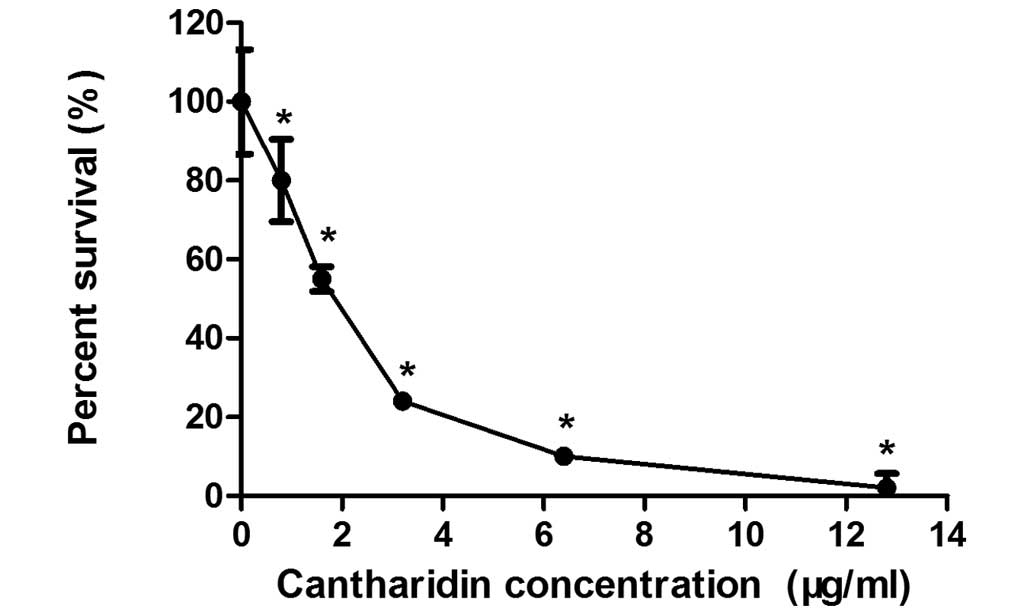
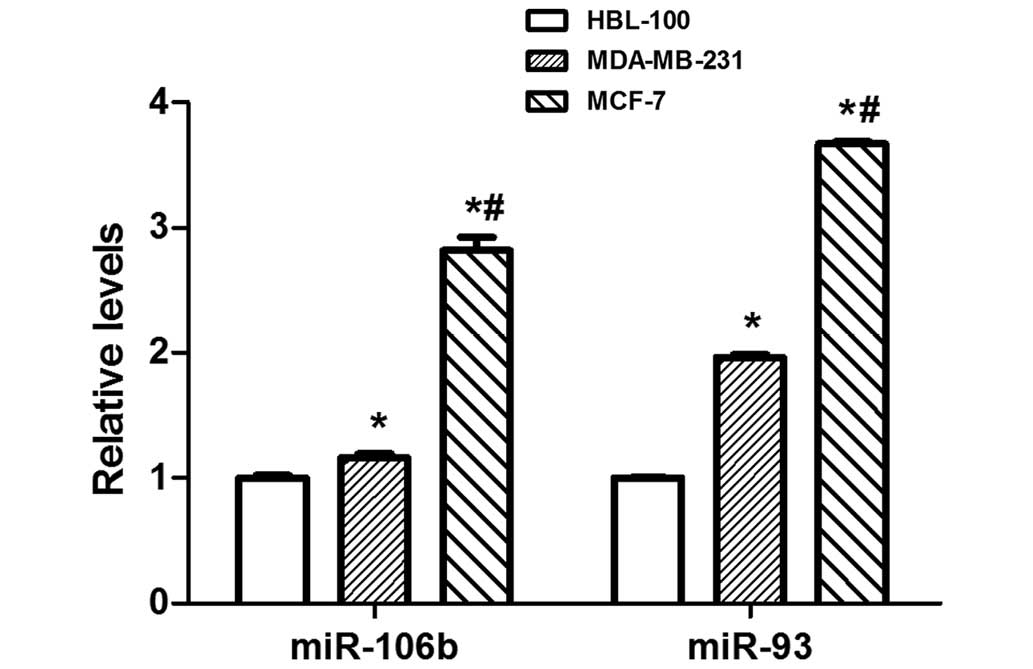
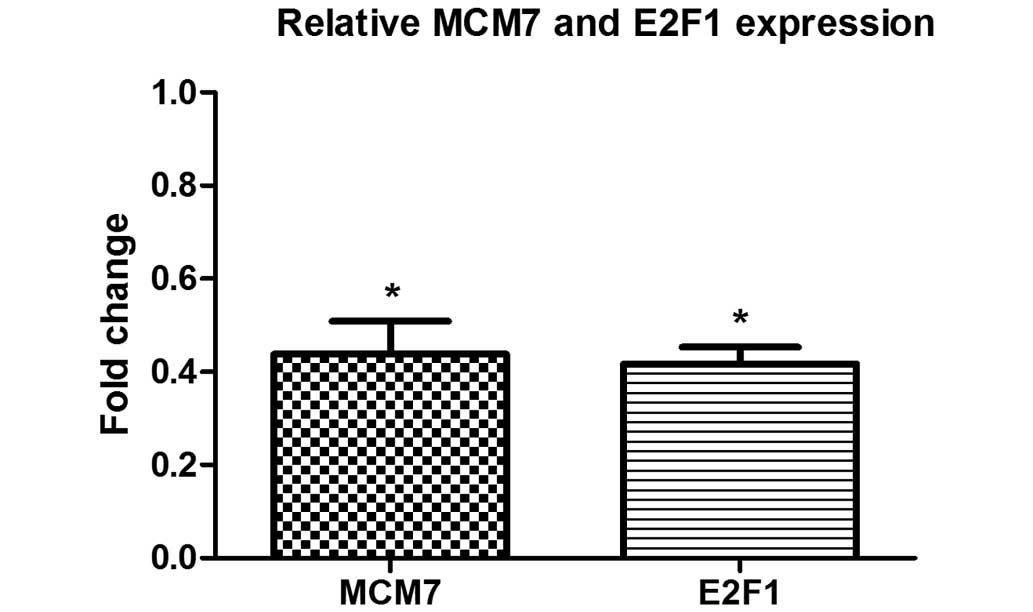
|
1
|
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN and
Sonenberg N: Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by
microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 9:102–114.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Griffiths-Jones S, Saini HK, van Dongen S
and Enright AJ: miRBase: Tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids
Res. 36:D154–D158. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, Byrom
M, Jarvis R, Cheng A, Labourier E, Reinert KL, Brown D and Slack
FJ: RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell.
120:635–647. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bonci D, Coppola V, Musumeci M, Addario A,
Giuffrida R, Memeo L, D'Urso L, Pagliuca A, Biffoni M, Labbaye C,
et al: The miR-15a-miR-16-1 cluster controls prostate cancer by
targeting multiple oncogenic activities. Nat Med. 14:1271–1277.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Si ML, Zhu S, Wu H, Lu Z, Wu F and Mo YY:
MiR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene. 26:2799–2803. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee DY, Deng Z, Wang CH and Yang BB:
MicroRNA-378 promotes cell survival, tumor growth and angiogenesis
by targeting SuFu and Fus-1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA).
104:20350–20355. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs:
microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hossain A, Kuo MT and Saunders GF:
Mir-17-5p regulates breast cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting
translation of AIB1 mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 26:8191–8201. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J and Weinberg RA:
Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast
cancer. Nature. 449:682–688. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A,
Lindow M, Krogh A and Lund AH: Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is
an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast
cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 283:1026–1033. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang V and Wu W: MicroRNA: A new player in
breast cancer development (Review). Cancer Mol. 3:133–138.
2007.
|
|
12
|
Liu G, Wong-Staal F and Li QX: Development
of new RNAi therapeutics. Histol Histopathol. 22:211–217.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Miller BA, Chu KC, Hankey BF and Ries LA:
Cancer incidence and mortality patterns among specific Asian and
pacific islander populations in the U.S. Cancer Causes Control.
19:227–256. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Efferth T, Rauh R, Kahl S, Tomicic M,
Böchzelt H, Tome ME, Briehl MM, Bauer R and Kaina B: Molecular
modes of action of cantharidin in tumor cells. Biochem Pharmacol.
