|
1
|
Stewart BW and Wild CP: Chapter title.
Oesophageal cancer. World Cancer Report. 2014.IARC Press. 2014.
|
|
2
|
Narasimhan P, Hitti IF, Awan A, Desai M,
Kanzer BF and McDonald E: Unusual presentations of prostatic
adenocarcinoma: Lymph node metastasis. Hosp Physician. 38:43–48.
2002.
|
|
3
|
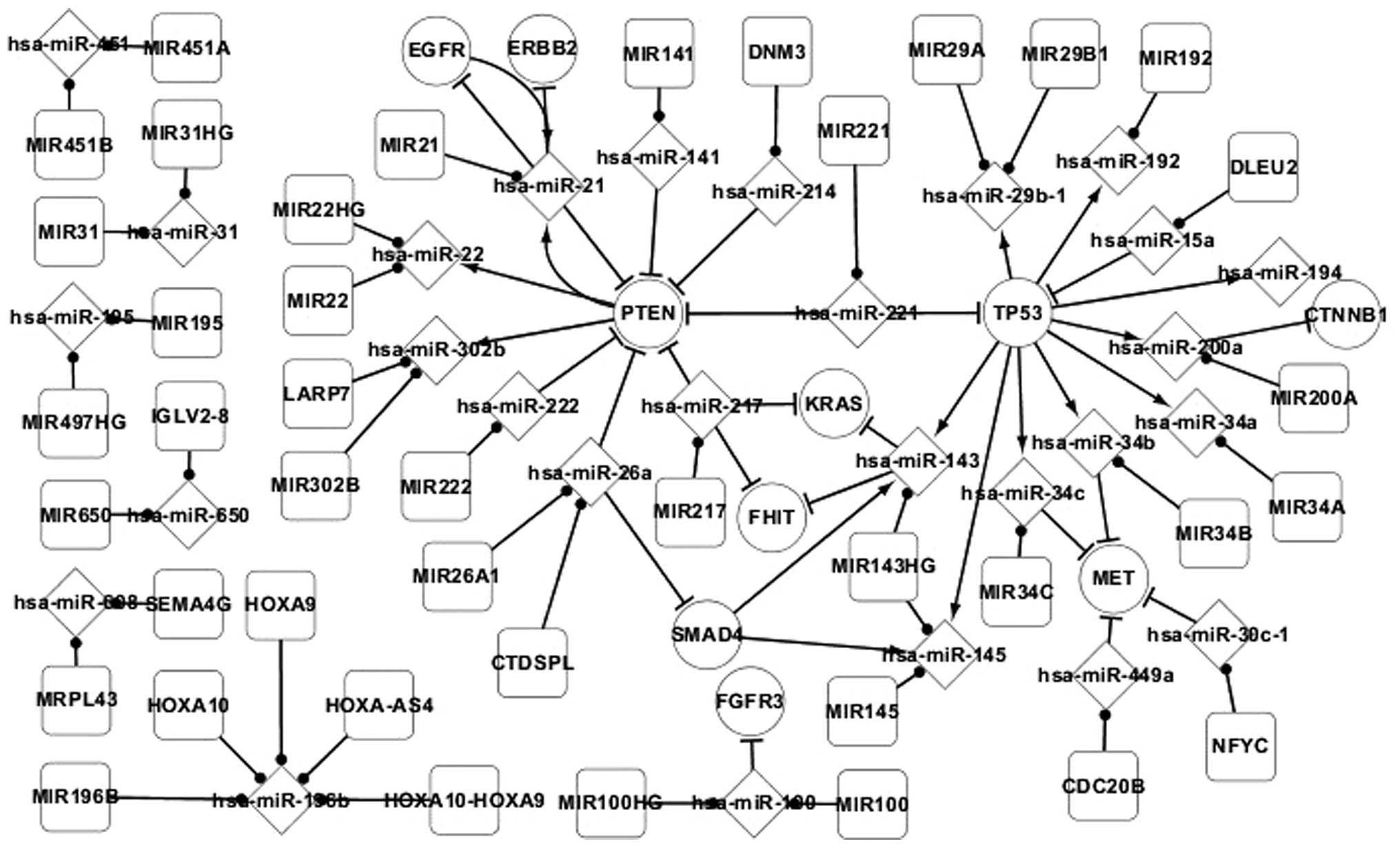
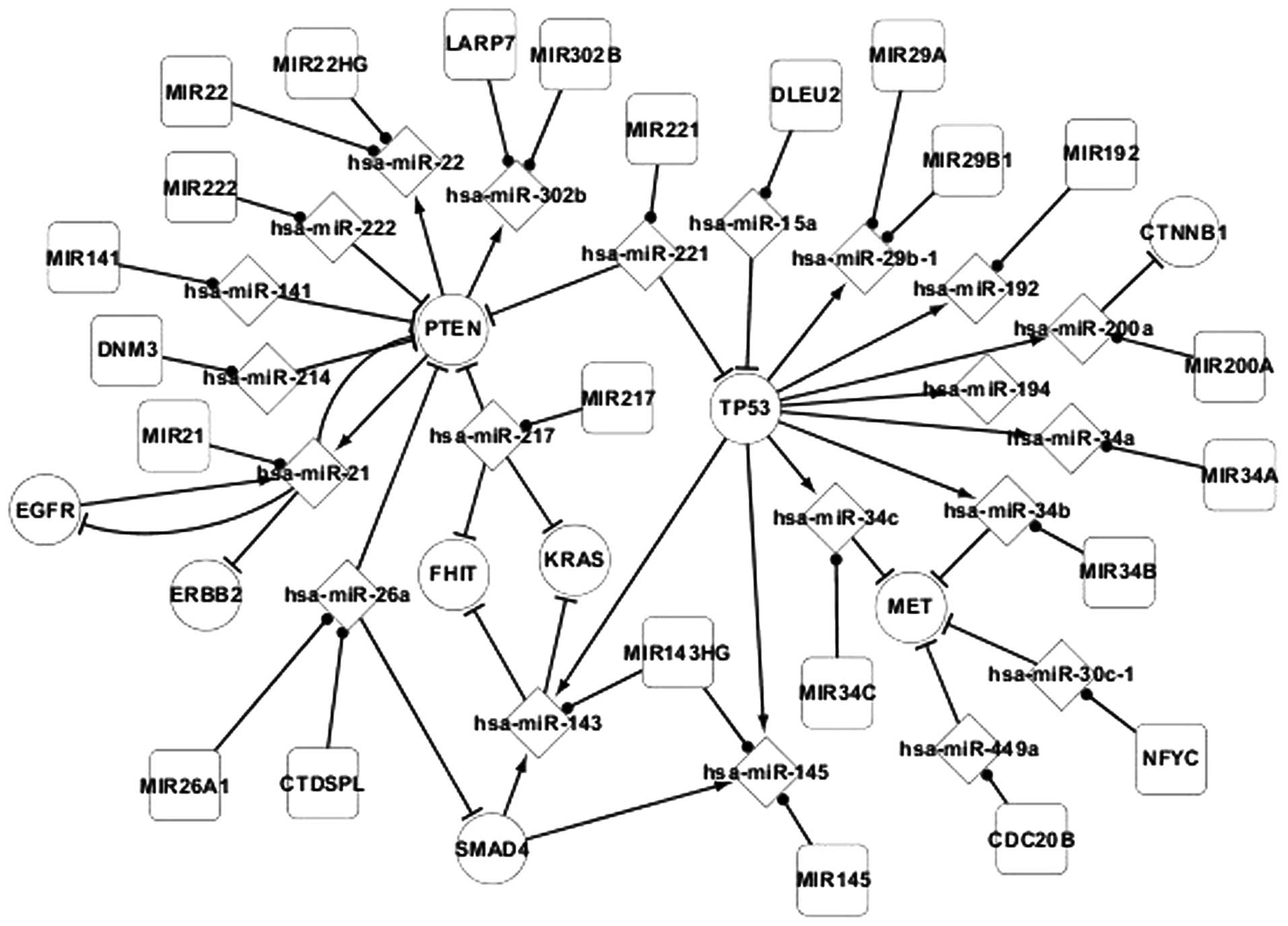
