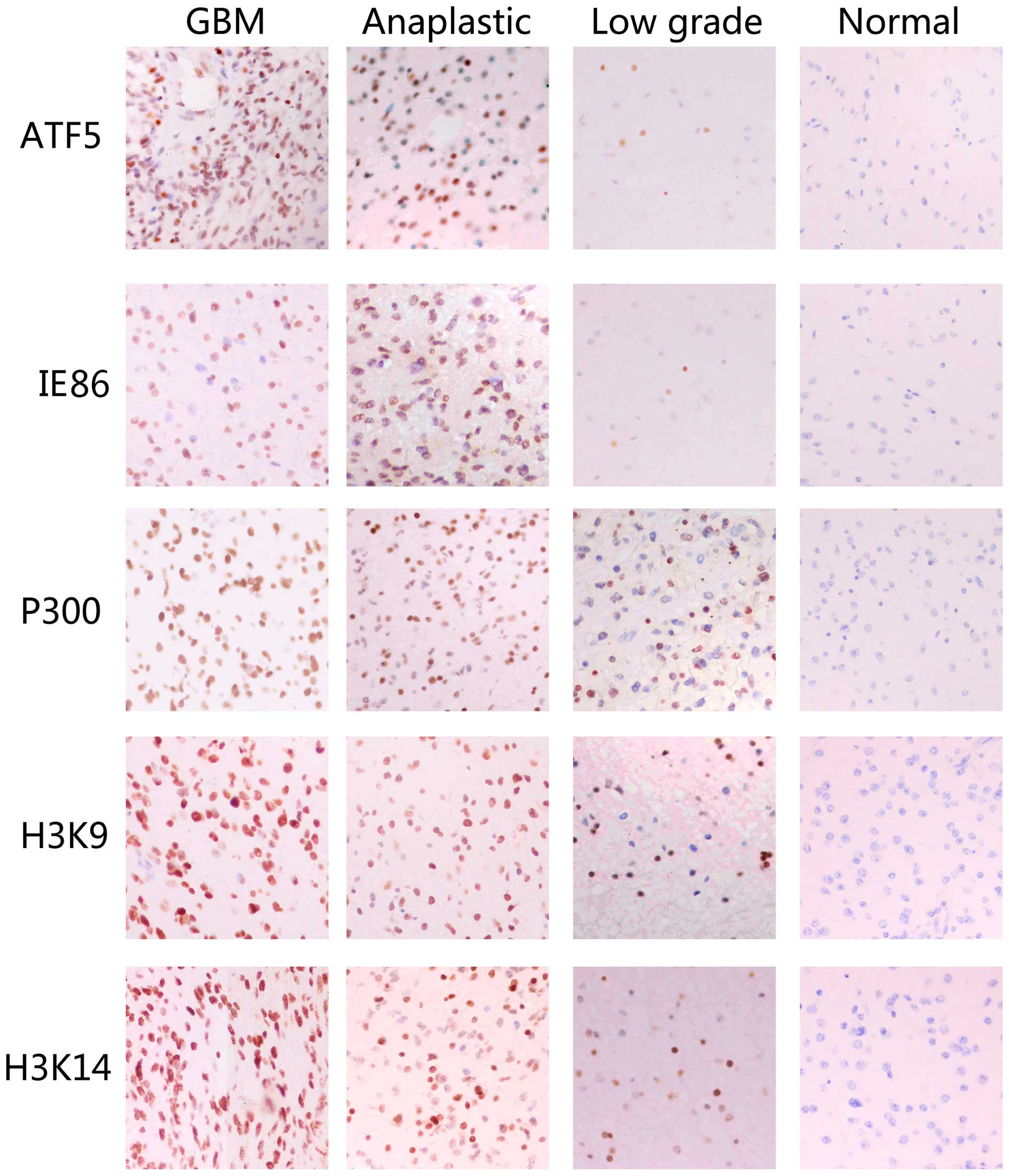
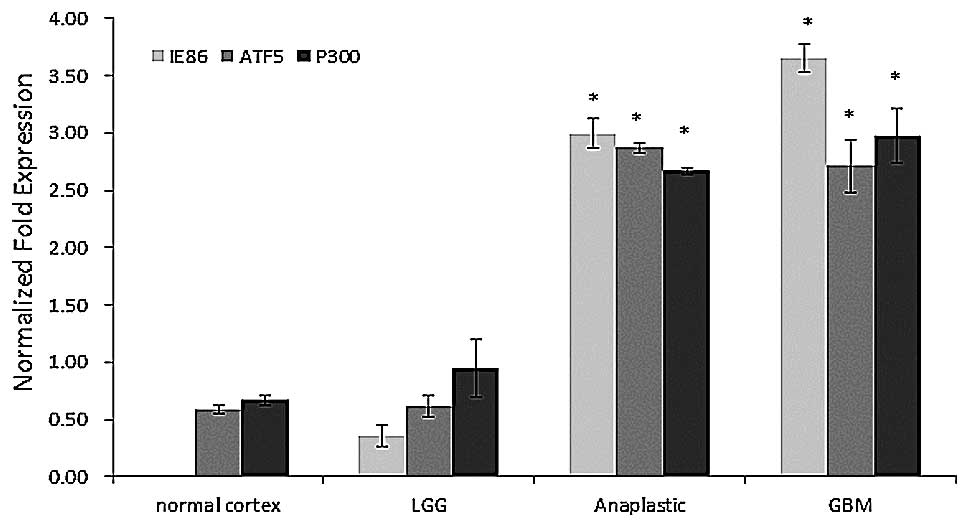
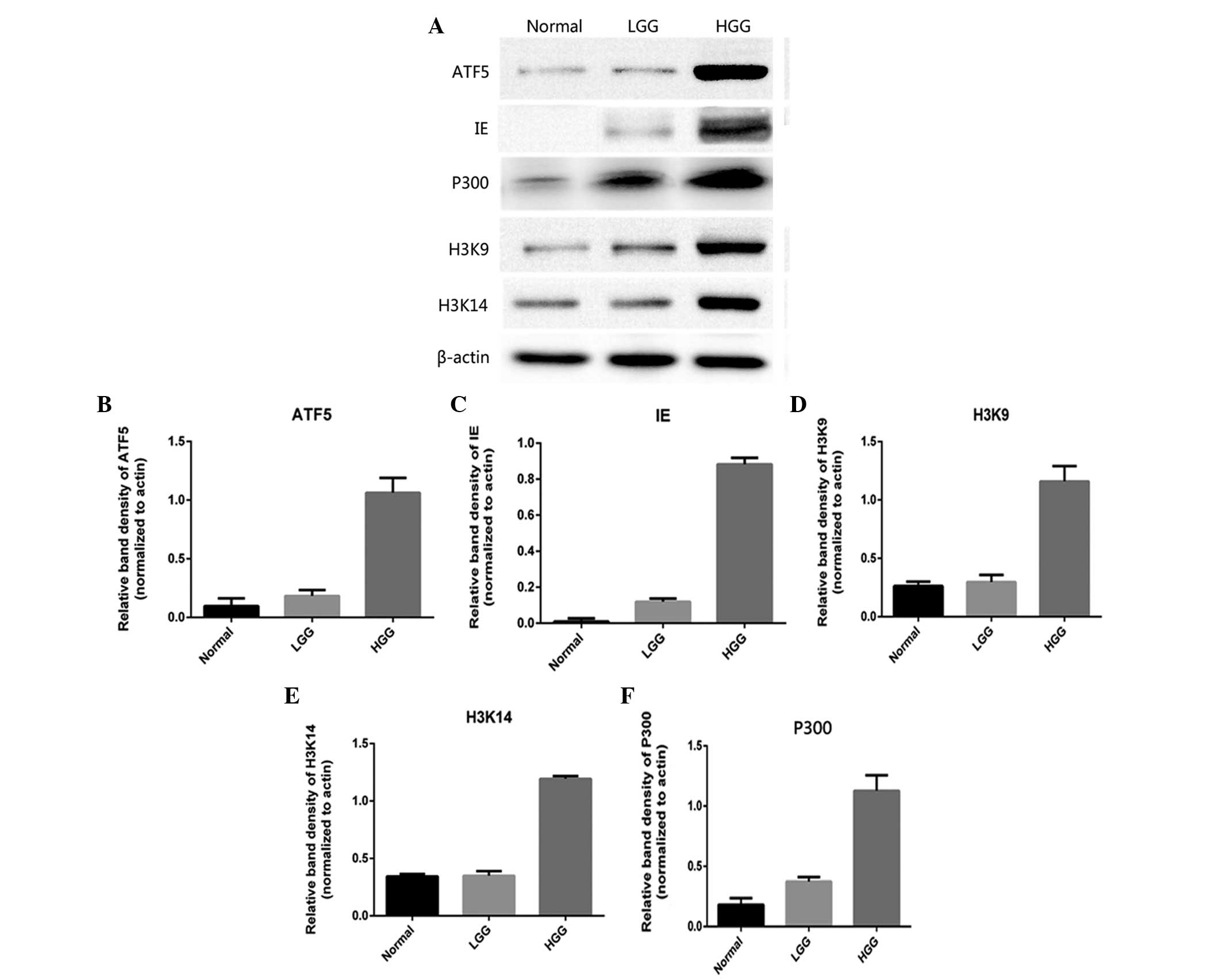
|
1
|
Ranganathan P, Clark PA, Kuo JS, Salamat
MS and Kalejta RF: Significant association of multiple human
cytomegalovirus genomic loci with glioblastoma multiforme samples.
