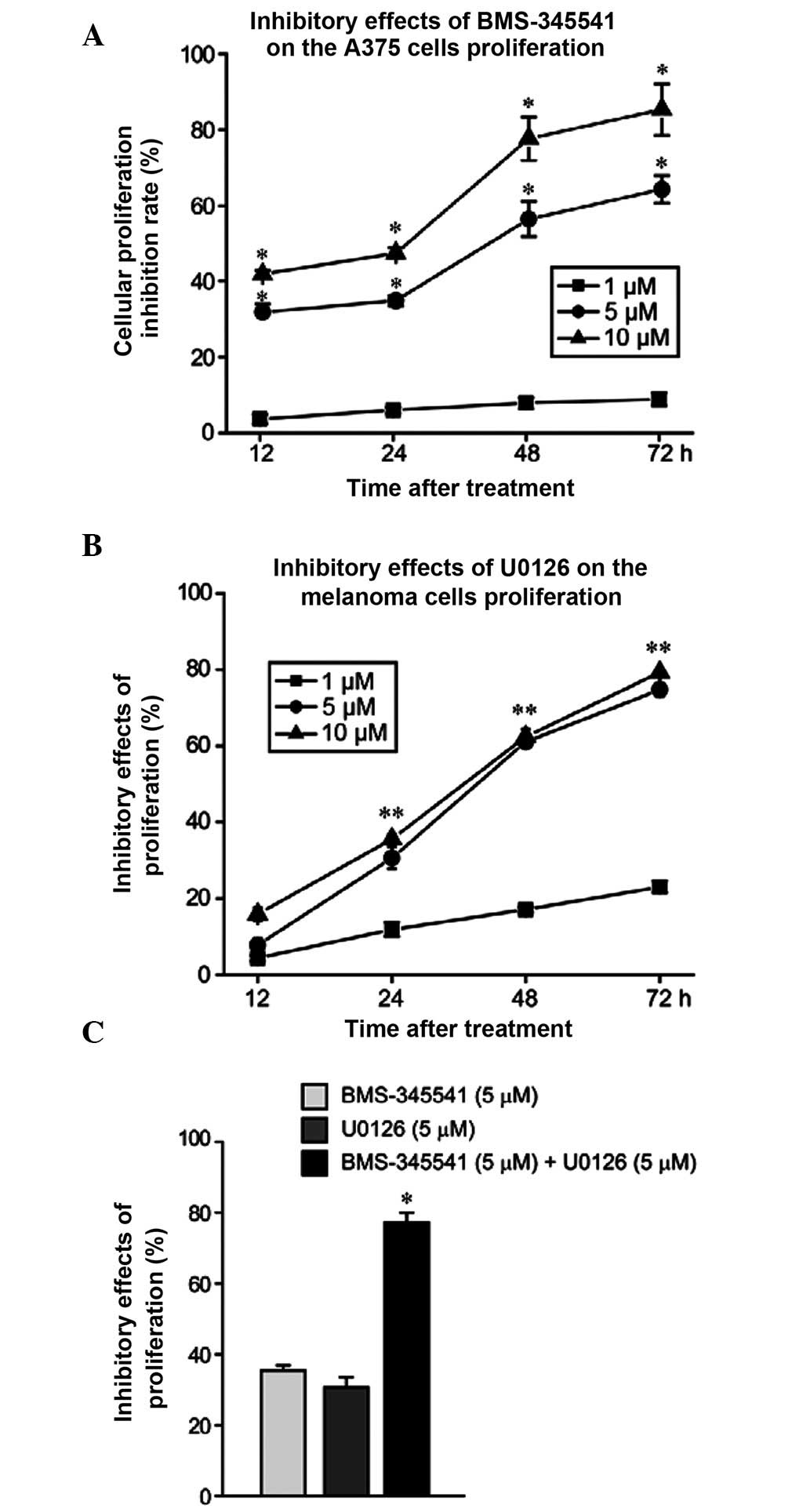
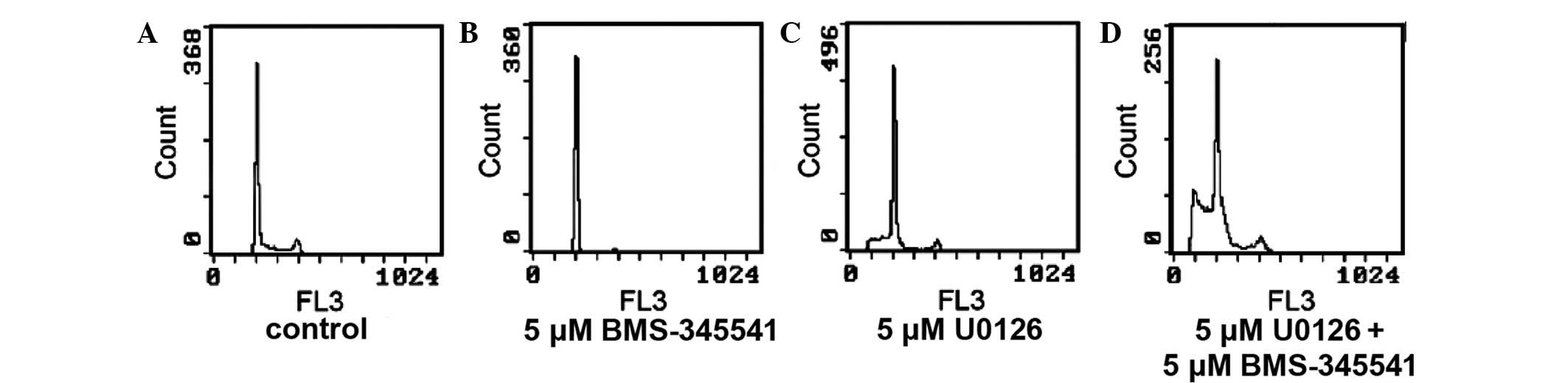
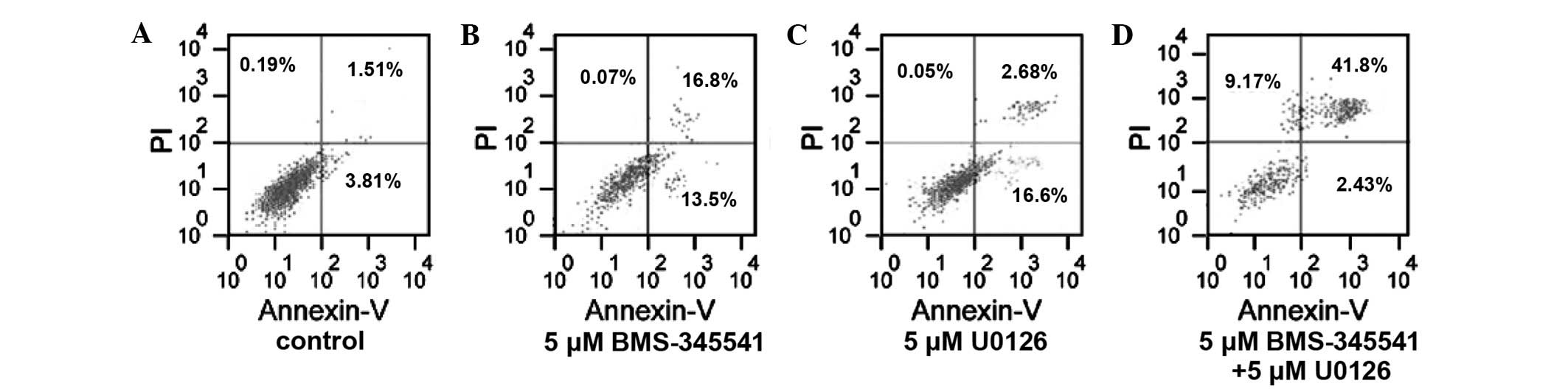
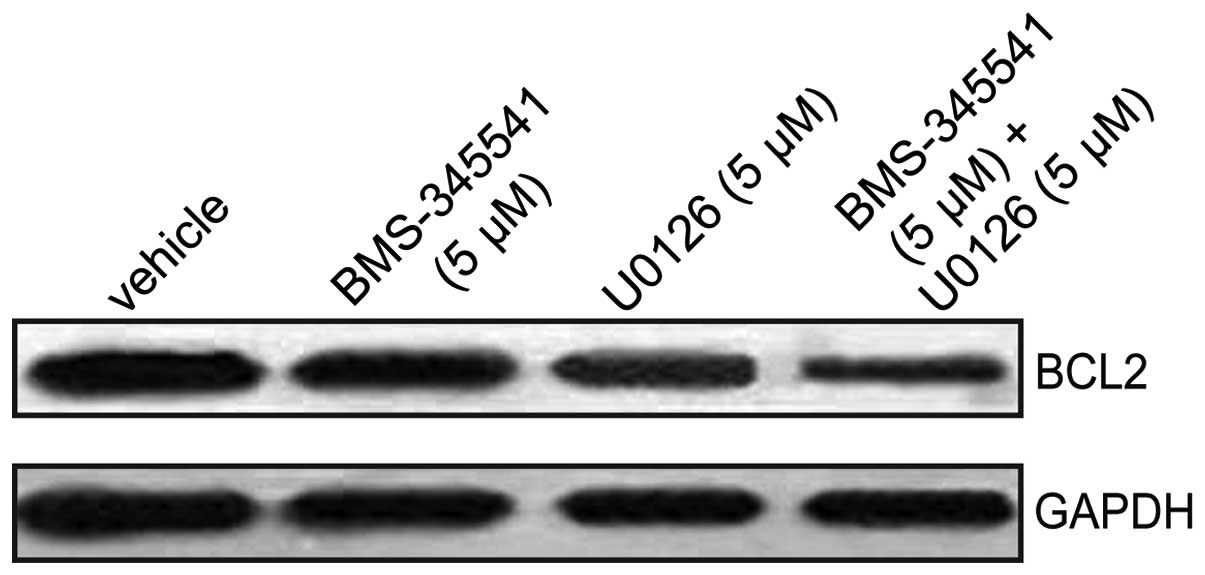
|
1
|
Bai J, Xie X, Lei Y, et al: Ocular
albinism type 1 induced melanoma cell migration is mediated through
the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Molecular Medicine Reports.
10:491–495. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Aris M and Barrio MM: Combining
Immunotherapy with Oncogene-Targeted Therapy: A New Road for
Melanoma Treatment. Front Immunol. 6:462015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Queirolo P, Picasso V and Spagnolo F:
Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition for the treatment of BRAF-mutated
metastatic melanoma. Cancer Treatment Reviews. 4:1–8. 2015.
|
|
4
|
Tuveson DA, Weber BL and Herlyn M: BRAF as
a potential therapeutic target in melanoma and other malignancies.
Cancer Cell. 4:95–98. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ning L, Xiao J and Min GP: The effects of
the MEK inhibitor on the proliferation of human melanoma cells.
Chin J Dermatovenereology. 26:961–965. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
6
|
Acquaviva J, Smith DL, Jimenez JP, et al:
Overcoming acquired BRAF inhibitor resistance in melanoma via
targeted inhibition of Hsp90 with ganetespib. Mol Cancer Ther.
13:353–363. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Deng LL, Shao YX, Lv HF, Deng HB and Lv
FZ: Over-expressing CYLD augments antitumor activity of TRAIL by
inhibiting the NF-κB survival signaling in lung cancer cells.
Neoplasma. 59:18–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Song B, Bian Q, Shao CH, Li G, Liu AA,
Jing W, Liu R, Zhang YJ, Zhou YQ, Hu XG and Jin G: Ulinastatin
reduces the resistance of liver cancer cells to epirubicin by
inhibiting autophagy. PLoS One. 10:1–15. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhao B, Fang GJ, Zhu J, et al: The
computing method of IC50 in determining cell
proliferation inhibition rate by MTT method. Anhui Med Pharm J.