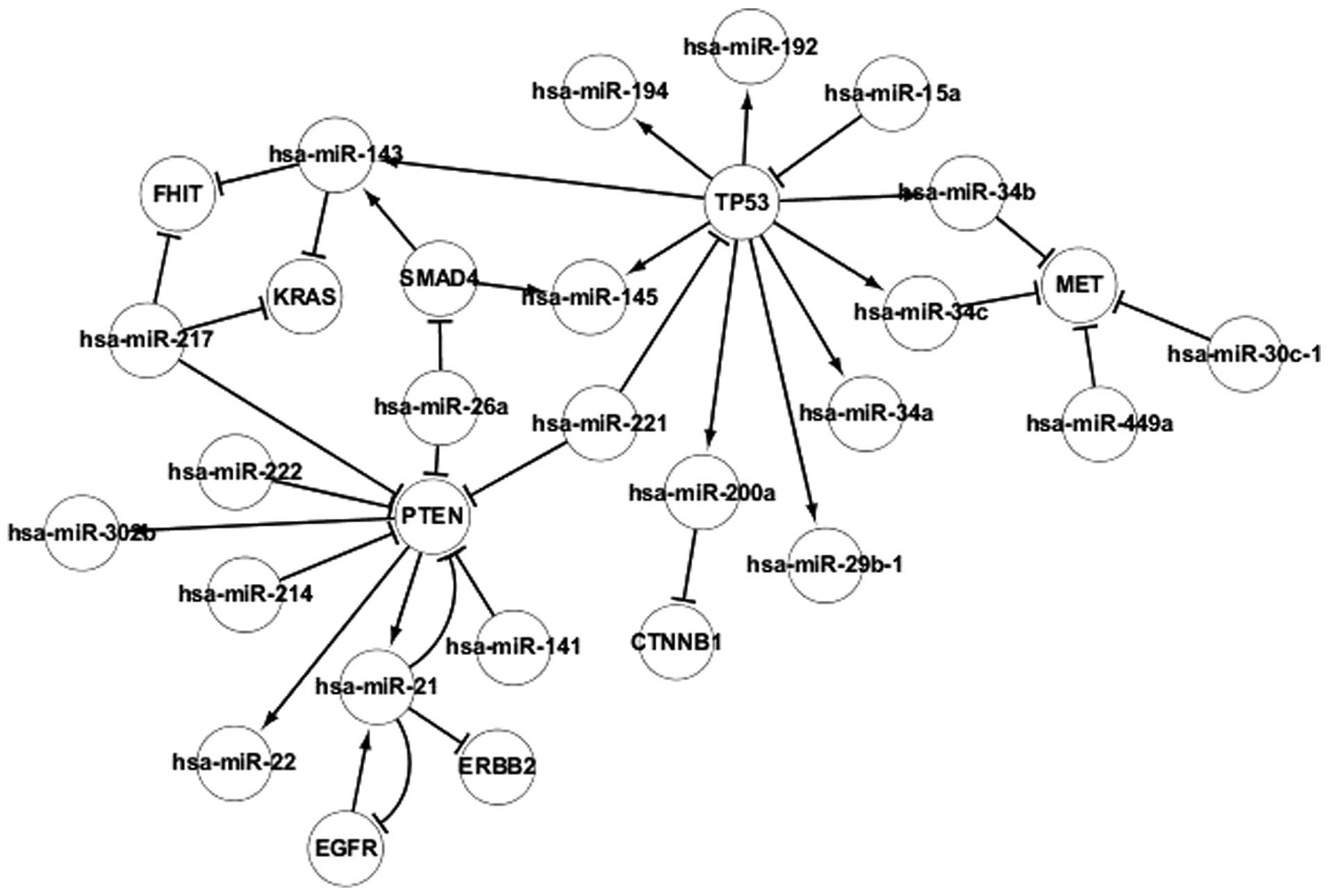
Shalgi R, Lieber D, Oren M and Pilpel Y:
Global and local architecture of the mammalian
microRNA-transcription factor regulatory network. PLoS Comput Biol.