69:811–818. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zheng LH, Bao YL, Wu Y, Yu CL, Meng X and
Li YX: Cantharidin reverses multidrug resistance of human hepatoma
HepG2/ADM cells via down-regulation of P-glycoprotein expression.
Cancer Lett. 272:102–109. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sagawa M, Nakazato T, Uchida H, Ikeda Y
and Kizaki M: Cantharidin induces apoptosis of human multiple
myeloma cells via inhibition of the JAK/STAT pathway. Cancer Sci.
99:1820–1826. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shivdasani RA: MicroRNAs: Regulators of
gene expression and cell differentiation. Blood. 108:3646–3653.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ross JS, Carlson JA and Brock G: miRNA:
The new gene silencer. Am J Clin Pathol. 128:830–836. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen CZ: MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor
suppressors. N Engl J Med. 353:1768–1771. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Reddy SD, Ohshiro K, Rayala SK and Kumar
R: MicroRNA-7, a homeobox D10 target, inhibits p21-activated kinase
1 and regulates its functions. Cancer Res. 68:8195–8200. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li D, Zhao Y, Liu C, Chen X, Qi Y, Jiang
Y, Zou C, Zhang X, Liu S, Wang X, et al: Analysis of MiR-195 and
MiR-497 expression, regulation and role in breast cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 17:1722–1730. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang C, Zheng X, Shen C and Shi Y:
MicroRNA-203 suppresses cell proliferation and migration by
targeting BIRC5 and LASP1 in human triple-negative breast cancer
cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 31:582012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Derfoul A, Juan AH, Difilippantonio MJ,
Palanisamy N, Ried T and Sartorelli V: Decreased microRNA-214
levels in breast cancer cells coincides with increased cell
proliferation, invasion and accumulation of the Polycomb Ezh2
methyltransferase. Carcinogenesis. 32:1607–1614. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ivanovska I, Ball AS, Diaz RL, Magnus JF,
Kibukawa M, Schelter JM, Kobayashi SV, Lim L, Burchard J, Jackson
AL, et al: MicroRNAs in the miR-106b family regulate p21/CDKN1A and
promote cell cycle progression. Mol Cell Biol. 28:2167–2174. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Feng M, Li Z, Aau M, Wong CH, Yang X and
Yu Q: Myc/miR-378/TOB2/cyclin D1 functional module regulates
oncogenic transformation. Oncogene. 30:2242–2251. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li Y, Tan W, Neo TW, Aung MO, Wasser S,
Lim SG and Tan TM: Role of the miR-106b-25 microRNA cluster in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 100:1234–1242. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kan T, Sato F, Ito T, Matsumura N, David
S, Cheng Y, Agarwal R, Paun BC, Jin Z, Olaru AV, et al: The
miR-106b-25 polycistron, activated by genomic amplification,
functions as an oncogene by suppressing p21 and Bim.
Gastroenterology. 136:1689–1700. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hui AB, Lenarduzzi M, Krushel T, Waldron
L, Pintilie M, Shi W, Perez-Ordonez B, Jurisica I, O'Sullivan B,
Waldron J, et al: Comprehensive MicroRNA profiling for head and
neck squamous cell carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 16:1129–1139. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Poliseno L, Salmena L, Riccardi L, Fornari
A, Song MS, Hobbs RM, Sportoletti P, Varmeh S, Egia A, Fedele G, et
al: Identification of the miR-106b~25 microRNA cluster as a
proto-oncogenic PTEN-targeting intron that cooperates with its host
gene MCM7 in transformation. Sci Signal. 3:ra292010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Petrocca F, Visone R, Onelli MR, Shah MH,
Nicoloso MS, de Martino I, Iliopoulos D, Pilozzi E, Liu CG, Negrini
M, et al: E2F1-Regulated MicroRNAs impair TGFbeta-dependent
cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Cell.
13:272–286. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Han S, Park K, Bae BN, Kim KH, Kim HJ, Kim
YD and Kim HY: E2F1 expression is related with the poor survival of
lymph node-positive breast cancer patients treated with
fluorouracil, doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 82:11–16. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|