J Virol. 86:854–864. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dziurzynski K, Wei J, Qiao W, Hatiboglu
MA, Kong LY, Wu A, Wang Y, Cahill D, Levine N, Prabhu S, et al:
Glioma-associated cytomegalovirus mediates subversion of the
monocyte lineage to a tumor propagating phenotype. Clin Cancer Res.
17:4642–4649. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Soroceanu L and Cobbs CS: Is HCMV a tumor
promoter? Virus Res. 157:193–203. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Barami K: Oncomodulatory mechanisms of
human cytomegalovirus in gliomas. J Clin Neurosci. 17:819–823.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Michaelis M, Doerr HW and Cinatl J: The
story of human cytomegalovirus and cancer: Increasing evidence and
open questions. Neoplasia. 11:1–9. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cinatl J, Scholz M, Kotchetkov R, Vogel JU
and Doerr HW: Molecular mechanisms of the modulatory effects of
HCMV infection in tumor cell biology. Trends Mol Med. 10:19–23.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Duan YL, Ye HQ, Zavala AG, Yang CQ, Miao
LF, Fu BS, Seo KS, Davrinche C, Luo MH and Fortunato EA:
Maintenance of large numbers of virus genomes in human
cytomegalovirus-infected T98 G glioblastoma cells. J Virol.
88:3861–3873. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dziurzynski K, Chang SM, Heimberger AB,
Kalejta RF, Dallas SR McGregor, Smit M, Soroceanu L and Cobbs CS:
HCMV and Gliomas Symposium: Consensus on the role of human
cytomegalovirus in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 14:246–255. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Luo MH and Fortunato EA: Long-term
infection and shedding of human cytomegalovirus in T98 G
glioblastoma cells. J Virol. 81:10424–10436. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cobbs CS, Harkins L, Samanta M, Gillespie
GY, Bharara S, King PH, Nabors LB, Cobbs CG and Britt WJ: Human
cytomegalovirus infection and expression in human malignant glioma.
Cancer Res. 62:3347–3350. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu X, Liu D, Qian D, Dai J, An Y, Jiang
S, Stanley B, Yang J, Wang B, Liu X and Liu DX: Nucleophosmin
(NPM1/B23) interacts with activating transcription factor 5 (ATF5)
protein and promotes proteasome- and caspase-dependent ATF5
degradation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem.
287:19599–19609. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sheng Z, Evans SK and Green MR: An
activating transcription factor 5-mediated survival pathway as a
target for cancer therapy? Oncotarget. 1:457–460. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Angelastro JM, Canoll PD, Kuo J, Weicker
M, Costa A, Bruce JN and Greene LA: Selective destruction of
glioblastoma cells by interference with the activity or expression
of ATF5. Oncogene. 25:907–916. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu DX, Qian D, Wang B, Yang JM and Lu Z:
P300-Dependent ATF5 acetylation is essential for Egr-1 gene
activation and cell proliferation and survival. Mol Cell Biol.