3:e1312007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
O'Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang
CV and Mendell JT: C-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1
expression. Nature. 435:839–843. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rodriguez A, Griffiths-Jones S, Ashurst JL
and Bradley A: Identification of Mammalian microRNA host genes and
transcription units. Genome Res. 14:1902–1910. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Baskerville S and Bartel DP: Microarray
profiling of microRNAs reveals frequent coexpression with
neighboring miRNAs and host genes. RNA. 11:241–247. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cao G, Huang B, Liu Z, et al: Intronic
miR-301 feedback regulates its host gene, ska2, in A549 cells by
targeting MEOX2 to affect ERK/CREB pathways. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 396:978–982. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tran DH, Satou K, Ho TB and Pham TH:
Computational discovery of miR-TF regulatory modules in human
genome. Bioinformation. 4:371–377. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
He L, He X, Lim LP, et al: A microRNA
component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature.
447:1130–1134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Naeem H, Küffner R and Zimmer R: MIRTFnet:
Analysis of miRNA regulated transcription factors. PLoS One.
6:e225192011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hobert O: Gene regulation by transcription
factors and microRNAs. Science. 319:1785–1786. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li M, Li J, Ding X, He M and Cheng Y:
microRNA and cancer. AAPS J. 12:309–317. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang J, Lu M, Qiu C and Cui Q: TransmiR: A
transcription factor-microRNA regulation database. Nucleic Acids
Res. 38:D119–D122. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Betel D, Wilson M, Gabow A, Marks DS and
Sander C: The microRNA.org resource: Targets and expression.
Nucleic Acids Res. 36:D149–D153. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Papadopoulos GL, Reczko M, Simossis VA, et
al: The database of experimentally supported targets: A functional
update of TarBase. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:D155–D158. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hsu SD, Lin FM, Wu WY, et al: miRTarBase:
A database curates experimentally validated microRNA-target
interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:D163–D169. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kozomara A and Griffiths-Jones S: miRBase:
Integrating microRNA annotation and deep-sequencing data. Nucleic
Acids Res. 39:D152–D157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bao J, Li Di, Wang L, et al: MicroRNA-449
and MicroRNA-34b/c function redundantly in murine testes by
targeting E2F transcription factor-retinoblastoma protein (E2F-pRb)
pathway. J Biol Chem. 287:21686–21698. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Revilla-Nuin B, Parilla P, Lozano JJ, et
al: Predictive value of MicroRNAs in the progression of barrett
esophagus to adenocarcinoma in a long-term follow-up study. Ann
Surg. 257:886–893. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
National Center for Biotechnology
Information: Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Database. simplewww.ncbi.nlm.gov/snpAccessed. May 10–2014
|
|
22
|
Xue Y, Tayoun AN Abou, Abo KM, et al:
MicroRNAs as diagnostic markers for pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma and its precursor, pancreatic intraepithelial
neoplasm. Cancer Genet. 206:217–221. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kaduthanam S, Gade S, Meister M, et al:
Serum miR-142-3p is associated with early relapse in operable lung
adenocarcinoma patients. Lung Cancer. 80:223–227. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Que R, Ding G, Chen J and Cao L: Analysis
of serum exosomal microRNAs and clinicopathologic features of
patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. World J Surg Oncol.
11:2192013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cai B, An Y, Lv N, et al: miRNA-181b
increases the sensitivity of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells
to gemcitabine in vitro and in nude mice by targeting BCL-2. Oncol
Rep. 29:1769–1776. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu FX, Su YL, Zhang H, et al: Prognostic
implications for high expression of MiR-25 in lung adenocarcinomas
of female non-smokers. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:1197–1203. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang R, Zheng S, Du Y, et al: Levels of
HOXB7 and miR-337 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients.
Diagn Pathol. 9:612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim J, Lim NJ, Jang SG, et al: miR-592 and
miR-552 can distinguish between primary lung adenocarcinoma and
colorectal cancer metastases in the lung. Anticancer Res.
