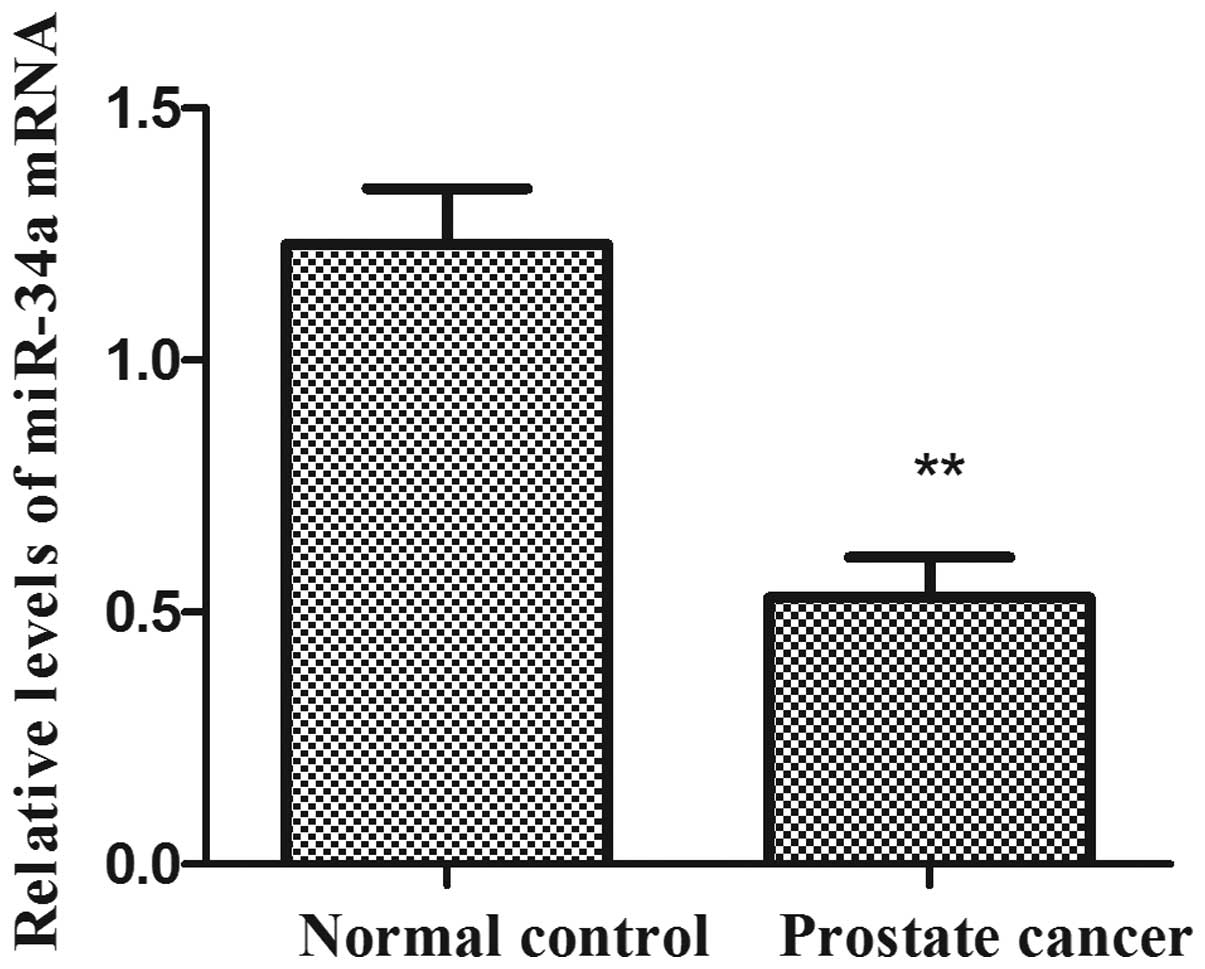
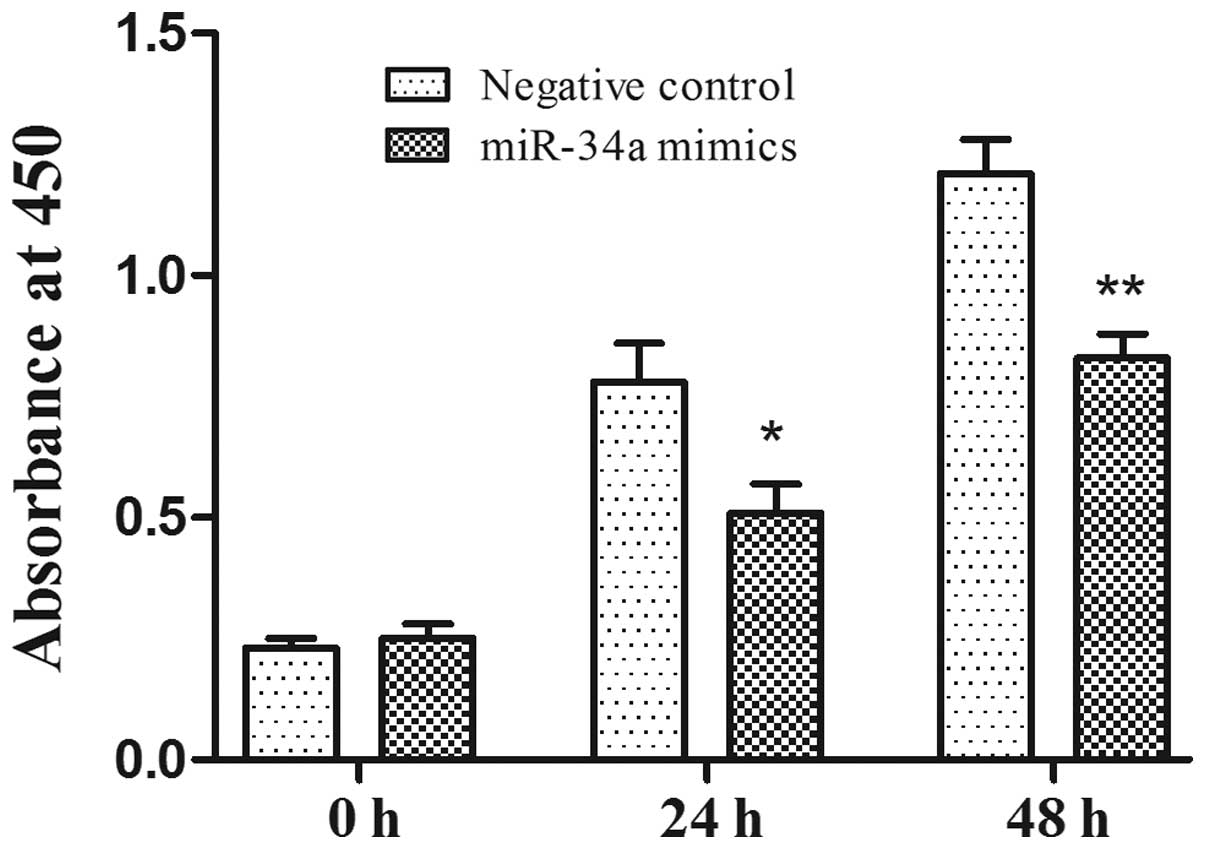
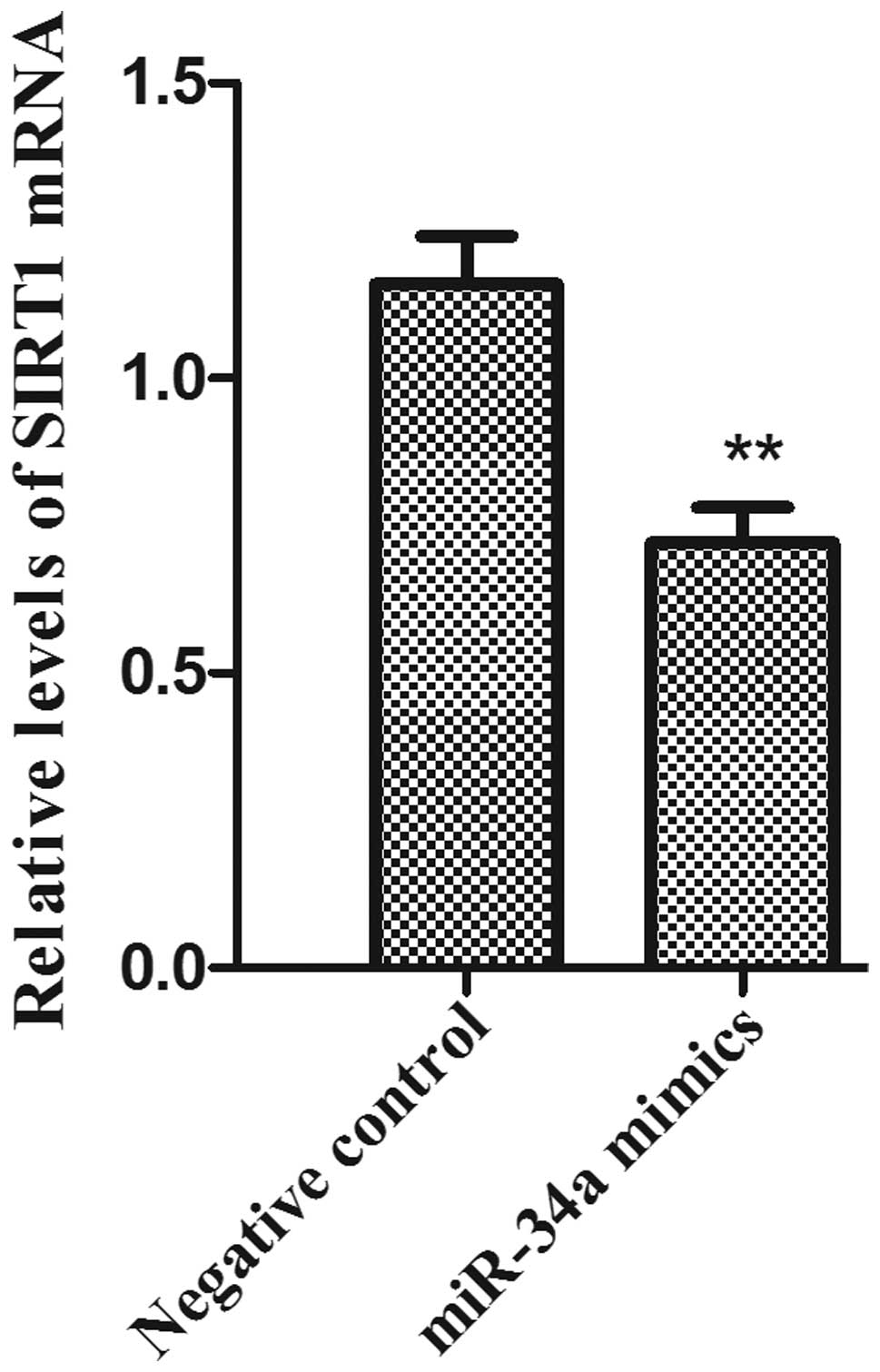
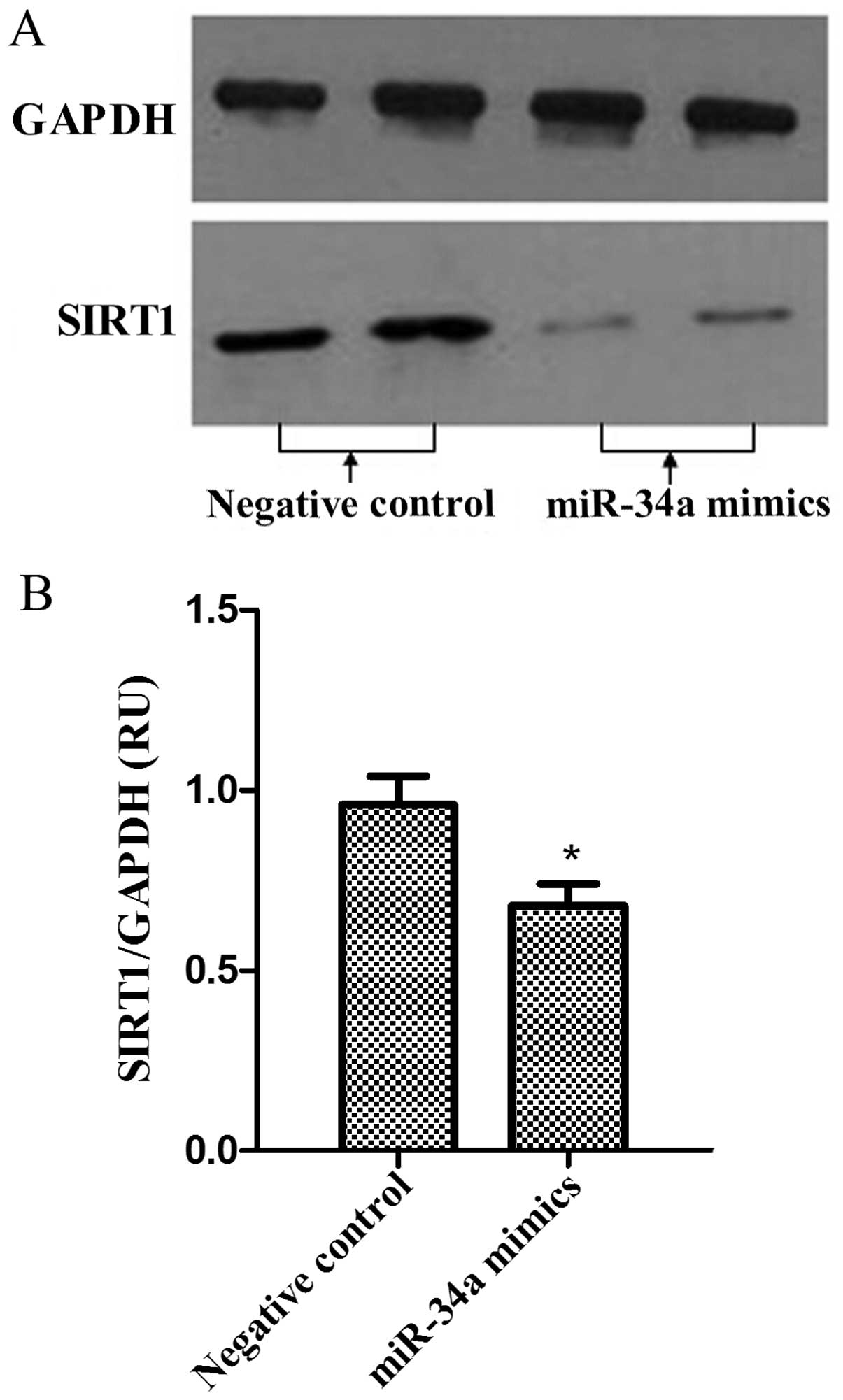
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods, and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gade TP, Hassen W, Santos E, Gunset G,
Saudemont A, Gong MC, Brentjens R, Zhong XS, Stephan M, Stefanski
J, et al: Targeted elimination of prostate cancer by genetically
directed human T lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 65:9080–9088. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Salter KH, Acharya CR, Walters KS, Redman
R, Anguiano A, Garman KS, Anders CK, Mukherjee S, Dressman HK,
