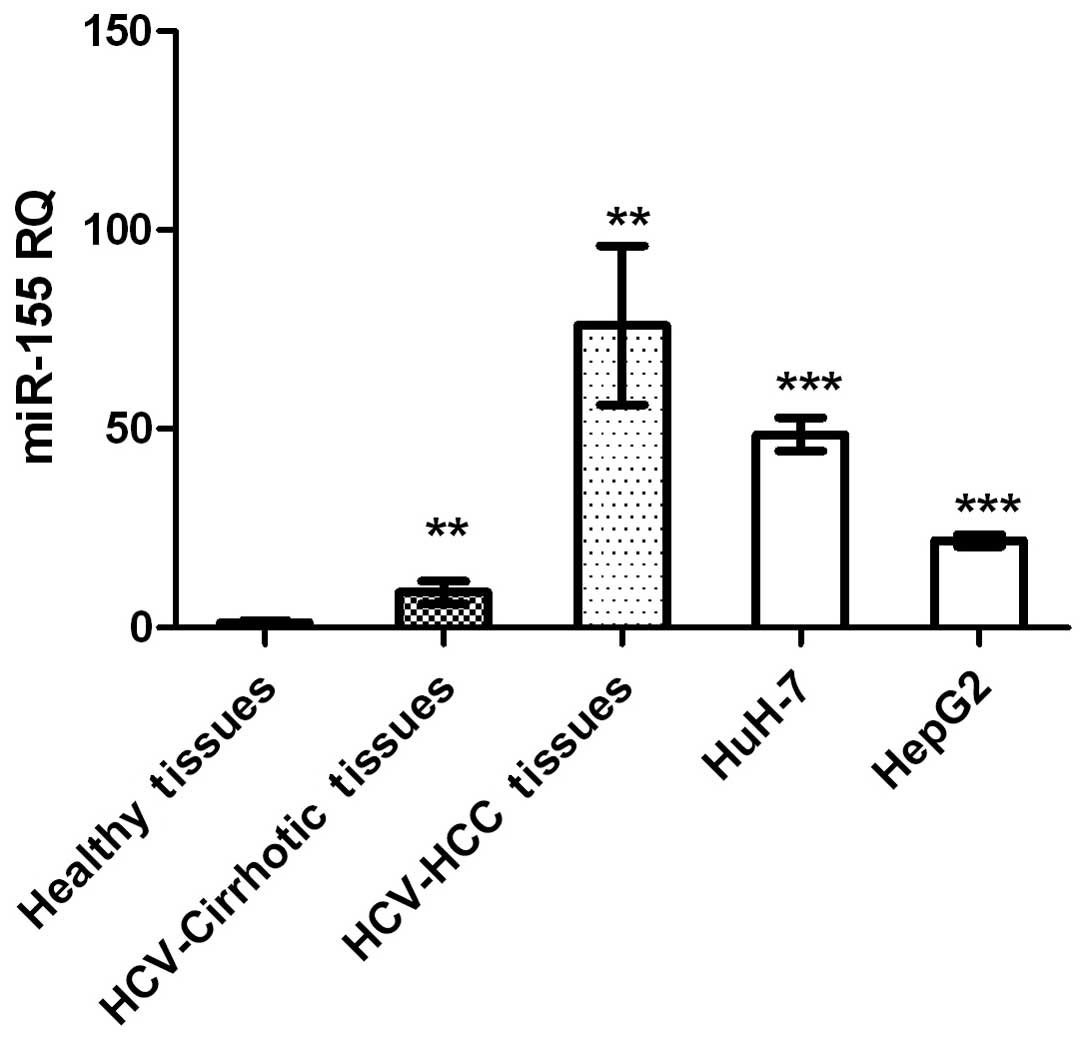
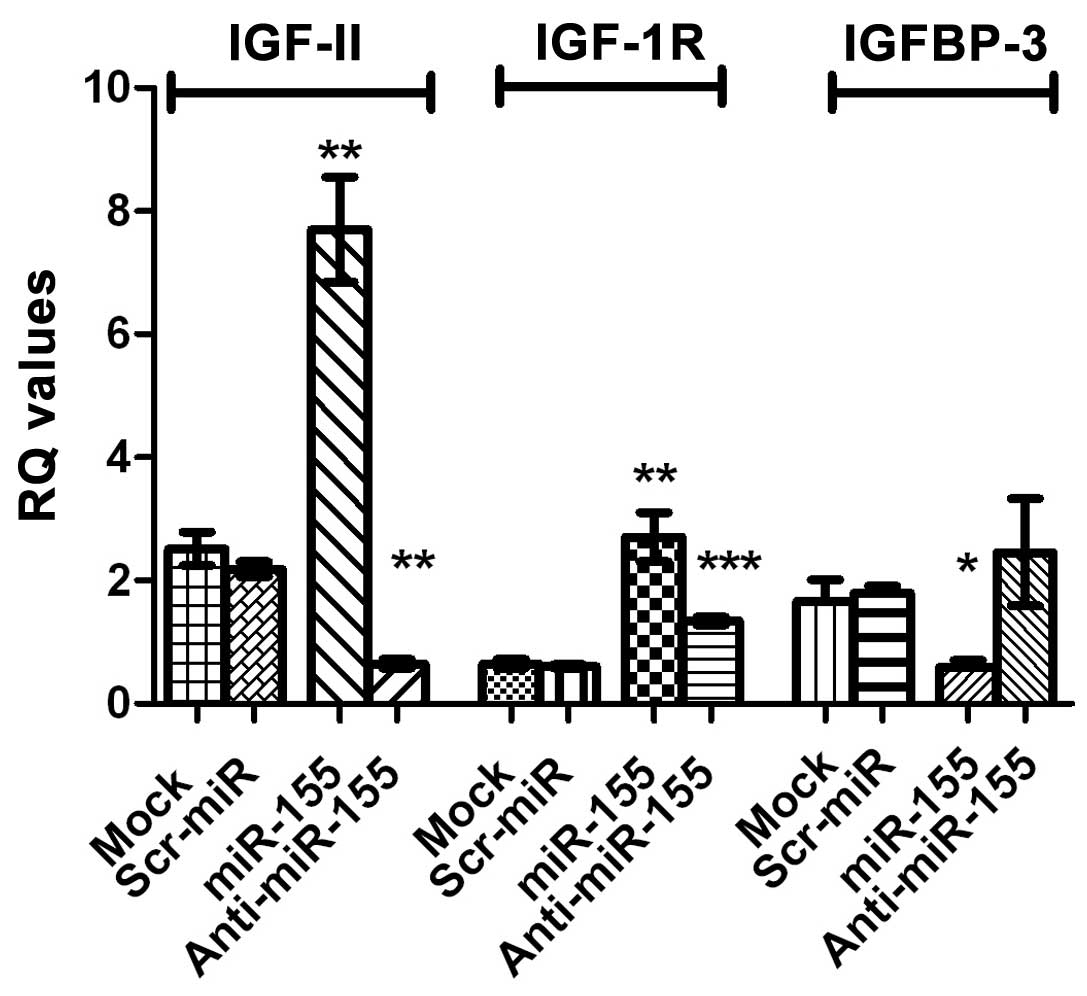
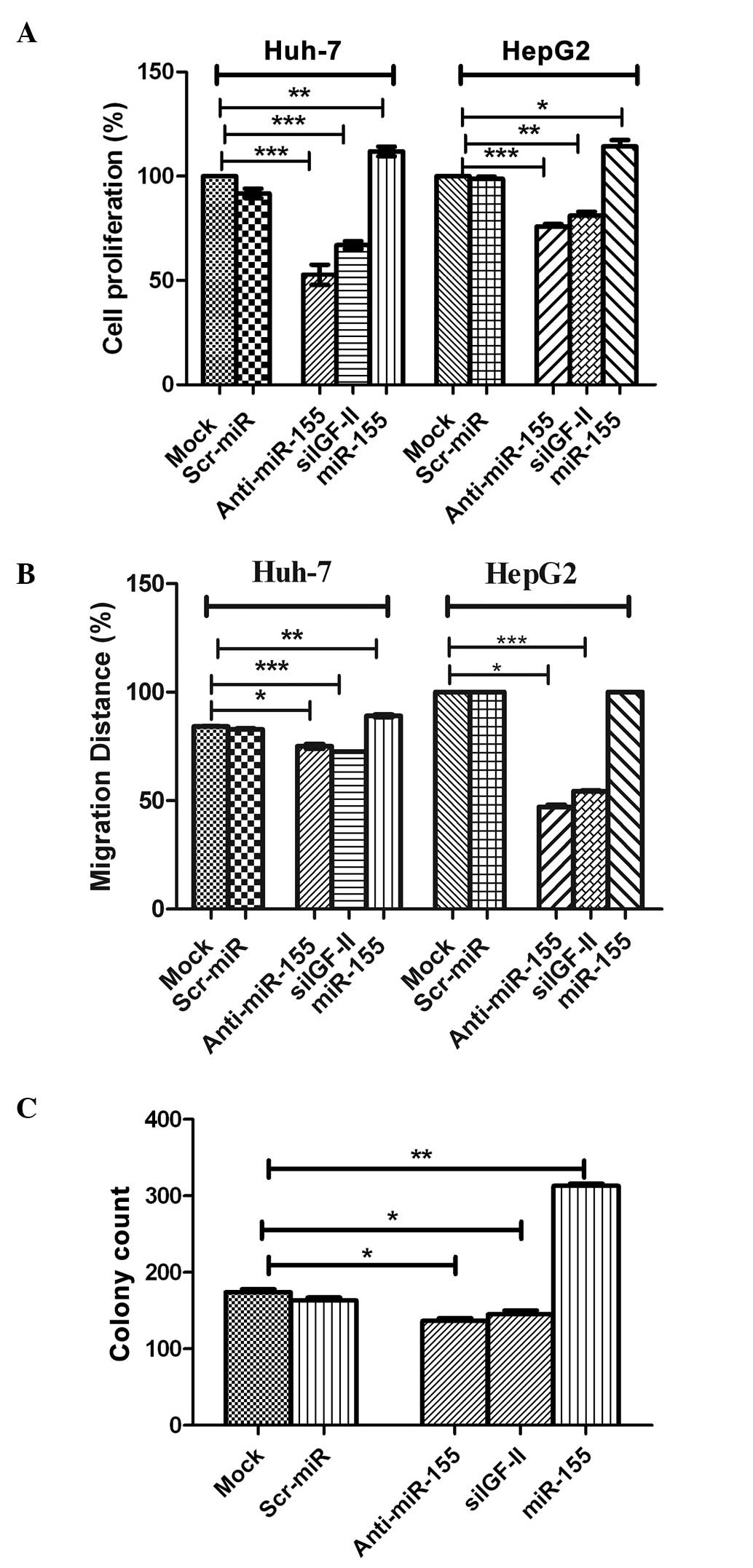
|
1
|
Sidhu K, Kapoor NR, Pandey V and Kumar V:
The ‘macro’ world of microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front
Oncol. 5:682015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pineau P, Volinia S, McJunkin K, Marchio
A, Battiston C, Terris B, Mazzaferro V, Lowe SW, Croce CM and
Dejean A: MiR-221 overexpression contributes to liver
tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:264–269. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yuan Q, Loya K, Rani B, Möbus S,
Balakrishnan A, Lamle J, Cathomen T, Vogel A, Manns MP, Ott M, et
al: MicroRNA-221 overexpression accelerates hepatocyte
proliferation during liver regeneration. Hepatology. 57:299–310.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jensen MR, Factor VM, Fantozzi A, Helin K,
Huh CG and Thorgeirsson SS: Reduced hepatic tumor incidence in
cyclin G1-deficient mice. Hepatology. 37:862–870. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Girard M, Jacquemin E, Munnich A, Lyonnet
S and Henrion-Caude A: miR-122, a paradigm for the role of
microRNAs in the liver. J Hepatol. 48:648–656. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gramantieri L, Ferracin M, Fornari F,
Veronese A, Sabbioni S, Liu CG, Calin GA, Giovannini C, Ferrazzi E,
Grazi GL, et al: Cyclin G1 is a target of miR-122a, a microRNA
frequently down-regulated in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer
Res. 67:6092–6099. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Datta J, Kutay H, Nasser MW, Nuovo GJ,