11:834–836. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Yeh YA, Herenyiova M and Weber G:
Quercetin: Synergisticaction with carboxamidotriazole in human
breast carcinoma cells. Life Sci. 57:1285–1292. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Duffy A and Kummar S: Targeting
mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) in solid tumors.
Target Oncol. 4:267–273. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pratilas CA, Hanrahan AJ, Halilovic E, et
al: Genetic predictors of MEK dependence in non-small cell lung
cancer. Cancer Res. 68:9375–9383. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sadaria MR, Yu JA, Meng X, et al:
Secretory phospholipase A2 mediates human esophageal adenocarcinoma
cell growth and proliferation via ERK 1/2 pathway. Anticancer Res.
33:1337–1342. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Walters DM, Lindberg JM, Adair SJ, et al:
Inhibition of the growth of patient-derived pancreatic cancer
xenografts with the MEK inhibitor trametinib is augmented by
combined treatment with the epidermal growth factor receptor/HER2
inhibitor lapatinib. Neoplasia. 15:143–155. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Madonna G, Ullman CD, Gentilcore G,
Palmieri G and Ascierto PA: NF-κB as potential target in the
treatment of melanoma. J Transl Med. 10:532012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Y, Zhou Y, Jia G, Han B, Liu J, Teng
Y, et al: Shikonin suppresses tumor growth and synergizes with
gemcitabine in a pancreatic cancer xenograft model: Involvement of
NF-κB signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 88:322–333. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Schmid JA and Birbach A: IkappaB kinase
beta(IKKbeta/IKK2/IKBKB) - a key molecule in signaling to the
transcription factor NF-kappaB. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
19:157–165. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Buontempo F, Chiarini F, Bressanin D, et
al: Activity of the selective IκB kinase inhibitor BMS-345541
against T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Involvement of FOXO3a.
Cell Cycle. 11:2467–2475. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang J, Amiri KI, Burke JR, Schmid JA and
Richmond A: BMS-345541 targets inhibitor of kappaB kinase and
induces apoptosis in melanoma: Involvement of nuclear factor kappaB
and mitochondria pathways. Clin Cancer Res. 12:950–960. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nesic-Taylor O, Cittelly D, Ye Z, et al:
Exogenous Bcl-xL fusion protein spares neurons after spinal cord
injury. J Neurosci Res. 79:628–637. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Han X, Lu M, Wang S, Lv D and Liu H:
Targeting IKK/NF-κB pathway reduces infiltration of inflammatory
cells and apoptosis after spinal cord injury in rats. Neurosci
Lett. 511:28–32. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang H, Cai X, Wang Y, et al:
microRNA-143, down-regulated in osteosarcoma, promotes apoptosis
and suppresses tumorigenicity by targeting Bcl-2. Oncol Rep.
24:1363–1369. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu DW, Wu TC, Wu JY, Cheng YW, Chen YC,
Lee MC, Chen CY and Lee H: Phosphorylation of paxillin confers
cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer via activating
ERK-mediated Bcl-2 expression. Oncogene. 33:4385–4395. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Berger A, Quast SA, Plötz M, Kammermeier A
and Eberle J: Sensitization of melanoma cells for TRAIL-induced
apoptosis by BMS-345541 correlates with altered phosphorylation and
activation of Bax. Cell Death Dis. 4:e4772013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xie J, Jin B, Li DW, Shen B, Cong N, Zhang
TZ and Dong P: ABCG2 regulated by MAPK pathways is associated with
cancer progression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Am J
Cancer Res. 4:698–709. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sullivan RJ and Atkins MB:
Molecular-targeted therapy in malignant melanoma. Expert Rev
Anticancer Ther. 9:567–581. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang H, Zhang S, He H, Zhao W, Ren K,
Chen J and Shao RG: RasGAP-derived peptide 38GAP potentiates the
cytotoxicity of cisplatin through inhibitions of Akt, ERK and NF-κB
in colon carcinoma HCT116 cells. Cancer Lett. 308:62–70. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|