Barry WT, et al: An integrated approach to the prediction of
chemotherapeutic response in patients with breast cancer. PLoS One.
3:e19082008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Denli AM, Tops BB, Plasterk RH, Ketting RF
and Hannon GJ: Processing of primary microRNAs by the
Microprocessor complex. Nature. 432:231–235. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huntzinger E and Izaurralde E: Gene
silencing by microRNAs: Contributions of translational repression
and mRNA decay. Nat Rev Genet. 12:99–110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kloosterman WP and Plasterk RH: The
diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease.
Dev Cell. 11:441–450. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li XJ, Ren ZJ and Tang JH: MicroRNA-34a: A
potential therapeutic target in human cancer. Cell Death Dis.
5:e13272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guessous F, Zhang Y, Kofman A, Catania A,
Li Y, Schiff D, Purow B and Abounader R: MicroRNA-34a is tumor
suppressive in brain tumors and glioma stem cells. Cell Cycle.
9:1031–1036. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ji Q, Hao X, Meng Y, Zhang M, Desano J,
Fan D and Xu L: Restoration of tumor suppressor miR-34 inhibits
human p53-mutant gastric cancer tumorspheres. BMC Cancer.
8:2662008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Maroof H, Salajegheh A, Smith RA and Lam
AK: Role of microRNA-34 family in cancer with particular reference
to cancer angiogenesis. Exp Mol Pathol. 97:298–304. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Satoh A, Stein L and Imai S: The role of
mammalian sirtuins in the regulation of metabolism, aging and
longevity. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 206:125–162. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kabra N, Li Z, Chen L, Li B, Zhang X, Wang
C, Yeatman T, Coppola D and Chen J: SirT1 is an inhibitor of
proliferation and tumor formation in colon cancer. J Biol Chem.