Wang B, Majumder S, Liu CG, Volinia S, Croce CM, Schmittgen TD, et
al: Methylation mediated silencing of MicroRNA-1 gene and its role
in hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 68:5049–5058. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang M, Tan LP, Dijkstra MK, van Lom K,
Robertus JL, Harms G, Blokzijl T, Kooistra K, van T'veer MB, Rosati
S, et al: miRNA analysis in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia:
Proliferation centres characterized by low miR-150 and high
BIC/miR-155 expression. J Pathol. 215:13–20. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jiang S, Zhang HW, Lu MH, He XH, Li Y, Gu
H, Liu MF and Wang ED: MicroRNA-155 functions as an OncomiR in
breast cancer by targeting the suppressor of cytokine signaling 1
gene. Cancer Res. 70:3119–3127. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bakirtzi K, Hatziapostolou M,
Karagiannides I, Polytarchou C, Jaeger S, Iliopoulos D and
Pothoulakis C: Neurotensin signaling activates microRNAs-21 and
−155 and Akt, promotes tumor growth in mice and is increased in
human colon tumors. Gastroenterology. 1411749–1761. (e1)2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xie Q, Chen X, Lu F, Zhang T, Hao M, Wang
Y, Zhao J, McCrae MA and Zhuang H: Aberrant expression of microRNA
155 may accelerate cell proliferation by targeting sex-determining
region Y box 6 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 118:2431–2442.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang B, Majumder S, Nuovo G, Kutay H,
Volinia S, Patel T, Schmittgen TD, Croce C, Ghoshal K and Jacob ST:
Role of microRNA-155 at early stages of hepatocarcinogenesis
