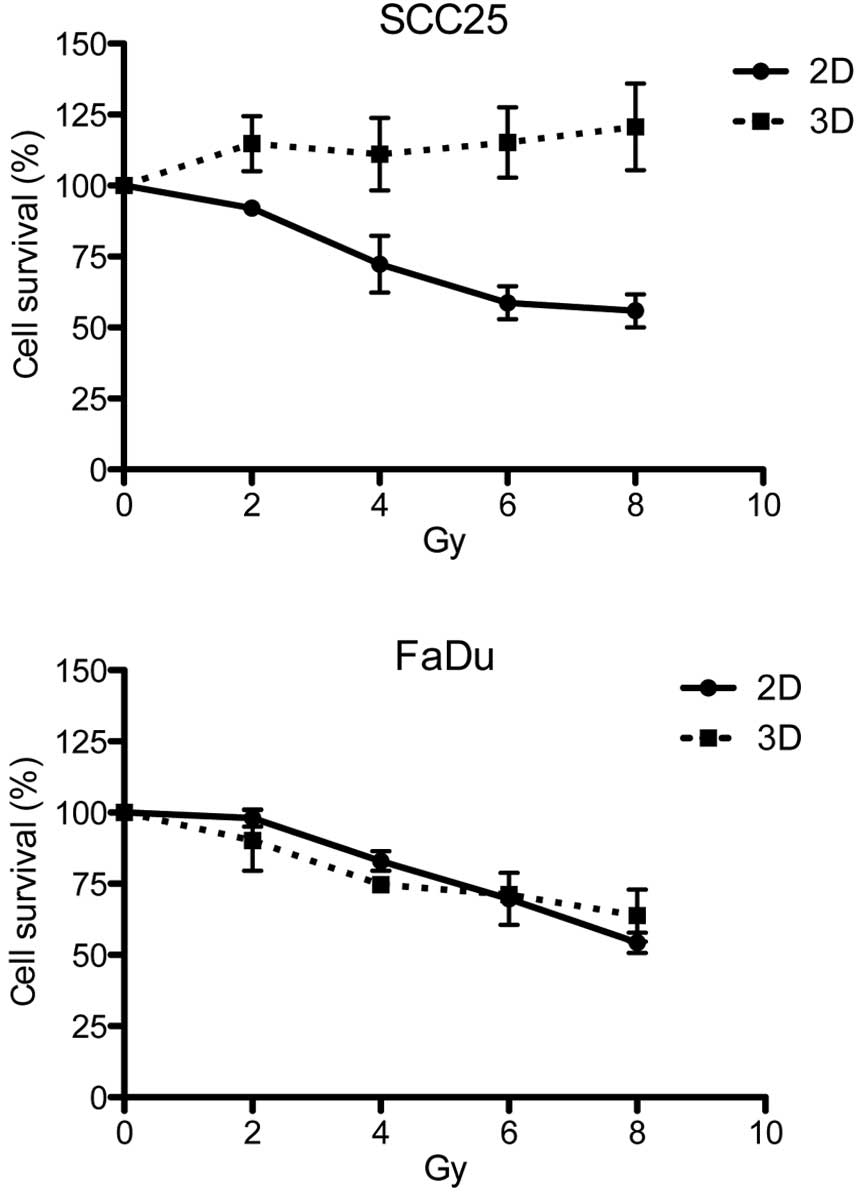
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Myers EN: Head and neck oncology — 2010,
part II. Otolaryngol Pol. 64:204–214. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Carvalho AL, Nishimoto IN, Califano JA and
Kowalski LP: Trends in incidence and prognosis for head and neck
cancer in the United States: A site-specific analysis of the SEER
database. Int J Cancer. 114:806–816. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kimlin LC, Casagrande G and Virador VM:
In vitro three-dimensional (3D) models in cancer research:
An update. Mol Carcinog. 52:167–182. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bokhari M, Carnachan RJ, Cameron NR and
Przyborski SA: Culture of HepG2 liver cells on three dimensional
polystyrene scaffolds enhances cell structure and function during
toxicological challenge. J Anat. 211:567–576. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shain KH and Dalton WS: Cell adhesion is a
key determinant in de novo multidrug resistance (MDR): New targets
for the prevention of acquired MDR. Mol Cancer Ther. 1:69–78.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Johnson JI, Decker S, Zaharevitz D,
Rubinstein LV, Venditti JM, Schepartz S, et al: Relationships
between drug activity in NCI preclinical in vitroin
vivo models and early clinical trials. Br J Cancer.
84:1424–1431. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Voskoglou-Nomikos T, Pater JL and Seymour
L: Clinical predictive value of the in vitro cell line,
human xenograft, and mouse allograft preclinical cancer models.