284:18210–18217. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jung W, Hong KD, Jung WY, Lee E, Shin BK,
Kim HK, Kim A and Kim BH: SIRT1 Expression Is Associated with Good
Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer. Korean J Pathol. 47:332–339. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim JR, Moon YJ, Kwon KS, Bae JS, Wagle S,
Yu TK, Kim KM, Park HS, Lee JH, Moon WS, et al: Expression of SIRT1
and DBC1 is associated with poor prognosis of soft tissue sarcomas.
PLoS One. 8:e747382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Leko V, Park G, Lao U, et al:
Enterocyte-specific inactivation of SIRT1 reduces tumor load in the
APC (+/min) mouse model. PLoS One. 8:e662832013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Knight JR, Allison SJ and Milner J: Active
regulator of SIRT1 is required for cancer cell survival but not for
SIRT1 activity. Open Biol. 3:130–135. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Revollo JR and Li X: The ways and means
that fine tune SIRT1 activity. Trends Biochem Sci. 38:160–167.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang XL, Chen ML and Zhou SL: Fentanyl
increases colorectal carcinoma cell apoptosis by inhibition of
NF-κB in a Sirt1-dependent manner. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:10015–10020. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
The American Joint Committee on Cancer:
The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of
TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Welch C, Chen Y and Stallings RL:
MicroRNA-34a functions as a potential tumor suppressor by inducing
apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. Oncogene. 26:5017–5022. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Moretti RM, Mareli M Montagnani, Taylor
DM, Martini PG, Marzagalli M and Limonta P: Gonadotropin-releasing
hormone agonists sensitize and resensitize, prostate cancer cells
to docetaxel in a p53-dependent manner. PLoS One. 9:e937132014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lodygin D, Tarasov V, Epanchintsev A,
Berking C, Knyazeva T, Körner H, Knyazev P, Diebold J and Hermeking
H: Inactivation of miR-34a by aberrant CpG methylation in multiple
types of cancer. Cell Cycle. 7:2591–2600. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yamakuchi M, Ferlito M and Lowenstein CJ:
MiR-34a repression of SIRT1 regulates apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
U S A. 105:13421–13426. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hwang BJ, Madabushi A, Jin J, Lin SY and
Lu AL: Histone/protein deacetylase SIRT1 is an anticancer
therapeutic target. Am J Cancer Res. 4:211–221. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao T, Li J and Chen AF: MicroRNA-34a
induces endothelial progenitor cell senescence and impedes its
angiogenesis via suppressing silent information regulator 1. Am J
Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 299:E110–E116. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Akao Y, Noguchi S, Iio A, Kojima K, Takagi
T and Naoe T: Dysregulation of microRNA-34a expression causes
drug-resistance to 5-FU in human colon cancer DLD-1 cells. Cancer
Lett. 300:197–204. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li L, Yuan L, Luo J, Gao J, Guo J and Xie
X: MiR-34a inhibits proliferation and migration of breast cancer
through down-regulation of Bcl-2 and SIRT1. Clin Exp Med.
13:109–117. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chapman EJ, Kelly G and Knowles MA: Genes
involved in differentiation, stem cell renewal and tumorigenesis
are modulated in telomerase-immortalized human urothelial cells.
Mol Cancer Res. 6:1154–1168. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Audrito V, Rossi D, Gottardi D, et al:
Nicotinamide blocks proliferation and induces apoptosis of chronic
lymphocytic leukemia cells through activation of the
p53/miR-34a/SIRT1 tumor suppressor network. Cancer Res.
71:4473–4483. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bommer GT, Feng Y, Kaczorowski AJ, Gerin
I, Kuick R, Love RE, Zhai Y, Giordano TJ, et al: p53-mediated
activation of miRNA34 candidate tumor-suppressor genes. Curr Biol.
17:1298–1307. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen F and Hu SJ: Effect of microRNA-34a
in cell cycle, differentiation and apoptosis: A review. J Biochem
Mol Toxicol. 26:79–86. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ito T, Yagi S and Yamakuchi M:
MicroRNA-34a regulation of endothelial senescence. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 398:735–740. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|