induced by choline-deficient and amino acid-defined diet in C57BL/6
mice. Hepatology. 50:1152–1161. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Y, Wei W, Cheng N, Wang K, Li B,
Jiang X and Sun S: Hepatitis C virus-induced up-regulation of
microRNA-155 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis by activating Wnt
signaling. Hepatology. 56:1631–1640. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yan XL, Jia YL, Chen L, Zeng Q, Zhou JN,
Fu CJ, Chen HX, Yuan HF, Li ZW, Shi L, et al: Hepatocellular
carcinoma-associated mesenchymal stem cells promote hepatocarcinoma
progression: Role of the S100A4-miR155-SOCS1-MMP9 axis. Hepatology.
57:2274–2286. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pollak M: Insulin and insulin-like growth
factor signalling in neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:915–928. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fürstenberger G and Senn HJ: Insulin-like
growth factors and cancer. Lancet Oncol. 3:298–302. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bae MH, Lee MJ, Bae SK, Lee OH, Lee YM,
Park BC and Kim KW: Insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) secreted
from HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells shows angiogenic
activity. Cancer Lett. 128:41–46. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lahm H, Gittner K, Krebs O, Sprague L,
Deml E, Oesterle D, Hoeflich A, Wanke R and Wolf E:
Diethylnitrosamine induces long-lasting re-expression of
insulin-like growth factor II during early stages of liver
carcinogenesis in mice. Growth Horm IGF Res. 12:69–79. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rodriguez-Tarduchy G, Collins MK, García I