34:2297–2302. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang W, Li F, Mao Y, et al: A miR-570
binding site polymorphism in the B7-H1 gene is associated with the
risk of gastric adenocarcinoma. Hum Genet. 132:641–648. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cortot AB, Younes M, Martel-Planche G, et
al: Mutation of TP53 and alteration of p14(arf) expression in EGFR-
and KRAS-mutated lung adenocarcinomas. Clin Lung Cancer.
15:124–130. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Heitzer E, Lax S, Lafer I, et al:
Multiplex genetic cancer testing identifies pathogenic mutations in
TP53 and CDH1 in a patient with bilateral breast and endometrial
adenocarcinoma. BMC Med Genet. 14:1292013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dulak AM, Stojanov P, Peng S, et al: Exome
and whole-genome sequencing of esophageal adenocarcinoma identifies
recurrent driver events and mutational complexity. Nat Genet.
45:478–486. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pérez-Mancera PA, Rust AG, van der Weyden
L, et al: The deubiquitinase USP9X suppresses pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. Nature. 486:266–270. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Orloff M, Peterson C, He X, et al:
Germline mutations in MSR1, ASCC1, and CTHRC1 in patients with
Barrett esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. JAMA. 306:410–419.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Safran M, Dalah I, Alexander J, Rosen N,
Stein T Iny, Shmoish M, Nativ N, Bahir I, Doniger T, Krug H, et al:
GeneCards Version 3: The human gene integrator. Database (Oxford).
2010:baq0202010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fujita PA, Rhead B, Zweig AS, Hinrichs AS,
Karolchik D, Cline MS, Goldman M, Barber GP, Clawson H, Coelho A,
et al: The UCSC genome browser database: Update 2011. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39:D876–D882. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhao Z, Han C, Liu J, et al: GPC5, a tumor
suppressor, is regulated by miR620 in lung adenocarcinoma. Mol Med
Rep. 9:2540–2546. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen W, Qin L, Wang S, et al: CPSF4
activates telomerase reverse transcriptase and predicts poor
prognosis in human lung adenocarcinomas. Mol Oncol. 8:704–716.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Allo G, Bandarchi B, Yanagawa N, et al:
Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-specific
immunohistochemical antibodies in lung adenocarcinoma.
Histopathology. 64:826–839. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sekine S, Ogawa R, Oshiro T, et al:
Frequent lack of GNAS mutations in colorectal adenocarcinoma
associated with GNAS-mutated villous adenoma. Genes Chromosomes
Cancer. 53:366–372. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen YW, Hsiao PJ, Weng CC, et al: SMAD4
loss triggers the phenotypic changes of pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma cells. BMC Cancer. 14:1812014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim HR, Cho BC, Shim HS, et al: Prediction
for response duration to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine
kinase inhibitors in EGFR mutated never smoker lung adenocarcinoma.
Lung Cancer. 83:374–382. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Luis-Ravelo D, Antón I, Zandueta C, et al:
RHOB influences lung adenocarcinoma metastasis and resistance in a
host-sensitive manner. Mol Oncol. 8:196–206. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mehra R, Vats P, Kalyana-Sundaram, et al:
Primary urethral clear-cell adenocarcinoma: Comprehensive analysis
by surgical pathology, cytopathology, and next-generation
sequencing. Am J Pathol. 184:584–591. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rondini EA, Fang H, Runge-Morris M and
Kocarek TA: Regulation of human cytosolic sulfotransferases 1C2 and
1C3 by nuclear signaling pathways in LS180 colorectal
adenocarcinoma cells. Drug Metab Dispos. 42:361–368. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Davison JM, Ellis ST, Foxwell TJ, et al:
MUC2 expression is an adverse prognostic factor in superficial
gastroesophageal adenocarcinomas. Hum Pathol. 45:540–548. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Priolli DG, Abrantes AM, Neves S, et al:
Microenvironment influence on human colon adenocarcinoma phenotypes
and matrix metalloproteinase-2, p53 and β-catenin tumor expressions
from identical monoclonal cell tumor in the orthotopic model in
athymic nude rats. Scand J Gastroenterol. 49:309–316. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|