Clin Cancer Res. 9:4227–4239. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sutherland RM, McCredie JA and Inch WR:
Growth of multicell spheroids in tissue culture as a model of
nodular carcinomas. J Natl Cancer Inst. 46:113–120. 1971.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Horning JL, Sahoo SK, Vijayaraghavalu S,
Dimitrijevic S, Vasir JK, Jain TK, et al: 3-D tumor model for in
vitro evaluation of anticancer drugs. Mol Pharm. 5:849–862.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Karlsson H, Fryknäs M, Larsson R and
Nygren P: Loss of cancer drug activity in colon cancer HCT-116
cells during spheroid formation in a new 3-D spheroid cell culture
system. Exp Cell Res. 318:1577–1585. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cordes N and Meineke V: Cell
adhesion-mediated radioresistance (CAM-RR). Extracellular
matrix-dependent improvement of cell survival in human tumor and
normal cells in vitro. Strahlenther Onkol. 179:337–344.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Khaitan D, Chandna S, Arya MB and
Dwarakanath BS: Establishment and characterization of multicellular
spheroids from a human glioma cell line; Implications for tumor
therapy. J Transl Med. 4:122006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lim Y, Keam B, Koh Y, Kim TM, Lee S-H, Hah
JH, et al: Clinical outcomes of radiation-based locoregional
therapy in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
patients not responding to induction chemotherapy. Oral Surg Oral
Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 116:55–60. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vermorken JB and Specenier P: Optimal
treatment for recurrent/metastatic head and neck cancer. Ann Oncol.
21(Suppl 7): vii252–vii261. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ho AS, Tsao GJ, Chen FW, Shen T, Kaplan
MJ, Colevas AD, et al: Impact of positron emission
tomography/computed tomography surveillance at 12 and 24 months for
detecting head and neck cancer recurrence. Cancer. 119:1349–1356.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Eke I, Schneider L, Förster C, Zips D,
Kunz-Schughart LA and Cordes N: EGFR/JIP-4/JNK2 signaling
attenuates cetuximab-mediated radiosensitization of squamous cell
carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 73:297–306. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Colley HE, Hearnden V, Avila-Olias M,
Cecchin D, Canton I, Madsen J, et al: Polymersome-mediated delivery
of combination anticancer therapy to head and neck cancer cells: 2D
and 3D in vitro evaluation. Mol Pharm. 11:1176–1188. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Eke I, Leonhardt F, Storch K, Hehlgans S
and Cordes N: The small molecule inhibitor QLT0267 Radiosensitizes
squamous cell carcinoma cells of the head and neck. PLoS One.
4:e64342009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kotowski U, Heiduschka G, Brunner M,
Czembirek C, Eder-Czembirek C, Schmidt R, et al: Radiosensitization
of head and neck cancer cells by the phytochemical agent
sulforaphane. Strahlenther Onkol. 187:575–580. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lill C, Schneider S, Pammer J, Loewe R,
Gedlicka W, Houben R, et al: Significant correlation of
peptidyl-prolyl isomerase overexpression in Merkel cell carcinoma
with overall survival of patients. Head Neck. 33:1294–1300. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu W: CD133 and Ki-67 expression is
associated with gastrointestinal stromal tumor prognosis. Oncol
Lett. 6:1289–1294. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gildener-Leapman N, Ferris RL and Bauman
JE: Promising systemic immunotherapies in head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 49:1089–1096. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Erjala K, Sundvall M, Junttila TT, Zhang
N, Savisalo M, Mali P, et al: Signaling via ErbB2 and ErbB3
associates with resistance and epidermal growth factor receptor
(EGFR) amplification with sensitivity to EGFR inhibitor gefitinib
in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res.
12:4103–4111. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ye Q, Cai W, Zheng Y, Evers BM and She QB:
ERK and AKT signaling cooperate to translationally regulate
survivin expression for metastatic progression of colorectal
cancer. Oncogene. 33:1828–1839. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Desoize B, Gimonet D and Jardiller JC:
Cell culture as spheroids: An approach to multicellular resistance.
Anticancer Res. 18:4147–4158. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Elliott NT and Yuan F: A review of
three-dimensional in vitro tissue models for drug discovery
and transport studies. J Pharm Sci. 100:59–74. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee GY, Kenny PA, Lee EH and Bissell MJ:
Three-dimensional culture models of normal and malignant breast
epithelial cells. Nat Methods. 4:359–365. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ingargiola M, Runge R, Heldt J-M,
Freudenberg R, Steinbach J, Cordes N, et al: Potential of a
Cetuximab-based radioimmunotherapy combined with external
irradiation manifests in a 3-D cell assay. Int J Cancer.
135:968–980. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rasanen K, Sriswasdi S, Valiga A, Tang
H-Y, Zhang G, Perego M, et al: Comparative secretome analysis of
epithelial and mesenchymal subpopulations of head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma identifies S100A4 as a potential therapeutic target.