and López-Rivas A: Insulin-like growth factor I inhibits apoptosis
in IL-3-dependent hemopoietic cells. J Immunol. 149:535–540.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rajah R, Valentinis B and Cohen P:
Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-3 induces
apoptosis and mediates the effects of transforming growth
factor-beta1 on programmed cell death through a p53- and
IGF-independent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 272:12181–12188. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nussbaum T, Samarin J, Ehemann V,
Bissinger M, Ryschich E, Khamidjanov A, Yu X, Gretz N, Schirmacher
P and Breuhahn K: Autocrine insulin-like growth factor-II
stimulation of tumor cell migration is a progression step in human
hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology. 48:146–156. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gong Y, Cui L and Minuk GY: The expression
of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 207:101–104. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Aleem E, Nehrbass D, Klimek F, Mayer D and
Bannasch P: Upregulation of the insulin receptor and type I
insulin-like growth factor receptor are early events in
hepatocarcinogenesis. Toxicol Pathol. 39:524–543. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Khandwala HM, McCutcheon IE, Flyvbjerg A
and Friend KE: The effects of insulin-like growth factors on
tumorigenesis and neoplastic growth. Endocr Rev. 21:215–244. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
LeRoith D and Roberts CT Jr: The
insulin-like growth factor system and cancer. Cancer Lett.
