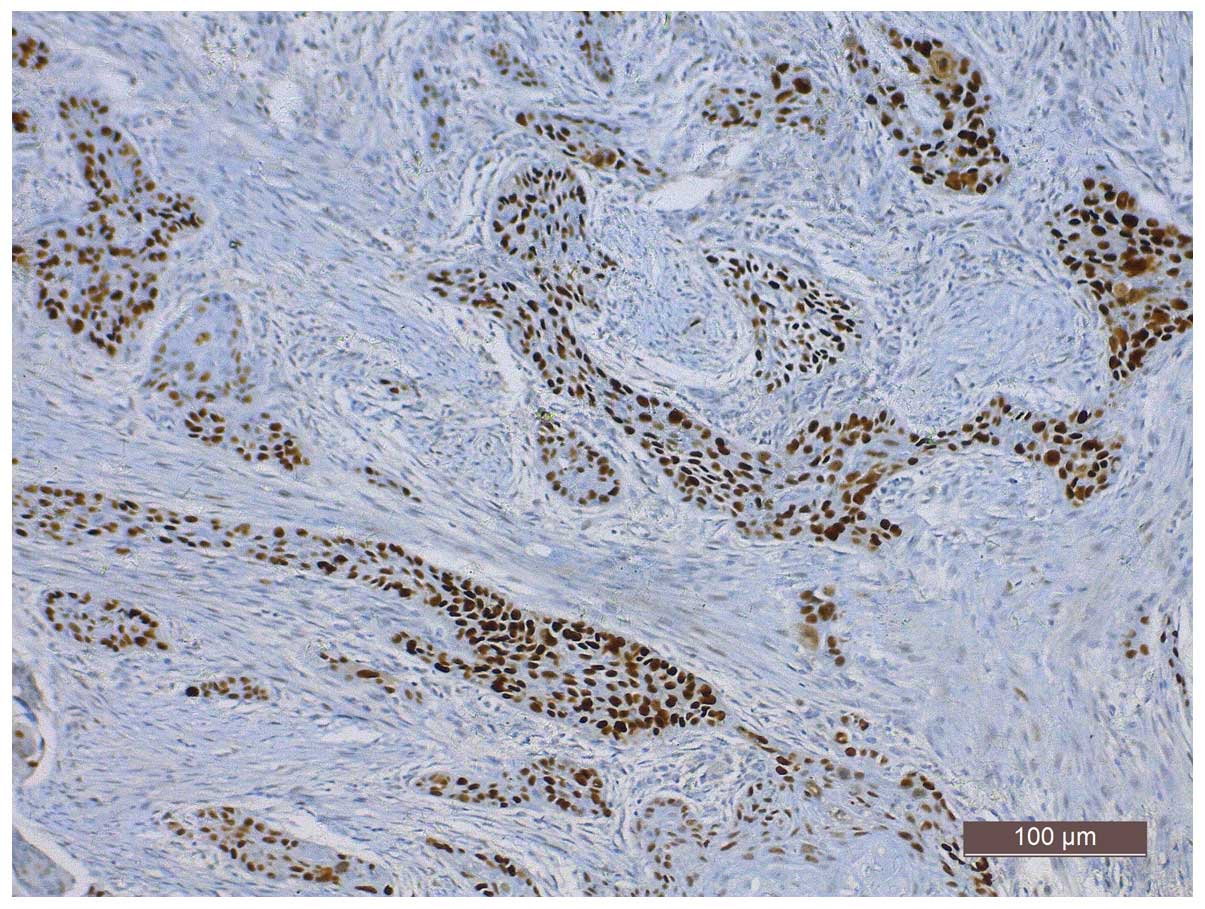
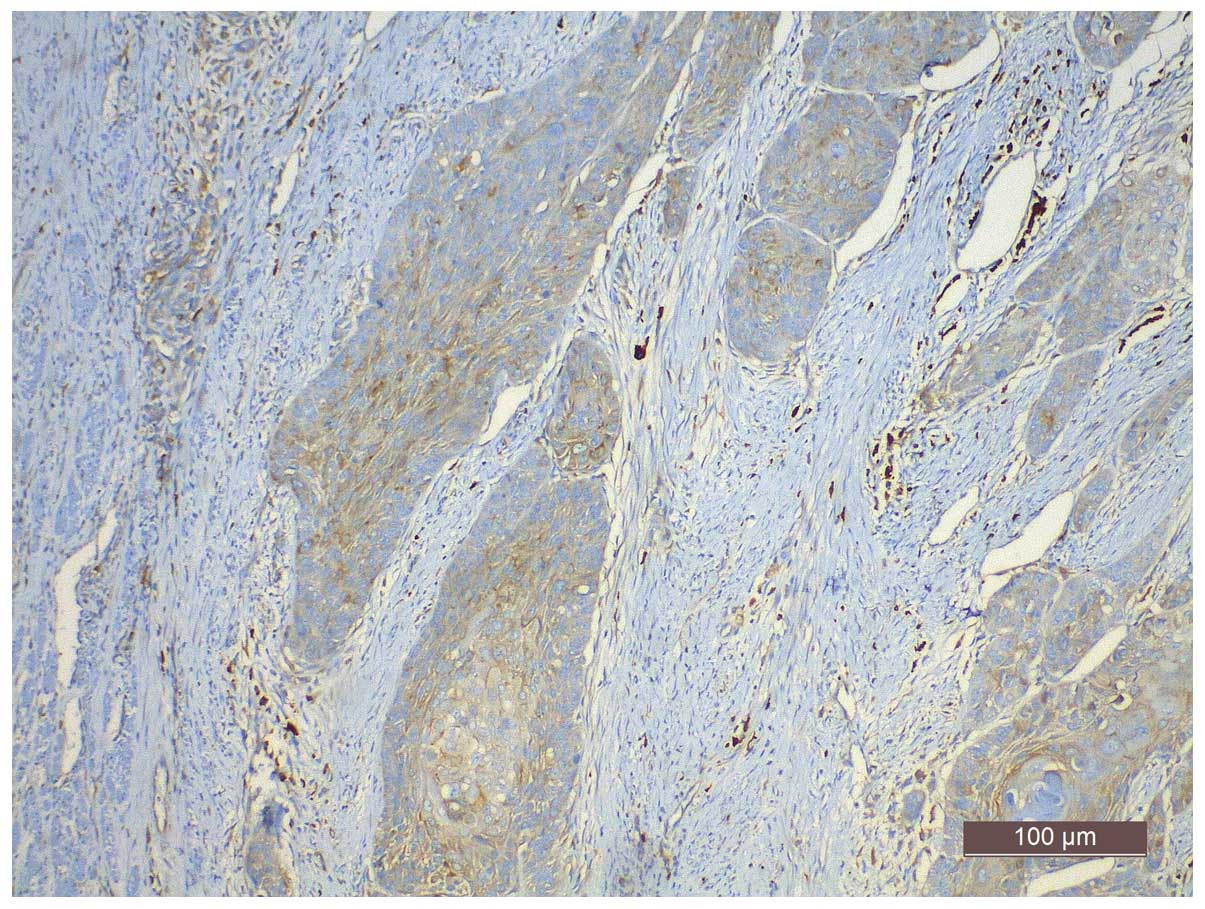
|
1
|
Huang JX, Chen WC, Lin M, Zhang YL, Li FY,
Song ZX, Xiao W, Chen P, Qian RY, Salminen E, et al:
Clinicopathological significance of cyclooxygenase-2 and cell
cycle-regulatory proteins expression in patients with esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Esophagus. 25:121–129. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Meng XY, Zhu ST, Zong Y, Wang YJ, Li P and
Zhang ST: Promoter hypermethylation of cyclooxygenase-2 gene in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Esophagus. 24:444–449.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Surget S, Khoury MP and Bourdon JC:
Uncovering the role of p53 splice variants in human malignancy: A
clinical perspective. Onco Targets Ther. 7:57–68. 2014.
|
|
4
|
Chandrasekharan NV and Simmons DL: The
cyclooxygenases. Genome Biol. 5:2412004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen LQ: Understanding and appraisal of
the new TNM classification for esophageal cancer in the AJCC cancer
staging manual (7th edition). Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi.
32:237–240. 2010.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kang SY, Halvorsen OJ, Gravdal K,
Bhattacharya N, Lee JM, Liu NW, Johnston BT, Johnston AB, Haukaas
SA, Aamodt K, et al: Prosaposin inhibits tumor metastasis via
paracrine and endocrine stimulation of stromal p53 and Tsp-1. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:12115–12120. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang H, Wang LF, Tian HM, Liu Y, Li M, Qu
P, Wang WR and Zhang W: Expression of retinoic acid receptor-beta
mRNA and p16, p53, Ki67 proteins in esophageal carcinoma and its
precursor lesions. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 27:152–155. 2005.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Do PM, Varanasi L, Fan SQ, Li CY, Kubacka
I, Newman V, Chauhan K, Daniels SR, Boccetta M, Garrett MR, et al:
Mutant p53 cooperates with ETS2 to promote etoposide resistance.
Genes Dev. 26:830–845. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee MH and Lozano G: Regulation of the
p53-MDM2 pathway by 14-3-3 and other proteins. Semin Cancer Biol.