Mol Cell Proteomics. 12:3778–3792. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yan M, Yang X, Wang L, Clark D, Zuo H, Ye
D, et al: Plasma membrane proteomics of tumor spheres identify
CD166 as a novel marker for cancer stem-like cells in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cell Proteomics. 12:3271–3284. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Waldron NN, Barsky SH, Dougherty PR and
Vallera DA: A bispecific EpCAM/CD133-targeted toxin is effective
against carcinoma. Target Oncol. 9:239–249. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang W-H, Lan H-Y, Tai S-K and Yang M-H:
Repression of bone morphogenetic protein 4 by let-7i attenuates
mesenchymal migration of head and neck cancer cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 433:24–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chang CC, Hsu WH, Wang CC, Chou CH, Kuo
MYP, Lin BR, et al: Connective tissue growth factor activates
pluripotency genes and mesenchymal-epithelial transition in head
and neck cancer cells. Cancer Res. 73:4147–4157. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dennis M, Wang G, Luo J, Lin Y, Dohadwala
M, Abemayor E, et al: Snail controls the mesenchymal phenotype and
drives erlotinib resistance in oral epithelial and head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma cells. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.
147:726–732. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Duarte S, Loubat A, Momier D, Topi M,
Faneca H, Pedroso de Lima MC, et al: Isolation of head and neck
squamous carcinoma cancer stem-like cells in a syngeneic mouse
model and analysis of hypoxia effect. Oncol Rep. 28:1057–1062.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen Y-S, Wu M-J, Huang C-Y, Lin S-C,
Chuang T-H, Yu C-C and Lo JF: CD133/Src axis mediates tumor
initiating property and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of head
and neck cancer. PLoS One. 6:e280532011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lim YC, Oh S-Y, Cha YY, Kim S-H, Jin X and
Kim H: Cancer stem cell traits in squamospheres derived from
primary head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Oral Oncol.
47:83–91. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Krishnamurthy S, Dong Z, Vodopyanov D,
Imai A, Helman JI, Prince ME, et al: Endothelial cell-initiated
signaling promotes the survival and self-renewal of cancer stem
cells. Cancer Res. 70:9969–9978. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kross KW, Heimdal JH, Olsnes C, Olofsson J
and Aarstad HJ: Co-culture of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
spheroids with autologous monocytes predicts prognosis. Scand J
Immunol. 67:392–399. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Harper LJ, Piper K, Common J, Fortune F
and Mackenzie IC: Stem cell patterns in cell lines derived from
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med.
36:594–603. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Olsnes C, Heimdal J-H, Kross KW, Olofsson
J and Aarstad HJ: Viable head and neck tumor spheroids stimulate
in vitro autologous monocyte MCP-1 secretion through soluble
substances and CD14/lectin-like receptors. Eur Arch
Otorhinolaryngol. 262:953–960. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kross KW, Heimdal J-H, Olsnes C, Olofsson
J and Aarstad HJ: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma spheroid-
and monocyte spheroid-stimulated IL-6 and monocyte chemotactic
protein-1 secretion are related to TNM stage, inflammatory state
and tumor macrophage density. Acta Otolaryngol. 125:1097–1104.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Heimdal JH, Olsnes C, Olofsson J and
Aarstad HJ: Monocyte and monocyte-derived macrophage secretion of
MCP-1 in co-culture with autologous malignant and benign control
fragment spheroids. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 50:300–306. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Heimdal JH, Aarstad HJ, Olsnes C and
Olofsson J: Human autologous monocytes and monocyte-derived
macrophages in co-culture with carcinoma F-spheroids secrete IL-6
by a non-CD14-dependent pathway. Scand J Immunol. 53:162–170. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Heimdal J, Aarstad HJ and Olofsson J:
Monocytes secrete interleukin-6 when co-cultured in vitro
with benign or malignant autologous fragment spheroids from
squamous cell carcinoma patients. Scand J Immunol. 51:271–278.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Fayad W, Brnjic S, Berglind D, Blixt S,
Shoshan MC, Berndtsson M, et al: Restriction of cisplatin induction
of acute apoptosis to a subpopulation of cells in a
three-dimensional carcinoma culture model. Int J Cancer.
125:2450–2455. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sminia P, Acker H, Eikesdal HP, Kaaijk P,
Enger PØ, Slotman B and Bjerkvig R: Oxygenation and response to
irradiation of organotypic multicellular spheroids of human glioma.
Anticancer Res. 23:1461–1466. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Shweiki D, Neeman M, Itin A and Keshet E:
Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor expression by
hypoxia and by glucose deficiency in multicell spheroids:
Implications for tumor angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
92:768–772. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sivaraj KK, Takefuji M, Schmidt I, Adams
RH, Offermanns S and Wettschureck N: G13 controls angiogenesis
through regulation of VEGFR-2 expression. Dev Cell. 25:427–434.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Töyli M, Rosberg-Kulha L, Capra J,
Vuoristo J and Eskelinen S: Different responses in transformation
of MDCK cells in 2D and 3D culture by v-Src as revealed by
microarray techniques, RT-PCR and functional assays. Lab Invest.
90:915–928. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|