195:127–137. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Han ZB, Chen HY, Fan JW, Wu JY, Tang HM
and Peng ZH: Up-regulation of microRNA-155 promotes cancer cell
invasion and predicts poor survival of hepatocellular carcinoma
following liver transplantation. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
138:153–161. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yoon SO, Chun SM, Han EH, Choi J, Jang SJ,
Koh SA, Hwang S and Yu E: Deregulated expression of microRNA-221
with the potential for prognostic biomarkers in surgically resected
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 42:1391–1400. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Eis PS, Tam W, Sun L, Chadburn A, Li Z,
Gomez MF, Lund E and Dahlberg JE: Accumulation of miR-155 and BIC
RNA in human B cell lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:3627–3632. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tili E, Michaille JJ, Wernicke D, Alder H,
Costinean S, Volinia S and Croce CM: Mutator activity induced by
microRNA-155 (miR-155) links inflammation and cancer. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 108:4908–4913. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang YH, Lin KH, Chen HC, Chang ML, Hsu
CW, Lai MW, Chen TC, Lee WC, Tseng YH and Yeh CT: Identification of
postoperative prognostic microRNA predictors in hepatocellular
carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e371882012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mattick JS and Makunin IV: Small
regulatory RNAs in mammals. Hum Mol Genet. 14:R121–R132. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N and Filipowicz W:
Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev
Biochem. 79:351–379. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Henke JI, Goergen D, Zheng J, Song Y,
Schüttler CG, Fehr C, Jünemann C and Niepmann M: MicroRNA-122
stimulates translation of hepatitis C virus RNA. EMBO J.
27:3300–3310. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Villanueva RA, Jangra RK, Yi M, Pyles R,
Bourne N and Lemon SM: MiR-122 does not modulate the elongation
phase of hepatitis C virus RNA synthesis in isolated replicase
complexes. Antiviral Res. 88:119–123. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Norman KL and Sarnow P: Modulation of
hepatitis C virus RNA abundance and the isoprenoid biosynthesis
pathway by microRNA miR-122 involves distinct mechanisms. J Virol.
84:666–670. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jopling CL: Regulation of hepatitis C
virus by microRNA-122. Biochem Soc Trans. 36:1220–1223. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tsai NP, Lin YL and Wei LN: MicroRNA
mir-346 targets the 5′-untranslated region of receptor-interacting
protein 140 (RIP140) mRNA and up-regulates its protein expression.
Biochem J. 424:411–418. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Moretti F, Thermann R and Hentze MW:
Mechanism of translational regulation by miR-2 from sites in the 5′
untranslated region or the open reading frame. RNA. 16:2493–2502.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yang F, Yin Y, Wang F, Wang Y, Zhang L,
Tang Y and Sun S: miR-17-5p Promotes migration of human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the p38 mitogen-activated
protein kinase-heat shock protein 27 pathway. Hepatology.
51:1614–1623. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
El Tayebi HM, Omar K, Hegy S, El Maghrabi
M, El Brolosy M, Hosny KA, Esmat G and Abdelaziz AI: Repression of
miR-17-5p with elevated expression of E2F-1 and c-MYC in
non-metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma and enhancement of cell
growth upon reversing this expression pattern. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 434:421–427. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|