31:3906–3916. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang T, Qian D, Hu M, Li L, Zhang L, Chen
H, Yang R and Wang B: Human cytomegalovirus inhibits apoptosis by
regulating the activating transcription factor 5 signaling pathway
in human malignant glioma cells. Oncol Lett. 8:1051–1057.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao Y, Zhang YD, Zhang YY, Qian SW, Zhang
ZC, Li SF, Guo L, Liu Y, Wen B, Lei QY, et al: P300-dependent
acetylation of activating transcription factor 5 enhances C/EBPβ
transactivation of C/EBPα During 3T3-L1 differentiation. Mol Cell
Biol. 34:315–324. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu L, Zhang X, Che Y, Zhang Y, Tang S,
Liao Y, Na R, Xiong X, Liu L and Li Q: A cellular response protein
induced during HSV-1 infection inhibits viral replication by
interacting with ATF5. Sci China Life Sci. 56:1124–1133. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nevels M, Paulus C and Shenk T: Human
cytomegalovirus immediate-early 1 protein facilitates viral
replication by antagonizing histone deacetylation. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 101:17234–17239. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hwang ES, Zhang Z, Cai H, Huang DY, Huong
SM, Cha CY and Huang ES: Human cytomegalovirus IE1-72 protein
interacts with p53 and inhibits p53-dependent transactivation by a
mechanism different from that of IE2-86 protein. J Virol.
83:12388–12398. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bryant LA, Mixon P, Davidson M, Bannister
AJ, Kouzarides T and Sinclair JH: The human cytomegalovirus
86-kilodalton major immediate-early protein interacts physically
and functionally with histone acetyltransferase P/CAF. J Virol.
74:7230–7237. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rodems SM, Clark CL and Spector DH:
Separate DNA elements containing ATF/CREB and IE86 binding sites
differentially regulate the human cytomegalovirus UL112-113
promoter at early and late times in the infection. J Virol.
72:2697–2707. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schwartz R, Helmich B and Spector DH: CREB
and CREB-binding proteins play an important role in the IE2
86-kilodalton protein-mediated transactivation of the human
cytomegalovirus 2.2-kilobase RNA promoter. J Virol. 70:6955–6966.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou Y, Xu Y, Wang H, Niu J, Hou H and
Jiang Y: Histone deacetylase inhibitor, valproic acid,
radiosensitizes the C6 glioma cell line in vitro. Oncol
Lett. 7:203–208. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lois DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee
WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW and Kleihues P: World
Organization Classification of tumours of the central nervous
system. Acta Neuropathol. 114:97–109. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Scheurer ME, Bondy ML, Aldape KD, Albrecht
T and El-Zein R: Detection of human cytomegalovirus in different
histological types of gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 116:79–86. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Caron C, Col E and Khochbin S: The viral
control of cellular acetylation signaling. Bioessays. 25:58–65.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cuevas-Bennett C and Shenk T: Dynamic
Histone H3 acetylation and methylation at human cytomegalovirus
promoters during replication in fibroblasts. J Virol. 82:9525–9536.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stinski MF and Petrik DT: Functional roles
of the human cytomegalovirus essential IE86 protein. Curr Top
Microbiol Immunol. 325:133–152. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Taylor RT and Bresnahan WA: Human
cytomegalovirus IE86 attenuates virus- and tumor necrosis factor
alpha-induced NFkappaB-dependent gene expression. J Virol.
80:10763–10771. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yoo YD, Chiou CJ, Choi KS, Yi Y, Michelson
S, Kim S, Hayward GS and Kim SJ: The IE2 regulatory protein of
human cytomegalovirus induces expression of the human transforming
growth factor beta1 gene through an Egr-1 binding site. J Virol.
70:7062–7070. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sheng Z, Li L, Zhu LJ, Smith TW, Demers A,
Ross AH, Moser RP and Green MR: A genome-wide RNA interference
screen reveals an essential CREB3L2-ATF5-MCL1 survival pathway in
malignant glioma with therapeutic implications. Nat Med.
16:671–677. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu DX, Qian D, Wang B, Yang JM and Lu Z:
p300-Dependent ATF5 acetylation is essential for Egr-1 gene
activation and cell proliferation and survival. Mol Cell Biol.
31:3906–3916. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Liao XH, Dong X, Wu C, Wang T, Liu F, Zhou
J and Zhang TC: Human cytomegalovirus immediate early protein 2
enhances myocardin-mediated survival of rat aortic smooth muscle
cells. Virus Res. 192:85–91. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|