16:225–234. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kirsch DG and Kastan MB: Tumor-suppressor
p53: Implications for tumor development and prognosis. J Clin
Oncol. 16:3158–3168. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fagundes RB, Mello CR, Tollens P, Pütten
ACK, Wagner MB, Moreira LF and Barros SG: P53 protein in esophageal
mucosa of individuals at high risk of squamous cell carcinoma of
the esophagus. Dis Esophagus. 14:185–190. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Han U, Can OI, Han S, Kayhan B and Onal
BU: Expressions of p53, VEGF C, p21: Could they be used in
preoperative evaluation of lymph node metastasis of esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma? Dis Esophagus. 20:379–385. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ye B, Wang X, Yang Z, Sun Z, Zhang R, Hu
Y, Lu Y and Du J: P53 and p73 expression in esophageal carcinoma
correlate with clinicopathology of tumors. Hepatogastroenterology.
59:2192–2195. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chino O, Kijima H, Shimada H, Nishi T,
Tanaka H, Kise Y, Kenmochi T, Himeno S, Machimura T, Tanaka M, et
al: Accumulation of p53 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int
J Mol Med. 8:359–363. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jin Y, Zhang W and Liu B: Abnormal
expression of p53, Ki67 and iNOS in human esophageal carcinoma in
situ and pre-malignant lesions. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi.
23:129–131. 2001.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Feletou M, Huang Y and Vanhoutte PM:
Endothelium-mediated control of vascular tone: COX-1 and COX-2
products. Br J Pharmacol. 164:894–912. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
O'Banion MK: Cyclooxygenase-2: Molecular
biology, pharmacology, and neurobiology. Crit Rev Neurobiol.
13:45–82. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Williams CS and DuBois RN: Prostaglandin
endoperoxide synthase: Why two isoforms? Am J Physiol.
270:G393–G400. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Willoughby DA, Moore AR and Colville-Nash
PR: COX-1, COX-2 and COX-3 and the future treatment of chronic
inflammatory disease. Lancet. 355:646–648. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xin X, Majumder M, Girish GV, Mohindra V,
Maruyama T and Lala PK: Targeting COX-2 and EP4 to control tumor
growth, angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis and metastasis to the lungs
and lymph nodes in a breast cancer model. Lab Invest. 92:1115–1128.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Misra S and Sharma K: COX-2 signaling and
cancer: New players in old arena. Curr Drug Targets. 15:347–359.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Okumura H, Uchikado Y, Setoyama T,
Matsumoto M, Owaki T, Ishigami S and Natsugoe S: Biomarkers for
predicting the response of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma to
neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy. Surg Today. 44:421–428. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kashiwagi S, Hosono K, Suzuki T, Takeda A,
Uchinuma E and Majima M: Role of COX-2 in lymphangiogenesis and
restoration of lymphatic flow in secondary lymphedema. Lab Invest.
91:1314–1325. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou BT, Yang W, Xu XH, Ai YG, Li XL and
Huang YJ: Correlation of cyclooxygenase 2 expression with
microlymphatic density and its clinical significance. Zhonghua Wei
Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 13:699–702. 2010.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Prins MJ, Verhage RJ, ten Kate FJ and van
Hillegersberg R: Cyclooxygenase isoenzyme-2 and vascular
endothelial growth factor are associated with poor prognosis in
esophageal adenocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg. 16:956–966. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Benoit V, de Moraes E, Dar NA, Taranchon
E, Bours V, Hautefeuille A, Tanière P, Chariot A, Scoazec JY, de
Moura Gallo CV, et al: Transcriptional activation of
cyclooxygenase-2 by tumor suppressor p53 requires nuclear
factor-kappaB. Oncogene. 25:5708–5718. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Song J, Wei Y, Chen Q and Xing D:
Cyclooxygenase 2-mediated apoptotic and inflammatory responses in
photodynamic therapy treated breast adenocarcinoma cells and
xenografts. J Photochem Photobiol B. 134:27–36. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cheng AS, Yu J, Lai PB, Chan HL and Sung
JJ: Cox-2 mediates hepatitis B virus X protein abrogation of
p53-induced apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 374:175–180.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Choi EM, Kim SR, Lee EJ and Han JA:
Cyclooxygenase-2 functionally inactivates p53 through a physical
interaction with p53. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1793:1354–1365. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ma XL, XS G and Sun HJ: Advance in
research on relations between cyclooxygenase-2 and P53 during
inflammatory stress and carcinogenesis. Int J Genet. 32:372–376.
2009.(In Chinese).
|